Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a progressive disease. This means that the system designed to keep your body healthy is mistakenly attacking parts of the body that are vital to daily functioning. The protective covering of nerve cells is damaged, leading to decreased function of the brain and spinal cord.
The first signs of sclerosis in young people appear between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Usually they go down, but then come back again. The patient may be bothered by one symptom, and then months or years pass without any manifestations of the disease. The problem can also happen only once, but then go away and never return. For some people, the condition worsens over weeks or months.
A timely visit to a doctor will allow you to control the disease and help the specialist understand how effective your treatment is.
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis in women
The disease's manifestations are vague and mimic many other neurological conditions. The clinical picture of MS is very diverse, depending on the shape, course and location of the lesion. It happens that a woman has only one symptom. More often - several.
- Movement disorders. What most often begins with multiple sclerosis. Motor disorders include paresis and paralysis. Paresis is an incomplete impairment of voluntary movement of the limbs. Paralysis is a complete impairment, without the ability to voluntarily move the limbs. This pathology is the main reason for the transformation of patients into disabled people.
- Sensitivity disorders. So-called paresthesia is a burning sensation, tingling in the limbs, comparable to goosebumps or muscle spasm. Other types of sensitivity are also impaired: vibration, joint-muscular, temperature. Sensitivity may decrease or disappear completely.
- Pathology of vision. Occurs due to changes in the optic nerve. Possible manifestations:
- decreased visual acuity;
- the appearance of a blind area of the visual field - scotoma;
- nystagmus - rapid uncontrolled movements of the eyeballs;
- incorrect color perception.
- in the lower extremities;
- in the pelvic area;
- headache;
- muscle and joint pain;
- pain on one side of the face (trigeminal neuralgia).
The very first changes can only be noticed by a neurologist during a clinical examination.
Expert opinion
Author: Alexey Vladimirovich Vasiliev
Neurologist, Head of the Research Center for Motor Neuron Disease/ALS, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune demyelinating disease. According to the World Health Organization, the number of people with this diagnosis has exceeded two million, with 2-3 times more women (researchers give different figures), but in men the disease is more severe.
The autoimmune nature indicates that the cause of the disease is inside the person, or more precisely, the immune cells attack the “wrong” target, in this case, the myelin sheath of the neuron, which is why the “signal disappears.” But why women? The fact is that when a woman is carrying a child, her immune system perceives this as a threat and its functioning may be disrupted.
Multiple sclerosis is not a disease of older people. The average age of onset of relapsing-remitting forms is 30 years, with women acquiring the disease earlier. 5% of MS cases are children under 18 years of age and approximately 10% are patients over 50.
Multiple sclerosis cannot be cured; therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms. With early detection and adequate treatment, the prognosis is good, but experts say that MS shortens life expectancy by 7-14 years.
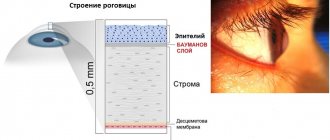
Optic nerve damage
A common vision problem called optic neuritis is considered an early indicator of MS. It is considered a more “specific” sign compared to “vague” neurological symptoms such as tingling or numbness.
Optic neuritis is characterized by:
- temporary loss of vision;
- color blindness;
- Pain in the eyes;
- double vision.
In addition to the optic neuritis that accompanies MS, involuntary eye movements are added.
Forms of female MS
Depending on the location of the lesion, the following forms of MS are distinguished:
- Cerebral. Manifested by impaired brain function and epileptic seizures.
- Stem. The fastest form of the onset and development of the disease, the patient often does not even have time to assess the situation.
- Optical. Visual impairment.
- Spinal. Spinal cord dysfunction.
- Cerebrospinal. Several body systems are affected at once. The most common form of MS.
- Cerebellar. It is characterized by damage to the cerebellum, which leads to impaired movements and hand tremors.
Make an appointment
Cerebral form
Characteristic in case of damage to the motor area (responsible for movement) of the brain. Changes in the cells of the central part of the brain lead to paralysis and paresis (decreased muscle strength) of various forms. If limbs on one side are involved in this process (for example, the right arm and leg), we can talk about hemiparesis; two limbs (for example, two arms or two legs) - about paraparesis; all four limbs (2 arms, 2 legs) - tetraparesis.
Stem form
It is localized in the brain stem - the place responsible for all our sensitivity in general. Violations here most often lead to problems with speech (it is impossible to pronounce words clearly, the tone and timbre of the voice changes) and breathing (the muscles in the larynx relax so that they block the access of air to the trachea). This form has a lightning-fast course: a person begins to choke, the temperature rises sharply and an unbearable headache appears. Only immediate resuscitation can help here, but death often occurs.
