Syphilis is a venereal disease, most often chronic, manifested in the form of gradual destruction of the skin, some organs and bones, and also affects the nervous system.
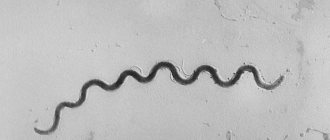
The causative agent of this common disease is Treponema pallidum. Today, the most popular way of contracting this disease is through sexual transmission of bacteria.
Today, syphilis can be treated, but only on condition that you do not let the disease progress.
A sexually transmitted disease (hereinafter simply STD) affects almost 50 people out of 100,000 thousand people per year.
The government of each country is trying to contribute to a significant reduction in the number of cases by informing the population about prevention and methods of protection.
Syphilis bacteria
We have known about syphilis since the beginning of the 20th century, when this disease was the most common, and every 5 people were infected with it.
At that time, this disease went by the more typical name for that time, “French disease.”
After a while, scientists concluded that this disease is bacterial in nature, and this significantly helped in its timely diagnosis and treatment.
Treponema pallidum first received this name due to the fact that when studying it under a microscope, scientists simply could not identify it.
After all, its entire structure, in fact, had no color, was simply transparent and at the same time very poorly painted by various methods.
To expose it, they used silver staining, the Gizma method, and a microscope with dark lenses.
With the help of further studies over time, it turned out that treponema can function and replicate only in a living organism.
The optimal temperature for the reproduction of this bacterium is the body temperature of a living organism 37 ° C; under optimal conditions, it divides every day.
Thanks to these data, a new treatment method was created: forcibly increasing body temperature to the maximum level, using the malaria virus.
Thus, it was easier for the patient to tolerate the manifestations of the underlying disease.
Chancroid in men
In men, a phenomenon called chancroid often occurs. The soft chancre is located in the same place as the hard chancre, is distinguished by a bright red bloody color, and produces abundant pus. It differs from hard chancre in that it has softer edges and also causes discomfort and pain. Soft chancroid, another name for which is chancroid, provokes inflammation of the lymph nodes, nausea and vomiting, weakness and dizziness may appear.
Chancroid is also a symptom of syphilis, and because of its peculiar characteristics it is called a venereal ulcer.
Unlike hard chancroid, the causative agent of which is Treponema pallidum, the occurrence of chancroid is provoked by a microorganism such as streptobacillus or chancroid bacillus. The incubation period for this infection is approximately ten days, after which the chancroid stick begins its active reproduction and spread throughout the host’s body.
The ulcer, formed as a result of the activity of the bacterium, has uneven edges and, when pressed, releases a lot of purulent fluid. In the absence of timely and correct treatment, this lesion of the epidermis deepens and expands, as a result of which the infection penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin.
Differences between hard and soft chancre:
- The hard one does not cause pain and inflammation of the skin around it, does not ooze pus or blood, unlike the soft one, in which there may be small inflammatory elements, redness or rash around the ulcer.
- A chancre does not have a hard base; the skin around it may peel and become inflamed; ulcers often appear, which subsequently merge with the main source of inflammation.
What does syphilis look like?
When Treponema pallidum enters the body of each of us, it goes through an incubation period, which can last from 1 week to 1.5 months.
At this time, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, so we may not even know who lives inside us.
With a simple examination during the incubation period, syphilis may not be found; all readings will be within normal limits.
During such a period, there is a high probability that one person who carries this disease in himself in the incubation phase and, not suspecting that he is a carrier, can transmit it sexually to his partners.
The disease begins to manifest itself after the incubation period has expired, when primary syphilis occurs.
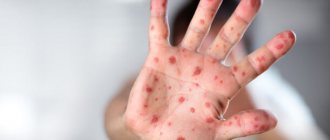
The first signs of the disease appear on the skin, in the form of a rash, hard dark brown spots (ulcers), as well as on the genitals, in the oral cavity (precisely on the mucous membrane of these organs).
