Classification of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Scientists have not yet created a unified comprehensive classification of ALS. There are several approaches to classifying the disease. For example, the North American approach involves identifying the following types of ALS: sporadic, familial, sporadic endemic. The classification of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis provides for the following forms of the disease: bulbar, lumbosacral, cervicothoracic and primary generalized. There are also several variants of the disease: mixed, pyramidal and segmental-nuclear.
Reasons for developing ALS
For a long time, the pathogenesis of the disease was unknown, but with the help of numerous studies, scientists were able to obtain the necessary information. The mechanism of development of the pathological process in ALS is a mutation in the disruption of the complex recycling system of protein compounds that are found in the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, as a result of which they lose regeneration and normal functioning.
Targets affected by ALS
There are two forms of ALS – hereditary and sporadic. In the first case, the pathology develops in people with a family history, in the presence of amniotic lateral sclerosis or frontotemporal dementia in close relatives. The overwhelming majority of patients (90-95% of cases) are diagnosed with a sporadic form of amyotrophic sclerosis, which occurs due to unknown factors. A connection has been established between mechanical injuries, military service, intense stress and exposure to harmful substances on the body, but it is not yet possible to talk about the exact causes of ALS.
BASS. Risk factors
Interesting: the most famous patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis today is physicist Stephen Hawking - the pathological process developed when he was 21 years old. At this time, he is 76 years old, and the only muscle he can control is the cheek muscle.
Stephen Hawking
Clinical picture of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
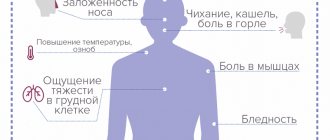
The most common initial symptoms of the disease include cramps (painful muscle spasms), lethargy and weakness in the distal arms, bulbar disorders, leg muscle atrophy, and weakness in the shoulder girdle. In addition, different variants of the disease are characterized by different clinical manifestations.
- Classic variant of ALS (with cervical onset). The first sign of the disease is the formation of asymmetric paraparesis with pyramidal signs. In addition, spastic paraparesis appears, which is accompanied by hyperreflexia. Over time, the patient begins to show signs of bulbar syndrome.
- Segmented variant of ALS (with cervical onset). This type of disease is manifested by the formation of asymmetrical flaccid paraparesis, which is accompanied by hyporeflexia. At the same time, patients retain the ability to move independently for some time.
- Classic variant of ALS (with diffuse onset). This variant of the pathology usually begins to manifest as flaccid asymmetric tetraparesis. In addition to it, patients are also diagnosed with bulbar syndrome, which manifests itself in the form of dysphagia and dysphonia. The patient often experiences a sharp decrease in body weight, shortness of breath and fatigue.
- Classic variant of ALS (with lumbar onset). This variant of pathology begins with lower flaccid paraparesis. Later, symptoms such as muscle hypertonicity and hyperreflexia are added. At the onset of the disease, patients can still move independently.
- Pyramidal variant of ALS (with lumbar onset). This type of disease begins with the occurrence of lower asymmetric paraparesis, which is then joined by upper spastic paraparesis.
- The classic variant of ALS (bulbar palsy is observed at the onset of the disease). This disease is characterized by dysphagia, dysphonia, dysarthria, upper and lower asymmetric paraparesis. The patient is rapidly losing weight and has respiratory problems.
- Segmented variant of ALS (with bulbar palsy). Nasophonia, dysphagia, and dysarthria are considered characteristic of this variant of the disease. As in the previous case, the patient loses body weight and develops respiratory pathologies.
Recommendations
Consultation with a neurologist and electroneuromyography are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Etiology and pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The exact causes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are still being investigated by scientists. However, several factors can be named that provoke the disease. For example, about 5% of diseases have a hereditary etiology. At least 20% of cases are associated with mutations in the superoxide dismutase-1 gene. Scientists have proven that high activity of the glutamatergic system plays an important role in the onset of the disease. The fact is that excess glutamic acid provokes overexcitation and sudden death of neurons. The molecular genetic mechanism of the pathology has also been proven. It is caused by an increase in the level of DNA and RNA in cells, which ultimately leads to disruption of protein synthesis.
Scientists also identify several predisposing factors that play an important role in the occurrence of ALS. First of all, such factors include age. The fact is that the disease usually develops in patients aged 30-50 years. It is worth remembering that only about 5% of patients have a hereditary predisposition to ALS. In the vast majority of cases of ALS, the cause of the pathology cannot be determined.