Optical form
MS in this case is localized in the occipital lobe of the brain, which is responsible for vision. The course of the disease in this case is usually as follows: first, the colors become duller, then visual acuity decreases, then vision deteriorates until complete blindness. The lesion can affect one or both eyes at once. If the disease is relapsing-remitting, vision may return to its previous state even without treatment.
Other symptoms may also occur: double vision, pain, inability to look to the side, eye twitching, etc.
Spinal shape
The source of the disease in this case is located in the spinal cord. Manifestations of this form of the disease are usually as follows:
- lower paraparesis (muscle weakness in both legs);
- decreased sensitivity;
- “shooting” in the arms and legs (Lhermitte syndrome);
- disruption of the functioning of the genitourinary system.
Cerebrospinal form
The most common form of MS. It affects both the brain and spinal cord simultaneously, and therefore the visual and vestibular apparatus. This form combines the symptoms of cerebral and spinal forms.
Cerebellar form
The location of the lesion is the cerebellum, which is responsible for the coordination of movements. Accordingly, the symptoms of this form will be as follows:
- impaired coordination of movements;
- inability to adequately estimate the distance to an object;
- trembling in the limbs;
- loss of the ability to move at all;
- severe headaches;
- impossibility of articulate pronunciation due to limited mobility of the speech organs (lips, tongue, soft palate).
What kind of disease is this?
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that occurs in genetically predisposed people after exposure to pathological external factors on their body. Most often, such factors are infectious diseases. Multiple sclerosis is also known medically as extensive or multiple sclerosis. The Latin name of the disease is sclerosis disseminata. Why is there another “name” of the disease in the medical literature – disseminated sclerosis.
The main essence of the pathology is that in the body of a sick person there are multiple lesions of the central nervous system (CNS) - the brain and spinal cord - in the form of damage to the white matter. Rarely, the process can also affect the peripheral nervous system.
The disease is characterized by an undulating clinical course, with gradual or, which is much less common, rapid progression.
Most often this diagnosis is made in residents of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand. Post-Soviet countries belong to the second most common region for this disease.
The disease practically does not threaten adolescents and the elderly. However, recently the incidence statistics among young people has increased significantly.
Signs of multiple sclerosis are more common in women than in men.
Not only geographical factors, but also the specifics of the diet, social and economic living conditions significantly influence the prevalence of the disease.
Types of PC
According to the clinical course, experts distinguish the following forms of MS:
- Relapsing-remitting form (RRMS). Secondary progressive form. It is characterized by rather pronounced manifestations. Exacerbations in this case are rare (or generally unnoticeable against the background of constant symptoms), but residual signs of multiple sclerosis are present during stabilization. 30–40% of patients are in this group.
- Primary progressive form (PPMS). The disease is constantly progressing, periods of improvement are insignificant. Exacerbations are not clearly identified. 10–15% of patients belong to this group. A striking example is when a patient’s vision begins to decline and is no longer restored (even for a short time), but only worsens.
- Secondary progressive course (SPRS). It is characterized by a slow deterioration of the condition, the occurrence of complications over a long period of time. This form of MS can be either active (with attacks) or not. Usually occurs after RRMS. Selective damage occurs to the myelin sheath that runs around the nerve fibers of the central nervous system.
- Progressive course with exacerbations. The disease is constantly progressing, with exacerbations occurring as MS develops. After each exacerbation, the patient's condition worsens. 5% of patients fall into this group.
To determine which group according to the course of the disease the patient belongs to, specialists prescribe a series of examinations.
Make an appointment
Relapsing-remitting form
As mentioned above, relapses in this form alternate with remission, during which no progression of the disease is observed.
To diagnose RRMS, a specialist needs to detect the spread of the disease in at least two areas of the central nervous system (affected areas of myelin, the substance that forms the sheath of nerve fibers). An important criterion here is the prevalence over time, that is, damage to these areas should occur at different times. If one of the criteria is not confirmed, a clinically isolated syndrome can be diagnosed with further clarification of the diagnosis.
With this form of the disease, patients usually experience the following symptoms:
- fatigue;
- numbness of the limbs;
- loss of vision;
- memory problems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system.
At the same time, people with progressive forms of MS are more likely to have problems related to the musculoskeletal system.
Primary progressive
This course of the disease is accompanied by sharp deterioration without early relapses and remissions. This form of MS is more difficult to diagnose. On average, PPMS occurs several years (about 8–10) after a relapsing-remitting course. Since in this course of MS the spinal cord is more often affected than the central nervous system, the patients’ problems are usually associated with walking, urinary and fecal incontinence.
