Indocollir eye drops are a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is used only for instillation into the eyes. When applied locally, they quickly relieve pain and reduce the severity of inflammatory processes. Most often they are used before and after surgical manipulations on the organs of vision.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
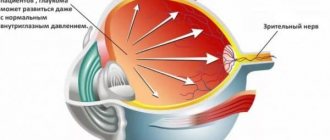
Indomethacin, the active component of the drug, inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins, eliminating pain and stopping the inflammatory process by reducing the activity of the cyclooxygenase enzyme. This substance is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, which, when applied topically, reduces the intensity of inflammation and the severity of pain by suppressing the production and transmission of pain impulses along nerve cells. Indomethacin also inhibits the synthesis of thromboxane type A, which leads to an increase in bleeding time.
The results of clinical studies indicate that indomethacin penetrates the anterior chamber of the eye. With a single instillation, the active component of the drug is detected in the moisture of the anterior chamber for several hours.
When the drug is applied topically, its systemic absorption is negligible.
Compatibility with other drugs
The penetration of the components of Indocollir drops into the systemic circulation is minimal, but despite this, when using it is necessary to take into account their drug interactions with certain drugs:
- Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diflunisal, heparin, indirect anticoagulants. These drugs in combination with Indocollir drops increase the likelihood of ulcers forming and bleeding, especially when combined with diflumitazole (although it increases the amount of indomethacin in the blood).
- Methotrexate. When taken simultaneously with an ophthalmic drug, the elimination of Methotrexate slows down, which is dangerous due to the development of a hematotoxic effect when taking the drug more than 15 mg/week. At a lower dosage, it is necessary to constantly monitor blood counts during the first 7 days of use, as well as kidney function in older people.
- Beta blockers reduce the effectiveness of eye drops.
- Pentoxifylline - increases the risk of bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
- NSAIDs in combination with Desmopressin increase its antidiuretic effect.
- Cyclosporine against the background of Indocollir exhibits a stronger nephrotoxic effect.
- Ticlopidine, thrombolytics - increase the risk of bleeding.
- Lithium preparations. The active component of eye drops increases its concentration in the blood, up to toxic, as they slow down its excretion from the body through the kidneys.
- Zidovudine - may exhibit toxic properties to reticulocytes, which can lead to anemia.
- Medicines that have an effect on the gastrointestinal tract (such as aluminum, salts, calcium, hydroxides and oxides of magnesium) reduce the absorption capacity of indomethacin.
- The simultaneous use of drops with ACE inhibitors and diuretics can lead to acute renal failure, as the body becomes dehydrated.
Read more Instructions for using nose drops Snoop
If it is necessary to use several ophthalmic agents at once, especially those containing corticosteroids, it is necessary to maintain an interval between instillations of at least 15 minutes.
Indications for use
- Inhibition of miosis during cataract surgery;
- Prevention and treatment of inflammatory processes on the eyeball after surgery;
- Prevention of cystoid macular edema after cataract surgery;
- Treatment of conjunctivitis of non-infectious origin;
- Prevention and treatment of inflammatory processes against the background of penetrating and non-penetrating injuries of the eyeball as part of complex local antimicrobial therapy.
"Uniclofen"
An ophthalmic agent for local use that has an analgesic effect. The pharmacological effect is due to the active substance (diclofenac), which almost does not enter the bloodstream when applied topically.
According to the instructions, the analogue of Indocollir eye drops contains an active ingredient that has anti-inflammatory activity. In addition, it provides an analgesic effect. When used topically, the medication reduces the severity of pain and swelling.
It is not recommended to prescribe Uniclofen for the following problems:
- Increased sensitivity.
- Aspirin asthma (pseudoallergic inflammation of the respiratory tract).
- Epithelial keratitis (a disease that is caused by a relapse of the herpes simplex virus in the cornea).
- Blood coagulation pathologies.
- Pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding.
Contraindications
- Breastfeeding period;
- From 6 to 9 months of pregnancy;
- Hypersensitivity to NSAIDs, including acetylsalicylic acid, manifested by acute rhinitis, attacks of bronchial asthma, urticaria;
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
It is recommended to use Indocollir with caution in patients with hemophilia, bleeding tendency and other diseases that cause blood clotting disorders and prolongation of bleeding time; epithelial herpetic keratitis (including a history); severe liver dysfunction.
The drug is prescribed during the first 5 months of pregnancy only if the expected benefit of treatment for the mother outweighs the potential harm and risk to the child.
Indocollyre
Although the systemic absorption of indomethacin when applied topically as eye drops is negligible, the risk of drug interactions with other drugs cannot be completely excluded.
Indirect anticoagulants, other NSAIDs, diflunisal, heparin.
