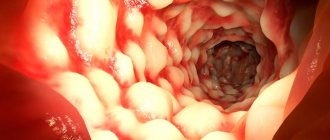
If a person develops inflammation of the stomach that affects the upper layers of the mucous membrane, then this is superficial gastritis (catarrhal). When making a diagnosis, we are often talking about a chronic form of the disease, but with proper treatment, diet and doctor’s recommendations, it can be slowed down and put into stable remission.
Superficial gastritis - what is it?
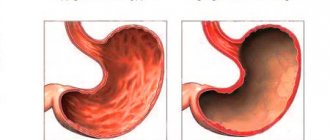
Superficial gastritis is a mild inflammatory disease of the stomach, affecting only the coolant; the glandular apparatus of the stomach functions normally.
Main symptoms:
- discomfort;
- Possible unexpressed pain in the upper abdomen;
- nausea;
- belching;
- heartburn.
When treating adults, antibiotics, antacids, and antisecretory drugs are used.
Electrolytic agents
Electrolytes are used to relieve symptomatic signs of stomach disease. Gastritis is accompanied by vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea, which inevitably leads to dehydration. Electrolytic preparations are intended to normalize water-salt balance. The atrophic type of the disease is characterized by a violation of the process of absorption and assimilation of consumed food, so taking electrolytic drugs is mandatory.
These drugs include:
- Dextrose solution;
- Regidron.
Superficial gastritis: symptoms in adults
Superficial gastritis can occur for a long time without visible signs - asymptomatic.
The main symptoms of superficial gastritis in adults:
- Discomfort in the epigastrium after eating difficult to digest or poor quality food. Some patients complain of dull pain that is diffuse in nature.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea, belching.
- Frequent constipation.
Women often face the problem of gastritis during pregnancy. The disease itself, although it does not affect the development of the fetus, causes discomfort in the woman, and adequate treatment during this period is very difficult.
Symptoms of superficial gastritis in adults
Antral gastritis in adults is most often associated with Helicobacter pylori and causes gastroduodenitis (combined inflammation of the stomach and duodenum). This infection provokes the transition of mild forms of the disease to atrophic gastritis, which threatens metaplastic degeneration of the mucosa and even cancer.
Chronic superficial gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori
When should you see a doctor?
Almost everyone has experienced the symptoms of gastritis. In most cases, they go away quickly and do not require medical attention. You should contact your doctor if symptoms last more than a week and if you have the following signs that indicate possible bleeding:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness or fainting;
- blood in vomit;
- black, tarry stool;
- blood in stool;
- weakness;
- pale skin.
Causes
All causes contributing to the occurrence of superficial gastritis are divided into:
- External:
- irregular meals, dry meals, abuse of spicy and too hot foods;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- uncontrolled use of medications (NSAIDs, anti-tuberculosis drugs, some antibiotics);
- Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Internal:
- anemia;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- CVS insufficiency;
- hypovitaminosis.
Classification of superficial gastritis
The following forms of superficial (catarrhal) gastritis are distinguished:
- spicy;
- chronic.
According to the prevalence of the inflammatory process:
- focal superficial gastritis (pathological foci are scattered in the form of inflammatory areas throughout the mucosa, they can be single or multiple);
- diffuse superficial gastritis - the entire coolant is involved in the inflammatory process.
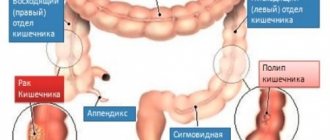
Sections of the stomach
By anatomical location:
- pyloric (affects the distal part of the stomach, consisting of the antrum adjacent to the body of the stomach and the pyloric part, which passes into the duodenum);
- fundal (the part of the fundus of the stomach located above and to the left of the cadia is affected).
Pyloric, fundal and diffuse superficial gastritis
By origin:
- bacterial (Helicobacter pylori - HP);
- autoimmune;
- iatrogenic;
- reflux gastritis (for duodenal-gastric reflux - gastroduodenitis, GIRD - biliary dyskinesia; for cardia insufficiency - esophagitis with chronic erosions, GERD, hiatal hernia).
In the chronic form of the disease there are phases:
- exacerbations - the symptoms of the disease are pronounced, the pathological process is actively occurring;
- remission - symptoms subside.
Sometimes, in the same patient, various forms of chronic gastritis occur. This pathology, most often found in HP-associated conditions, is called mixed gastritis.