Syphilitic leukoderma or pigment syphilide
One of the manifestations of secondary syphilis is leucoderma. Its appearance is associated with damage to the nervous system. Disorders of pigment formation in the form of hypo- and hyperpigmentation are caused by trophic disorders. Leukoderma is most often localized on the posterolateral areas of the neck (“necklace of Venus”), less often on the back, torso, lower back and limbs. Against the background of pale yellow hyperpigmentation, round spots of depigmentation appear. They can be isolated or merge, taking on the appearance of “lace”. Leucoderma does not peel off or become inflamed and lasts for months and years. Cases of disappearance of leukoderma within a few days have been described. There are no Treponema pallidums in the affected areas. Under the influence of specific therapy, pigmentary syphilide does not disappear. Diseases such as pseudoleukoderma, vitiligo, plaque parapsoriasis and cicatricial atrophy have similar symptoms.
Rice. 26. A sign of secondary syphilis is leucoderma.
Transmission routes
Syphilis is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Transmission is ensured through traditional sexual intercourse, anal and oral sex, even if the carrier has syphilis in the incubation phase.
After the incubation period, a small ulcer will appear at the site where the treponema pallidum bacterium passes, which will only grow if measures are not taken to treat the disease.
When caring for a patient, infection is possible through contact with his personal belongings and the carrier himself.
With this method of infection, signs of syphilis will initially appear on the skin of the legs and arms, and after chancre will form on the genitals.
This sexually transmitted disease can be transmitted, like everything else, through blood. When reusing syringes, razors and other personal hygiene items.
Differences in syphilis by gender
As for women, after an asymptomatic period (about a month after syphilis enters your body), the time comes for the disease to manifest itself in all its glory.
The first sign is the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, labia or anus. An ulcer (chancre) manifests itself as a response of our immune system to the invasion of harmful bacteria.
A chancre is an inflammatory area of the skin or mucous membrane, usually round in shape and having a flat base.
At first, the growth on the skin will not show painful spasms, but later it will definitely be accompanied by a rash on different parts of the body and mucous areas.
The course of syphilis in men is no different from the manifestations of the disease in women. Most often, in men, syphilis first appears on the penis, its base and head.
But, despite this, ulcers (chancres) can also occur in the above mentioned places (oral cavity, anus).
The subsequent treatment regimen is not divided according to genital characteristics; the treatment is the same for men and women.
Syphilitic alopecia
Hair loss due to syphilis can be diffuse, finely focal and mixed. Hair falls out quickly (overnight) or within 1 - 1.5 months. Eyelashes and eyebrows are often affected. For eyebrows with syphilis, small focal loss is typical. In place of the fallen eyelashes, they grow back, as a result of which they differ in different lengths (step-shaped eyelashes). The skin on the head does not become inflamed, there is no peeling or itching.
Similar signs are present with alopecia areata, superficial trichophytosis, microsporia, early baldness, lichen planus and lupus erythematosus.
Rice. 24. Alopecia is one of the signs of secondary syphilis.
Rice. 25. Alopecia in men.
From the birth of syphilis to chronic disease
Not many people with the capabilities of modern medicine go through all the existing stages of development of this disease.
With the last stage, a person can live from 10 to 20 years, followed by death. Let's take a closer look at each stage of this disease.
Incubation period
Duration up to six months. During this period, there are no visible manifestations on the body or in the body itself. If infection occurs several times in different places, then this period is reduced to 7-14 days.
This stage is prolonged due to the person taking strong immunoprotective drugs, such as antibiotics for influenza.
The end of the incubation period can be taken as the appearance of an ulcer on the skin, followed by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
In the case when the penetration of syphilis bacteria occurred directly through the blood, then syphilis bypasses the primary stage and immediately passes into the second.
Primary syphilis
Symptoms of primary syphilis include the following:
- The appearance of ulcers on the skin and mucous membranes. Initially, it will not cause any problems or complaints. In the future, it will acquire a more bluish or even purple tint, which will mean an inflammatory process that will lead to pain;
- After 7 days, inflammation begins in the lymph nodes and in the vessels around the previously manifested ulcers. Inflamed nodes are a growth with swelling near the chancre. If the chancre is located in the mouth, then swelling of the tonsils and throat is possible, which makes it difficult to breathe and swallow saliva. The occurrence of these symptoms makes it difficult to walk, defecate, eat, etc.
The transition to the second stage of syphilis can be considered the manifestation of a syphilitic rash on visible parts of the body.
Modern medicine can diagnose such a disease after the first signs appear.
For this, modern medicine uses specialized tests:
- ELISA is a qualitative and quantitative immunological method for isolating almost all combinations, molecules and viruses;
- PCR is one of the biological methods that allows us to increase the density of our DNA in one sample of genetic material.