Secondary progressive
This form can only be diagnosed in a patient already diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. To understand whether the transition from RRMS to SPMS has taken place, it is necessary to be constantly monitored by a neurologist and periodically do MRI. Due to the appearance of new foci in this course, exacerbations and relapses are possible, as with RRMS. The nature of the disease slowly moves from the demyelinating stage to the neurodegenerative stage, characterized by damage to nerve fibers and tissues.
Progressive with exacerbations
The rarest form in which the disease, starting with a remitting course, becomes primary progressive. In this case, symptoms increase, and neurological functions do not recover after exacerbations.
Cerebellar disorders
Coordination problems are common in multiple sclerosis and arise mainly from pathology in the cerebellum itself or when brain connections are disrupted. Patients may have either acute dysfunction associated with an acute exacerbation or chronic cerebellar problems with progressive disease.
Involvement of the cerebellar and brainstem connections occurs quite often during an exacerbation. Relapse of the cerebellum early in the development of the disease is associated with an increased risk of cerebellar damage during the subsequent course of MS. Experience shows that cerebellar involvement early in the disease worsens the prognosis. In a recent database study of approximately 15,000 patients who experienced a total of 50,000 exacerbations, cerebellar relapses accounted for approximately 10% of the total. They were more common in younger men and those with longer duration of progression.
It is estimated that 80% of patients with established MS experience tremors, which are especially common in patients with advanced disease. This is a consequence of unstable functioning of the cerebellum. Tremor can affect the limbs, trunk, vocal cords and head, but such a severe form is a relatively rare consequence of sclerosis.
Thus, cerebellar dysfunction may be a clear indicator of progressive MS. In general, this entails increased disability and poor prognosis.
Causes
As we said above, women are more susceptible to this disease than men. But, interestingly, their immune system resists MS better than men’s.
Until now, the nature of MS remains a mystery. However, thanks to laboratory and clinical studies, the mechanism of MS development is known. Based on this, the most important factors were identified:
- Infections. There is no single infectious disease that leads to MS. However, some infectious agents cause specific autoimmune reactions that may be responsible for multiple sclerosis. Among them:
- herpes virus;
- endogenous retroviruses;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- various bacterial infections.
Classification
Manifestations of the disease are very individual. Therefore, the generally accepted classification is based on the nature of the pathological process.
The following types of sclerosis are distinguished:
- Remitting. The most common type of multiple sclerosis. It affects approximately 80% of all patients. It is characterized by the presence of clearly defined exacerbations and remissions.
- Secondary progressive. Develops after remitting. On average, the transition to this form takes about 10 years. Characterized by short periods of remission, the disease gradually becomes chronic.
- Primary progressive - characterized by gradual but steady development. Every day the disease progresses, the health of patients becomes worse. Exacerbations are absent or occur very rarely. This form affects every tenth patient.
- Progressive-relapsing is the least common type and combines the features of primary progressive and remitting.
The disease is most easily treated in a remitting form. The main goal of therapy is to avoid further development of the disease.
Diagnostics
MS is a disease in which the timing of diagnosis plays a critical role. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the patient's chances for a normal life. Neurologists first collect anamnesis, then prescribe tests and examinations. An initial survey helps specialists predict the stage of development of the disease and its form. But for a more detailed picture, the following is carried out:
- Objective neurological examination. This inspection is carried out with a special hammer. The doctor evaluates the movement, tone and strength of the patient’s muscles, sensitivity (superficial and deep), nerve function, etc.;
- Laboratory diagnostics: general blood test (allows us to exclude a number of diseases similar in symptoms to MS);
- Lumbar puncture - taking fluid from the spinal cord. This analysis is mandatory if MS is suspected. Although this manipulation is unpleasant, it does not cause any harm to the spinal cord, and the discomfort disappears within a few days.
- Hardware diagnostics.
At the moment, specialists use the following hardware diagnostic methods:
- Superposition electromagnetic scanning is a modern method that allows one to determine the activity of enzymes in nervous tissue.
- Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy - this procedure is used to assess the level of brain metabolism, as well as the state of the psyche.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most effective diagnostic methods: MRI images show the current state of the brain and problem areas, if any. Since the picture is taken in three projections, it is possible to see even the smallest plaques.
- Electroencephalography is a method that allows you to determine the state of brain activity and the integrity of nerve fibers. Since MS is often localized in the visual area, if symptoms are present, special attention is paid to it on the EEG.
