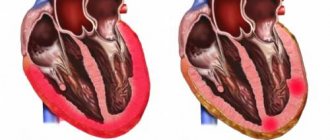
Vascular diseases can manifest themselves in the form of various angiopathies, which cause irreversible changes in the body. In some cases, they are quite dangerous, as they lead to disability or even death for the patient. Therefore, in such cases, correct diagnosis and effective treatment are necessary.
Angiopathy (AP) is characterized by damage to blood vessels, most often small and medium-sized, resulting in the development of a corresponding clinical picture. It occurs against the background of various diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, due to injury), and is therefore considered a complication of them.
The long course of angiopathy threatens the occurrence of chronic disorders in the blood supply system, which leads to disruption of the functioning of various organs and parts of the body.
Examination of patients with angiopathy plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis, since it is important to determine the main cause of the development of the pathology. The course of AP may be more or less pronounced, but appropriate treatment must be carried out. Otherwise, the tissues that supplied blood to the affected vessels begin to die.
Video Hypertensive retinal angiopathy. What is it and why is it dangerous?
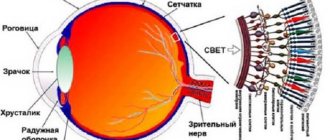
Retinal angiopathy
Retinal angiopathy Source: moj-doktor.ru
Retinal angiopathy is a pathological change in the vessels of the retina, which is caused by disorders of the nervous regulation of vascular tone and difficulties in the inflow and outflow of blood in the lumen.
This pathological condition can be detected in a variety of diseases; for this reason, it is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of another pathological process in which blood vessels, including the retina, are affected.
The disease manifests itself as temporary and reversible vascular spasms, dystonia and vascular paresis.
Angiopathy of the retinal vessels of the retina is a condition characterized by changes in the blood vessels and capillaries, caused by obstructed outflow and inflow of blood, as well as a disorder of the nervous regulation of vascular tone.
This pathological condition is characterized by vascular paresis and temporary spasms in them, dystonia. Angiopathy is a consequence of diseases that affect the vessels of the entire body. During ophthalmoscopy, which is performed by a specialist ophthalmologist, degenerative changes can be detected.
The patient may experience progressive retinal dystrophy and myopia, due to the fact that angiopathy often leads to disruptions in the functioning and nutrition of the eyes.
Retinal angiopathy is a vascular disease that impairs the blood supply to the fundus of the eye. In a general sense, angiopathy is pathogenic changes in blood vessels caused, for example, by atherosclerosis.
Small vessel disease is called microangiopathy. The retinal vessels also fall under the category of small ones. Therefore, the cause of retinal vascular damage is microangiopathy.
It can develop under the influence of various circumstances - from traumatic injuries to pressure surges. In childhood, vascular damage to the visual apparatus is congenital.
In adults suffering from metabolic disorders, diabetic retinopathy is often diagnosed.
General characteristic symptoms of any vascular disease of the retina:
- deterioration of vision, blurred vision in the eyes, up to blindness (which is especially dangerous, for example, diabetic retinopathy)
- progressive myopia
- dystrophic changes in the retina (death of nerve photoreceptor cells)
- "lightning" in the eyes
- nosebleeds
For effective treatment of retinal angiopathy, it is very important to understand and know the causes of the disease. With timely identification and effective treatment of the causes of the disease, angiopathy is treatable.
In Germany, they attach great importance to detailed diagnosis of the disease and analysis of the causes (diabetes, hypertension, head injury, etc.). This explains the high efficiency of treatment of angiopathy in ophthalmology clinics in Germany.
In any case, it is important to know what contributes to the development of the pathology, as well as what its main manifestations are, in order to be able to consult a doctor for help as quickly as possible in order to prevent the development of a late stage of the disease. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of full recovery.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
When a person who is suspected of having some form of angiopathy consults a doctor, an external examination is carried out, palpation of the affected areas, collection of patient complaints and medical history. Further, to obtain an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe several additional examinations to the patient:
- — Ultrasound of blood vessels, which provides information about the current state of the vascular walls and blood flow speed;
- - a specific study called fundus graphy, which provides data on the condition of the vessels of the retina of the eyeball;
- - angiography - assessment of vascular patency using x-ray examination and injection of a contrast agent into the patient’s blood;
- — MRI is a procedure that makes it possible to visualize the condition and structure of the body’s soft tissues on a computer screen;
- — CT is a procedure aimed at obtaining detailed layer-by-layer images in the area of the pathological process, allowing one to assess its extent.