These diagnostic methods can only be prescribed by your personal therapist or venereologist.
The cost of such tests will not hit your pocket hard, but it will certainly confirm or refute the previously made diagnosis.
But do not forget that such tests will give results and show an accurate picture only at the primary stage of the disease.
Primary syphilis is characterized by the appearance of chancres (ulcers) of varying diameters on the skin; it is hard in nature and follows as a response of the immune system to the penetration of harmful bacteria into your body.
Places of its manifestation: the oral cavity (the tongue with syphilis can also be dotted with ulcers), fingers, anus, genitals.
It doesn’t cause much concern, which most often does not contribute to an early visit to specialists at the clinic. This is followed by the development of chancre and inflammation of the lymph nodes near its location.
Associated symptoms are: frequent and severe dizziness, increased body temperature, painful condition.
When infected with Treponema pallidum through the blood, after the incubation period the second stage follows or the disease goes into a latent stage.
Second stage
The main signs of the second stage of syphilis include:
- The skin around the chancre is dotted with spots reaching up to 1.1 cm in diameter. Such a rash can grow over time and, increasing its area, turn into large spots. In this case, it can be flat pink or red up to 5 cm in diameter, flat with conical growths along the entire diameter, or purulent pimples may form due to syphilis. You can easily find photo reports on what these symptoms of syphilis look like on the World Wide Web;
- With the appearance of lesions on the skin, the central nervous system begins to suffer, mainly: vision, memory, attentiveness, ease and smoothness of movements. A quick response and taking measures to treat syphilis can stop further damage to the nerves, but not restore them;
- One of the last symptoms of the second stage is hair loss. First the head: split hairs appear, then they become much thinner, and then they simply fall out. Even after intensive and timely treatment, the hairline is not restored.
Experts divide it into 4 successive phases:
- Early phase - begins after 2 months from the date of infection, lasting up to 14 days. During this period, our immunity begins to actively respond to the release of toxins from syphilis bacteria, that is, multiple ulcers appear on the body. The main impact falls on internal organs, the central nervous system and bone tissue. Associated symptoms: body temperature up to 38°C, cough, painful condition, rhinitis, inflammation of the eye mucosa. Inflammation of the lymph nodes, absence of pain, mild or complete hair loss.
- The latent phase begins 2 months after infection. Throughout its life, Treponema pallidum bacteria can be stopped by the human immune system. The chancre no longer spreads throughout the body, and the rash is no longer observed. But this is not the end, each of us should know that in the fight against this difficult disease, the return of syphilis is always possible.
- Latent phase - during this period, a global resumption of the primary symptoms of the disease is possible. This is possible due to severe stress, colds, injuries, or simply poor nutrition throughout the day. In this case, absolutely all the symptoms are repeated, starting from the primary stage with a new formation of chancre.
- Primary neurosyphilis - usually this period occurs no earlier than 2 years after the disease. Its main destructive effect affects the central nervous system, brain, heart, liver, bones and joints of the human skeleton. An accompanying symptom is necessarily meningitis. Pressure increases in the blood vessels of the brain, which leads to frequent and severe headaches. When the central nervous system is damaged, abilities such as memories, attentiveness, simplicity and ease of movement begin to weaken. Such changes do not return to normal.
Third stage
It is also divided into several phases:
- Latent persistent syphilis – the period of manifestation is up to 20 years. It often happens that people who are carriers of syphilis at this stage are not even aware of the development of such a disease within themselves. After the next resumption of the disease, when the immune system simply cannot cope, the person may receive lifelong disability or it may end in death;
- Tertiary form - during this period almost the entire body suffers. There is an active formation of purulent tumors in the vessels of the brain. It is not uncommon that in the process such tumors attract many other bacteria, which subsequently lead to gangrene and abscess.
- The final stage lasts from 10 to 20 years and leads to a serious degree of disability followed by death. Complete damage to the central nervous system, paralysis, mental disorders, tumors of the brain and bones.
Causes of the disease
Before you find out what chancre looks like with syphilis, you need to familiarize yourself with the various methods of infection with treponema. This is very important to take the necessary preventive measures and minimize the occurrence of the disease.
