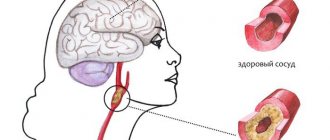
The functioning of the brain depends on the condition of the blood vessels and blood circulation through them. Dyscirculation is manifested by impaired blood flow, which leads to the development of a pathological condition of the brain - encephalopathy. That is, discirculatory encephalopathy (DEP) occurs, the distinctive feature of which is the diffuse spread of numerous small foci of ischemia. As a result of impaired blood supply, brain neurons die, neurological disorders occur: speech impairment, gait, confusion.
Treatment consists of eliminating damage to the blood vessels of the brain and taking preventive measures aimed at maintaining normal blood flow.
Discirculatory encephalopathy - what is it?
DEP is chronic ischemia (impaired blood supply) to the brain. The development of the disease is provoked by damage to small and tiny vessels - capillaries, which leads to the development of ischemia and the appearance of neurological symptoms: motor and cognitive disorders. With dyscirculatory encephalopathy, mental disorders also occur.
The disease develops gradually and has a progressive course. In severe cases, DEP causes stroke, paralysis, dementia, urinary incontinence and other serious health and mental disorders.
Causes and mechanism of development of the disease
There are several main causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the brain, these are:
- Atherosclerosis;
- Arterial hypertension (hypertension);
- Kidney pathologies, renovascular hypertension;
- Damage to blood vessels and heart as a result of exposure to pathogenic microorganisms, rheumatism;
- Vascular calcification.
Pathological changes in the brain as a result of discirculatory encephalopathy are caused by damage to the arteries, especially in weak areas where the vessels branch, and the speed of blood flow slows down, which can lead to congestion and the formation of large atheromas.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerotic plaques (atheromas) - pathological growths on the wall of a vessel, can form on both the internal and external surfaces - significantly narrow the lumen of the arteries, compress the walls, until the blood flow completely stops, which is the cause of such a disease as discirculatory encephalopathy. Loose atheromas are also dangerous in that they can break away from the wall and cause blockage of a smaller vessel, which leads to ischemia and microinfarctions.
Pathological changes occur even when blood circulation is impaired at the level of the smallest vessels, which form an extensive vascular network and play an important role in the blood supply to the brain. Due to their small vascular lumen, they can quickly become clogged and lose functionality. Massive damage to capillaries during discirculatory encephalopathy, serious damage to the capillary network - leads to dystrophic processes in brain cells. They stop receiving the necessary nutrition and oxygen through the capillaries and die. The more brain tissue atrophies, the stronger discirculatory encephalopathy manifests itself.
As a result of atherosclerotic deposits in the vessels and calcification provoked by excess calcium deposition, a pathological decrease in the elasticity of the vascular wall also occurs. Loss of vessel elasticity leads to the fact that red blood cells cannot squeeze through the capillaries, they stick together, the overall viscosity of the blood increases, which causes congestion and can lead to a stroke.
Cholesterol
The occurrence of atherosclerotic plaques, as one of the reasons for the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, is usually blamed on “bad” cholesterol. But this substance itself is useful for the body: it ensures the resistance of cell membranes to damage, and takes part in the synthesis of important hormones.
Helpful information
The human body produces 80% of cholesterol on its own and only 20% comes from food. Moreover, cholesterol is present exclusively in products of animal origin.
Excess cholesterol when consuming large amounts of butter, dairy products, eggs, fatty meat leads to metabolic disorders. The body simply does not need as much cholesterol, and if there is too much of it circulating in the blood, the liver cannot cope with its utilization. In this case, deposits of excess of this substance occur in the vessels.
It is the complex combination of cholesterol and proteins that is of clinical importance, not pure cholesterol. As a result, various types of lipoproteins are formed. HDL - high-density lipoproteins - are considered “good” cholesterol and are found in fairly large quantities in the body, performing various useful functions, including “restoring” the walls of blood vessels where it is really needed. HDL is considered “good” because it is highly soluble and does not form deposits. Low and very low density lipoproteins (LDL and VLDL) are the so-called “bad” cholesterol - and unlike the previous category, these lipoproteins tend to precipitate and form atherosclerotic plaques even where “repair” of the damaged vascular wall is not required.
But the problem lies not in cholesterol itself and its compounds, but in its excess intake into the body along with fatty animal foods. The body cannot remove the excess, as a result, vascular pathologies arise, provoked by the occurrence of large atheromas and narrowing of the vascular lumen, against which discirculatory encephalopathy of the brain develops.
