The lymphatic system is an integral part of the vascular system of the human body. It performs a number of functions, participates in metabolic processes, and works as a cleansing and protective mechanism. The system of lymph nodes and ducts transports proteins and tissue fluid from the interstitial space into the blood vessels, and transfers fats from the small intestine there. In the space of the lymphatic system, fluid circulates - lymph.
Role of lymph nodes
The function of the lymph nodes is to protect the body from external bacteria and infections, as well as to prevent the proliferation of pathological cells within the body. Lymph nodes in the neck, the location of which makes it possible to fight infectious diseases of the ENT organs, also respond to pathologies of the teeth and oral cavity: caries, gingivitis, stomatitis.
In some people, the cervical lymph nodes become inflamed during the growth of wisdom teeth, as the load on them increases. To stop the infection, these organs actively produce leukocytes and phagocytes that can resist the active phase of virus development.
When a foreign agent is introduced into the body, the body’s immune reaction is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased size of lymph nodes;
- redness of the skin over the organ;
- easy palpation and clear visibility of the filtering organs.
The more dangerous the infection, the stronger the immune response will be, which is reflected in the size of the cervical lymph node.
Where are the internal lymph nodes located?
Internal lymph nodes are divided:
Pharyngeal lymph nodes or tonsils . Located in the mouth on the palate, in the pharynx, on the tongue. Neutralizes infections that enter through the nose and mouth.
Main pharyngeal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes around the lungs, intrapulmonary, near the trachea . This group of lymph nodes is the most numerous in the human body. Fights infections that enter the lungs and bronchi.
Major lymph nodes of the chest
The peri-abdominal lymph nodes are located near the spleen, stomach, liver, and intestines, and destroy harmful bacteria from these organs.
The main lymph nodes located in the abdominal cavity
Attention . We do not see internal lymph nodes, and you can only see them if your doctor prescribes an ultrasound.
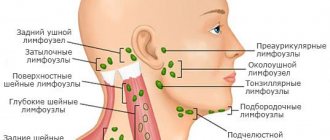
Location of lymph nodes in the neck
According to the existing classification, in medicine there are 6 levels, and the same number of sublevels of cervical lymph nodes.
Level I: submental (IA), submandibular (IB)
The location of lymph nodes in the neck of sublevel IA is under the lower jaw, between the anterior parts of the digastric muscles and above the hyoid bone. This group includes the mental lymph nodes, consisting of the mental, sublingual, suprahyoid and thyroglossal-facial protective organ.
Sublevel IB is located under the mandible and above the body of the hyoid bone, between the anterior part of the digastric muscle and the stylohyoid muscle. This group includes submandibular lymph nodes, consisting of preglandular, postglandular, retrovascular and postvascular organs.
Level II: upper jugular
This level includes all lymph nodes located in the lateral triangle of the neck. They are also divided into 2 sublevels. Group II A is located at the base of the skull, above the conventionally designated horizontal line along the lower edge of the hyoid bone. Between the stylohyoid muscle and the posterior edge of the accessory nerve.
This sublevel consists of the retropharyngeal, tonsillar and jugular-digastric lymph node.
Lymph nodes in the neck have different locations.
The photo shows what they are called. Sublevel IIB is located under the base of the skull, above the level of the lower edge of the hyoid bone, between the accessory nerve and the posterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It consists of superficial cervical lymph nodes.
Level III: middle jugular
This level is located below the inferior line of the hyoid bone and above the inferior line of the cricoid cartilage. Between the anterior and posterior regions of the sensory branch of the cervical plexus. The middle jugular lymph nodes will include the superior thyroid and deep lateral.
Level V: rear nodes
This level consists of two sublevels. The VA group of lymph nodes is located at the angle of intersection of the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles, but above the lower edge of the cricoid cartilage. Between the posterior region of the sensory branch and the trapezius muscle. The VA sublevel consists of the intercalary and posterior cervical lateral types of nodes.
Lymph nodes in the neck, the location of which is indicated by sublevel V B, are located under the lower edge of the cricoid cartilage, but above the clavicle. Between the trapezius muscle and the posterior region of the sensory branch. This subgroup consists of transverse cervical, supraclavicular (without Virchow) and lower deep lateral lymph nodes.