The early course of the disease is characterized by symptoms such as convulsions, twitching, muscle numbness, difficulty speaking, and weakness in the limbs. Since such symptoms are characteristic of many neurological diseases, diagnosing ALS at an early stage is difficult. In most cases, the disease can be diagnosed at the stage of muscle atrophy.
Depending on the disease affecting different parts of the body, ALS of the extremities and bulbar ALS are distinguished. In the first case, patients experience deterioration in ankle flexibility, awkwardness when walking, and they begin to stumble. Bulbar ALS is manifested by difficulty speaking (nasal sound, difficulty swallowing). Soon the patient finds it difficult to move or can no longer move independently. Usually the disease does not have a detrimental effect on the patient’s mental abilities, but it leads to severe depression. In most cases, about three to five years pass from the appearance of the first symptoms to death.
Treatment of ALS
There are no therapeutic methods that can cure ALS - treatment is aimed at prolonging the life of patients and improving its quality. The only drug that can slow down the development of the pathological process and delay death is the drug Rilutek. It is mandatory prescribed to people with this diagnosis, but in general it has virtually no effect on the patient’s condition.
"Rilutek"
For painful muscle spasms, muscle relaxants and anticonvulsants are prescribed; for the development of intense pain, strong analgesics, including narcotics. Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis often experience emotional instability (sudden, unreasonable laughter or crying), as well as manifestations of depression; psychotropic drugs and antidepressants are prescribed to eliminate these symptoms.
Pharmacological effects of muscle relaxants
To improve muscle condition and motor activity, therapeutic exercises and orthopedic devices are used, including cervical collars, splints, and devices for grasping objects. Over time, patients lose the ability to move independently, as a result of which they have to use wheelchairs, special lifts, and ceiling systems.
HAL therapy. Used in clinics in Germany and Japan. Allows you to improve the patient's mobility. The treatment method slows down muscle atrophy, but does not affect the rate of death of motor neurons and the patient’s life expectancy. HAL therapy involves the use of a robotic suit. It takes signals from nerves and amplifies them, causing muscles to contract. In such a suit a person can walk and perform all the necessary actions for self-care
Wheelchairs for disabled people
As the pathology develops, patients' swallowing function is impaired, which interferes with normal food intake and leads to a deficiency of nutrients, exhaustion and dehydration. To prevent these disorders, patients are given a gastrostomy tube or a special probe is inserted through the nasal passage. As a result of weakening of the muscles of the pharynx, patients stop talking, and they are recommended to use electronic communicators to communicate with others.
Installed gastrostomy tube
In the last stages of ALS, patients' diaphragm muscles atrophy, which makes breathing difficult, not enough air gets into the blood, shortness of breath, constant fatigue, and restless sleep are observed. At these stages, a person, if there are appropriate indications, may need non-invasive ventilation using a special device with a mask connected to it.
If you want to find out in more detail the diagnosis of ALS - what it is, you can read an article about it on our portal.
Good results in eliminating the symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are provided by massage, aromatherapy and acupuncture, which promote muscle relaxation, blood and lymph circulation, and reduce anxiety and depression.
Acupuncture
An experimental method of treating ALS is the use of growth hormone and stem cells, but this area of medicine has not yet been fully studied, so it is not yet possible to talk about any positive results.
Important: the condition of people suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis largely depends on the care and support of loved ones - patients require expensive equipment and round-the-clock care.
Support from loved ones is very important
Lifts for the disabled
Diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Since ALS is an incurable disease that rapidly shortens a person’s life, the patient’s examination must be comprehensive and accurate. It is extremely important to make a correct diagnosis of the patient in order to promptly begin to relieve his main symptoms, as this can prolong the patient’s life. The examination plan usually includes a history of life and illness, a neurological and physical examination, MRI of the spinal cord and brain, EMG, and laboratory tests.
- History taking and examination
- Instrumental research methods
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a detailed interview with the patient. Namely, the doctor needs to clarify whether the patient complains of muscle spasms and twitching, weakness and stiffness, impaired movement of the hands, speech, walking, swallowing, salivation, frequent lack of air, weight loss, fatigue, shortness of breath during exercise . In addition, the doctor should ask whether the patient has noticed double vision, memory loss, crawling sensations on the body, or urinary problems. It is imperative to ask the patient about his family history - whether he has any relatives with chronic movement disorders.