Arterial hypertension
Hypertension also provokes pathological changes in blood vessels in response to high blood flow pressure, which injures the membranes. Studies of the relationship between hypertension and dyscirculatory encephalopathy have revealed a direct relationship between severe chronic hypertension, in which there is no decrease in blood pressure even at night, and the progression of DEP. In cases where the pressure could be stabilized, the intensity of damage to the blood vessels of the brain decreased, and therefore the risk of stroke decreased.
Increased blood pressure with hypertension and pathological deformation of the vascular wall, including cholesterol growths, indicate a serious problem in the vascular system.
Renovascular hypertension
This pathology is not a very common type of hypertension, but it often leads to the development of systemic hypertension, that is, a general increase in blood pressure, and to the next pathological link, the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Renovascular hypertension is a consequence of a narrowing of the lumen of the renal arteries by more than 65%. The cause is also pathological deformation of the vascular wall, mainly from atherosclerosis. As a result, the blood supply to the kidneys is disrupted, leading to loss of functionality. There is a direct connection between kidney function, fluid circulation in the body, blood supply and the state of the vascular system, so the condition of the kidneys is also taken into account in the diagnosis of DEP. Renal pathologies worsen the condition of the vascular system, which also affects the cerebral vessels.
Damage to the vascular wall due to inflammation
The supporting frame of the vascular wall consists of connective tissue. This type of tissue is susceptible to inflammatory processes. Inflammation can occur for many reasons. One of them is tissue damage by pathogenic microorganisms. Agents of inflammation can be viruses, for example, herpes virus, bacteria, fungi.
The spread of streptococcal infection can lead to the development of rheumatism - inflammation of the lining of the heart and blood vessels, as a result of which their condition worsens.
Although discirculatory encephalopathy is not an inflammatory disease, it can occur as a consequence of inflammatory processes in the vessels that cause pathological changes.
Vascular calcification
Excess calcium, like excess cholesterol from food, also has a bad effect on vascular health, causing calcification and impaired elasticity of the vascular wall, which leads to the vessels becoming fragile and brittle. The problem is aggravated by high pressure on the walls as a result of hypertension and the deposition of excess cholesterol. The accumulation of calcium in the body is possible with excessive consumption of dairy products, mineral or too hard drinking water with a high content of calcium salts. Calcinosis is neutralized by eating plant foods containing large amounts of magnesium, these include green vegetables, sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds, and wheat bran.
Thus, dyscirculatory encephalopathy is a consequence, among other things, of poor nutrition, which also causes atherosclerosis and hypertension.
Physiotherapy
Discirculatory encephalopathy is such a complex disease that its treatment also includes various therapeutic procedures. The course of each of them is about 15 visits.
Electroson
This procedure applies a low-frequency current to the brain, which stimulates its activity. During this procedure, electrodes are placed on the patient's eyelids, through which a weak current enters the brain through capillaries and nerve bundles.
Thanks to this effect, new neural connections are formed in the brain, the interaction of gray and white substances is normalized.
Ultra-high frequency procedures
This physiotherapy accelerates the blood well due to the influence of a high-frequency electromagnetic field. The speed of its movement through the vessels increases, and the cells receive more oxygen.
Exposure to galvanic current
Galvanotherapy is used to increase the lumen of blood vessels and increase blood flow in the cervical region and head. During the procedure, the neck and shoulder areas receive a weak continuous current. In some cases, the effect is enhanced by applying iodine or orotic acid to the collar area. Galvanotherapy eliminates neck pain, migraines, and also improves cellular metabolism and nutrition.
Laser therapy
This procedure is based on the effect of infrared radiation on the neck areas.
Laser therapy:
- has a warming effect;
- thins the blood;
- increases blood flow;
- activates metabolic processes and the functioning of nerve cells.
Baths
Baths are mainly used:
- radon;
- carbon dioxide;
- oxygen
They have a wide spectrum of action:
- improve sleep;
- increase blood flow by dilating blood vessels;
- restore impaired blood circulation in small capillaries;
- calm the nerves;
- eliminate tinnitus;
- normalize blood pressure;
- restore metabolic processes in cells.
Massage
There are 3 types of massage for the treatment of vascular encephalopathy:
| Medicinal |
|
| Acupuncture | When affecting certain points on the human body, such a massage is capable of:
|
| Lymphatic drainage |
|
Types of disease
The diagnosis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy should be distinguished from other types of encephalopathies, including stroke. DEP is characterized by a gradual chronic course. Brain damage in this pathology is diffuse, small and multifocal, formed from microstrokes and microinfarctions.
The following types of DEP are conventionally divided:
- atherosclerotic type;
- hypertensive;
- mixed.
With discirculatory encephalopathy, neuronal atrophy occurs, damage occurs to the pathways in the white matter, which leads to a disconnection of the interaction between the cortical and subcortical structures of the brain. In DEP, such pathological changes often form in the frontal lobes of the brain, which determines cognitive neurological disorders. Damage to the cerebellar zone causes motor disorders.