- Differential diagnosis allows you to determine an accurate diagnosis by excluding diseases with a similar course.
Make an appointment
MRI for diagnosing MS
MRI is one of the most highly informative methods for diagnosing MS. It allows you to detect plaques on the surface of the brain, expansion of the cavity of the cerebral ventricles and atrophy of the cortex.
To make the image even more informative, contrast fluid is often used during MRI. It accumulates in places where myelin has been destroyed, and in the pictures such areas are visible even better.
Spinal puncture
This study is mandatory if MS is suspected, but requires psychological preparation of patients, since many fear possible damage to the spinal cord during manipulation. If the patient is sick, an increased number of lymphocytes and an increased level of immunoglobulins G will be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This test will help both in detecting MS and in excluding other diagnoses.
Study of bioelectrical activity of the brain
An electroencephalograph is a device that allows you to study signals from the central nervous structures of the brain. During the study, it is easy to determine the presence or absence of damage to nerve fibers, as well as their degree. Also, using this diagnostic method, you can monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Problems in diagnosing MS in the early stages
How to recognize multiple sclerosis and seek help? As can be seen from the above signs of the development of the disease, the symptoms are quite vague. It is almost impossible to determine an accurate diagnosis on your own; moreover, there are various diseases similar to multiple sclerosis. They begin in exactly the same way as MS begins; to exclude them, the neurologist prescribes special tests (biopsy, blood test, MRI). Only a qualified specialist can determine whether a person has multiple sclerosis or not.
The list of diseases similar to multiple sclerosis is huge. Diseases similar to multiple sclerosis: Infections affecting the central nervous system. These include:
- Lyme disease.
- AIDS virus.
- Syphilis.
- Leukoencephalopathy
Inflammatory processes affecting the central nervous system:
- Sjögren's syndrome.
- Vasculitis.
- Lupus.
- Behçet's disease.
- Sarcoidosis.
Genetic disorders:
- Myelopathy.
- Cerebral arteriopathy is autosomal dominant.
- Leukodystrophy.
- Mitochondrial disease.
Brain tumors:
- Metastases.
- Lymphoma.
Deficiency of vital microelements:
- Copper deficiency.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency.
Lesions to tissue structure:
- Cervical spondylosis.
- Disc herniation.
Demyelinating disorders:
- Devic's disease.
- Disseminated encephalomyelitis.
In addition to these diseases, the first manifestations of the disease may be similar to the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, and it, unlike MS, is completely harmless to the human body. VSD is not fatal. It, like multiple sclerosis, is also characterized by dizziness, loss of coordination, spasms, and weakness. What problem attacked the patient - VSD or multiple sclerosis - will be determined by a qualified neurologist. The main thing is not to delay visiting the clinic.
Treatment
At the moment, treatment for MS is quite effective (10–20 years ago this disease led to disability in most cases), it includes:
- Drugs that change the course of multiple sclerosis and have a positive effect on the immune system.
- Hormonal agents. Designed to suppress exacerbations. It is worth noting that new hormones do not produce the same side effects as the previous generation of drugs.
- Exercise therapy is an important method in the treatment of MS, since the less the patient moves, the more muscle dystrophy develops.
- Drugs that restore nervous tissue are being developed (they are not currently registered in the Russian Federation)
The psychological attitude of the patient, the person’s readiness to overcome his illness every time it manifests itself again, is also very important.
The cost of treatment for multiple sclerosis in Moscow is calculated individually, as it may include different treatment regimens. An appointment with a neurologist starts from 5,150 rubles.
How is it diagnosed?
As you know, the earlier a disease is detected, the easier it is to cure it. But early diagnosis of sclerosis is quite difficult. In order to facilitate the diagnosis of pathology, an algorithm for identifying the disease was developed. According to him, multiple sclerosis should make itself felt before the age of fifty-nine with at least two lesions of the white brain matter. At the same time, they need to be identified with a time interval of at least one month.
This criterion is the main one for a confident diagnosis. But it is necessary to accurately exclude all other causes of damage to the central nervous system.
Neurophysiological and instrumental diagnostic methods are widely used. At the same time, some have to be confirmed by others. The first of these methods make it possible to determine the symptoms of focal lesions of the nervous system at the preclinical stage, when it is quite easy to prevent the progression of the disease. The probability of making a correct diagnosis is about sixty percent.
In almost all cases, multifocal lesions can be confirmed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It allows you to diagnose focal increases in signal intensity in the brain or spinal cord on images obtained in a special mode. Sometimes, in the presence of an advanced chronic process, it is possible for foci of pathology to merge and form zones with a hyperintense signal from them. In this case, secondary atrophy of the medulla is detected.