What is focal superficial gastritis
Focal superficial gastritis is a lesion of the gastric mucosa, in which only one of the sections of the stomach is involved in the process - the fundic or pyloric. This is the initial, mildest stage of the disease.
The most common forms of superficial focal gastritis are antral and distal (pyloric) localization.
The main cause of the disease is Helicobacter pylori. Its symptoms are mild or not expressed at all. The main complaint of patients is epigastric pain.
Frequent symptoms of the disease are: lack of appetite, heartburn, belching, flatulence, stool disorders. Treatment of superficial gastritis includes diet, medications (usually in the form of tablets), herbal medicine, and normalization of lifestyle. With timely treatment, the prognosis is quite favorable.
But patients often do not seek help, and the disease progresses. Cellular elements are activated in the coolant, causing secondary damage to epithelial cells - gastric epithelial cells. Chronic erosions occur, often with a hemorrhagic component.
How to treat erosive gastritis and what medications are used
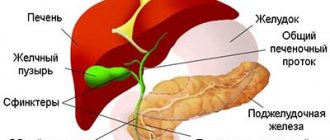
Further activation of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori provokes the development of mucosal atrophy, and the processes of cellular regeneration are disrupted. A mixed form of gastritis occurs, represented by both superficial and atrophic forms. As a result, bicarbonates, necessary for alkalizing food before entering the intestines, cease to be produced. Symptoms of duodenitis and increased pressure in the duodenum occur. The closing function of the pylorus suffers, and DGR occurs. The effect on the antral mucosa of refluxate (which includes bile acids, salts of pancreatic enzymes, duodenal contents) causes reflux gastritis.
Fully or partially limited products
- Soups with meat broth, with not pureed vegetables, first courses with cabbage.
- Radishes, radishes, white cabbage, turnips, beans, peas, rutabaga, onions, canned vegetables, sorrel, garlic, mushrooms are excluded from the diet on an ongoing basis - all of them have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane. You should also not eat pickled and pickled vegetables.
- Fruits raw and with peel. Sour or unripe fruits. Even during the period of remission, it is not recommended to consume grapes due to the rough skin and the ability to cause fermentation and melon as a difficult to digest product.
- Millet, pearl barley, corn, barley cereals, legumes, and coarse large pasta are excluded.
- Fresh bread, pastry, puff pastry, brown bread
- Fatty fish and meat (pork, goose, duck, lamb), animal fats, canned meat, sausages and smoked meats.
- Spicy seasonings and dishes, horseradish, mustard, tomato sauce, pepper.
- Chocolate, coffee, cakes, pastries, nuts, ice cream.
- Alcohol, carbonated drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diffuse superficial gastritis - what is it?
Diffuse superficial gastritis is a chronic inflammation of almost the entire gastric mucosa; the process is localized only in the superficial layer and does not affect the glandular apparatus of the stomach. The disease lasts a long time with periods of remission and exacerbation.
DPG is a pathological diagnosis established using FGDS. The duodenum is often involved in the process, resulting in bulbitis, insufficiency of the pyloric sphincter, and reflux gastritis.
Intestinal refluxate, acting on the inflamed mucosa of the antrum, causes erythematous changes with erosions of the mucosa.
Although the process has a total spread throughout the organ, it affects only the coolant, therefore, with a moderate degree of activity, timely recognition of the disease and adequate treatment, it is possible to cure the disease forever. How much and how the disease is treated is influenced by the activity of the pathological process and its severity. Treatment includes antibacterial therapy, antacids, antisecretory drugs, as well as antispasmodics, anticholinergics, and vitamins.
Menu (Power Mode)
The longest period of time is therapeutic nutrition during the recovery period and during remission. The complete composition of the diet allows you to constantly adhere to it. We can say that this is a healthy, balanced and moderately gentle diet. The patient’s condition determines the need to wipe foods or the ability to eat them unprocessed.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Mixed superficial and atrophic gastritis - what does it mean?
The main cause of atrophic gastritis is superficial inflammation of the mucous membrane, which is practically asymptomatic. Over time, long-term inflammation leads to profound dystrophic and degenerative changes in the mucosa, the gastric glands atrophy, and a mixed form of gastritis occurs.
There are several types of atrophy of the gastric mucosa:
- Subatrophic gastritis is the earliest form of the disease, which develops against the background of superficial gastritis in the stage of moderate inflammation.
- Atrophic antral gastritis - a form of the disease associated with N.R. Without proper treatment, the process tends to spread and gradually becomes diffuse.