Kinds
Source: okardio.com
There are several types of retinal angiopathy depending on its causes: hypertensive, diabetic, hypotenic, traumatic. Let's consider each of them separately.
- Hypertensive
Caused by arterial hypertension. With it, high pressure on the walls of blood vessels leads to their damage. Progressive hypertension is expressed by changes in the fundus of the eye: uneven narrowing of the arteries, pinpoint hemorrhage, dilation and branching of the veins.
In the unadvanced stage of the disease, it is possible to restore the healthy state of the retina if the pressure is normalized.
Symptoms:
- Blurred vision due to pressure changes.
- Slight visual impairment during the second stage of the disease.
- Serious visual impairment, up to blindness in the third stage of the disease.
- Fatty deposits or yellow spots on the eyes.
- Diabetic
Caused by diabetes. There are two forms of the disease: micro and macroangiopathy. In the first form, the capillary walls become thin, which causes hemorrhages and a general disruption of blood circulation.
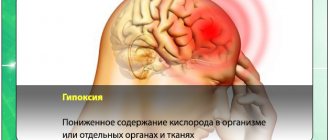
Macroangiopathy causes injuries to the large vessels of the eyes. In severe cases, tissue hypoxia and hemorrhages occur, which cause visual impairment.
- Traumatic
Occurs with prolonged compression of blood vessels, after a cranial injury, injury to the chest, or cervical spine. A sharp increase in pressure caused by injury causes hemorrhages in the retina. This causes a decrease in vision, which is not always restored.
- Hypotonic
Occurs when blood pressure is low, due to slow blood flow and congestion of small vessels. The disease is characterized by dilated arteries, tortuous vessels, and pulsation of veins.
- Youth
In addition to the types described above, there is also juvenile retinal angiopathy, also called Eales disease. This rare disease develops in childhood and adolescence. With juvenile angiopathy, the blood vessels of the eyes become inflamed, and frequent hemorrhages occur in the retina.
The causes of this form of the disease are not fully understood, but it is known that the pathology can result in glaucoma, cataracts, or even complete blindness.
Causes of retinal angiopathy
In fact, retinal vascular angiopathy does not occur on its own without underlying diseases. This problem develops against the background of a complex change in the functioning of the body’s blood vessels.
Often changes in blood vessels occur not even against diseases, but against conditions of the body, for example, retinal angiopathy during pregnancy.
Since retinal angiopathy is not an independent pathological condition, there are many reasons for its occurrence:
- Osteochondrosis;
- Intoxication;
- Blood diseases;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Brain and spinal cord injuries;
- Features in the structure of blood vessels;
- Elderly age;
- Increased ICP.
The problem is that the blood supply to the fundus of the eye is deteriorating. Against this background, the vessels become too fragile, their walls become thinner, and the vessels can easily collapse.
The situation is complicated by the fact that such changes are irreversible. If a section of the retina has already detached or necrotic changes in blood vessels have begun, then it is no longer possible to establish normal blood supply there.
If we consider in more detail the causes of most angiopathy, then we should first of all immediately determine the nuance: this pathology is usually considered not an independent disease, but a symptom. Therefore, it is important to determine which diseases caused such manifestations.
In addition, you need to understand that there is a certain risk group - people who, due to some characteristics of the body, are predisposed to such manifestations.
Based on this, we must understand that if a person has some kind of disease that can provoke such a diagnosis, then it is necessary to at least minimize the influence of factors that only aggravate the situation and further provoke this disease.
It can also occur with various diseases of the blood or immune system and with various age-related changes (for example, at a young age, when the body and all its systems undergo restructuring).