Level VI: anterior nodes
This level is located under the hyoid bone, but above the jugular notch of the sternum. Between the carotid arteries on both sides. This group consists of pre- and paratracheal, precricoid and perithyroid types of lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes not included in the classification
In addition to the listed types of cervical nodes, there is a separate category that is not included in the general classification.
It includes the following organs of the immune system:
- behind the ear;
- suboccipital;
- parotid (near and inside the parotid salivary gland);
- retropharyngeal;
- facial;
- superior mediastinal.
Features of treatment
Since an enlarged lymph node on the left side of the neck is only a consequence of the development of another disease, it should be treated by eliminating the root cause. The following types of therapy can be used for this:
- Medication. Since in most cases, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck occur due to an infection, treatment involves taking antibiotics. The patient is prescribed those drugs to which the pathogen identified in him is sensitive.
- Physiotherapy. It is usually used as maintenance therapy to enhance the effect of medications. The most popular technique is electrophoresis.
- Chemotherapy and radiation. They are used if the enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is of an oncological nature.
- Operation. It is performed to remove tumors or lymph nodes in which a purulent process has developed.
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck are not a fatal diagnosis, but it is a disease that requires immediate treatment. There is no need to wait until the disease develops into a chronic or purulent form. It is best to consult a doctor at the first suspicion of inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Related Articles
Lymph nodes in the neck: structure and size, causes and symptoms of inflammation
What are lymph nodes: location, functions, norm and pathology
Lymph node under the arm: location and functions, causes of inflammation
Why does a child have enlarged lymph nodes: norm and pathology?
Lymph nodes in the groin: where are they located, how to feel them and why do they become inflamed?
Are there lymph nodes on the back: location of lymph nodes in the human body
Symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
The lymph nodes in the neck (their location makes it possible to control the penetration of infection through the upper respiratory tract) react with certain symptoms when a threat appears. This feature makes it easier to diagnose and allows you to take timely measures to eliminate the threat to health.
Symptoms characterizing inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes may differ depending on the location of the organ. At the same time, a slight increase in size and slight pain upon palpation is considered a borderline condition, which is not dangerous if it is detected after an illness or against the background of organic health problems.
As soon as the blood test shows the normal concentration of leukocytes in the body, the size of the lymph node will return to its previous parameters.
But there are a number of signs that should not be ignored:
- swallowing causes pain;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- regular headache;
- fever;
- chills;
- pain on palpation of the inflamed area;
- lacrimation;
- shooting pain in the ear;
- skin redness;
- compacted consistency of the filter element.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a person notices an increase in lymph nodes in the neck in himself or his child, it is necessary to visit a therapist. After the examination, he can refer you to other highly specialized specialists, the list of which includes:
- infectious disease specialist;
- endocrinologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- venereologist;
- oncologist;
- hematologist.
The list is not exhaustive. In 65% of cases, inflammation can be predicted after a standard examination and palpation of the neck. Additionally, all patient complaints are taken into account. However, in some cases, research may be required. The doctor may order an X-ray of the neck tissue or a biopsy. Additionally, the patient is sent for a general blood and urine test. If necessary, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography may be performed. Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed.
Causes of enlarged lymph nodes
An increase in the size of an organ is a sign of increased stress on it. This can trigger the development of an infectious or bacterial disease that the immune system is trying to fight.
Lymph nodes in the neck, the location of which allows you to control the penetration of harmful microorganisms through the nose, ear and mouth, often become inflamed with ARVI, rubella and scarlet fever. But depending on the location of the pathological process, it is possible to quickly establish the disease and identify the main cause.
Common diseases that cause inflammation of a certain type of cervical lymph nodes:
| Name of lymph nodes | Characteristic signs of inflammation | Provoking factors |
| Submandibular |
|
|
| malignant tumor in the jaw, oral cavity, salivary gland | |
| Anterior cervical |
|
|
| Cancerous tumor in the area of the lips, mouth, jaw, thyroid gland | |
| Cervical |
|
|
| malignant neoplasm in the back of the head |
Purpose of jugular lymph nodes
The anterior cervical lymph nodes perform several functions:
- Metabolic – participation in metabolic processes at the cellular level.