Magnetic resonance imaging using contrast agents is especially effective. For this purpose, Magnevist and gadolinium-based drugs are widely used. They make it possible to enhance signals from inflammatory foci, which helps to identify “young” areas of increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier. In this way, the activity of pathological processes can be monitored.
However, as already indicated, only a combination of additional research techniques with clinical methods allows one to confidently establish a diagnosis.
Due to its accessibility and lack of fear among the population of ultrasound examination (ultrasound), it becomes the first of the instrumental methods of confirming the diagnosis. Due to the characteristic features of this method, it is often impossible to confirm or refute sclerosis. After all, an ultrasound will show only gross changes in the brain matter, which are characteristic of severe stages.
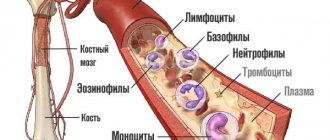
Biochemical methods to confirm the diagnosis are also used. These include determining indicators of the immune response from peripheral blood, which indicate an imbalance of the immune system. He says about this:
- Decrease in the number of T-cells;
- Impaired activity of specific and nonspecific suppressor cells;
- An increase in the number of B lymphocytes in combination with their polyclonal activation;
- Increased levels of activated cytokines and antibodies to myelin.
Using these tests, you can determine the severity of the pathology. But they are not used as independent diagnostic methods.
They also resort to determining the level of hormones of the adrenal glands and hypothalamus.
Treatment goals
Any woman with this diagnosis needs therapy. Her tasks:
- avoid exacerbations;
- eliminate exacerbation;
- improve the course of the disease;
- alleviate symptoms.
Treatment of exacerbation
Medicines from the glucocorticoid group (GCS) are used. They suppress immune responses. Their action in relation to MS:
- relieve inflammatory and autoimmune reactions;
- reduce the duration of exacerbation, but do not affect subsequent relapses;
- are not used long-term due to serious side effects.
If the course is malignant, in addition to GCS, cytostatics are prescribed.
Make an appointment
Multiple Sclerosis Modifying Drugs (MSMDs)
Modern and most effective treatments for MS. Their main effect is to improve the course of the disease. After taking DMTRS, the frequency of exacerbations decreases, the disease becomes more stable.
At the moment there are two PITRS lines:
- β-interferon preparations;
- Immunoglobulins, strong immunosuppressants, autologous bone marrow cell transplantation.
Symptomatic treatment
Patients with MS, in addition to specific treatment, require medications to relieve symptoms:
- Spasticity: muscle relaxants, M-anticholinergics, botulinum therapy.
- Epileptic seizures: anticonvulsants.
- Sleep problems: anxiolytics, sleeping pills.
- Bladder problems: anticholinesterase drugs.
- Depression, mood swings: antidepressants, mood stabilizers.
Any medicine is prescribed only by a doctor. Drugs from the above groups may be incompatible with each other! When prescribing, the doctor takes into account the patient’s condition, MRI results, laboratory values and side effects of various drugs.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
A relatively new technique based on stimulating cells with a magnetic field. Used for both treatment and diagnosis.
- relieves muscle spasticity;
- determines the excitability of the cerebral cortex;
- acts precisely on individual zones of the cortex.
Emotional disorders
Emotional disturbances are often common in MS and include mood changes and affective states. Important mood disorders include major depression, panic attacks, and anxiety. Their relationship to disease is multifactorial and complex, and the extent to which they are direct consequences of disease remains unclear.
Symptoms of mood disorders in young people with MS do not differ from those in healthy people and respond just as well to standard treatment. Affect disorders include euphoria, pathological laughter and crying, and other symptoms. These abnormalities are the result of a lack of myelin and are one of the most characteristic indicators of multiple sclerosis.
Mood and affective disorders can cause enormous pain and distress to the patient and lead to disruption of family, career and social life. Doctors who can effectively diagnose and treat this can have a significant impact on patients' quality of life.
Complications of multiple sclerosis
MS itself has severe symptoms, the progression of which leads to disability. The most serious consequences of MS:
- Paralysis. The woman finds herself in a wheelchair and requires constant care.
- Pneumonia. It is often the cause of death in MS patients.
- Muscle weakness in walking patients increases the risk of falls and fractures, and in bedridden patients - the development of bedsores;
- With MS, irreversible changes occur in the brain, so the patient may become depressed: this complication occurs in approximately 50% of cases;
- Urinary system infections. They threaten with such a serious condition as urosepsis - the spread of infection from the urinary system throughout the body. Urosepsis is lethal.