So, first of all, the disease is transmitted sexually. Therefore, beware of promiscuity and avoid unprotected sex. This is necessary because the largest number of bacteria is concentrated in sperm, as well as on chancre located in the vagina and on the penis. We'll talk about what syphilis looks like on this organ later.
Moreover, the disease can be transmitted not only through intimate contact, but also through everyday contact. If an infected person has a syphilitic rash in the mouth or on the skin, then Treponema pallidum can be transmitted to another even with an innocent kiss or handshake. The disease can also enter the body through shared dishes, towels, bed linen, and clothing. Places where people gather, such as bathhouses, swimming pools, hotels, and public transport, should not be excluded. Therefore, try to avoid places where household items accessible to everyone are not properly disinfected. What does syphilis look like on the skin or oral mucosa? We'll talk about this later.
Another way of transmitting the disease may be blood transfused to a patient and not sufficiently tested. The same applies to a transplanted organ, but this happens quite rarely. Newborns can become infected with Treponema pallidum from an infected mother both during fetal development and during delivery.
Sometimes syphilis can be an occupational disease if it occurs in people who come into contact with excrement and blood during their work activities. Here we are talking about doctors (especially surgeons), laboratory assistants, tattoo or manicurists. If, due to your professional activities, you find yourself in a risk zone, then you need to be extremely careful. Never touch someone else's biomaterial with your bare hands, especially if you have scratches or wounds on your skin.
And the most important thing. Most often, people become infected with syphilis when their body is weakened and their immune system fails. Therefore, strengthen your immunity with good nutrition and additional intake of vitamin complexes. If your body is depleted due to any disease, then try to take care of yourself and not expose yourself to unnecessary risks.
Now let's discuss what the initial stage of syphilis looks like. This is very important, since the life of not only the patient himself, but also his loved ones may depend on timely treatment.
Attention, abnormal!
After the incubation period, the time comes for the formation of ulcers and, accordingly, the disease enters the first stage.
But, despite the presumptive outcome for each phase, abnormal phenomena on the skin are possible.
Based on this, unexpected manifestations are divided into several categories:
- Damage to skin vessels that occur around syphilitic chancre. This symptom changes the color of the penis, scrotum of men and female genitalia to a darker color with a blue tint. Women are more likely to experience syphilis on the lips. It is often confused with other gynecological inflammatory processes. However, only syphilis is characterized by swelling, which during diagnosis will not show any deviations from the norm, but the person’s lymph nodes will be inflamed.
- Idiopathic syphiloma is an inflammation that causes Treponema pallidum on the three main fingers of the hand. Pieces of skin peel off at the affected areas, which leads to slight blood loss, more similar to a recent moderate burn.
- Syphilitic amygdalitis is an inflammation of the submandibular or cervical tonsil. With this anomaly, the structure of the tonsil itself does not change, only an inflammatory process is present, which makes it difficult to swallow saliva and food. All accompanying symptoms are more reminiscent of a sore throat (fever, pain, pain when swallowing), but in our case, inflammation is present in only one tonsil.
What happens in the tertiary period
As mentioned above, at the last stage of the disease, gummas are formed - dangerous lesions of the skin and internal organs. They not only disfigure the patient’s appearance, but also destroy the body from the inside. How do internal disorders manifest themselves? Here are some features:
- The wall of the aorta becomes thinner, resulting in the formation of an aneurysm. This is dangerous because the bulging wall of the aorta can rupture and lead to death. This situation is accompanied by general weakness, headache and dizziness.
- Bones are affected by gums, which is why they are destroyed, and cavities form at the site of inflammation. As a result, the risk of fractures increases.
- From the nervous system, unpleasant symptoms such as paralysis of the limbs, deterioration of vision and hearing, and mental disorders are observed.
From birth side by side with danger
Syphilis can be transferred from mother to child during pregnancy, which negatively affects the fetus during the prenatal period.
Modern medicine has identified the main indicators by which it can be judged that syphilis affected intrauterine growth:
- Interstitial keratitis is an inflammation of the outer mucous membrane of the eye and the eyeball. This can be observed as significant redness and suppuration of the eyes. After completing the course of treatment, traces of surgical intervention will remain on the eyeball, and leukoma (white mesh) will also appear on the eyes. Typically, such changes also lead to a significant decrease in vision, pain and tearing of the eyes.
