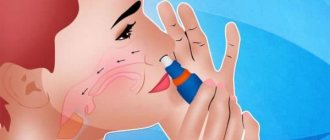
It is used only intranasally, that is, through the nasal passages.
"Tafen nasal" must be used correctly, then it is possible to completely avoid side effects. Before spraying the product, it is necessary to completely clear the nasal passages of mucus that interferes with the effect of the drug on the nasal mucosa.
You can use a sodium chloride solution purchased at a pharmacy.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Tafen nasal
Budesonide is a synthetic corticosteroid with pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects. When used in therapeutic doses, it is almost not resorbed. Does not exhibit mineralocorticoid activity and is well tolerated with long-term treatment. The drug inhibits the release of mediators of the inflammatory response, increases the synthesis of anti-inflammatory proteins, reduces the number of mast cells and eosinophilic granulocytes. Budesonide reduces the release of toxic proteins from eosinophilic granulocytes, free radicals from macrophages and lymphokines from lymphocytes. It also reduces the binding of adhesion molecules to endothelial cells, and thus reduces the number of white blood cells at the site of allergic inflammation. Budesonide increases the number of beta-adrenergic receptors in smooth muscle. The drug inhibits the activity of phospholipase A2, which slows down the synthesis of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and PAF, which induce an inflammatory response. Budesonide also inhibits histamine synthesis, which leads to a decrease in histamine levels in mast cells. Tafen nasal reduces the severity of symptoms in allergic rhinitis, suppressing the late and early phases of the allergic reaction and reduces the severity of inflammation in the upper respiratory tract. Improvement in condition is noted 2–3 days after the start of treatment. Budesonide is a mixture of two epimers in a 1:1 ratio. The 22R epimer has 2–3 times more activity than the 22S epimer. After inhalation of 400 mcg of budesonide through the nose, the maximum concentration is reached after 0.7 hours and is 1 nmol/l in blood plasma. After inhalation through the nose, about 20% of the administered budesonide enters the systemic circulation. The systemic bioavailability of budesonide is low, since about 90% of the portion that is absorbed is inactivated during one-step metabolism in the liver. The 22R and 22S epimers are biotransformed into beta-hydroxybudesonide and alpha-hydroxyprednisolone, respectively. Metabolites exhibit less than 1% glucocorticoid activity; excreted by the kidneys (70%) and through the intestines. The half-life is 2–3 hours.
Tafen Nasal nasal spray 50 µg/dose 200 doses bottle 1 pc. in Moscow
Pharmacological action: Glucocorticosteroid with pronounced glucocorticoid and weak mineralocorticoid activity. In standard in vitro
and animal models have shown that the affinity of budesonide for specific glucocorticoid receptors exceeds that of cortisol by 200 times, and the local anti-inflammatory effect of budesonide is 1000 times higher than that of cortisol. When studying the systemic activity of budesonide in animal experiments, it was shown that when administered subcutaneously, the effect of budesonide was 40 times stronger than that of cortisol, and when administered orally, it was 25 times stronger.
Inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes and PGs, inhibits the production of cytokines, prevents the migration and activation of inflammatory cells.
Increases the number of active beta-adrenergic receptors, restores the body's response to beta-adrenergic bronchodilators after their long-term use.
Rapidly absorbed from the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. When administered intranasally, very little is absorbed from the nasal mucosa (only 20% enters the systemic circulation). After inhalation, about 25% of the dose enters the alveoli. The part that enters the gastrointestinal tract is almost completely (90%) destroyed (inactive metabolites are formed) during the “first pass” through the liver. Bioavailability is 10% of the amount that enters the stomach; 25–30% of budesonide that enters the alveoli is absorbed. Cmax in the blood is reached 15–45 minutes after inhalation and intranasal administration. Plasma protein binding is 88%. Has high systemic clearance (84 l/h). T1/2 from plasma - 2.8 hours. Excreted in urine, partially in bile in the form of metabolites.
After oral administration, Cmax and Tmax values are variable (Tmax in individual patients - from 30 to 600 minutes). Systemic availability after a single dose is higher in patients with Crohn's disease compared to healthy volunteers (21% and 9%, respectively), but approaches that of healthy volunteers after repeated doses. About 90% of absorbed budesonide is metabolized during the “first pass” through the liver with the participation of microsomal enzymes (mainly CYP3A4) to 2 main metabolites - 6-beta-hydroxy-budesonide and 16-alpha-hydroxyprednisolone (the glucocorticoid activity of the metabolites is less than 1/100 of the activity of budesonide , of the remaining amount, about 90% binds to albumin and is in an inactive state.
