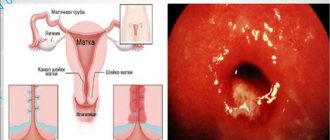
Salpingoophoritis is a disease otherwise called adnexitis. The disease is one of the most common gynecological pathologies, which is a simultaneous inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. At first, the inflammatory process directly affects the uterine appendages, after which harmful bacteria penetrate into the thickness of the ovaries - swelling develops, and purulent contents may appear in these organs.
Salpingoophoritis has a negative impact on the condition of the woman’s reproductive system, since it results in obstruction of the patency of the fallopian tubes. In such a situation, the egg simply will not be able to penetrate the uterine cavity, so this disease also increases the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy. In the content of this article you can find answers to the following questions: “Salpingoophoritis - what is it, what are the symptoms of this disease?” “How is this pathology treated in women?”
What is salpingoophoritis
Salpingoophoritis (adnexitis) is an inflammatory and infectious change that occurs in the uterine appendages (ovaries, fallopian tubes and ligaments) resulting from exposure to pathogenic microflora. First, the fallopian tubes are affected, then the ovaries become involved in inflammation.
Salpingoophoritis - what is it? This is inflammation of the fallopian tube.
Salpingo-oophoritis is accompanied by swelling of the ovaries and the accumulation of mucopurulent contents in them. Salpingoophoritis causes dysfunction of the reproductive system due to obstruction of the fallopian (uterine) tubes. Because of this, it is difficult for the egg to penetrate the uterine cavity, which leads to the development of pregnancy, which is localized outside the uterine cavity.
Causes and development factors
The main etiological factor in the occurrence of salpingo-oophoritis is the introduction of an infectious pathogen into the mucous membranes of the uterine appendages.
The main pathogenic microorganisms that cause salpingoophoritis are:
- staphylococcal and streptococcal flora;
- E. coli;
- chlamydial infection;
- gonococcal pathogen;
- Koch's wand.
Pathogens of the first 2 groups enter the appendages by an ascending route, and Koch’s bacillus – by a hematogenous route from infected foci (with blood flow in tuberculosis of the lungs, intestines, kidneys),
Risk factors include women of reproductive age with:
- increased fatigue;
- a sharp decrease in the state of immunological protection;
- sexual infections;
- frequent changes of sexual partners;
- poor nutrition;
- chronic fatigue.
This category also includes women:
- suffered from hypothermia;
- recently had an abortion;
- frequently exposed to stressful situations.
Salpingo-oophoritis is a female disease that, in acute and chronic form, can lead to serious health problems in women (adhesions, chronic pelvic pain), and even infertility.
Provoking factors
In a healthy woman, the introduction of pathogens into the appendages is prevented by a system of protective barriers, through which only aggressive gonococcus can penetrate. Other microorganisms gain access to them as a result of some failure in protection. Possible causes of infection:
- General or local hypothermia;
- Acute infectious diseases;
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- Therapeutic and diagnostic interventions in the uterus (abortion, endometrial curettage, hysteroscopy, intrauterine contraception);
- Abdominal surgeries;
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, obesity);
- HIV infection.
Development mechanism
There are several mechanisms for the development of the disease. The most common are infections of the appendages through ascending and descending routes. The ascending path is characterized by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria from the uterine cavity into the lumen of the fallopian tubes from the vagina through the cervical canal.
The spreading inflammatory-exudative process covers all the walls of the fallopian tubes with the development of salpingitis, and then all structures of the ovary are affected, and oophoritis develops. Later in the process it moves to the uterine ligamentous apparatus and salpingoophoritis develops.
The leading role is given to chlamydial and gonococcal pathogens. They provoke the formation of inflammatory fluid, which accumulates in the tubular structures of the uterus and can lead to adhesion (sticking together) and obstruction of the lumen of the fallopian tube. This, in turn, causes the formation of sactosalpins - sac-like “balls” in the cavity of the fallopian tube.
Accumulation of mucopurulent fluid leads to the development of pyosalpinx (pus in the tube). If the fluid is serous, hydrosalpinx develops.
The microbe penetrates the ovarian tissue, secretes toxins that participate in the formation of purulent cavities - abscesses. These abscesses can merge with each other and melt the ovarian tissue. The ovary takes on the appearance of a sac filled with pus.