- Urinary incontinence. An unpleasant symptom that makes life difficult.
- Complications from hormonal drugs. Long-term use of corticosteroids causes:
- osteoporosis - decreased bone density;
- stomach ulcer;
- decreased immunity;
- cataract.
- flu-like syndrome, manifested by chills and headache;
- changes in laboratory parameters (liver transaminases, platelets).
Possibilities of modern medicine
Treatment for multiple sclerosis should begin as soon as possible after a woman's first symptoms appear and diagnosis is made. Only the early phase of the disease can be treated, i.e. stage of inflammation. In the phase of neuronal destruction (neurodegeneration), therapy does not affect the course of MS.
Methods
Unfortunately, today there are no drugs that can effectively slow down neurodegeneration or replace damaged nerve fibers. Therefore, MS remains an incurable disease.
Treatment options:
- acute attacks: high doses of corticoids (Methylprednisolone), usually 1 g for 5 days;
- prevention of attacks and progression during remission: β-interferon, glatiramer acetate, azathioprine or immunoglobulins in appropriate immunosuppressive doses;
- chronic course: corticosteroids with Cyclophosphamide or Mitoxantrone;
- symptomatic treatment;
- spasticity - central muscle relaxants (Baclofen, Tinazidine, Tetrazepam);
- sphincter problems - anticholinergic drugs;
- pain, paresthesia – Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Carbamazepine;
- depression - SSRIs;
- fatigue - regular exercise, vitamin therapy;
- cerebellar symptoms – Physostigmine;
- tremor – Clonazepam;
- incontinence - Imipramine, Oxybutynin.
Modern drugs
New drugs include Cladribine, Teriflunomide (cytostatic), Dimethyl fumarate (synthetic immunomodulator). Their immunomodulatory effects have been recognized in other autoimmune diseases.
Medicines specifically developed for the treatment of MS are Fingolimod and Laquinimod (synthetic immunomodulators). Potentially suitable substances are statins, which also have an immunomodulatory effect.
Other monoclonal antibodies are also being tested, of which Natalizumab is currently used.
Drugs with neuroregenerative and neuroprotective effects are being developed, and various forms of cell transplantation into areas with large lesions of the central nervous system are being sought. The use of growth factors and drugs that block the apoptosis of nerve cells is being tested, and other methods are being sought.
Caring for sick women
Patients with MS need constant care, so if the patient has no relatives, he is often transferred to inpatient treatment. A patient with MS needs the following help:
- ensuring physical mobility to prevent muscle atrophy;
- walking assistance;
- control of the frequency of trips to the toilet;
- creating a positive emotional mood;
- light massage of the limbs (as recommended by a doctor), etc.
Make an appointment
What do the patient's relatives need to know?
It is worth remembering that MS is a disease that currently cannot be completely cured. But, at the same time, you should not treat a patient with multiple sclerosis as a disabled person. For a long time, people with this diagnosis are able to take care of themselves and even work, so do not interfere with this. Create an atmosphere of care and love around you: exercise with the patient, prepare food for him that corresponds to the diet prescribed by the doctor, and simply be there to help in moments of exacerbation of the disease.
Currently, patients with MS can live a full life up to 72-75 years, but only if treated and followed the doctor’s recommendations. How you can support the patient:
- Never say that recovery is possible; there is no need for false promises. Only stabilization and reduction of symptoms is possible.
- Encourage interest in treatment and rehabilitation. The Yusupov Hospital has a rehabilitation center for patients with MS. With the help of modern equipment and the use of new techniques, patients begin to feel more confident.
- Offer feasible tasks. This way the patient will feel needed and important.
- Do not scold the patient for clumsiness or inattention. These are symptoms of the disease. Man cannot control them in any way.
- Encourage the person to be physically active if possible.
- Control your diet. You should not eat food high in animal proteins and fats. Find the person an adequate replacement for his favorite products.
- Help me find friends. A person needs communication not only in his usual circle. If the patient cannot leave the house, you can find friends on social networks, for example, in multiple sclerosis groups. This way she will feel that she is not alone in her illness.
Reasons to see a doctor as soon as possible
The signs of MS vary from person to person. If you notice increasing fatigue that appears in the afternoon, an overly sensitive reaction to heat (for example, headaches may appear after taking a hot shower), dizziness, numbness in the limbs, deterioration in visual acuity, immediately go to the doctor.
Remember that it is important to start the treatment process before MS attacks begin. Even if MS is diagnosed, your doctor will help determine the true causes of your symptoms and prescribe the right treatment that can save your life.
