What it is
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils in the throat, mainly the palatine tonsils, which is caused by an infection (viral, bacterial, fungal).
There are two forms of inflammation with tonsillitis - acute and chronic.
To determine whether there is tonsillitis, it is enough to first examine the throat.
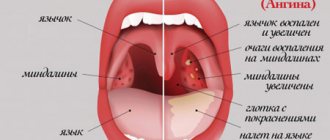
Figure 1. What a healthy (left) and infected (right) throat looks like. Source: Wikimedia
Chronic tonsillitis can be cured. It is important to consult a doctor (general practitioner or otolaryngologist) in time, who will select the correct therapy so that the inflammation does not become acute.
Prevention
Prevention of acute tonsillitis consists of the following measures:
- avoiding hypothermia and timely treatment of pathologies of other organs;
- assessment of nasal breathing - it should always be normal;
- strengthening the immune system, including hardening both the whole body and the pharyngeal mucosa in particular;
- balanced diet;
- periodic sanitization of the nose, throat and mouth with antiseptic agents;
- timely sanitation of teeth and foci of infection.
How is it different from a sore throat?
The acute form of tonsillitis is a sore throat. Most often it affects children, although sore throat also occurs in adults. To determine the causative agent of the infection, the doctor prescribes a smear from the surface of the tonsils. If it turns out to be class A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the risk of autoimmune damage to the joints, heart and kidneys increases. To prevent such complications, antibiotics are prescribed. Chronic tonsillitis usually develops after repeated tonsillitis. In this case, the infection settles in the tissues of the tonsils, waiting for the right moment to cause a new exacerbation.
During pregnancy
Tonsillitis is dangerous at any stage of pregnancy: it can harm both the woman and the fetus. In the early stages, the disease can cause spontaneous abortion, and in the later stages it can cause toxicosis.
In addition, the pathology significantly reduces a woman’s immunity, preventing her from coping with other diseases.
Tonsillitis requires immediate treatment and medical supervision. Often the disease suffered by a woman carrying a baby is an indication for a caesarean section.
Causes
Acute inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis) is most often caused by adeno-, entero- and cytomegaloviruses, pathogens of influenza, parainfluenza and herpes. Sore throat usually develops against the background of acute respiratory viral infections and childhood infections. Another cause may be a bacterial infection - then purulent plugs appear in the tonsils. Sometimes a viral infection is complicated by a bacterial one. In any case, the doctor will determine the exact cause and prescribe treatment, including the use of antibiotics, if necessary. It is better not to self-medicate, otherwise, if the drugs are selected incorrectly, the inflammatory process in the tonsils can become chronic.
The development of chronic tonsillitis is promoted by:
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- inflammation of the paranasal sinuses;
- caries;
- other foci of chronic infection in the body (pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.);
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- a special structure of the tonsils with too deep lacunae, with a reduced ability to effectively cleanse themselves of plaque, plugs and pathogenic microorganisms.
Surgical removal of tonsils
If we talk about the removal of the tonsils, then the operation to completely remove the tonsil tissue is called a bilateral tonsillectomy.
Partial removal of the tonsils is called a bilateral tonsillotomy.
It is extremely rare that the palatine tonsil is removed routinely on one side. There is also a practice of a number of hospitals (they like to do this in the Pirogov City Clinical Hospital No. 1) of removing the palatine tonsil or tonsils in case of a paratosillar abscess. This operation is called abscessonsillectomy. But it must be remembered that against the background of severe pain caused by an abscess, removal of the tonsil is extremely painful. Due to the purulent process, it is impossible to provide adequate anesthesia. Therefore, it is necessary to anesthetize the peri-almond tissue only with strong anesthetics: Ultracaine and Ultracaine DS-forte.
Routinely, palatine tonsils can be removed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. Previously, this operation was performed only under local anesthesia.
Fortunately, there is now modern equipment that allows removal of palatine tonsils under general anesthesia or under anesthesia using cold plasma coagulation - Coblator.