In the absence of treatment and long-term progressive salpingo-oophoritis, a tubo-ovarian abscess may occur. With such an abscess, a combination of pyosalpinx and ovarian abscess occurs. When an abscess ruptures, infectious agents enter the abdominal cavity, namely the pelvic cavity.
This leads to the formation of pelvioperitonitis - inflammatory changes in the pelvic peritoneum. If left untreated, other parts of the abdominal cavity are also affected. Late diagnosis of pelvioperitonitis can lead to the development of interintestinal abscesses and purulent-inflammatory changes in the rectal uterine cavity.
The descending path consists in the spread of pathogenic pathogens from the structures of the large intestine through the peritoneum, or through the lymphogenous route. Most often these are inflammations of the cecum and sigmoid colon.
With frequent changes of partners and sexual contacts during the menstrual cycle, there is a high risk of microorganisms entering the uterus and its appendages. Stages and types Salpingoophoritis (adnexitis) is a common pathology that causes infertility.
Along the flow they distinguish:
- acute adnexitis – rapidly increasing clinical signs of the disease.
- subacute adnexitis – moderate increase in clinical symptoms.
- chronic adnexitis is a common outcome of acute adnexitis with incomplete cure.
Salpingoophoritis is classified by location. It can be one-sided or two-sided.
Causes of adnexitis
To trigger pathology, predisposing factors are necessary. They weaken the female body and provoke the development of the disease. These include:
- hypothermia;
- infection with a sexually transmitted infection;
- insolation;
- poor adherence to hygiene rules;
- stress;
- hypovitaminosis;
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- grueling physical activity.
Pathogens penetrate the reproductive organs hematogenously, lymphogenously, descending from the large intestine through the peritoneum or ascending from the vagina. Any microorganism can cause an infectious process:
- streptococcus;
- enterococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- gonococcus;
- fungi;
- viruses;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- coli;
- chlamydia.
The cause of the disease determines the symptoms and medical tactics. In some cases, microbial associations (usually Escherichia and staphylococcus) become the causative agent of salpinoophoritis. Typically, the infection is resistant to many antibacterial drugs, which complicates therapy.
Symptoms
Salpingoophoritis is an inflammatory disease of the uterine appendages, including the ovary, fallopian tube and adjacent tissue, which is common in modern gynecological practice. Clinical symptoms depend on the course and location.
The following clinical manifestations are characteristic of acute salpingoophoritis:
- Pain syndrome . Characterized by pain in the lower abdomen of various types (aching, stabbing).
- Pathologies of the ovarian-menstrual cycle and reproductive dysfunction are manifested by delayed menstruation, severe pain during menstruation and heavy discharge. Decreased libido and desire for a sexual partner due to fear of developing discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
- Intoxication syndrome , manifested by a persistent increase in body temperature to febrile numbers of 38-400, general weakness, nausea, dizziness.
- Purulent discharge from the vagina and other parts of the genital tract.
- Dysuric disorders , characterized by intense pain during urination, frequent painful urges, urination in small portions.
- Dyspeptic syndrome (single vomiting, perversion of taste).
It is important to know! The clinical picture of the acute stage depends on the state of the immune system and the virulence of the pathogen. If the state of immunity is sharply weakened, then virulence is high, which leads to a severe course of the disease.
In acute adnexitis, there is a high risk of developing ovarian abscesses, tubo-ovarian abscesses and pelvioperitonitis. This is due to the rupture of the fallopian tube and the entry of its contents into the free abdominal cavity.
Acute salpingoophoritis combines 2 successive phases:
- toxic - pronounced intoxication syndrome, the leading role is assigned to aerobic microorganisms.
- sepsis - anaerobic microbes join, the manifestations of clinical symptoms intensify, an abscess develops, followed by its perforation.
Subacute salpingoophoritis is characterized by less pronounced clinical symptoms. This stage can progress to both acute and chronic forms.
Forecast
It is possible to cure adnexitis with timely recognition of the symptoms of the disease and timely initiation of correct treatment. This allows salpingo-oophoritis not to become chronic or worsen by the development of purulent complications or inflammation of the peritoneum.
The adhesive process, which is one of the symptoms of chronic adnexitis, affects the possibility of conception and increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment of adhesions is a long process that involves the use of enzyme preparations (Longidaza, Wobenzym) and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Knowing how salpingoophoritis can be treated, it is also necessary to find out how to prevent it. Prevention of adnexitis consists of the following measures:
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Using a condom during sexual intercourse.