The main purpose of the physical examination is to assess the patient's constitution, weigh him, measure his height, and calculate his body mass index. The neurological examination usually includes neuropsychological testing. When assessing bulbar functions, the doctor pays attention to the timbre of the voice, speed of speech, pharyngeal reflex, the presence of tongue atrophies, and paresis of the soft palate. In addition, during the examination, the strength of the trapezius muscles is checked.
The main instrumental method for diagnosing the disease is needle EMG. This technique allows you to identify signs of the disease such as acute or chronic denervation. In the early stages of the disease, stimulation EMG is ineffective because it does not detect noticeable signs of ALS.
In the process of diagnosing the disease, doctors also use neuroimaging methods. MRI of the spinal cord and brain plays a great role in the differential diagnosis of ALS. During MRI, in 17-67% of patients it is possible to identify symptoms of degeneration of the pyramidal tracts and atrophy of the motor cortex of the brain. However, it is worth noting that this technique is ineffective when diagnosing the disease in patients with bulbar syndrome.
Many laboratory tests are performed during the diagnosis of ALS. In particular, doctors can prescribe clinical and biochemical blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid tests, and serological tests. However, the only effective and reliable method of analysis is still considered to be molecular genetic analysis. The presence of mutations in the superoxide dismutase-l gene is considered a suspicion for ALS.
Diagnosis of the disease
Patients with suspected ALS should undergo the following diagnostic tests:
- consultation with a neurologist;
- electromyography;
- MRI, CT;
- laboratory examinations (general clinical tests, biochemistry, microscopy and culture of cerebrospinal fluid);
- PCR tests (detection of mutations in certain genes).
The doctor carefully interviews the patient, clarifying the family history. The survey determines whether any of the relatives suffered from chronic progressive movement disorders.
For reference. The diagnosis is confirmed by electromyography, which reveals rhythmic fasciculatory potentials with an amplitude of up to 300 μHz and a frequency of 5-35 Hz (ri).
MRI and CT scans should exclude all other possible diseases of the nervous system that have similar symptoms.
Differential diagnosis
Since the symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are similar in many ways to the manifestations of other neurological pathologies, doctors must carry out a differential diagnosis. The most accurate diagnosis can be made using MRI of the brain and spine. First of all, ALS must be differentiated from muscle diseases, which include Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman dystrophic myotonia, myositis with cellular abnormalities, and oculopharyngeal myodystrophy.
It is also necessary to distinguish ALS from spinal cord pathologies:
- chronic vertebrogenic ischemic myelopathy;
- Kennedy bulbospinal amyotrophy;
- syringomyelia;
- tumors;
- familial spastic paraplegia;
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- hexosaminidase deficiency;
- lymphoma.
Differential diagnosis is also necessary in order to distinguish the disease from systemic pathologies, lesions of the neuromuscular synapse, and brain pathologies such as multiple system atrophy, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, and syringobulbia.
A little terminology
To understand the essence of this terrible disease, you need to understand a little about such complex neurological terminology as central and peripheral motor neuron, bulbar and pseudobulbar syndromes. Since these words will not mean anything to a person far from medicine.
The central motor neuron is located in the precentral gyrus of the cerebral cortex, the so-called motor area. If damage to this part of the brain occurs, central (spastic) paralysis develops, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- muscle weakness of varying degrees of severity (from complete lack of movement to slight awkwardness of movements);
- increased muscle tone, development of spasticity;
- strengthening of tendon and periosteal reflexes;
- the appearance of pathological foot signs (Babinsky’s symptom, Rossolimo’s, Openheim’s, etc.).
Peripheral motor neurons are localized in the nuclei of the cranial nerves, in the thickenings of the spinal cord at the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral levels in its anterior horns. That is, in any case, below the cortical motor neurons. When these nerve cells are damaged, symptoms of peripheral (flaccid) paralysis occur:
- weakness in the muscles innervated by this group of cells;
- decreased tendon and periosteal reflexes;
- the appearance of muscle hypotonia;
- development of atrophic changes in muscles, due to their denervation;
- there are no pathological symptoms.
In ALS, damage occurs to both peripheral and central motor neurons , which causes the appearance of signs of central and peripheral paralysis in this pathology.