The effectiveness of budesonide (oral dosage form) has been shown for inflammatory bowel diseases, incl. with collagenous colitis.
The intranasal form is effective in the treatment of non-infectious inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity, to prevent the recurrence of polyps in the nasal cavity after their surgical removal and complete healing of the mucous membrane.
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, effect on fertility
The potential carcinogenicity of budesonide was assessed in long-term studies in rats and mice. No carcinogenic effect of budesonide was detected in mice when administered orally for 91 weeks at doses up to 200 mcg/kg/day (600 mcg/m2/day, approximately 0.1 MRDC based on body surface area).
A two-year study in Sprague-Dawley rats revealed a statistically significant increase in the incidence of gliomas in male rats receiving an oral dose of budesonide 50 mcg/kg/day (300 mcg/m2/day); similar changes were not observed in males at doses of 10 and 25 μg/kg/day (60 and 150 μg/m2/day) and in females at all doses tested. In 2 additional two-year studies in male Fischer and Sprague-Dawley rats at doses of 50 μg/kg/day (less than the MRV when converted to body surface area), there was no increase in the incidence of gliomas compared with other glucocorticoids (prednisolone and triamcinolone). However, with all 3 glucocorticoids studied, a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular tumors in rats was observed.
No mutagenic or clastogenic properties of budesonide were detected in a number of standard tests.
With subcutaneous administration of budesonide to rats in doses up to 80 mcg/kg/day (less than the MRDC when calculated per body surface area), no adverse effects on fertility were recorded, but a decrease in weight gain in females was noted along with a decrease in the viability of pups in the prenatal period, at birth and during the lactation period. At doses of 5 mcg/kg/day (30 mcg/m2/day), similar effects were not observed.
Pregnancy
Like other corticosteroids, budesonide was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rabbits and rats. Experimental studies on animals (rats, rabbits) have shown that subcutaneous administration of budesonide leads to congenital malformations in the fetus (mainly skeletal defects).
Use of the drug Tafen nasal
adults and children aged 6 years and older. The initial dose is 400 mcg of budesonide per day: 2 doses (100 mcg of budesonide) in each nostril 2 times a day. The usual maintenance dose is 200 mcg of budesonide per day: 1 dose (50 mcg of budesonide) in each nostril 2 times a day or 2 doses in each nostril once a day in the morning. Maintenance therapy should be at the lowest dose level that eliminates the symptoms of rhinitis. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible, but not less than 1 hour before the next dose. When stopping the use of the drug, the dose is reduced gradually. When used correctly, Tafen nasal reduces the frequency of adverse reactions and improves the therapeutic effect:
- Clean the nasal passages (if possible with sodium chloride solution).
- Remove the cap from the bottle.
- Shake the bottle.
- When using the bottle for the first time, release some spray into the air. Press the nasal adapter down several times until a light mist appears. The same procedure must be repeated if the drug has not been used for several days. If the adapter is blocked, you need to gently press it and clean it.
- Tilt your head forward (so that you can see your toes). Insert the nozzle from the right side into the left nostril and point it towards the outer wall.
- Press the adapter down to release one dose of spray and inhale it.
- Insert the nozzle from the left side into the right nostril and point it towards the outer wall; Squeeze out one dose of the spray and inhale it.
- After use, wipe the adapter with a clean cloth and replace the cap. Store the bottle in an upright position with the cap facing up.