Initial manifestations (stage 1)
According to the Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, there are 3 stages of DEP.
Stage 1 – initial. Discirculatory encephalopathy with a slight degree of neurological damage is characterized by symptoms such as:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- the appearance of noise in the head;
- daytime sleepiness;
- decreased concentration;
- memory impairment;
- walking slower;
- the appearance of irritability.
Helpful information
Such symptoms worsen the patient’s quality of life, but performance at this stage is maintained. Therefore, in most cases, such painful manifestations are ignored, which leads to the further development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Symptoms of stages 2 and 3
At these stages, the disease manifests itself with a more pronounced clinical picture of neurological disorders.
Symptoms of stage 2 with dysfunction of the frontal lobes and cerebellum:
- progressive impairment of memory, attention, thinking;
- decreased self-control;
- apathy, depression;
- increased irritability;
- significant decrease in performance;
- the appearance of frequent urination, including at night.
Stage 2 dyscirculatory encephalopathy leads to a decrease in social adaptation, and professional qualities are lost. But at the same time, the patient is still able to care for himself.
Symptoms of stage 3 DEP:
- severe cognitive impairment, moderate dementia;
- loss of self-control, inability to adequately assess one’s condition;
- severe gait disturbances and problems with balance appear;
- Parkinsonism develops.
At stage 3, the patient completely loses his ability to work and loses self-care skills, which corresponds to disability group 1-2.
Symptoms
In the first stages of development, the manifestations of the disease are insignificant and hardly noticeable. A person lives unaware of a cerebrovascular accident until the first signs appear:
- Asthenia (muscle weakness).
- Pain in the head area.
- Dizziness, transient confusion.
- Increased fatigue.
Symptoms of grade 1 DEP are mild, which makes it difficult to determine the diagnosis and choose treatment. Similar symptoms are characteristic of many neurological and somatic diseases (mental disorders, infectious diseases in the prodromal phase), which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis based on single symptoms. The diagnosis is made if abnormalities typical for the pathology are observed for 6 months or more. Symptoms of progressive pathology moving into stages 2 and 3:
- Increasing deterioration of cognitive abilities. At stage 3, vascular dementia develops.
- Psychovegetative disorders - anxiety, depression, asthenia, changes in sensitivity and reaction to external stimuli.
- Movement disorders of the pyramidal type (spasticity, seizures).
- Motor disorders of the extrapyramidal type (hypokinesia, parkinsonism).
The severity of cognitive disorders depends on the volume of brain tissue that has undergone atrophic changes. DEP is often accompanied by cephalgic seizures. The following syndromes develop: pseudobulbar (impaired swallowing functions, speech impairment, involuntary laughter, crying), amyostatic (slowing of voluntary movements, limitation of motor activity), vestibulocerebellar (impaired balance and motor coordination).
Diagnosis of the disease
Identification of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is carried out based on the collection of patient complaints and the results of diagnostic studies of the brain (CT, MRI). Tomography reveals multiple cysts, dilatation of the ventricles, atrophy and replacement of dead neurons with auxiliary glial cells, which leads to disruption of brain function.
Neuropsychological and neurological symptoms are identified:
- emotional-volitional disorders;
- disturbance of gait and coordination.
When diagnosing DEP, a history of risk factors such as:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- rheumatism;
- IHD;
- vasculitis;
- blood diseases;
- thrombosis;
- hemodynamic disorders;
- frequent headaches;
- head injuries;
- neurosurgical operations on the brain;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- depression.
When properly diagnosing DEP, the emotional and psychological state of the patient is given no less attention than neurological disorders. This is especially important in the initial stage of the disease.
Treatment methods
Treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is aimed primarily at identifying the underlying cause of vascular damage.
DEP can be both a cause and a consequence of heart attacks and strokes. In this case, one vascular pathology provokes the occurrence of another. The vicious circle can only be broken if we take a comprehensive approach to the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Drug treatment
For arterial hypertension, drug therapy is aimed at stabilizing blood pressure and maintaining normal pressure levels, usually with the help of antihypertensive drugs. It is recommended to avoid a sharp decrease in blood pressure, especially when treating elderly patients, as well as those who have bilateral stenosis of the main arteries of the head.
The following drugs are used in the treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
- hypotensive;
- diuretics;
- anticoagulants;
- venotonic;
- nootropics;
- antidepressants;
- sedatives.