Bulbar palsy that develops in Lou Gehrig's disease occurs due to the degeneration of neurons located in the nuclei of the IX, X, XII pairs of cranial nerves. These structures are located in the brain stem, namely in the medulla oblongata (from the Latin bulbus). This syndrome manifests itself as weakness in the muscles of the pharynx, larynx, tongue and soft palate. Here are its main symptoms:
- dysarthria (impaired articulation due to weakness and atrophy of the tongue muscles);
- dysphonia (impaired voice formation) and nasolalia (nasal tone of voice);
- dysphagia (swallowing disorder);
- sagging of the soft palate and displacement of the uvula to the healthy side;
- loss (absence) of the pharyngeal reflex;
- drooling (occurs as a result of impaired swallowing);
- fibrillary twitching in the tongue (detected as small muscle contractions, fluttering).
Pseudobulbar palsy, which includes almost all of these symptoms, develops due to a bilateral violation of the structure of the corticobulbar tracts (that is, the nerve fibers connecting the cerebral cortex with the bulbar group of cranial nerve nuclei). A distinctive feature of this syndrome is:
- preservation of the pharyngeal reflex;
- absence of atrophy and fibrillation in the tongue;
- increased mandibular reflex;
- the appearance of pathological reflexes of oral automatism (they are considered normal for childhood - proboscis, sucking, etc.);
- violent (involuntary) crying and laughter.
Considering that with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, degeneration of both upper (central) and lower (peripheral) motor neurons occurs, bulbar palsy is very often combined with pseudobulbar palsy. In some forms of ALS, these syndromes may be the only manifestation of the disease; the rest simply do not have time to develop, since the symptoms of respiratory failure increase very quickly.
Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The main goals of treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are considered to be to slow the progression of the disease, as well as eliminate its symptoms, which significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life. It should be remembered that ALS is a serious incurable disease that shortens a person’s life expectancy. That is why the doctor has the right to inform the patient of the diagnosis only after a comprehensive and thorough examination.
Treatment of the disease includes drug and non-drug therapy. The latter implies security measures. The patient should limit physical activity, which can accelerate the progression of ALS. In addition, it is very important to eat properly and nutritiously. Drug therapy is divided into two types: pathogenetic and palliative.
Forecast
The prognosis for ALS is unfavorable - the disease leads to death, which usually occurs from paralysis of the muscles responsible for breathing. Life expectancy depends on the clinical course of the disease and the condition of the patient’s body - with the bulbar form, a person dies after 1-3 years, and sometimes death occurs even before loss of motor activity. On average, patients can live 3-5 years, 30% of patients live more than 5 years and only 10-20% live more than 10 years. At the same time, medicine knows of cases when the condition of people with this diagnosis spontaneously stabilized and their life expectancy did not differ from the life expectancy of healthy people.
The prognosis for ALS is unfortunately unfavorable.
There are no preventive measures to prevent amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, since the mechanism and causes of the development of the disease are practically not studied. When the first symptoms of ALS appear, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. Early use of symptomatic treatment methods makes it possible to increase the patient’s life expectancy by 6 to 12 years and significantly alleviate his condition.
Video - ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis)
Pathogenetic therapy
To date, the only drug that can slow the progression of ALS is riluzole. It has been proven that taking it can prolong the patient’s life by an average of three months. This drug is indicated for patients whose disease duration is less than 5 years. The patient should receive 100 mg of the drug daily. In order to avoid the risk of drug-induced hepatitis, it is necessary to check the levels of AST, ALT and LDH every three months. Since men and smokers have lower concentrations of riluzole in the blood, they should either limit themselves to smoking or completely get rid of this bad habit. You will need to take the drug for life.
Scientists have repeatedly tried to use other drugs for pathogenetic therapy. However, such experiments did not prove effective. Among them were:
- xaliprodene;
- metabolic agents;
- anticonvulsants;
- antiparkinsonian drugs;
- antibiotics;
- antioxidants;
- calcium channel blockers;
- immunomodulators.
The effectiveness of taking high doses of Cerebrolysin has also not been proven, despite the fact that this drug can slightly improve the condition of patients.
Famous people with ALS
Mao Zedong.
Photo from pinterest.ru Mao Zedong (1893-1976) - Chinese politician. At the age of 80, he was diagnosed with ALS, but died two years later from a heart attack.
Lou Gehrig (1903-1941) was an outstanding American baseball player. He was diagnosed with ALS at age 36, in 1939.
Dmitry Shostakovich (1906-1975) is a great composer. He suffered from ALS for about ten years and died of a heart attack.
Stephen Hawking (1942-2018) is a famous British physicist. Lived with ALS for over 50 years.