Multiple Sclerosis Center
Yusupov Hospital will be the best choice for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Highly qualified neurologists with many years of experience work here. Patients receive not only medicinal and non-medicinal support (physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy, etc.), but also psychological help, which is especially important for patients with multiple sclerosis. The hospital is equipped with the latest technology, specialists use the latest examination methods. The correct diagnosis will be made quickly, which means the patient will receive treatment sooner. It is in this case that the prognosis for MS is good: the person will be able to live normally, and the risk of disability will be minimized.
Pathogenesis and etiology
The etiopathogenesis of MS is not fully understood; The influence of genetic factors and environmental influences are taken into account. For 2021, the main one is the genetic theory, complicated by the influence of certain external factors. Epigenetic and stochastic influences are also taken into account.
Supposed causes of multiple sclerosis in young women:
- genetic predisposition;
- difficult labor;
- difficult pregnancy;
- injuries;
- excessive amounts of lead or mercury in the body;
- gluten allergy;
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- autoimmune diseases;
- fungal growth in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- slow viral infections (eg after vaccination).
Myelin destruction is the main cause of the disease
Forecast
It is not yet possible to completely eliminate the symptoms of MS, but maintenance therapy will help prevent the onset of disability, which in itself is very important. It is necessary to remember the following risks for patients diagnosed with MS:
- before 15 and after 40 years, the risk of complications increases;
- mental disorders or concomitant disorders/diseases can hasten death;
- disruptions in the functioning of vital organs (kidneys, lungs, heart) can lead to instant death.
To prevent any of this from happening, you need to constantly monitor the patient’s condition and consult a specialist in time to prevent complications. As for the life expectancy of people with MS, much depends on how quickly the correct diagnosis was made. A diagnosis made at an early stage and proper treatment are the key to a long and happy life for the patient.
Onset of the disease
As a rule, the debut of the disease is the first clinical manifestation of the disease. By that time, the attacks of multiple sclerosis themselves may have been present for several years. Almost the debut of multiple sclerosis is noted within the first 5 years of the autoimmune process. This period is quite late, it reduces the chances of improving the patient’s condition, but this does not mean that achieving long-term remission becomes impossible.
One of the most typical debuts of MS is considered to be complete or partial damage to the optic nerve. Manifestations of such a debut are:
- sudden deterioration of vision;
- sudden onset of color blindness;
- cloudiness or blurred vision;
- a black dot flashing in front of the eye;
- constant feeling of the presence of a foreign body;
- pain in the eyeball, increasing when the pupil moves;
- impaired reaction to light (increased photosensitivity);
- flashing objects before the eyes;
- blurred contours of visible objects.
As a rule, visual impairment occurs very suddenly. In this case, symptoms may appear for about a week, then pass. Complete restoration of vision occurs in 70% of cases.
Prevention
Since at the moment science has difficulty determining the exact causes of MS, there are no specific preventive measures. But one thing is for sure - maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an excellent preventive measure for most diseases. Namely:
- play sports (it’s enough to run in the morning or do exercises);
- avoid stress;
- give up bad habits;
- normalize nutrition and weight;
- sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- Be periodically examined by a neurologist.
Such simple rules are suitable for both healthy people and those already suffering from multiple sclerosis: it is important for them not to aggravate the course of the disease.
How is this disease treated?
At the moment, science is unable to establish the exact cause of multiple sclerosis. Therefore, no medications have been developed for etiotropic therapy. In fact, the symptoms of the disease are treated.
Therapy depends on the individual characteristics of a particular patient, the activity of immunopathology at a certain moment, the severity and duration of the disease, the presence or absence of certain symptoms.
The action of pathogenetic therapy drugs is aimed at preventing exacerbations and progression of pathology. These medications include medications from the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive groups. Their use helps prevent destructive processes in brain tissue that are induced by immune cells and toxins.
Recently, medications have appeared in medicine that, with long-term use, can reduce the frequency of exacerbations and slow down the development of sclerosis. Thus, they have a preventive effect.
Correctly selected symptomatic therapy and rehabilitation of patients (both physical and medical-social) play an extremely important role.
Symptomatic treatment allows you to maintain and correct brain functions and compensate for lost ones.
The role of drugs that improve metabolism, promote the restoration of areas of damage to myelin fibers and can strengthen their own mechanisms of control of the immune response should not be underestimated.
This treatment helps prevent the development of the disease. It is especially effective in the early stages. As the pathology progresses, the effect of therapy decreases. Terminal stages cannot be treated.