Symptoms
Chronic tonsillitis differs from acute tonsillitis in a number of signs.
| Chronic tonsillitis | Acute tonsillitis |
| Frequently recurring tonsillitis - several times a year, symptoms persist for more than two weeks | Rare cases of sore throat, lasting 3 to 14 days |
| Tonsils are loose, compacted, deformed, enlarged. There may be plugs or liquid pus in the lacunae | Tonsils with white coating, purulent plugs |
| The throat is sore or sore, there is no obvious pain | Throat red and sore |
| Bad breath | Pain when swallowing or difficulty swallowing |
| Periodic increase in temperature | Temperature above 38 degrees |
| The submandibular and cervical lymph nodes are constantly enlarged, which is especially noticeable during an exacerbation of the process | Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and under the lower jaw return to normal within a month after recovery |
| Not contagious | Contagious as long as symptoms persist. If the cause is a bacterial infection, then it is not contagious for 24 years after taking antibiotics |
Figure 2. Memo: symptoms of tonsillitis, when to see a doctor. Source: verywellhealth.com
Is it possible to not have a temperature?
Yes maybe. With chronic tonsillitis, body temperature rises only sometimes.
Important! At the height of a sore throat, the temperature is usually high - more than 38 degrees. However, it all depends on its shape. Relatively mild forms of angina (catarrhal and lacunar) can occur with a slight increase in temperature (up to 37.5 degrees).
Varieties and atypical forms
Acute tonsillitis is classified into two classes: normal and atypical.
The first includes:
- Catarrhal tonsillitis, characterized by shallow lesions of the tonsils, which become swollen and in some places covered with a thin film of pus and mucus.
- The follicular form, which causes harm to the follicular zone of the tonsils, has a more pronounced picture. The tonsils swell and increase in size. The further course of the disease is accompanied by the opening of the follicles with the formation of purulent plaque.
- Lacunar tonsillitis is symptomatically similar to the previous type, but with a more severe course. Here the pus spreads not only to the tonsils, but to the entire palate.
- The fibrinous form of sore throat is characterized by the formation of a white-yellow coating that extends beyond the tonsils. It develops both against the background of the previous type of tonsillitis, and independently.
Atypical forms include:
- Phlegmonous tonsillitis, characterized by an increase in size and suppuration of one of the tonsils.
- An ulcerative-membranous form of tonsillitis, manifested in necrosis of the surface of the pharynx of one of the tonsils and the formation of ulcers.
- Herpetic sore throat, caused by the Coxsackie virus and characteristic of a child's body.
Treatment of tonsillitis
The doctor should not only examine the throat, but also take a swab from the throat to determine the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. Sometimes a laboratory examination is prescribed: general blood and urine tests.
Here's what you can do for tonsillitis yourself:
- Rest more often. It's better not to spend too much time in an upright position and get more sleep.
- You need to drink enough fluids to keep your throat moist and prevent dehydration.
- Not only antihistamines will help with a sore throat - you can try sucking on a piece of ice or eating ice cream.
- The air should be well humidified. Dry air irritates the mucous membranes, so it is a good idea to place a humidifier in the patient's room.
- It is important to keep your home free of cigarette smoke or cleaning product fumes, which can also damage your respiratory tract.
- If a person is worried about a high temperature, it can be brought down with over-the-counter antipyretics.
Antibiotics
If the cause of tonsillitis (whether acute or chronic) is bacterial in nature, the doctor prescribes antibiotics. If there is a virus – painkillers and/or anti-inflammatory drugs. Antibiotics do not act on viruses, but the doctor can use them to prevent and treat bacterial complications.
Penicillin is most often prescribed for tonsillitis. It effectively fights the most common causative agent of the disease - group A streptococcus. There are always alternatives to antibiotics, so even with an allergy to penicillin a person will receive treatment.
If a bacterial infection is left untreated and left untreated, the condition may worsen or the infection may spread to other parts of the body. Not taking a full course of antibiotics can, among other things, increase a person's risk of developing rheumatic fever and serious kidney inflammation.
