The drug Afobazole is a selective anxiolytic used in psychiatry.
It has a mild effect, so its use in the treatment of severe mental disorders is inappropriate.
One of the few drugs in this group that can cause minimal side effects. But, despite this, Afobazol is not intended for pregnancy, for nursing women, as well as for children and adolescents.
Composition per tablet:
Active substance: fabomotizole (fabomotizole dihydrochloride) – 5 mg and 10 mg. Excipients: potato starch - 48 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 40 mg (for a dosage of 5 mg) and 35 mg (for a dosage of 10 mg), lactose monohydrate - 48.5 mg, medium molecular weight povidone (medium molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone medical, Kollidon 25) - 7 mg, magnesium stearate - 1.5 mg.
Description: white or off-white tablets, flat-cylindrical with a bevel .
Pharmacotherapeutic group: anxiolytic agent (tranquilizer).
ATX code : N05BX.
Overdose
Despite the fact that Afobazole is considered a relatively safe drug that does not cause sedation or muscle relaxant effects, increasing the maximum therapeutic dose can lead to drowsiness without muscle relaxation.
Although the drug does not cause addiction, it is the manifestations described above that do not allow taking Afobazol constantly.
To relieve symptoms of overdose, subcutaneous administration of a solution of caffeine sodium benzoate in an amount of 1 ml is necessary two to three times a day.
Pharmacodynamics:
Afobazole® is a selective non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic.
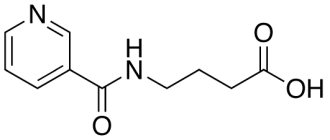
Acting on sigma-1 receptors in nerve cells of the brain, Afobazol® stabilizes GABA/benzodiazepine receptors and restores their sensitivity to endogenous inhibitory mediators. Afobazole® also increases the bioenergetic potential of neurons and has a neuroprotective effect: it restores and protects nerve cells.
The effect of the drug is realized primarily as a combination of anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) and mild stimulating (activating) effects. Afobazol® reduces or eliminates feelings of anxiety (preoccupation, bad feelings, fears), irritability, tension (fearfulness, tearfulness, anxiety, inability to relax, insomnia, fear), depressive mood, somatic manifestations of anxiety (muscular, sensory, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal symptoms), autonomic disorders (dry mouth, sweating, dizziness), cognitive disorders (difficulty concentrating, impaired memory), incl. arising from stress disorders (adaptation disorders). The use of the drug is especially indicated in persons with predominantly asthenic personality traits in the form of anxious suspiciousness, uncertainty, increased vulnerability and emotional lability, and a tendency to emotional stress reactions.
The effect of the drug develops on days 5-7 of treatment. The maximum effect is achieved by the end of 4 weeks of treatment and persists after the end of treatment for an average of 1-2 weeks.
Afobazole® does not cause muscle weakness, drowsiness and does not have a negative effect on concentration and memory. When using it, addiction does not form, drug dependence does not develop, and “withdrawal” syndrome does not develop.
Side effects
Side effects are rare; most often patients complain of the development of allergies.
Therapy may also be accompanied by:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- mild depression, apathy.
If undesirable reactions are detected, you should consult your doctor; you may need to reduce the dose of the drug.
It is important to note that the above symptoms are not a reason to discontinue Afobazole as the main drug in the patient’s therapy.
Pharmacokinetics:
After oral administration, Afobazole® is well and quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
The maximum concentration of the drug in plasma (Cmax) is 0.130+0.073 mcg/ml; time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) – 0.85+0.13 hours.
Metabolism: Afobazole® undergoes a “first pass effect” through the liver; the main directions of metabolism are hydroxylation at the aromatic ring of the benzimidazole ring and oxidation at the morpholine fragment.
Afobazole® is intensively distributed throughout well-vascularized organs; it is characterized by rapid transfer from the central pool (blood plasma) to the peripheral (highly vascularized organs and tissues).
The half-life of Afobazole® when taken orally is 0.82+0.54 hours. The short half-life is due to intensive biotransformation of the drug and rapid distribution from blood plasma to organs and tissues. The drug is excreted primarily in the form of metabolites and partially unchanged in urine and feces.
Reviews from doctors
Reviews from neurologists about the effect of the drug:
Kostenko B.A.:
Afobazole is a new generation selective anxiolytic used for mental disorders of mild to moderate severity. Requires strict adherence to dosage, depending on the patient’s diagnosis. It is strictly unacceptable to use the medicine for self-medication; how to take Afobazole should be determined by the attending physician depending on the patient’s condition.
Anisimova G.P.:
Therapy with Afobazol gives positive results in the treatment of 96% of patients. For severe forms of the disease, I prescribe complex therapy in combination with other antipsychotics. The advantages of the drug include good tolerability by patients and a minimal number of adverse reactions, which occur in no more than 20% of patients.
Neurologists speak positively about the effect of the drug, so they trust it with the health of their patients.