At-risk groups
If we consider the potential risk group, we can identify the following categories of people who are initially most predisposed to the development of such diseases:
- Aged people. According to statistics, in people under 30 years of age, diagnosis practically does not show the presence of this disease.
- Smokers.
- Pregnant women.
- Overweight people.
- Specialists whose retinas are constantly exposed to significant stress at work (for example, welders, workers at metallurgical enterprises).
- People whose body is systematically exposed to intoxication. This means not only workers in such industries, but also patients who are forced to take harmful drugs consistently for a long time.
- Those who have congenital disorders of vascular development.
This does not mean guaranteed development of such a disease if a person has some underlying pathologies or provoking factors. This can be completely avoided. By the way, it is clear that this does not mean the need to urgently quit your job, even if there are no symptoms.
This just means that if a person is initially at risk, then he must not forget about periodic diagnosis. This is what will prevent the serious development of the problem until a late stage. With timely treatment, it is quite possible to soon forget about this disease.
In addition, in the presence of provoking factors, it is important to follow basic safety rules, and also not to forget about eye exercises, adequate rest, sunglasses, limited time watching TV and working at the computer.
Causes, risk factors
In 90% of cases, angiopathy is a secondary disease. This means that it is a consequence, complication or manifestation of a number of other diseases. It is rarely identified as an independent pathology - in 10% of cases.
The main causes of angiopathy:
- diabetes;
- arterial hypertension;
- injuries and hypothermia;
- chronic intoxication of the body, accompanied by the accumulation of abnormal proteins (amyloidosis);
- diseases of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves and autonomic nervous system;
- systemic connective tissue lesions (with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus);
- diseases of the blood system, manifested by an excess of blood cells (leukemia, thrombocytosis, polycythemia).
Risk factors:
- age after 50 years;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- congenital vascular anomalies;
- work in conditions of occupational hazards;
- metabolic disorders - high cholesterol and atherosclerosis.
They occur in 70–80% of angiopathy.
Symptoms of the disease
Source: okodent.ru
It should be noted that the patient may not present any complaints for a long time and not notice deterioration in vision. This is a reversible disease, but only in the initial stages and in cases where the root cause can be accurately determined.
Retinal angiopathy, as a rule, is not an independent disease; it is a consequence of other pathologies in which vascular damage occurs. These may include hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus and other diseases.
In most cases, angiopathy occurs simultaneously in both eyes. The disease can occur in people of any age, but is more common after 30 years of age.
The main symptom of the disease - damage to the retinal vessels - can be seen during hardware examination. This may be a narrowing or dilatation of the blood vessels of the eyes, minor hemorrhages. Here are some symptoms:
- Blurred vision, flashing dots before the eyes;
- Discomfort and pain in the eyes;
- Bloody discharge in the urine;
- Pain in the joints, pain in the legs when walking;
- Nosebleeds;
Often, patients at the initial stage of the disease may not even pay attention to it, explaining the symptoms as simple overwork. They think that if the retina is damaged, it will go away on its own soon.
In the modern rhythm, many people work on computers and therefore are forced to subject their eyes to increased stress. In this case, it is precisely necessary to check the eyes as often as possible so as not to miss important signs that may indicate the development of a serious and complex pathology.
Gradually, the symptoms increase and become much more obvious. Symptoms appear more clearly after work that requires concentration and strain on the eyes.
In later stages, serious visual impairment occurs, which gradually leads to its complete loss.
Usually the disease does not progress too quickly and therefore it is quite possible to seek help from a doctor. Deteriorating vision is already a sufficient reason to go to the hospital.
Prognosis and prevention
In the majority of patients (about 85% of cases) who adhere to medical recommendations, the disease progresses poorly and does not contribute to the development of severe complications.
In the case of a malignant course of the underlying disease (hypertension, diabetes mellitus), in 99% of cases angiopathy also develops unfavorably. In such cases, blindness, kidney failure or tissue death develop. Therefore, the earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of maintaining health.
4.67 Aug. rating ( 92 % score) – 9 votes – ratings
Diagnosis of the disease
Source: oglazax.ru
To make a diagnosis, you need to contact an ophthalmologist. The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, as well as a detailed examination of the vessels.