If you suspect this disease, you should not delay visiting a doctor or resort to traditional medicine, as this can significantly harm your health.
Doctors' recommendations
Recommendations for women with multiple sclerosis:
- Avoid infections. They adversely affect the course and occurrence of exacerbations.
- Lead an active lifestyle, but make sure there is no excessive physical activity or overwork. Any physical activity should be discussed with your doctor in advance.
- Do not visit the sauna and bathhouse, do not take hot baths. High temperatures provoke exacerbations.
- Give up bad habits - they contribute to exacerbations.
- Follow the principles of nutrition for MS. It is necessary to avoid animal fats and proteins, reduce the amount of fat in food, and include foods high in vitamin D in the diet.
- Follow the recommendations of your doctor. Don't forget to take your medications.
- Attend a rehabilitation center. Talk to a psychologist about your state of mind.
If you suspect multiple sclerosis or for the treatment and rehabilitation of patients with this diagnosis, you can contact the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow.
Make an appointment
Answers to popular questions
- How long do people live with multiple sclerosis? The patient’s life expectancy depends on the timeliness of starting therapy, the nature of the disease, and the presence of concomitant pathologies. If there is no therapy, the patient will not live more than 20 years from the date of diagnosis. When negative impact factors are minimized, the average human life expectancy is reduced by an average of 7 years compared to the life expectancy of a healthy person. In addition, life expectancy is influenced by the age at which the disease manifested. The older a person is, the higher the risk of rapid development of sclerosis and death during the first five years.
- Is multiple sclerosis inherited? Multiple sclerosis is not considered a hereditary disease, although there is a tendency for it to run in families. Doctors explain this by the uniformity of provoking factors influencing the development of the disease in the same family.
- Can you drink alcohol if you have multiple sclerosis? Bulgarian scientists conducted a study that found that light alcohol consumption has an anti-inflammatory effect in multiple sclerosis. However, doses are important in this regard. When intoxication occurs, patients have more pronounced coordination and speech disorders, and with alcohol abuse, the number of exacerbations of the disease increases. In addition, some doctors insist that the prognosis worsens even with small doses. Therefore, the question of the compatibility of alcohol and multiple sclerosis still remains open and each person makes his own decision.
- Is it possible to take a steam bath if you have multiple sclerosis? No you can not. Any increase in body temperature (while in a bathhouse, during summer heat, during fever, etc.) leads to a deterioration in the patient’s condition and to disruption of nerve conduction. While visiting the bathhouse, the feeling of numbness in the limbs, fatigue, and tremors will increase. In addition, visual impairment worsens and cognitive abilities decrease. However, it is worth considering that the symptoms of the disease will decrease as the body temperature decreases. That is, being in a bathhouse will not lead to persistent organic lesions due to sclerosis.
Dr. Myasnikov about multiple sclerosis:
Symptoms
The disease can debut at any time of the year. This mainly happens in the spring, when the body is weakened after a long winter. The youngest patient to become a victim of multiple sclerosis was only 10 years old at the time of diagnosis of the disease. The average age for women is 26 years. Various symptoms may indicate the presence of this disease. The problem is that most of them are common, and they are common in other diseases:
- Pain syndrome (muscle pain and headaches).
- Depression, smoothly transforming into euphoria; emotional instability; frequent mood changes; decreased mental abilities and other behavioral changes noticeable to others.
- Visual impairment, ranging from incorrect color perception to insufficient clarity of images.
- Decreased libido.
- Urinary dysfunction. If the disease progresses rapidly, the patient may experience urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Changes in the functioning of the facial, hypoglossal, trigeminal, oculomotor nerves.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- The appearance of a feeling of fatigue, dizziness, cramps.
First signs
They appear at the moment when the immune system destroys approximately 50% of tissues. The symptoms that appear are not the same and manifest themselves differently in different people. For example, a patient’s condition may worsen sharply if she takes a hot bath or spends even a short time in a stuffy room with a high temperature. Alarm bells also include:
- Involuntary shaking of limbs. You should pay attention to trembling hands and a changed gait.
- Unpleasant sensations when turning the head. Some women characterize them like this: “It’s like an electric shock.”
- Reduced skin sensitivity.
- The appearance of stabbing pain. An example is tingling in the fingertips.
- Problems with the visual organs. Decreased vision is not the only symptom, as some patients find it difficult and painful to “rotate” their eyes.
- Numbness of the extremities, sometimes leading to numbness in the lower body. Sometimes there is a feeling that the right arm (leg) has become weaker than the left and vice versa.