Medicines for the treatment of DEP are taken as prescribed by the attending physician.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of DEP is used for stenosis (narrowing) of the main arteries by more than 70%. Elimination of vascular obstruction is carried out on the internal carotid arteries. Surgical intervention is also advisable when large loose atheromas are detected, as a preventive measure for the detachment of microthrombi and the formation of thromboembolism.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are most effective in the initial stage of development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. The following methods are used:
- Massotherapy. With cervical osteochondrosis, you can perform self-massage, which quite effectively relieves muscle spasms and improves cerebral blood flow, especially if the procedure is performed regularly;
- Acupuncture. Goes well with massage;
- Hirudotherapy. When used correctly, this method of improving blood quality can replace the use of synthetic anticoagulants and significantly reduce the risk of stroke and ischemia;
- exercise therapy;
- Capillary therapy according to Dr. Zalmanov’s method is one of the most effective ways to improve cerebral circulation at home. For DEP, this method is especially effective, since the emphasis in capillary therapy is on opening clogged capillaries, which helps improve blood circulation in areas of cerebral ischemia and restore nerve cells.
Physiotherapy is an effective tool in the treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, especially when combining several methods simultaneously. The result largely depends on the regularity of the procedures. With complex systematic treatment, it is possible to restore the functioning of damaged vessels and reduce the negative consequences of chronic ischemia.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, dyscirculatory encephalopathy does not limit a person’s life.
But there are several critical situations when the disease becomes a death sentence for the patient:
- A rapidly progressing vascular encephalopathy, in which every few years it progresses to a more severe stage.
- When the disease is aggravated by diabetes mellitus, hypertension or coronary heart disease.
In these cases, in accordance with the severity of encephalopathy, the patient is assigned one of the disability groups:
- Group 3 : the disorder reaches stage II, when pathologies become noticeable:
- body control; speeches; vision; thinking.
- Group 2 : vascular encephalopathy progresses and is in stage II or III, when a person: begins to have strokes; the perception of the surrounding world is disrupted; convulsions occur; thoughts are confused; unrelated speech begins; Loss of control over your movements.
- Group 1 : the disease reaches stage III. At this stage, a person has almost completely: blood circulation in the brain is impaired; there is no even short-term memory; dementia developed.
Despite the unfavorable prognosis, the patient can live with the diagnosis for decades without deterioration in quality of life. People with slowly progressing discirculatory encephalopathy are not assigned a disability, since they are able to work independently and take care of themselves.
Discirculatory encephalopathy has a disappointing prognosis, but this diagnosis is not hopeless. With such a disease, with adequate and competent treatment, patients can live for many more years without any problems.
Author of the article: Shalunova Anna
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Prevention
General health methods work well as a preventive measure for vascular pathologies, which include dyscirculatory encephalopathy. In order to maintain brain performance at a high level for many years, it is recommended to adhere to the following simple rules:
- Quit smoking as a cause of vascular damage;
- Set up nutrition. That is, replace the consumption of harmful foods with healthy ones. Gradually form the right eating habits that will allow the body to receive from food everything it needs for self-healing, including the regeneration of damaged blood vessels. Such healthy products are fresh vegetables, herbs and fruits. They contain all the necessary components to maintain health, including vitamins C and PP, which are needed for blood vessels;
- Regularly spend time in the fresh air and ventilate the room. This is necessary as a prevention of hypoxia. Oxygen starvation also leads to atrophy and death of nerve cells, as does a lack of nutrients when the transport function of blood vessels is impaired;
- It is necessary to maintain the vascular system in good shape with moderate and regular physical activity. Regular walking in nature is beneficial for cerebral circulation.
It is much more effective to prevent or treat vascular damage and chronic cerebral ischemia at the onset of the disease than to try to restore lost mental abilities at stages 2-3 of dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Conservative therapy
Since surgical intervention is a big risk for the health and life of patients, the neurologist selects conservative treatment methods whenever possible. It includes following a strict diet to reduce the patient’s weight, various physical therapy and the use of folk remedies.
Conservative treatment includes:
- restoration of metabolic processes in the body;
- weight loss through diet;
- giving up all bad habits;
- normalization of sleep;
- simple physical exercises.
Since excess weight provokes the formation of blood clots, increased blood pressure and malfunctions of internal organs, patients with DEP are advised to follow not only a diet, but also a daily routine, spend more time in the fresh air and exercise.
Patients with discirculatory encephalopathy should eat only low-fat foods, reducing the amount of salt consumed per day to 5 g or practically eliminating it from the diet. You should also avoid eating fatty and fried meat. The diet should consist of fish and vegetables. This approach allows not only to reduce a person’s weight, but also to get rid of swelling and pressure surges.
During the diet you should also consume:
- potato;
- tomatoes;
- garlic;
- onion;
- pumpkin;
- any greens;
- natural fermented milk products;
- cereals;
- nuts;
- apples;
- pears;
- figs;
- cucumbers;
- carrot;
- red cabbage
It is allowed to eat a small amount of lean meat - beef and turkey.