- Focal atrophic gastritis is a lesion of the stomach in conditions of moderately expressed activity of the inflammatory process, gastric secretion suffers little, the number of atrophic foci is insignificant, their size is minimal.
- Multifocal atrophic gastritis is a highly active diffuse process characterized by damage to the antrum and body of the stomach. Against the background of progressive atrophy of almost the entire coolant, a hyperplastic process with intestinal metaplasia begins. What is dangerous about this common form of atrophy is its frequent malignancy.
Mixed superficial and hyperplastic gastritis with glandular hypertrophy
Hyperplastic gastritis is a special type of lesion of the gastric mucosa, with intense proliferation of epithelial cells. Characterized by the formation of polyps and thick rigid folds, mucosal hyperplasia. The pathology does not appear for a long time.
In advanced cases, symptoms appear:
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- minor bleeding.
Often the disease occurs with increased secretory function, but unlike hyperacid gastritis, this condition is not based on an inflammatory reaction, but on hypertrophy of the gastric glands.
The etiology of the disease has not been sufficiently studied, so treatment is symptomatic: in case of increased acidity, antisecretory drugs are prescribed, and in case of atrophy, replacement therapy is prescribed. If malignancy is suspected, surgical treatment is indicated.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of chronic gastritis is usually not difficult. Diagnostics is aimed at determining the clinical course of the disease.
The main methods are:
- FGDS - determines the morphological features of gastritis in a patient (signs of inflammation, localization, atrophy, metaplasia).
- X-ray with contrast - reveals thickening of the folds of the mucous membrane, characteristic of chronic gastritis, and the presence of multiple erosions.
- Long-term measurement of acidity in the stomach - used to determine the clinical form of gastritis.
- Testing exhaled air for the presence of Hp. (in doubtful cases, antibodies to Helicobacter in the blood are determined).
- Study of gastric juice - evaluates the secretory function of the stomach: total acidity, mucus content, enzymes.
- Laboratory research methods.
- peripheral blood analysis reveals a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin - symptoms of anemia;
- in the coprogram, a large number of undigested muscle fibers and granular accumulations of starch are found, which means a dysfunction of the entire digestive tract.
Treatment of superficial gastritis (inflammation of the stomach)
Treatment of superficial gastritis is carried out mainly on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of a gastroenterologist or therapist. This pathology is rarely treated in a hospital. The treatment regimen includes diet, medication, and possibly the use of traditional medicine. How to treat a particular patient, what medications and how long to take them is decided by the attending physician, based on the symptoms and results of the studies.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy includes etiotropic and symptomatic treatment.
Etiotropic treatment:
- Antibiotics. Before starting treatment, the degree of Helicobacter infection is determined (high, medium, low). Depending on this, the duration of treatment is determined (most often 7-14 days) and the dose of antibiotics. Usually 2-3 antibiotics are taken for up to 2 weeks. First-line drugs are: Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin, Metronidazole.
- Antisecretory drugs for gastritis with high acidity: IGR (Famotidine, Cimetidine, Roxatidine); PPI (Omez, Rabeprazole).
- Bismuth (De-nol) is used in patients with a pronounced decrease in secretory function during atrophic processes.
- Antacids reduce the concentration of H+ in the stomach and provide cytoprotection by enveloping the mucous membrane (Phosphalugel).
The usual treatment regimen for superficial gastritis in adults includes: PPI at the maximum dose, or two antibiotics (Klacid + Amoxicillin). The course of treatment for superficial gastritis is determined by the activity of Helicobacter pylori (usually 7-10 days).
Symptomatic medications are prescribed: antispasmodics, enzymes, vitamins.
In the presence of atrophy in the case of a mixed nature of superficial gastritis, the following is prescribed:
- replacement therapy (Abomin, Creon);
- anticholinergics and antispasmodics for pain relief (No-shpa, Metacin);
- prokinetics (Motilium, Cerucal).
Nutrition for superficial gastritis
The diet for superficial gastritis is table No. 5 according to Pevzner, individually modified by the attending physician.
What you can eat and include in your daily menu:
- meat, preferably dietary (rabbit, chicken);
- fish (pollock, pink salmon, cod);
- vegetables and fruits, boiled and baked;
- cereals (rice, oatmeal);
- pasta;
- dairy products (cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, kefir);
- sweets (honey, marshmallows, diet cookies);
- drink: weak tea, herbal teas, rosehip decoction, still mineral water.