It is known that the use of indomethacin in other dosage forms simultaneously with indirect anticoagulants, other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in their daily dose of 3 g and above (including salicylic acid derivatives, for example, acetylsalicylic acid, etc.), diflunisal and heparin increases the risk of gastrointestinal tract infections. intestinal tract ulcers and bleeding, and in combination with diflunisal, even fatal.
In turn, diflunisal can increase the concentration of indomethacin in the blood plasma.
Lithium preparations.
Indomethacin may increase the concentration of lithium in the blood to toxic levels due to a decrease in lithium excretion by the kidneys.
Methotrexate (at a dose of 15 mg per week or more).
Due to a decrease in the excretion of methotrexate by the kidneys when taken simultaneously with indomethacin and/or other anti-inflammatory drugs, its hematotoxic effect increases.
Indomethacin is used with caution with methotrexate (at a dose of less than 15 mg/week) -
weekly monitoring of blood counts is necessary in the first weeks of combined use, as well as monitoring for renal dysfunction, especially in the elderly.
Ticlopidine.
Indomethacin enhances the antiplatelet effect of ticlopidine and increases the risk of bleeding.
Indomethacin when used in combination with beta-blockers
may weaken their effect.
Indomethacin may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of cyclosporine
, especially in elderly patients.
NSAIDs may enhance the antidiuretic effect of desmopressin
.
Use caution when concomitantly using indomethacin with diuretics
and
ACE inhibitors
, since in dehydrated patients there is a risk of acute renal failure (due to decreased glomerular filtration rate by inhibition of vasodilatory prostaglandins after taking NSAIDs) and reduced antihypertensive effect.
In such situations, it is necessary to provide the patient with water and monitor kidney function at the beginning of treatment.
Combined use with pentoxifylline -
increased risk of bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (use under medical supervision and control the duration of bleeding).
Drugs that affect the gastrointestinal mucosa (salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium)
reduce the absorption of indomethacin from the gastrointestinal tract; Separate administration with antacids is recommended (if possible, an interval of more than 2 hours).
NSAIDs, including indomethacin, may increase the toxic effects of zidovudine
on reticulocytes with transition to acute anemia 8 days after the start of NSAID therapy.
Combined use with thrombolytics increases the risk of bleeding.
There is an assumption that when using indomethacin there is a possible risk of rupture of the implantable intrauterine device.
When using the drug Indocollir simultaneously with other eye drops, including those containing corticosteroids, to avoid the effect of “washing out” (decrease in concentration), the drugs should be administered at intervals of at least 15 minutes.
Instructions for use of Indocollir: method and dosage
Indocollir eye drops are instilled into the conjunctival sac of the eye.
The drug is prescribed 1 drop, the frequency of instillations depends on the clinical indications and the severity of the condition, and can be from 3 to 4 times a day, for 1-4 weeks.
To inhibit miosis during surgery, the drug begins to be instilled 2 hours before surgery, 1 drop at 30-minute intervals, 4 drops in total.
To prevent cystoid macular edema, the drug is prescribed 1 drop 3-4 times a day. The course of therapy after surgery is 1 month.
Interaction
When Indocollir is combined with indirect anticoagulants, their therapeutic effect is enhanced, which increases the likelihood of bleeding and problems with the blood coagulation system.
The drug should not be used simultaneously with acetylsalicylic acid or other anti-inflammatory medications, as this increases the likelihood of general negative effects and blood clotting disorders.
When using Indocollir with beta-blockers, the therapeutic effect of the latter may be weakened. If necessary, drops can be combined immediately with other ophthalmic agents, but before using medications, a time interval of 10 minutes should be maintained.
special instructions
Patients with contact lenses should remove the lenses before instillation and reinsert them no earlier than 15 minutes after the procedure.
After each use of the drug, the bottle must be tightly closed. Do not allow the tip of the pipette to touch the eye or other objects.
Patients in whom the action of the drops causes a temporary loss of clarity of vision, immediately after instillation of the drug, should refrain from driving vehicles and machinery or from working with complex machinery and equipment.
Does the drug have any restrictions?
"Indocollir" can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. Before using the medication, you must read the instructions.
According to the instructions for use for Indocollir, eye drops have certain prohibitions:
- Individual intolerance to the components included in their composition.
- Hypersensitivity.
- Bronchial asthma (inflammation of the airways, which is caused by asthma attacks).
- Allergic rhinitis (inflammatory process of the nasal mucosa, which occurs as a result of exposure to various allergens).
Indocollir is prescribed with extreme caution if a person has the following problems:
- Epithelial herpetic keratitis (an inflammatory process occurring in the cornea of the eye, which can lead to partial or complete loss of vision, caused by the herpes simplex virus).
- Hemophilia (hereditary blood disease that is caused by a congenital absence or decrease in the amount of blood clotting factors).
In addition, it is necessary to be extremely careful when prescribing medications to patients with blood clotting disorders.