For this purpose, X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasound are used. Depending on the diagnosis and nature of the disease, proper treatment is prescribed.
Important
As a rule, angiopathy must be treated comprehensively. That is why treatment is prescribed not only by an ophthalmologist, but also by a cardiologist, neurologist and therapist.
Treatment of diabetic angiopathy is based on a special diet low in carbohydrates. Dosed physical activity will help lower sugar and strengthen the cardiovascular system.
It is recommended to make preventive visits to an ophthalmologist at least once a year. Examination of the fundus is a simple, quick and painless procedure that allows the doctor to diagnose even the initial signs of angiopathy and begin treatment on time.
What can an ophthalmologist see during an examination?
This disease is characterized by disturbances in the lumen of blood vessels; they can be narrowed, tortuous or full-blooded, dilated, their condition depends on the cause of the disease. Angiopathy can affect two eyes at once.
There are such lesions of the retinal vessels:
- traumatic (traumatic retinopathy);
- hypotonic;
- juvenile (Iles disease);
- hypertensive;
- diabetic.
Causes of retinal angiopathy Retinal angiopathy affects people over 30 years of age, and in some cases this condition is observed in children and adolescents, which is called juvenile angiopathy (Eales disease).
This is a rather rare pathology, the etiology of which is currently unclear. The reasons for the development of retinal angiopathy may include:
- intoxication of the body;
- arterial hypertension;
- systemic vasculitis with an autoimmune nature;
- congenital structural features of the walls of blood vessels;
- elderly age;
- work in hazardous industries;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes;
- smoking;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- traumatic eye injuries;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- disturbance of nervous regulation, which responds to vascular tone.
Risk group
The following categories of citizens are at risk of developing vasopathy:
- diabetics;
- persons suffering from hypertension;
- people of retirement age;
- young people aged 14 to 19 years;
- lovers of too salty foods;
- people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
If primary signs of angiopathy are detected, a visit to a hematologist or vascular surgeon is required. Timely therapy will help avoid worsening the condition.
The material was prepared specifically for the website venaprof.ru, edited by pharmacist M.N. Aleksandrova.
Conservative treatment of angiopathy
When considering how to treat such a disease, one should immediately note the need to first deal with the root cause of the pathology. Having correctly developed treatment tactics, you can quickly eliminate the symptoms.
Angiopathy is a symptom rather than an independent pathology, so it is important to eliminate the root cause. Next, you should move on to directly eliminating the main symptoms of the disease.
In any case, the treatment method will directly depend on the exact stage of the disease and what caused it.
Diagnosis and treatment are carried out only by a qualified specialist. To begin with, medications are prescribed that improve microcirculation in the vessels of the retina and eyeball.
These include such products as “Mildronat”, “Solcoserial”, “Trental”, “Emoxipin”, arbiflex, vazonit, pentilin. It should be noted that these drugs have a beneficial effect on the bendability of red blood cells, which facilitates their free passage through the capillaries.
When treating angiopathy with increased vascular fragility, the doctor prescribes calcium dobesilate, which improves microcirculation in blood vessels, helps normalize the permeability of blood vessels to nutrients and reduces blood viscosity.
To treat diabetic angiopathy, the doctor must prescribe the patient a special diet, which the patient must strictly follow. The diet excludes foods rich in carbohydrates.
Such patients are recommended moderate and dosed physical activity, which improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system and promotes the active use of sugar by muscles.
In the treatment of hypertensive angiopathy, an important place is occupied by normalizing blood pressure levels and following a diet that reduces cholesterol levels in the blood. This treatment is prescribed jointly by a cardiologist and a therapist.
Eye drops
The ophthalmologist, for his part, can prescribe the patient vascular eye drops (emoxipine, taufin), eye vitamins (Anthocyanin Forte, Lutein Complex) in order to improve microcirculation in the vessels of the eyeball and preserve the patient’s vision.
In advanced cases, the patient may be prescribed hemodialysis aimed at cleansing the blood.