Indications for use:
Afobazol® is used in adults for anxiety conditions: generalized anxiety disorders, neurasthenia, adaptation disorders, in patients with various somatic diseases (bronchial asthma, irritable bowel syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, coronary heart disease, hypertension, arrhythmias), dermatological, oncological and other diseases. In the treatment of sleep disorders associated with anxiety, neurocirculatory dystonia, premenstrual syndrome, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, to alleviate the “withdrawal” syndrome when quitting smoking.
Afobazole and alcohol: compatibility
After using Afobazole tablets for nerves, it is unacceptable to drink alcohol. Any medications that directly affect the nervous system should not be combined with alcohol.
Alcohol can greatly enhance the effect of an anxiolytic, which will result in overdose, poisoning, or severe intoxication of the body.
There are known cases of death when large doses of Afobazole are combined with alcoholic beverages.
Is it possible to drink constantly?
The duration of taking Afobzole can only be determined by a doctor. It depends on various factors. In general, the answer to the question: “How long can you take Afobazol without a break?” depends on the level of anxiety, self-doubt and character traits such as increased vulnerability, a tendency to emotional stress reactions, and much more.
When starting to take Afobazole, you should pay attention to the fact that the medicine will not show maximum effectiveness from the first day. Basically, the first results can be noticed on the 5-7th day of treatment, since it is during this time that the drug accumulates in the body, and the maximum effect is usually achieved by the end of the first month of use.
The standard course of treatment is usually a month, but often its duration varies from 2-3 months.
After finishing taking the drug, the effect lasts for another 1-2 weeks. It is worth emphasizing once again that the most accurate answer to the question: “how long can you take Afobazol?” Only a doctor can give it.
Before determining how often to take Afobazole, you must be aware of the contraindications of the drug. While expecting a child or immediately after its birth, a woman’s body is rebuilt; various hormonal changes occur in it, which can lead to anxiety, worries, and excessive irritability.
Which is better: Persen or Afobazol?
The intense rhythm of modern life and stressful situations negatively affect the state of the nervous system. As a result of emotional overstrain, disruptions in its functioning occur, which sometimes have to be eliminated with the help of medications. In such cases, experts often recommend Afobazole or Persen. Malfunctions in the functioning of the nervous system sometimes have to be eliminated with the help of Afobazole or Persen. Medicines belong to different pharmacological groups. Afobazole is an anxiolytic, Persen is a sedative drug of plant origin.
The action of the first drug is aimed at eliminating generalized anxiety conditions and disorders associated with them.
The second drug calms the nervous system well and relieves spasms. Therefore, there are a number of differences in the indications for the use of drugs. Afobazole has a wider spectrum of action. This feature should be taken into account during therapy.
Which drug to choose largely depends on the diagnosis and severity of the disease.
Afobazole has a more pronounced effect in cases of neurasthenia, neuroses and other mental disorders. Therefore, its use is indicated in the treatment of severe forms of pathology. Persen is suitable for those who have minor nervous disorders. The choice of drug is influenced by the lifestyle and type of activity that the patient is engaged in.
Adaptol or Afobazol: which is better?
These tools have a lot in common. A comparative description of their features will help you decide between them. Both drugs were developed by domestic pharmacists and belong to the non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics. They restore circadian rhythms, normalize behavioral reactions, and regulate mood. Relieves various manifestations of anxiety:
- feeling of fear;
- nervousness;
- causeless agitation;
- tearfulness;
- fussiness;
- irritability;
- hyperactivity;
- tremor
These medications are available only in tablet form. They do not have hypnosedative and muscle relaxant properties, do not cause behavioral deviations, increased affectivity and agitation, insomnia, or psychophysiological dependence with long-term use. Their active components do not accumulate in tissues after repeated administration. Cases of the development of adverse symptoms requiring discontinuation of medication are rare; there is no withdrawal effect.
Adaptol is a traditional tranquilizer that has been used in clinical practice since 1979. The active substance is the bicyclic compound mebicar, which is close in structure to natural purines. The medicine is used regardless of food intake. The duration of the treatment course is up to 100 days. The medication is valid for 4 years from the date of production. To purchase it you need a prescription. Afobazole is a new generation drug that has been used since the early 2000s. The active component used here is fabomotizole, which is a derivative of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole.
Which is better: Afobazole or Tenoten?
If you compare Afobazole and Tenoten, the main difference immediately becomes noticeable: Afobazole is a “regular” drug, and Tenoten is a homeopathic one. To date, official science has no evidence of any effectiveness of homeopathic medicines. At the same time, Afobazole has studies indicating its effectiveness, comparable in strength to the widely used tranquilizer Diazepam (New anxiolytic “Afobazole” in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: results of a comparative study with Diazepam; Avedisova A.S., Chakhava V.O. , Less Yu.E., Malygin Ya.V.) In this regard, Afobazol is stronger and more effective than Tenoten in coping with anxiety.
If both drugs can be given to an adult patient, then for children, according to the instructions, only Tenoten is suitable.