Surgery
Surgery to remove the tonsils (tonsillectomy) may be used to treat frequently recurring tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis, or bacterial tonsillitis that does not respond to antibiotics. You can read more about this operation in our material.
Tonsillectomy is usually performed on an outpatient basis, unless the patient is very young or has complex underlying medical conditions. Full recovery usually takes seven to 14 days.
Chronic tonsillitis
Treatment usually also focuses on controlling symptoms. Perhaps the doctor will recommend changing your lifestyle, quit smoking.
The following are recommended as auxiliary methods:
Tonsils are removed when there are frequent exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis and the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment. In children under 8 years of age, they try not to remove the tonsils, so as not to provoke the development of allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and frequent and severe colds.
Acute tonsillitis
In case of acute tonsillitis, bed rest must be observed. Make sure that food is not too hot, spicy or hard. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids.
Antiseptic throat sprays or tablets help with pain, sore throat and cough. Gargling with warm salt water has the same effect. The doctor may recommend lubricating the tonsils with Lugol's solution, but you cannot perform the procedure yourself. To relieve a sore throat, you can suck on a piece of ice or drink a cold drink.
Important! You should not take antibiotics on your own. Antibiotics are useless against a viral infection.
Why are tonsils needed?
The tonsils are an integral part of our immune system. And their main purpose is to protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In total, a person has six of them: palatine and tubal (paired), pharyngeal and lingual. By their names you can roughly understand in which part of the pharynx they are located. Their general arrangement resembles a ring. This ring acts as a kind of barrier for bacteria. When we talk about inflammation of the tonsils, we mean only the palatine tonsils (aka tonsils). Let's look at them in more detail.
If you open your mouth wide, then in the mirror you can easily see two formations that look like almonds - tonsils, these are tonsils. Each tonsil consists of small openings (lacunae) and winding canals (crypts).
Bacteria that enter the air, in contact with the tonsils, are rebuffed and are immediately disposed of, without having time to cause an outbreak of a particular disease. Normally, a healthy person does not even suspect that real fighting is taking place inside him. Now you understand the importance of the mission of the palatine tonsils. Therefore, a good otolaryngologist will never rush to recommend their removal. Although to hear from a doctor, speaking about tonsils: “They need to be removed!” - a common phenomenon in our time. Unfortunately, today not all clinics can offer high-quality treatment for tonsillitis, and sometimes the turnaround rate is off the charts. That is why it is sometimes easier for a doctor to brush it off and refer the patient for surgery.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapeutic treatment of chronic tonsillitis can be effective during remission - laser therapy is recognized as very effective due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect due to its direct effect on the tonsils. Short-wave UV radiation of the throat and oral cavity is also used.
There are methods of ultrasonic treatment of the tonsils, which act on the source of the disease itself, destroying the structure of the resulting cheesy mass. Using ultrasound, you can also irrigate the tonsils with antiseptic solutions.
An effective remedy is inhalation of wet steam. But there is one contraindication here - high temperature, so the temperature must first be lowered, and only then inhalation. Inhalations can be used using various medicinal herbs - chamomile, calendula, etc., chlorhexidine solution, or you can simply breathe over potatoes. You should not take deep breaths when inhaling, because in the case of tonsillitis, only the inflamed tonsils need to be affected.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the doctor palpates the lymph nodes and examines the tonsils directly. But experts do not limit themselves to this, given how many complications can be caused by this disease. The contents of the lacunae are also sampled and sent for analysis. Taking material for laboratory testing is carried out by pressing on the tonsil, from which pus is released. If the pus has a mucous structure and an unpleasant odor, then most likely there is a chronic form of tonsillitis. But even this analysis cannot show the complete clinical picture and accurately determine the diagnosis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors pay attention to the general condition of the body and the presence of deviations from the norm. Such deviations are primarily considered to be thickened edges of the palatine arches and hyperthermia. Experts also determine cicatricial adhesions between the palatine arches and tonsils.
Tonsils, in the chronic form of tonsillitis, have a loose appearance and a scar-altered surface. In the lacunae of the tonsils there are purulent plugs or purulent discharge.