- Barrier – an obstacle to the penetration of pathological microorganisms into the oral cavity.
- Immune – the production of lymphocytes (immune cells), which are part of the general human immune system.
- Hemolytic - lymphocytes are an integral part of the blood.
- Stimulating – promotes the reproduction of healthy cells and the restoration of damaged ones.
Classification of cervical lymphadenitis
In medicine, there are several classifications of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes (lymphadenitis). The data indicated in them is used to determine the diagnosis.
Depending on the duration of the transition period of lymphadenitis from the latent state to the active phase:
- Spicy . It is characterized by vivid clinical symptoms and lasts about 15 days. This form often develops when wounds become infected and as a result of postoperative complications.
- Chronic . Duration is about 1 month or more. This form is characteristic of protracted infectious pathologies, as well as autoimmune disorders and cancer.
- Recurrent . This type is characterized by periodic episodes of exacerbations and periods of relief of the same lymph nodes, but inflammation can switch to nearby organs.
Depending on the etiology of the pathological process:
- nonspecific form - the causative agent is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, which, under favorable conditions, develops into a pathogenic state that can be quickly cured;
- specific form - develops when exposed to pathogens of a certain type, as a result of which lymphadenitis acts as a symptom of the underlying disease.
According to the nature of the pathological process, lymphadenitis occurs:
- serous - characteristic of viral and oncological etiology;
- purulent - develops in the chronic form of a bacterial disease.
How to treat lymph nodes with lymphadenitis?
Lymph nodes can also become inflamed and painful. This disease is called lymphadenitis . It doesn't happen by itself. It may be preceded by the following untreated diseases:
- Long-lasting infected wounds
- The presence of large boils or other purulent inflammations on the body
To prevent all lymph nodes from becoming inflamed, you need to respond in a timely manner to small enlarged lymph nodes and treat diseases indicated by inflamed lymph nodes.
We need lymph nodes in the body, but if they have enlarged and continue to hurt, and do not decrease (and this happens with lymphadenitis), in modern medicine they are treated:
- Therapy (tablets)
- Combination therapy
- By cutting
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
Enlarged lymph node - lymphadenitis
Diagnostic methods
The first sign of the development of lymphadenitis is an increase in lymph nodes by 1.5 or 2 times. This occurs as a result of an increase in the supply of tissue fluid in the parenchyma of the organ and an increase in the concentration of white blood cells, due to the body’s protective reaction to the invasion of infection.
This sign is fundamental in diagnosing the disease. Combining it with a medical history, additional pathological symptoms and bacteriological studies allows the doctor to accurately establish a diagnosis.
Main types of diagnostic tests and studies:
- general blood test - to determine the number of leukocytes in the plasma and identify the causative agent of the pathology;
- bacterial culture - to confirm or refute the presence of streptococci and staphylococci;
- Ultrasound;
- biopsy - to identify rare types of infections and atypical cancer cells.
Which lymph nodes become inflamed during tuberculosis?
If a person falls ill with tuberculosis , then the causative agent of this disease, Koch's bacillus, first enters the internal lymph nodes around the lungs, and then into the external ones: cervical, sometimes under the armpits and inguinal, causing them to enlarge. If the disease is not treated, the superficial lymph nodes can adhere to the skin, and suppuration and fistulas form.
Attention . A sign of tuberculosis: against the background of general malaise, coughing for a long time, a large number of lymphocytes are produced.
Another sign of tuberculosis is enlarged lymph nodes
Treatment of inflamed lymph nodes with drugs
Based on the established diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment using anti-inflammatory drugs and medications that reduce unpleasant symptoms. The duration of administration and dosage are determined by a specialist based on the type and severity of the pathology, as well as taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Groups of drugs used to treat lymphatic dermatitis:
- Antibacterial (Amikacin, Norfloxacin) - inhibit the viability of bacteria by destroying the cell membrane; drugs are prescribed if the disease has a bacterial form.