Taking both drugs at the same time is not recommended. There are no data on the interaction of Tenoten with Afobazole, and therefore there is a risk of developing unpredictable adverse reactions. Persen is a plant-based drug: it contains extracts of valerian, lemon balm, and mint. It has a mild calming effect and makes it easier to fall asleep. At the same time, Persen is not able to have a sufficient effect to eliminate anxiety. If you choose between Persen, Tenoten and Afobazol, then the first will be more effective for improving sleep, and the latter - for the general elimination of irritability and anxiety.
Phenibut or Afobazole: which is better?
Phenibut and Afobazole are drugs that have an anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effect and protect nerve cells from various damaging factors, increasing their survival in conditions of oxygen deficiency. It is not entirely correct to say which of these two drugs is more effective, since they belong to different pharmacological groups. Phenibut is a nootropic drug, a stimulator of nerve cells in the brain, improving memory, concentration, and accelerating all intellectual processes. This effect is achieved by improving brain nutrition, activating blood flow, and accelerating the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers. An additional effect of the drug is its anti-anxiety effect, reducing excitability and normalizing sleep.
Afobazole is an anxiolytic with a mild stimulating effect, relieves irritability, tension, and mild depressive disorders. The drug also activates brain function, restores and protects nerve cells under adverse conditions (including stress). If a person is in a state of stress for a long time, without cerebral circulation impairment, then Afobazol will be the best. If there are cerebral circulation disorders or the child needs treatment, then it is better to choose Phenibut. It is not easy to reliably determine which drug is stronger: it all depends on the situation in which they are prescribed and on the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Afobazole or Novopassit: which is better?
Safe medications that are dispensed from pharmacies without a prescription include Afobazol and Novopassit. The first is a chemical anxiolytic, and the second contains natural ingredients. Which is better - Afobazol or Novopassit, when are the drugs prescribed and are they compatible? What is stronger - Afobazol or Novopassit? The herbal preparation also copes well with its functions - it gently calms, eliminates anxiety and mental tension, and also has a hypnotic effect. The main side effect of Novopassit is drowsiness, decreased attention and weakness.
It should be borne in mind that there is a risk of developing allergic reactions to medicinal herbs included in the sedative.
Fabomotizol does not enhance the effect of ethanol, and the natural drug is contraindicated in alcoholism. Both medications are non-addictive, however, the herbal remedy is not recommended to be taken while driving vehicles, as well as during work that requires increased attention. Afobazole and Novopassit can be taken together on the recommendation of a doctor. Simultaneous use of drugs will lead to a more pronounced elimination of anxiety, while the sedative effect will not change. The dose of medication is selected individually, based on the characteristics of the situation and the age of the patient.
Which is better: Afobazole or Glycine?
Which drug is better to choose depends on the purpose of its use. Afobazol is more effective in the treatment of NCD, anxiety disorders, and prolonged stress. However, it has little effect on the quality of sleep, only indirectly, relieving nervous tension. Therefore, if you have insomnia, it is better to choose Glycine forte. A higher dose of the drug (0.3 g and above) will help you fall asleep faster.
The effect of Glycine on the body is not limited to the regulation of the mental and autonomic components. It accelerates brain recovery during strokes, injuries, and encephalopathies. Afobazole does not have this ability.
Glycine is more affordable. Even tablets with the highest dose of the active substance (“extra”) cost 100 rubles less than Afobazol. Another advantage of Glycine is its convenient dosage form - tablets that dissolve in the mouth. You can drink them even on the road or at work, without drinking water, regardless of meals. Afobazole is approved for use only in adults; Glycine, if necessary, is prescribed even to children in the first year of life. Drinking it during pregnancy and lactation is also acceptable.
Thus, it is better to prescribe Glycine in the following cases:
- strokes;
- encephalopathies;
- insomnia;
- nervous diseases and NCD in children;
- pregnancy and lactation in women with neurological problems.
Afobazole is advisable to use for:
- NCD in adults;
- increased anxiety, excitability;
- stressful situations;
- PMS;
- mental disorders due to alcohol withdrawal;
- quitting smoking.
Contraindications
Before starting a therapeutic course of Afobazole, you should make sure that the patient does not have the following contraindications:
- hypersensitivity to substances included in the drug;
- glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome;
- The patient's age is under 18 years.
The drug is also prohibited for use in pregnant women and during breastfeeding.
Use of the drug in the presence of contraindications may lead to side effects.
What to replace it with?
Today, pharmaceutical companies offer a wide selection of sedative drugs of both natural and synthetic origin. If necessary, you can choose a substitute for the drug “Afobazol”. Analogues will have other active ingredients in their composition, but the therapeutic effect will be identical. Medications that can relieve anxiety and confusion syndromes include:
- "Diazepam";
- "Adaptol"
- "Phenazepam";
- "Elinium";
- "Amizil";
- "Atarax";
- "Tenoten";
- "Persen";
- "Mebix";
- "Phenibut";
- "Tranquesipam";
- "Neurofazol" (synonym for the drug "Afobazol").
Substitutes have a similar therapeutic effect, but they cannot be compared with the original remedy. The optimal remedy should be selected by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s diagnosis and the presence of individual intolerance to the components. It is quite difficult to cope with the manifestation of neurosis on your own, because drugs can only remove the symptoms of the disease, but not solve the cause of the problem.