- Preventive treatment with antibiotics for any gynecological interventions.
- Increasing the body's defenses.
Chronic salpingoophoritis
Salpingo-oophoritis of chronic origin is the outcome of the first two pathological conditions, if they were not fully treated. Characterized by frequent relapses. They occur against a background of stress, hypothermia and physical fatigue.
Chronic salpingoophoritis can have 2 phases: exacerbation and remission. During remission, clinical manifestations are practically not expressed. Adnexitis can only be detected using diagnostic research methods.
The exacerbation period includes the following symptoms:
- general weakness, lethargy;
- the occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen, may be periodic or constant, most often unilateral pain;
- discharge of a sanguineous nature from the vagina;
- hyperthermia.
In addition, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted, causing:
- heavy bleeding more than 150-200 ml per day;
- uterine bleeding;
- a small amount of blood released during menstruation;
- severe pain during the menstrual cycle.
Pain during sexual intercourse, decreased libido, and impaired digestive and urinary functions (such as colitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis) are also characteristic.
Does it happen during pregnancy?
Salpingoophoritis is an inflammation of the uterine appendages that can occur during pregnancy. The organs in the abdominal cavity are located close to each other. If there is an inflammatory process in one organ, the inflammation can spread to another. Diagnosis and treatment of adnexitis in the early stages of the disease during pregnancy is important.
This is due to the fact that it can lead to spontaneous miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, infection and even fetal death.
Pathogens
Inflammation of the uterine appendages is caused by both STI pathogens and opportunistic microflora that normally populate the lower genital tract. In the latter case, activation of pathogens occurs with a decrease in general and local immune defense. Among opportunistic microflora the following are important:
- Escherichia;
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococci;
- Enterococci.
Among the causative agents of STIs, adnexitis is caused by:
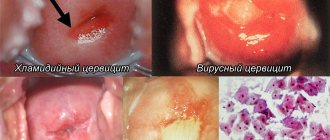
- Chlamydia is an intracellular parasite that is sexually transmitted . Chlamydia is the leading causative agent of adnexitis in young women under 25 years of age. It extremely rarely causes acute forms of the disease and tends to have a long, latent course. Chronic inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes and ovaries leads to infertility, ectopic pregnancies, and hormonal imbalance. Patients usually learn about their disease by undergoing examination after unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant.
- Mycoplasma - like chlamydia, parasitizes inside the host cells. Infection occurs during the birth of a girl through the mother's reproductive tract or after the start of sexual activity from an infected partner. In addition, the microorganism lives in the oral cavity and can be transmitted through oral sexual contact. Mycoplasma can be part of the opportunistic microflora, causing inflammatory diseases of the genital organs when the immune defense is reduced, injuries, or invasive interventions. The infection tends to be chronic.
- Ureaplasma - lives in the genitourinary tract of men and women and is transmitted during unprotected sexual intercourse. Causes acute and chronic (usually) adnexitis, often complicated by arthritis and immunodeficiency.
- Gonococcus - synthesizes and releases aggressive factors into the surrounding tissues that can destroy the protective barriers of the genital organs. Infection occurs through sexual contact, after which the pathogen quickly penetrates all parts of the female reproductive system, including the uterine appendages. Gonococcus causes acute adnexitis, which often becomes chronic. Without treatment, it parasitizes inside cells for a long time, supporting the inflammatory process.
In the vast majority of cases, salpingoophoritis occurs under the influence of a microbial association: pathogens of sexually transmitted infections, together with opportunistic microflora, affect the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Treatment in such situations requires determining the sensitivity of each microorganism and prescribing several antibiotics.
Tuberculous adnexitis is caused by Koch bacilli, which penetrate into the appendages with blood or lymph from other foci of infection (lungs, lymph nodes, bones, skin). The genital herpes virus can cause adnexitis in cases of severe immunodeficiency, for example, in HIV-infected women.
Diagnostics
If such symptoms occur, you should consult a gynecologist at your local clinic. After collecting complaints and identifying possible causes of the disease, the doctor must conduct a general and gynecological examination.
During a general examination, the tongue of patients is covered with plaque. Upon palpation examination, local pain is noted in the lower parts of the lumbar column, in the pelvic area. Often pain can radiate to the back and suprapubic region.