- Antiviral (Amantandin, Remantandin) - prevent the spread of viral infection by suppressing DNA replication; medications are prescribed if the causative agent of the pathological process is a virus.
- Antifungals (Diflazon, Mikosist) - inhibit fungal spores from the inside, penetrating the cell membrane, used for fungal pathogens of lymphadenitis.
- Antiseptics (Levomekol, Dioxidin) - have an inhibitory effect on infection when the integrity of the skin in the neck and face is damaged.
- NSAIDs (Nurofen, Ketanov) - prevent the synthesis of prostaglandins, reduce pain, fever, inflammation.
- Antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin) - used if inflammation was provoked by an allergen, they contribute to vasoconstriction and reduce the permeability of capillary walls in the area of inflammation, which allows the lymph node to restore its normal size.
Diseases that affect the lymphatic system
There are diseases of the lymphoid system itself, or a consequence of other diseases. These diseases can affect individual organs of the lymphoid system, for example lymph nodes, or they can affect the entire system as a whole. Since one of the main tasks of the lymphoid system is to cleanse the body and produce antibodies to fight pathogens, it reacts to any infection that enters the body.
Diseases affecting the lymphatic system include acute respiratory viral infections, tuberculosis, rubella, syphilis, various oncological and autoimmune diseases, HIV infections, lymphadenitis, lymphangitis and many others, as well as diseases that arise from traumatic lesions of the lymphoid system, not very good heredity, bad habits and natural environmental factors.
Lymphadenitis
The most common and most common disease of the human lymphatic system. This inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes and is caused by infection, virus, or trauma to the lymph nodes. Almost always, inflammation of the lymph nodes with lymphadenitis is manifested by its thickening, swelling, redness of the skin around the lymph nodes, and pain on palpation.
ARVI
Some of the most common infections are:
- cytomegalovirus;
- adenoviral;
- rhinovirus;
- chicken pox;
- rubella.
With infectious mononucleosis, the main symptom is an increase in cervical lymph nodes. For other viral infections, an increase in several groups of lymph nodes on the human body is typical, most often lymph nodes of the neck, less often lymph nodes of the head.
Tuberculosis
LU tuberculosis is a very serious human disease. Most often it develops together with diseases of the lungs and respiratory system. Surprisingly, but true, women are more often susceptible to tuberculosis. LU tuberculosis causes global changes in lymphoid tissue. Damage to lymphoid tissue begins when bacteria enter tuberculosis (Koch bacilli).
Tuberculosis develops in lymph nodes with a significant difference than in other tissues and organs. With lymph node tuberculosis, not only the size of the lymph nodes increases, but there is also a multiple increase in the production of lymphocytes. If, on the one hand, this improves the quality of lymph, then on the other, if there is a large amount of it in one place, granulomas may begin to form.
With tuberculosis of lymph nodes on the human body, in 70-80% of cases, cervical lymph nodes are affected, and only in 15-20% are axillary lymph nodes and inguinal lymph nodes enlarged. Only in isolated cases are other lymph nodes affected.
Syphilis
Syphilis is an infection caused by a pathogenic microbe - Treponema pallidum. A surprising feature of this disease, Treponema pallidum affects only humans. Lymph nodes on the human body become enlarged, just like with other infections. The increase in lymph nodes of that particular group completely depends on the site of infection - chancre.
When it appears on the genitals, the first reaction will be in the inguinal group of lymph nodes and the pelvic group of lymph nodes. When a chancre appears on the chest, there is an immediate reaction in the axillary lymph nodes and periosternal lymph nodes; if chancre affects the lips or tongue, the first reaction is visible on the cervical lymph nodes, facial lymph nodes, and head lymph nodes.
Less commonly, when chancre appears on the extremities, the lymph nodes of the arms or lymph nodes of the legs may enlarge. Very often, LUs are connected to each other and can form chains and entire conglomerates. Syphilis is congenital and can be transmitted from mother to child.
The consequences of congenital syphilis can be very dire. When the process develops in utero, this microbe lives and multiplies in the child’s body. Consequently, treponema circulates throughout the child’s lymphatic system, damaging his internal organs and tissues.