In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures (for example, magnetic therapy, acupuncture, laser irradiation) have proven themselves well in the treatment of retinal angiopathy.
Typically, angiopathy of the retina or both eyes requires an integrated approach to treatment: the recommendations of an ophthalmologist alone are not always important, but advice from a cardiologist and a neurologist may also be required.
To treat retinal vascular angiopathy, it is necessary to select complex therapy, as well as carry out measures that will be aimed at combating tissue hypoxia.
Drops are considered a symptomatic treatment method, given the variety of causes of this disease. Below we will consider drugs that can only be prescribed by a specialist - an ophthalmologist.
In addition, for any form of angiopathy, the doctor prescribes drugs that help improve blood microcirculation in the retina and blood vessels of the eyeballs.
In case of increased fragility of blood vessels, the patient is prescribed calcium dobesilate, which helps improve microcirculation in the vessels, normalize their permeability to nutrients and reduce blood viscosity. In severe cases, the patient may be prescribed hemodialysis to cleanse the blood.
Physiotherapy methods are also used, including acupuncture, magnetic therapy, and laser irradiation. In addition, there is a special device “Sidorenko glasses”, which are used to improve vision at home.
They perform a whole range of procedures: phonophoresis, pneumomassage, infrasound and color therapy. Such a device brings good results, helping to improve vision in a short time.
Medicines
Surgical intervention for such problems is practically not practiced. Even with a severe form of the disease, doctors practically do not resort to this. If the disease is detected at an early stage, then there is no need for this at all. Conventional, properly selected drug treatment is sufficient.
It should be noted right away that this therapy must be fully consistent with the chosen treatment of the underlying diseases.
Example
If, for example, vision problems are caused by diabetes, then first of all they choose treatment for this disease, and only then select drugs to normalize vision, taking into account the compatibility of the drugs.
If we talk about the direct treatment of this pathology, then there are several groups of drugs that are prescribed by the doctor in combination. You must take the course 2 times a year.
Depending on the patient’s health condition, it lasts 2-3 weeks on average. The groups of medications that must be prescribed when making a diagnosis include:
- Agents that reduce the ability of platelets to stick together (Acetylsalicylic acid).
- Vitamin complexes (various vitamins of groups B, C, E).
- Drugs whose action is aimed at strengthening the walls of blood vessels and reducing their permeability (Parmidin).
- Medicines that improve blood circulation and blood supply (Pentilin, Vazonit).
Most often, these drugs are prohibited from being used during pregnancy or for young children. But sometimes the doctor may prescribe a lower dosage even for such groups of patients. It all depends on each specific case.
In different situations, various drugs may be prescribed, the names and dosage of which are selected depending on the characteristics of the body, the stage and characteristics of the pathology, and concomitant diagnoses.
It is important not to forget about taking medications to normalize blood sugar and blood pressure.
Even if initially there are no diagnoses such as hypertension or diabetes mellitus, you should still monitor the indicators constantly and, as soon as necessary, consult a doctor to prescribe a suitable drug to stabilize the condition.
What drops should I use?
Three main drugs are usually prescribed: tauphron, emoxypine and isotin.
- Taufon
Taufon - drops that come in 5 and 10 ml bottles, the active substance is taurine.
Taufron works due to the active substance taurine, which helps stabilize cell membranes, stimulates metabolic and energy processes in the eyes, and also helps to quickly heal existing damage and wounds.
When using this remedy, eye pressure is normalized, and in general this medicine is effective for moderate forms of angiopia. The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor, but on average lasts 1-3 months when instilling 1-2 drops into each eye three times a day.
The drug is used for:
- stabilization of cell membranes;
- activation of healing of corneal injuries;
- stimulating energy and metabolic processes in eye tissues;
- normalization of IOP.
This product is contraindicated for minors (under 18 years of age), and is also not recommended for use by pregnant women. If the patient becomes allergic to the components of the medication, the medication is discontinued.
- Emoxipin
Instead of taufron, you can use emoxipine, which helps improve blood circulation in the vessels and strengthens them. If a patient has severe photophobia during angiopia, emoxypine helps reduce such sensations.