Analogs
Not only Tafen Nasal has an anti-inflammatory effect and reduces the severity of symptoms of rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Structural analogues of the drug are:
- Budenofalk;
- Pulmicort;
- Benacort;
- Budiair;
- Apulein;
- Benarin;
- Tafen.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Tafen nasal
Be careful when switching from the use of systemic corticosteroids to treatment with Tafen nasal due to the risk of developing adrenal insufficiency. Rapid reduction of the dose of corticosteroids in patients with asthma can provoke a serious deterioration of the disease. Discontinuation of the drug Tafen nasal should be gradual. GCS may mask signs of infection, and new infections may develop during their use. Patients with untreated fungal, bacterial or viral infections (transmitted by airborne droplets) require special attention. Sometimes, to prevent the appearance of pathological symptoms of the organ of vision caused by allergic rhinitis, concomitant treatment may be necessary. With prolonged use of the drug, it is recommended to examine the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity 1-2 times a year to determine the possible development of atrophic rhinitis or pharyngeal candidiasis. In patients with liver cirrhosis or hypothyroidism, the systemic effect of budesonide may be increased. Due to the inhibitory effect of GCS on wound healing, Tafen nasal should be used with caution in patients with recent surgery or trauma to the nasal cavity. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is only possible if absolutely necessary. In infants and nursing mothers who have used budesonide, it is necessary to exclude the presence of hypofunction of the adrenal glands. Impact on psychophysical abilities. The drug does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and other machinery.
Release form, composition
Tafen nasal spray is available in the form of a suspension. It consists of the active substance budesonide, as well as many auxiliary elements.
The basis for the suspension is water in which methyl parahydroxybenzoate, propyl parahydroxybenzoate, sucrose, propylene glycol, polysorbate 80, simethicone emulsion, disodium edetate, MCC and hydrochloric acid are dissolved.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to use the drug:
- hypersensitivity to any components of the drug;
- pulmonary tuberculosis during exacerbation;
- lactation;
- age up to 6 years.
During pregnancy
During gestation, the use of the drug can be started only if there are indications, if the child will suffer more from a runny nose, as well as the infection that causes it, than from the components of Tafen nasal.
If the use of this drug is indicated for nursing mothers, it is recommended that you stop breastfeeding your baby while using it.
Interaction with other drugs
Data on the outcome of the interaction of ketoconazole with budesonide are unknown, however, when analyzing blood plasma, a slightly higher than normal level of budesonide is noticed.
Try to avoid mixing these drugs to avoid causing health risks. The interval between taking medications with these two components should be increased as much as possible.
Itraconazole may also cause an increase in budesonide plasma levels. In this case, it is recommended to reduce the dose of budesonide.
Side effects
Negative effects resulting from the use of Tafen nasal appear very rarely , usually due to non-compliance with the rules of use and regular excess of the dosage.
Quite often, minor or even very noticeable irritation of the respiratory tract occurs. Sometimes, only at the very beginning of therapy with this drug, short-term negative effects may occur, such as rhinorrhea, the formation of a large number of crusts, and nosebleeds are also possible. In the latter case, it is advisable to stop using the drug so as not to violate the integrity of nearby vessels.
Also in many cases there is sneezing and dyspnea. The voice may become slightly hoarse as a result of slight swelling of the vocal cords. The breathing may become wheezing, which means it will be audible to other people.
Pain or discomfort in the nasal cavity is also often observed. The mucous membrane of the throat may lose normal moisture during the first stages, which is usually quickly restored.
The skin may also react negatively to taking Tafen nasal, but this is extremely rare. Typical allergies are possible, such as non-acute urticaria, dermatitis, swelling of the skin and underlying fatty tissue. Regular itching may also be noticed.
Changes in the nasal area occur quite rarely. Caused by respiratory tract candidiasis, which may require additional treatment. If the drug has been used for a very long time or even constantly, atrophic processes in the nasal cavity may begin.
It is extremely rare that ulcers may appear on the mucous membrane, as well as perforation of the nasal septum. If large doses of budesonide are used for a long time, there is a risk of developing systemic negative effects.
The adrenal glands may be depressed, and sometimes growth may be delayed, which only applies to children and adolescents. Bone mineral density may be impaired, which may require additional long-term rehabilitation measures. Signs of hypercortisolism may gradually appear. Sometimes cataracts or glaucoma develop.
Common, unpleasant symptoms such as increased heart rate, anosmia, and constant dizziness are also possible. A clear sign that the medication needs to be stopped is nasal congestion for a long time without additional symptoms.
Pain in the head and throat may occur. Redness of the conjunctiva is possible, which can be confused with conjunctivitis, but in this case this phenomenon will be of an allergic nature. Such unpleasant conditions as unjustified drowsiness, myalgia, and causeless reflex cough can also be caused.
An overdose of the drug is not very scary . If it happened accidentally, then most likely it will not cause any acute side effects. Acute overdose is not possible.
If excessive doses are taken for a long time, especially when combined with similar drugs, hypercortisolism may begin. In this case, you should immediately stop taking the drug.