Vladimir Migulya (1945-1996) – composer, author of music for the songs “Grass at the House”, “Talk to Me, Mom”, “Stuntmen”, etc. The disease was discovered in 1993.
Jason Becker (born 1969) is an American composer and guitar virtuoso. He fell ill with ALS at the age of 20, in 1989.
Fernando Ricksen (born 1976) is a Dutch footballer. He was diagnosed with ALS in 2013 and lost the ability to speak in 2021.
Palliative care
Palliative therapy is intended to eliminate a complex of symptoms of the disease and thereby improve the patient’s quality of life. To eliminate certain symptoms of ALS, the following techniques are used:
- spasticity - baclofen and tizanidine are prescribed;
- fasciculations (muscle twitching) - in addition to baclofen and tizanidine, carbamazepine is also prescribed;
- depression and emotional lability - fluoxetine and amitriptyline;
- walking impairment - walkers, canes and strollers are indicated to eliminate this symptom;
- deformation of the feet - the patient should wear orthopedic shoes;
- neck paresis - a rigid or semi-rigid head holder is indicated;
- thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities - elastic leg bandaging is prescribed;
- rapid fatigue - performing gymnastic exercises, as well as taking amantadine and ethosuximide;
- humeroscapular periarthrosis - compresses with procaine, dimethyl sulfoxide solution, hyaluronidase are prescribed;
- oral hypersecretion syndrome - to eliminate this symptom, correction of dehydration, portable suction, mucolytics and bronchodilators are indicated;
- sleep apnea syndrome - fluoxetine;
- respiratory disorders - periodic non-invasive ventilation is prescribed;
- dysphagia - adherence to a special diet (exclusion of dishes with hard and dense ingredients, preference for pureed dishes, soufflés, porridges, purees);
- dysarthria - taking muscle relaxants, applying ice to the tongue, using electronic typewriters, a special computer typing system, following speech recommendations compiled by the British ALS Association;
- salivation - regular sanitation of the oral cavity (it is necessary to brush your teeth three times a day, often rinse the cavity with antiseptic solutions), limiting the consumption of fermented milk products, taking atropine and amitriptyline.
To improve muscle metabolism, a patient with ALS can be prescribed the following medications: creatine, carnitine, levocarnitine solution, trimethylhydrazinium propionate. Multivitamin therapy is also indicated for patients, which involves taking multivitamins (neuromultivit, milgamma) and thioctic acid.
In most patients with ALS, the disease is accompanied by serious motor impairments, including limited mobility. Of course, this causes great discomfort to the patient, who constantly needs help from other people. Orthopedic correction techniques help eliminate some movement disorders. The doctor must explain to the patient that the use of assistive devices does not indicate his disability, but only reduces the difficulties caused by the disease.
The most life-threatening symptom of the disease is considered to be respiratory failure. Its earliest symptoms will be morning fatigue, vivid dreams, daytime sleepiness, and dissatisfaction with sleep. To detect respiratory failure at an early stage, polysomnography and spirography are performed. To eliminate apnea, medication and non-invasive ventilation are indicated. It has been proven that these techniques can prolong a patient’s life by one year. If the patient needs assisted breathing for more than 20 hours, the doctor raises the question of a complete transition to invasive ventilation.
Patients who have undergone an initial examination or a repeated diagnosis of the disease must remain under outpatient observation. As any new symptoms appear, they should also receive qualified advice. Patients must take most medications regularly. Only vitamins and myotropic drugs are taken in courses in stages.
Every three months the patient must undergo spirography. If he takes riluzole regularly, he needs to have LDH, AST, and ALT checked every six months. If the patient has dysphagia, blood glucose levels and trophic status should be measured periodically. Patients have a choice of treatment regimen: they can either stay at home or stay in a hospice.
How to improve the patient's quality of life
If patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis have problems chewing and swallowing food, they should prepare liquid and ground meals. Soups and porridges can be blended with a blender. When a patient loses the ability to swallow food on his own, surgeons at the Yusupov Hospital perform gastrostomy surgery. After this, food is introduced directly into the stomach through a tube inserted through a stoma in the anterior abdominal wall. In some cases, parenteral nutrition is carried out - mixtures that contain all the necessary ingredients are administered intravenously.
If speech is impaired, ALS patients lose the ability to speak. In this case, they can communicate with others using a printing device. Also for this purpose, systems with automatic sensors located on the eyeballs are used.