Drug interactions
According to the instructions, Indocollir is not recommended for use in combination with other NSAIDs, including acetylsalicylic acid in high doses (3 g or more per day); diflunisal (due to the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract).
The drug may enhance the effect of lithium preparations and indirect anticoagulants.
When taken simultaneously, indomethacin may weaken the therapeutic effect of beta-blockers and saluretics.
If necessary, the drug can be used in combination with other eye drops, including those containing glucocorticosteroids, maintaining an interval between instillations of at least 5 minutes.
INDOCOLLIR eye drops 0.1% vial - cap. 5 ml
Although the systemic absorption of indomethacin when applied topically as eye drops is negligible, the risk of drug interactions with other drugs cannot be completely excluded.
Indirect anticoagulants, other NSAIDs, diflunisal, heparin.
It is known that the use of indomethacin in other dosage forms simultaneously with indirect anticoagulants, other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in their daily dose of 3 g and above (including salicylic acid derivatives, for example, acetylsalicylic acid, etc.), diflunisal and heparin increases the risk of gastrointestinal tract infections. intestinal tract ulcers and bleeding, and in combination with diflunisal, even fatal.
In turn, diflunisal can increase the concentration of indomethacin in the blood plasma.
Lithium preparations.
Indomethacin may increase the concentration of lithium in the blood to toxic levels due to a decrease in lithium excretion by the kidneys.
Methotrexate (at a dose of 15 mg per week or more).
Due to a decrease in the excretion of methotrexate by the kidneys when taken simultaneously with indomethacin and/or other anti-inflammatory drugs, its hematotoxic effect increases.
Indomethacin is used with caution with methotrexate (at a dose of less than 15 mg/week) -
weekly monitoring of blood counts is necessary in the first weeks of combined use, as well as monitoring for renal dysfunction, especially in the elderly.
Ticlopidine.
Indomethacin enhances the antiplatelet effect of ticlopidine and increases the risk of bleeding.
Indomethacin when used in combination with beta-blockers
may weaken their effect.
Indomethacin may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of cyclosporine
, especially in elderly patients.
NSAIDs may enhance the antidiuretic effect of desmopressin
.
Use caution when concomitantly using indomethacin with diuretics
and
ACE inhibitors
, since in dehydrated patients there is a risk of acute renal failure (due to decreased glomerular filtration rate by inhibition of vasodilatory prostaglandins after taking NSAIDs) and reduced antihypertensive effect.
In such situations, it is necessary to provide the patient with water and monitor kidney function at the beginning of treatment.
Combined use with pentoxifylline -
increased risk of bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (use under medical supervision and control the duration of bleeding).
Drugs that affect the gastrointestinal mucosa (salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium)
reduce the absorption of indomethacin from the gastrointestinal tract; separate administration with antacids is recommended (if possible, an interval of more than 2 hours).
NSAIDs, including indomethacin, may increase the toxic effects of zidovudine
on reticulocytes with transition to acute anemia 8 days after the start of NSAID therapy.
Combined use with thrombolytics increases the risk of bleeding.
There is an assumption that when using indomethacin there is a possible risk of rupture of the implantable intrauterine device.
When using the drug Indocollir simultaneously with other eye drops, including those containing corticosteroids, to avoid the washout effect (decrease in concentration), the drugs should be administered at intervals of at least 15 minutes.
Reviews of Indocollir
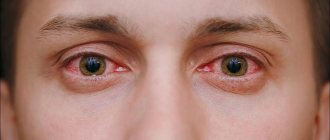
Despite the average cost of the drug and the impossibility of purchasing it in pharmacies without a prescription, reviews of Indocollir are quite numerous and contradictory. Some patients claim that after using the drops they encountered such unpleasant side effects as hyperemia and burning in the eye area, other patients note the high effectiveness of the drug as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent for various ophthalmological diseases and mechanical eye injuries.
Negative effects
The medicine is usually well tolerated by patients when used correctly. In rare situations, with increased sensitivity to Indocollir substances, the following negative phenomena are likely to occur:
- Sensation of a foreign object in the organs of vision.
- Redness.
- Swelling.
- Severe itching in the eye.
- Rash around the eyelids.
- Vomit.
- Stool disorders.
- Changes in the clinical blood picture.
If all recommendations are followed, drug overdose is extremely rare. With prolonged use of Indocollir and uncontrolled instillation of the medication, the side effects listed above are likely to occur.
"Tobradex"
The drug is an antimicrobial agent with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect for local use in ophthalmology.
According to the instructions for use, Tobradex eye drops are recommended for people over two years of age to instill one drop into the conjunctiva. The drug is instilled up to six times a day, every four hours. The duration of therapy, as a rule, does not exceed five to seven days, but if signs of the disease persist, a person should consult a doctor.