- Chronic lack of hearing - the fetus during intrauterine growth is subject to an active attack by Treponema pallidum, as a result of which hearing loss is one of the main symptoms of a woman suffering from syphilis during pregnancy;
- Hutchinson's teeth are unfinished development of dental tissue during pregnancy in the fetus. In this case, the teeth have an unpleasant appearance, may grow sparsely, and are not completely covered with enamel. And all this leads to their early destruction.
If a woman has undergone a course of treatment and got rid of Treponema pallidum, the child will still have a chronically weakened immune system.
But with incorrect and untimely treatment, the child will definitely have external abnormalities after birth.
Breastfeeding in the presence of syphilis is strictly prohibited for mothers; milk with Treponema pallidum bacteria automatically passes to the child, causing only harm.
A woman after treatment for syphilis can have children, but for a more accurate conclusion, you need to get a referral from your GP for the two main tests described above.
Treatment
The main treatment for syphilis is taking antibacterial drugs.
Drug therapy
Penicillin antibiotics are used to treat syphilis. In this case, the choice of a specific drug and the regimen for its administration will depend on the specific case of the disease, the stage of its detection, and the presence/absence of an allergy to penicillin in the patient, which is often the case. That is why it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician, undergo intermediate treatment monitoring and, if any questions arise, contact the clinic. The main drugs are benzathine benzylpenicillin sustained release (Bicillin LA) - also suitable for pregnant patients - and benzathine penicillin G.
If there is an allergy to penicillin drugs, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines or cephalosporins. However, they are less effective and therefore are not the main drugs for treating syphilis.
In the later stages of the disease (very rarely), the doctor may prescribe mercury or bismuth preparations. Immunomodulators can be used as maintenance therapy.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is considered an auxiliary treatment method. Using exclusively physiotherapeutic methods, syphilis cannot be cured. However, in the later stages of the disease, physical therapy can help manage symptoms of the disease caused by damage to the nervous system.
Folk remedies
There are no folk recipes for getting rid of syphilis. It is dangerous to rely on home remedies, ignore symptoms, and expect the disease to go away on its own. When entering the latent phase, syphilis may not manifest itself for years, but in the end the consequences of untreated syphilis can be catastrophic.
Depending on the stage of syphilis, medical tactics differ. In the early stages, antibiotics are prescribed, and if treatment was started in a timely manner, this approach gives the expected result. In the later stages, when pathological changes occur in the internal organs, hospitalization is required; many patients are forced to undergo inpatient treatment for several months.
Taken from the article: Treatment of syphilis
Treatment during pregnancy
Syphilis during pregnancy significantly increases the risks of premature birth, stillbirth and pathologies in the fetus. If the mother is infected at the beginning of pregnancy, there is a high probability of miscarriage and intrauterine fetal death; if the mother is infected in late pregnancy, specific damage to the internal organs of the fetus occurs. Therefore, all pregnant women registered at the antenatal clinic are repeatedly tested to detect treponema pallidum in the body.
If the disease is detected, the doctor assesses the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome of the pregnancy and may recommend its termination - abortion. However, in most cases (in the initial stages of development), syphilis in pregnant women can be treated with antibiotics. In this case, drugs are chosen that will not harm the fetus.
Syphilis in pregnant women, discovered for the first time, is treated in two stages. Penicillin antibiotics are used - they do not have a toxic effect on the fetus. If there is an allergy to penicillins, a woman must undergo desensitization (reduction of sensitivity) to these drugs, since alternative antibiotics are contraindicated during pregnancy.
The first stage of treatment is always carried out inpatiently in an infectious diseases hospital, immediately after detection of the disease. Then, at 20-24 weeks of pregnancy, repeated preventive treatment is carried out. The patient is sent to the infectious diseases maternity ward to give birth.
If a pregnant woman has had syphilis before and has already been treated, the doctor may also prescribe her to undergo preventive treatment in later stages - at the end of the second or third trimester. At this time, the placenta is already fully formed, and the fetus is able to receive the necessary medications.
A child whose mother had syphilis before or during pregnancy is examined immediately after birth and then observed for several years (since late congenital syphilis is possible, in which the child is born apparently healthy). Infection can be indicated by alarming symptoms or an increasing titer of antibodies to the pathogen in the newborn’s blood.