If the patient loses the ability to move independently, they resort to orthopedic devices, use special shoes, canes and strollers. The head is fixed with a special holder. As the disease progresses, the patient should be provided with a functional bed.
Weakness in the legs
Dmitry Shostakovich.
Photo from pinterest.ru ALS is very difficult to diagnose. Firstly, because it is a rare disease that doctors are poorly aware of. Secondly, early symptoms are quite minor: clumsiness, clumsiness in the hands, slightly slurred speech. Thirdly, the disease manifests itself differently in each patient.
The first and most common symptoms of ALS are weakness in the arms or legs. Objects begin to fall out of the hands, the person stumbles when walking, and drags his foot. There is a sensation of muscle contractions under the skin (fasciculations). Painful cramps and spasms may occur. Fatigue increases.
Difficulties begin with speech, swallowing, and chewing. It becomes difficult to breathe.
Some ALS patients may cry or laugh involuntarily. The reasons for this are not psychological, but physiological: the disease affects areas responsible for emotional reactions. Sometimes there are problems with memory and concentration.
What help does the patient and his family need?
Photo by Yuri Mozolevsky from the website sb.by
A person with ALS may need consultations with a neurologist, a respiratory support specialist, a physical therapist, an occupational therapist, a nutritionist, a speech therapist, a music therapist, a psychologist, a palliative physician, as well as the help of a medical and visiting nurse.
The family will have to provide him with certain equipment. This could be a wheelchair, walker, multifunctional bed, ventilator or NIV, aspirator (saliva ejector), cougher, lift (for example, for moving from a bed to a wheelchair or from a stroller to a bath). In addition, the patient needs medicine, nutritional therapy, hygiene products, etc.
Each patient with ALS needs an individual route of care, as the disease can progress in different ways.
What happens to the patient
Photo from the site syl.ru
The average life expectancy for ALS is from two to five years from the moment the first symptoms appear. There are cases when the disease lasts several decades. For example, Stephen Hawking lived with ALS for more than 50 years. And there are patients who leave a few months after the diagnosis is made.
As ALS progresses, a person experiences increasingly serious difficulties with moving, speaking, swallowing, and breathing. Therefore, doctors advise relatives to immediately adapt housing for the patient and buy special equipment.
If the disease begins in the legs, then at first it becomes difficult for the patient to walk and maintain balance; he may lean on pieces of furniture, so they must be stable. Then the patient begins to use a walker or wheelchair, and it is important to free up space in the house for this.
Gradually, it becomes difficult for a person to raise his arms, so it is recommended to place all necessary things no higher than 1 m from the floor. There are adapted forks, spoons and knives with thicker handles and even with straps; they allow the patient to go longer without assistance when eating.
To communicate with the outside world, such patients eventually have to resort to special devices. Stephen Hawking, for example, used a special computer system that was controlled by the cheek muscle. And Jason Becker uses a board with letters that he points to with his eyes. Many people benefit from the Tobii device, which connects to a regular computer and allows you to move the cursor and type on the keyboard with your eyes.
Sooner or later, a person's respiratory muscles are affected and he loses the ability to breathe on his own. Then there is a need for breathing equipment.
What research is being done to beat ALS?
Image from the site syl.ru
In motor neurons affected by ALS, pathological clots (aggregates) of protein molecules are found. Typically, proteins stick together as a result of some defect in the gene that encodes them.
In 20% of cases of hereditary and in 2% of sporadic forms of ALS, the disease is caused by a mutation of the SOD-1 gene. This mutation was first discovered in 1993.
A mutation in the TAR DNA binding protein (TDP-43) gene has been found in some families of ALS patients. In 3-5% of patients with a hereditary form of ALS and in 1% with a sporadic form of ALS, a mutation of the FUS protein gene occurs.
In 2011, scientists discovered the C9ORF72 gene mutation. It turned out that it is present in 25−40% of families where there is a patient with ALS, and in 7−10% of patients with a sporadic form of the disease.
In 2014, thanks to the IceBucketChallenge flash mob, when thousands of people around the world were doused with ice water, more than $100 million was raised to research the causes of ALS and find a cure for this disease.
Research is going in two directions. The first is the search for genes that cause the hereditary form of the disease. The second is the identification of “susceptibility genes” that increase the risk of the disease in a family where no one has previously had ALS. Understanding the mechanisms of the disease will help find a cure for it in the future.