Rubella
The virus initially enters the nasopharynx, then into the blood and spreads through the circulatory and lymphatic systems throughout the human body. Naturally, the immune system reacts to the pathogen with inflammation of the lymph nodes, as well as numerous rashes on the skin. The lymph node is clearly defined under the skin.
In rare cases, in infected people, the spleen and sometimes the liver become enlarged due to the accumulation of the virus inside itself. The peculiarity of the virus is that a person has persistent immunity for life, after recovery.
The rubella virus has a clearly defined cytopathic effect, that is, it affects the cytoplasm and embryonic cells, which very often leads to various mutations in these cells and fetal malformations. Therefore, the disease poses a great danger to expectant mothers during pregnancy.
HIV infection
HIV infection is one of the newest diseases in the modern world. The disease is widespread on all inhabited continents of the planet, in all races and age categories of people. The clinical picture is also very diverse, with many different pathologies.
This also applies, of course, to the immune system and pathologies of lymph nodes in HIV infections. The study of the symptoms accompanying this infection, together with a quick response to the incidence, is the main direction for the prevention and diagnosis of HIV
A very common symptom accompanying HIV infection is lymphadenopathy. This disease is a direct attack on the human immune system. When the immune system is damaged, widespread inflammation of the lymph nodes on the human body occurs, since they are the first to respond to HIV and the virus directly multiplies in the lymph nodes.
The infection most affects the cells - lymphocytes.
Especially their subtype – T-helpers. These cells are responsible for the strength of the immune response. DR in HIV does not increase immediately after infection, but after a long period of time, up to several months or years. But when HIV infection gains strength, and the increase in DR occurs everywhere. Then the recovery of DR and HIV infection is significantly complicated.
Oncology
Oncology of the lymphatic system, mainly lymph node cancer, is a disease with systemic development and covering the entire body. The pathology is initially similar to an autoimmune process. The tumor can affect both superficial lymph nodes and deep lymph nodes. The most common localization of lymphoma is in the armpits, collarbone and groin.
Lymph, by cleansing and at the same time nourishing cells, helps remove infections from the body, and this is a huge burden on the body and its lymph system. Very often the immune system cannot cope with such loads. It is very important to identify signs of pathology in advance, in the early stages, namely changes occurring in the lymph nodes.
There are a lot of direct and indirect factors that accelerate the possibility of developing oncological processes associated with oncology of the lymphatic system. These include: age (with age the risk of getting sick increases), various pathologies of the immune system, heredity, environmental and natural factors.
Lymphoma is a very aggressive disease and multiplies at a high rate throughout the human body. In this case, the affected cells accumulate and concentrate in the lymph nodes.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases include those that are provoked by the person’s own immune system. With these diseases, a malfunction occurs in the body or a malfunction of the immune system, and as a result of these malfunctions, blood leukocytes begin to fight certain cells of our body, considering them harmful and foreign.
Autoimmune diseases are systemic and complex. The complex and systemic nature of these diseases is manifested by the fact that both a separate organ, some kind of life support system, and the entire body as a whole can be affected.
Failures in which autoimmune diseases can occur can be divided into several subgroups. Subgroups include external and internal causes, in which white blood cells become aggressive and multiply completely uncontrollably.
- Internal reasons. Internal causes include certain mutations that occur in genes of types I and II, when leukocytes cease to identify a certain type of cell in the body. Lymphocytes, as one of the varieties of non-granular leukocytes, are orderly cells that can begin to multiply uncontrollably and cause various autoimmune diseases. Internal causes include the consequences of very severe, long-term infectious diseases and their long-term drug treatment, after which the immune system fails and cells begin to multiply uncontrollably.
- External reasons. External causes include harmful effects from the environment, for example, radiation, electromagnetic or solar radiation; water and air pollution, industrial emissions.
Treatment with folk remedies. Recipes and regimens
In addition to medications, it is permissible to use medicinal folk remedies if the doctor recommends their use. This allows you to speed up recovery, relieve inflammation and return the lymph node to its usual size.