Typically, this remedy helps with diabetic angiopathy, but is also suitable for other types of disease.
Emoxipine is a synthetic antioxidant that is widely used in ophthalmology; its action can contribute to:
- resorption of minor hemorrhages on the retina;
- protecting the retina from bright light;
- strengthening the vessels of the eyeball, reducing the permeability of their walls;
- activation of blood flow in the tissues of the eye.
1-2 drops are instilled per day, but the course of treatment, depending on the severity and characteristics of the disease, can last from several days to one month.
Sometimes during the first procedures the following side effects may appear: burning in the eyes; swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye and its redness; itching in the eyes; surges in blood pressure. In such cases, emoxipine is discontinued.
- Aisotin
Strengthen and restore vision in ophthalmic diseases. Available in 10 ml. in bottles. Aisotin An alternative to such medications is the softer aisotin, but not everyone considers it traditional, since aisotin is based on Ayurvedic herbs.
Indications for use:
- post-operative recovery (laser operations and surgical interventions);
- conjunctivitis;
- redness of the eyes;
- glaucoma;
- eye burns;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- various vision pathologies.
Use for two or more months, 2 drops three times a day.
Aisotin is a dietary supplement that can be used to prevent complications of this disease.
The following drugs are also used:
- Quinax
The action of the drug is aimed at:
- regulation of metabolism in eye tissues;
- antioxidant effect;
- increasing the transparency of the lens.
- Emoxy optic
It is a cheap analogue of Emoxipin.
Has the following properties:
- antihypoxic (increasing the resistance of visual tissues to insufficient oxygen);
- antioxidant (prevents lipid oxidation);
- angioprotective (strengthening the walls of blood vessels);
- antiplatelet (blood thinning, activation of its microcirculation, resorption of hemorrhages inside the eye).
Based on everything described, we can come to the conclusion that these medications help preserve vision, improve microcirculation directly in the blood vessels of the eyes, and also have a strong physiotherapeutic effect.
Our advantages
"Moscow Eye Clinic" offers comprehensive diagnostics and effective treatment of eye diseases. The use of modern equipment and the experience of specialists working in the clinic eliminate diagnostic errors.
Based on the results of the examination, each visitor will be given recommendations on choosing the most effective methods of treating the eye pathologies identified in them.
The high level of theoretical training and practical experience of our doctors guarantees the achievement of good treatment.
Laser therapy
Source: Serdechka.ru
Modern effective methods of treating the retina with vascular damage (especially in diabetes) are associated with the use of laser technology.
Laser coagulation is carried out, depending on the nature and extent of the lesion, in two modes:
- Panretinal coagulation.
Laser "striations" are applied to the retina in a grating pattern, in more than a thousand points (usually up to two thousand). The macula area, responsible for particularly acute vision, is not affected. Laser “puncture” affects only the outer zones of the retina, without penetrating the photoreceptor layer.
Therefore, vision is not impaired due to such “exposure”. However, laser-treated retinal points change their physiological properties and require less oxygen. The retina becomes less dependent on angiopathic vessels that cannot cope with the increased oxygen supply.
But the macula gets more oxygen, as a result of which its condition improves. Vision in general also improves.
- Focal coagulation.
This technique is especially effective against macular swelling. A laser beam is used to seal the permeable walls of blood vessels, which causes swelling to develop. As a result, the swelling subsides and visual acuity improves.
Injection therapy
Drug injection is an ancient medical procedure. However, injection of edematous retina is, on the contrary, a new and very promising technique from the category of those innovations, thanks to which retinal angiopathy has become curable.
Firstly, modern instruments make the technique of intravitreal injection (that is, inside the vitreous) painless and non-traumatic. Secondly, the use of a new generation of medications makes this effect particularly effective.
The drug line used for intravitreal injections is divided into two directions:
- Corticosteroids (dexamethasone). They reliably relieve retinal swelling - however, a consistent course of injections is required, and not one-time procedures that give only temporary results.