What not to eat: prohibited foods:
- spices, smoked meats, pickles;
- fried food;
- fatty food;
- citrus;
- chocolate, cocoa;
- fresh bread, baked goods;
- carbonated water, coffee, alcohol in any form and quantity.
Diets should be followed during the acute stage. Outside of an exacerbation, a diet is not necessary, but the rules of eating should always be followed.
Treatment of superficial gastritis with folk remedies
Even inactive catarrhal gastritis should not be treated only at home, this can lead to a worsening of the condition, and it is hardly possible to cure the disease with folk remedies. Moreover, there are many different recipes, so it can be very difficult to figure out what to treat and how. Here you need to consult a doctor.
The most popular and effective ways to relieve symptoms of inflammation in superficial gastritis is treatment with juices:
- half a glass of potato juice before meals, three times a day;
- cabbage juice, half a glass an hour before meals, twice a day (contraindicated in case of exacerbation);
- fresh juice from green apples and carrots (mix juices in equal quantities, take a glass in the morning).
Special mention should be made of the benefits of sea buckthorn oil. It has an anti-inflammatory, healing, enveloping, antibacterial effect. Usually take a teaspoon of oil half an hour before meals. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor and carried out against the background of drug therapy or immediately after its completion.
Delicious diet recipes
It is wrong to think that switching to a diet will force you to spend hours in the kitchen. Everything is much simpler - you can buy an electric steamer, and the now fashionable multicooker, and save yourself the trouble. We suggest you prepare vegetable stew with a minimum of time.
Vegetable stew
You will need:
- 1 young zucchini.
- 1 large carrot.
- 1 medium onion.
- 2-3 potatoes.
- 4-5 broccoli florets.
- Salt, vegetable oil, a little milk.
Preparation: wash the vegetables, cut them into large cubes of equal size, put them in a thick-walled pan, add salt. Add a tablespoon of vegetable oil and a little water to the vegetables, so that they cover 1/3 of the vegetables. Cover the pan with a lid and simmer for 15 - 20 minutes. 5 minutes before the end of cooking, you can add 2 - 3 tablespoons of milk - the taste of the stew will be softer.
The recipe is simple, it can be prepared either stewed or baked. It’s even easier - in a double boiler, in which case the taste of the vegetables will appear brighter.
Chicken balls with carrots
You will need:
- 500 grams of minced chicken fillet without skin.
- 1 medium carrot.
- 1 small onion.
- 1.5 table. l. semolina.
- Vegetable oil, salt.
Preparation: Prepare minced chicken by passing the skinless fillet through a meat grinder twice. Chop the carrots and onions together with the chicken. Add semolina to a homogeneous mass, stir and add salt. Let the minced meat stand for 30 minutes until the semolina swells. Then form the balls and bake in the oven, or cook in a double boiler. The dish turns out juicy, very tasty, and does not at all remind you of a diet.
Do they take into the army with chronic superficial gastritis?
The diagnosis of “Chronic superficial gastritis” is not a reason for exemption from military service. Article 59 “Schedule of Diseases” states that young men with severe forms of gastritis can be exempted from military service when:
- exacerbations occur at least 2 times a year;
- long-term treatment is required (at least 2 months as an inpatient for a year);
- long-term and adequate treatment is unsuccessful;
Superficial gastritis cannot provide such a clinic, so those with chronic superficial gastritis are recruited into the army.
The only reason for temporary release, which is provided for in Art. 59 – exacerbation of the disease during conscription. In this case, the conscript undergoes the VKK. If the commission concludes that the disease is in the acute stage, the young man is assigned fitness category G - a deferment from military service for the period of treatment.
Prevention
General preventive measures that will help not only avoid the development of superficial gastritis, but also increase the period of remission in patients with an already established diagnosis:
- Changing your lifestyle (observing work, sleep and rest schedules), giving up bad habits.
- If negative symptoms appear, do not self-medicate and consult a specialist in a timely manner. If necessary, issue a sick leave certificate.
- Avoid stressful situations, strive to develop stress resistance.
- Try to eat foods whose temperature is approximately +37 degrees. Products above +60 degrees and below +15 degrees are prohibited.
- Try to consume foods in liquid and crushed form. Preference is given to porridge-like foods and purees.
- Food should be taken 6-8 times a day, and long periods of fasting should not be allowed, after which there is a high risk of overeating.
- The last meal is 2 hours before going to bed.
- The amount of food consumed per day should not exceed 3 kg (30% for breakfast, 15% for second breakfast, 40% for lunch and 15% for dinner).