Effective recipes:
- Combine the herbs chamomile, calendula, mint in equal proportions . Steam 30 g of the mixture with 250 ml of boiling water, leave for a minute, peel. Use to rinse the mouth and throat every 2 hours. Therapy is carried out until the pathological process is completely eliminated.
- Fill a glass container with fresh walnut leaves. Pour medical alcohol and leave in the dark for 10 days. During this time, shake the medicine periodically. When ready, peel the tincture and use it as a compress, applying it to inflamed areas. Carry out therapy daily until complete recovery.
- Grind the peeled echinacea root. Pour 30g of the mixture into 2 liters of water and boil for 2 hours, not allowing the broth to boil. After removing from heat, cover with a lid and let stand for 12 hours; after the time has elapsed, peel. Take the decoction orally, 80 ml in the morning and evening. The course of therapy is 10 days.
- Dissolve 5 g of salt and baking soda in 200 ml of water at a comfortable temperature. It is recommended to gargle and rinse the mouth and throat with a medicinal solution every 2 hours a day. It is recommended to do 4-5 procedures. The duration of treatment is until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated.
- Cut 2-3 lower leaves from aloe plants older than 3 years of age. Rinse them and dry with a paper towel. Place in the refrigerator for 3 days. After the allotted time, grind to a paste. Take the medicine daily, 20 ml. The duration of treatment is 7 days.
Examination of the lymph nodes of the head
Palpation of lymph nodes includes a certain sequence. Initially, the occipital lymph nodes are palpated, after which the postauricular lymph nodes are approached to be examined. Parotid lymph nodes are diagnosed in the area where the salivary glands are located.
Mandibular lymph nodes or submandibular lymph nodes are subject to inflammation when various harmful processes occur in the nasopharynx; they are palpated under the skin of the lower jaw. Facial lymph nodes are located quite deep and inflammation in these lymph nodes rarely occurs. For the diagnosis of diseases, they are not of great practical importance.
What should not be done if the cervical lymph nodes are enlarged?
When the cervical lymph nodes are inflamed, you need to know what is strictly prohibited to do, so as not to provoke even greater health problems.
It is forbidden:
- Warm the inflamed areas, since the infection becomes more active when heated and quickly spreads throughout the body, and first of all, this threatens the penetration of bacteria into the brain.
- Do a massage , since when the lymph flow increases, pathogens penetrate into all parts of the body, which can cause blood poisoning.
How to diagnose and what measures to take?
If enlarged lymph nodes are present, consultation with a physician is required. Only a doctor is able to carry out the necessary accurate diagnosis; you may need to do an ultrasound, then there will be a referral to one of the specialized specialists, who can be a dentist, otolaryngologist, surgeon, oncologist and others.
impossible to accurately carry out an independent qualified diagnosis , since the number of diseases that have a reaction of the lymphatic system is about a hundred, and only a doctor can evaluate many accompanying symptoms.
Among other features, it can be noted that if after several months of treatment efforts, the standard sizes have not been restored, then we are talking about the presence of a chronic infection in the body. With this development of events, a comprehensive examination will be required to identify the original source of inflammation.
The presence of symptoms that are hard and painful when palpating a lymph node for six months is likely the presence of a tumor of the lymphatic tissue.
Why self-medication is dangerous
All medications have a dual effect. Prescribing them in the correct dosage, commensurate with the form and severity of the disease, has benefits for the body. But using medications independently, at your own discretion, can have serious health consequences.
Only a doctor can determine the balance between the benefits of a drug and possible negative effects on the body by studying the medical history, the patient’s condition and his individual characteristics. In most cases, self-medication provokes the development of a number of side effects, which further aggravates the problem.
The danger that threatens when self-medicating:
- Treatment failure . Medicines may not correspond to the type of disease, since completely different types of pathogens can provoke the pathological process.
- Tolerance to the effects of drugs . Uncontrolled use can lead to the emergence of resistance of harmful microorganisms to the action of the drug. As a result, this will only complicate the situation and weaken the immune system.