- Drugs that inhibit angiogenesis (bevacizumab, ranibizumab, pegaptamib). Angiogenesis is the process of formation of new blood vessels. In many circumstances, proliferation of the vasculature is a pathogenic factor.
Retinal angiopathy is one such circumstance. Hypertrophied vasculature under the retina leads to swelling and other damage to the optic nerve. Effectively counteracting angiogenesis returns the retina to its normal state.
In addition to the injections, the patient receives protein kinase C inhibitors (in tablets). This is another type of newer drug that works well against swelling of the middle layers of the retina.
Traditional methods of treatment
Source: 1000listnik.ru
Folk remedies for the treatment of angiopia cannot be the basis of the entire course: such a disease requires not only an integrated approach, but also the use of specially developed and clinically tested medications. However, such methods can help with treatment and speed up the healing process.
For 20 grams of horsetail grass, take 30 grams of the knotweed plant and 50 grams of hawthorn flowers. This mixture of herbs is poured with 200 grams of boiling water and left to infuse for half an hour. The broth is then filtered through cheesecloth to remove any remaining herbs.
Take the product half an hour before meals (three times a day), one tablespoon.
Crushed valerian root (15 grams) is mixed with the same amount of lemon balm, and then 50 grams of yarrow are added to this mixture.
This mixture should be poured with a glass of water and placed in the refrigerator for three hours (but not in the freezer). After this, the product needs to be heated for 15 minutes in a water bath, and the cooled product is diluted with boiled water so that the result is 250 grams.
This glass of infusion must be drunk throughout the day, but not in one gulp, but in portions of several sips.
Every day during the course of treatment, which can be continued at your discretion, you need to prepare a new remedy. Take half a tablespoon of chamomile and St. John's wort and pour 500 grams of boiling water.
20 minutes is enough for the product to infuse, after which it is filtered and ready for use. One part of the product is drunk in the morning on an empty stomach, the second after dinner. These drugs should not be abused and you should not continue treatment with them for more than one or two weeks.
Forecasts
If treatment for retinal angiopathy is not started in a timely manner, it may gradually peel off. When such a problem affects both eyes at the same time, then in the future you can completely lose your vision.
But there is no need to worry too much about this. If timely diagnosis is carried out and comprehensive treatment is started, then it will be possible to restore visual acuity. The most important thing is to consult a doctor as soon as the first symptoms appear.
In order to initially prevent retinal angiopathy, you need to carefully monitor your overall health. If a person is at risk, it is important to avoid bad habits.
If he has a diagnosis that can become the root cause of the pathology, then it is important to approach it responsibly and begin comprehensive treatment. If you contain the pathologies that provoke the development of this problem, then retinal angiopathy will not arise initially.
Important
It is important to remember that periodic diagnosis is very important if a person is at risk. If, when the first symptoms occur or simply for prevention, regular examinations are carried out, then the disease can be detected at an early stage.
Then it will be possible to start treatment at an early stage. In this case, you can completely deal with this problem easily and quickly without any significant consequences.
The need for diagnosis remains even after treatment. Even with complete restoration of vision, you still need to undergo periodic examinations.
Often it is not possible to eliminate the provoking factors completely, so it is important to concentrate on the fact that, unfortunately, this manifestation may return again. That's why it's important to prevent this from happening.
If left untreated, retinal angiopathy can lead to a narrowing of the visual field, optic nerve atrophy, and partial or complete blindness.
In the treatment of this disease, the main thing is to identify the root cause. A comprehensive examination and consultation with a cardiologist, therapist and ophthalmologist will help with this. If the cause is eliminated, curing the disease will become much easier.
Possible complications
APS is a rather dangerous disease, complications from which depend on the location of the lesions.
| No. | Localization area | Possible complications |
| 1 | Heart | Heart attack |
| 2 | Brain | Stroke |
| 3 | Eyes | Loss of vision. |
| 4 | Lower limbs | Gangrene or necrosis |
| 5 | Arteries and veins of the abdominal cavity | Heavy bleeding |
| 6 | Kidneys | Serious problems with filtration. |
Lack of treatment leads to disability or death. To avoid consequences, it is recommended to contact a medical facility.