- Drug incompatibility . Many drugs are not compatible with each other, so their simultaneous use can either weaken or enhance the effect of the active components, which threatens the development of side effects, deterioration of well-being, further spread of infection and the development of complications.
Why is inflammation dangerous?
If inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs, a decrease in the body’s protective functions is observed. The main danger of this is the following:
- the body cannot fully protect itself from viruses and bacteria penetrating into it;
- the likelihood of harmful microorganisms entering tissues, internal organs and the circulatory system increases;
- the chance of developing cancer also increases.
The appearance of inflammation can be caused by a whole list of factors. A person often experiences pain, general weakness and malaise, and discomfort when swallowing. The body's protective functions are significantly reduced.
Consequences and prognosis
With timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis for the patient is favorable and allows surgical intervention to be avoided. Otherwise, untreated inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes can have serious consequences for the patient.
Possible complications:
- An abscess is a thin-walled capsule filled with purulent contents that ruptures with slight impact and provokes further spread of infection.
- Phlegmon - purulent pathology that spreads unhindered to adjacent tissues, involving them in the inflammatory process.
- Sepsis - causes the rapid spread of infection throughout the body, which can be fatal for humans.
- Phlebitis - tissue fluid from an inflamed node penetrates the veins, causing inflammation and causing the formation of blood clots.
- A malignant tumor - chronic lymphadenitis over time can provoke the degeneration of inflamed organ cells into cancerous ones.
The lymph nodes in the neck perform an important function in the body, as their location helps control the effects of bacteria and infections on the upper respiratory tract, oral cavity and hearing organs.
Therefore, any inflammatory process should not be ignored, since the immune system does not always have enough strength to resist pathogens. The sooner treatment is carried out, the less harm they can cause to the body.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Inflammation of the cervical nodes: characteristics of the concept
Lymph nodes tend to become inflamed and increase in size. Why is this happening? The problem is the development of lymphadenitis.
Lymphadenitis is a disease associated with a specific or nonspecific inflammatory process in the nodes. An increase in the size of the nodes is accompanied by a feeling of pain in them. In addition, a person develops a headache, general malaise and weakness, low-grade fever or, less commonly, high fever.
Most often, pathology occurs as a secondary complication in the presence of inflammatory processes of any localization. Infectious agents, together with the toxins they secrete, penetrate into the regional lymph nodes along with the lymph flowing from the primary lesion. In some cases, this focus has already disappeared by the time lymphadenitis appears, and it cannot be recognized. Sometimes the disease occurs as a result of infection entering directly into the lymphatic network through damage to the mucous tissue or skin.
The developing inflammatory reaction is a protective function of the lymphatic system: with the help of such a barrier, the body limits the further spread of pathogenic particles through tissues, organs, and blood.
At the same time, along with the development of inflammation in the nodes, a person may begin to develop purulent processes - sepsis and adenophlegmon. The danger of this condition lies in the approach of the infected lymph flow to the brain. If the fluid with the infection it contains enters the brain, it becomes infected, and then serious complications, disability, and sometimes death occur.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck is not an independent disease - it is a signal of the presence of other pathologies and disorders. In addition, inflammation is accompanied by disruption of the entire system of lymph nodes and blood vessels.
Medical diagnosis
To find out the cause of inflammation, it is necessary to undergo examination by specialists: a therapist or pediatrician, an otolaryngologist. To determine the pathogen, studies are prescribed:
- physical examination;
- biochemical and general blood analysis;
- throat swab (nose, mouth);
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- radiography;
- puncture.
A biopsy is performed to study the specific type of inflammation. Additionally, tuberculosis tests and fluorography may be prescribed.
Treatment is carried out with antiviral, symptomatic agents recommended by the attending physician.
Examination of axillary lymph nodes
To examine the axillary lymph nodes, the patient's arms are moved in different directions. Slightly bent fingers are placed on the palpated area and inserted deep into the armpit, without pressure. Then the abducted arms are lowered, but not pressed tightly against the body.
Afterwards, the axillary lymph nodes are palpated from top to bottom. If upon palpation there is a strong enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes, these signs may indicate unfavorable processes in the arms and chest, up to metastasis, in breast cancer.