A gynecological examination reveals discharge from the vagina and cervical canal of a sanguineous-purulent nature. When examined in the mirrors, you can see the uterine appendages increased in thickness. They are often swollen and painful.
When abscesses and pyosalpinx form, upon palpation you can feel large, painful “tumors” that do not move, have unclear contours and different consistency. They often merge with the body of the uterus and form a dense conglomerate.
The main tests that a doctor should prescribe if acute salpingoophoritis is suspected:
- Complete blood count (characteristic signs of inflammation: increased leukocyte levels ≥9*109/l, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate ≥12 mm/hour).
- Biochemical blood test (increased amount of C-reactive protein, decreased amount of albumin and globulin).
- Bacterioscopy of smears from the vagina and cervical canal (increased leukocyte levels, detection of pathogenic microflora, identification of the pathogen).
- Bacteriological study of discharge from the genital tract (detection and identification of the type of pathogen - bacteria, fungi of the genus Candida).
Instrumental research methods include:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy or puncture . These are minimally invasive surgical interventions that are performed under anesthesia using special instruments to examine the pelvic cavity. They use a video camera and instruments to collect material and send it for bacteriological examination. They assess the prevalence of the inflammatory process, identify pelvioperitonitis, the condition of the fallopian tubes, the presence of exudates of various types in the pelvic cavity, compaction and hyperemia of the uterine appendages, the presence of pus in their lumen, the formation of adhesions, and identification of perforations.
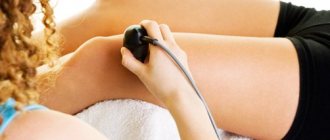
- Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to visualize the fallopian tubes (they are dilated, swollen, and can be obstructed), examine the pelvic cavity (identify purulent and purulent-suppurative exudate, determine the localization of formed abscesses and their structure).
- Computed tomography – visualization of the abdominal organs and identification of pathological inflammatory foci.
Chronic salpingoophoritis is difficult to diagnose. Symptoms of chronic adnexitis are characteristic not only of this disease. Pain in the lower abdomen occurs with endometritis, tumors, and pelvic neuralgia. Diagnosis consists of bimanual examination of the pelvic organs, ultrasound diagnostics and hysterosalpingography.
During a gynecological examination, the following is revealed:
- limited movement of the uterus due to many adhesions;
- the uterine appendages are elongated.
Hysterosalpingography visualizes adhesions in the appendages. Currently rarely used. Diagnostic laparoscopy is also performed for differential diagnosis.
Diet for adnexitis
Nutrition for adnexitis in women does not require particularly strict restrictions. During the acute phase of the disease and aggravated symptoms of chronic adnexitis, it is recommended to avoid heavy foods (fried foods, pickles, smoked meats). You should include in your diet foods rich in vitamin C (citrus fruits, black currants, bell peppers, parsley) and fiber (fresh vegetables and fruits, bran, cereals). Fluid consumption during salpingoophoritis should be at least 2.5 liters per day.
To normalize intestinal function during salpingoophoritis, it is recommended to consume low-fat fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, natural yogurt, ayran), and add a small amount of vegetable oil (olive, flaxseed or sunflower) to dishes. Vegetable and fruit juices will be useful.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of acute salpingoophoritis is carried out in a hospital setting. A gentle diet with easily digestible food and liquid (fruit drinks, teas) is prescribed. Create favorable conditions for the patient’s mental health. The diet excludes allergenic foods - eggs, chocolate, beets, sweets.
In the remission phase of chronic adnexitis, inpatient treatment is not carried out. For preventive purposes, various physiotherapy procedures are prescribed.
In the acute phase, inpatient drug treatment is recommended. After the process subsides, patients are discharged and continue outpatient treatment. Drug treatment
The main groups of drugs for the treatment of salpingoophoritis are:
- Antibacterial agents (aimed at destroying the pathogen).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (reduce the inflammatory process, have antipyretic and analgesic effects).
- Desensitizing drugs (suppress immune and allergic inflammation).
The choice of antibacterial agent depends on the pathogen. Until the results of bacteriological culture come back, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
Antibiotic table:
| 1. Penicillins – Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Oxacillin; |
| 2. Cephalosporins – Ceftriaxone, Cefepime; |
| 3. Fluoroquinolones – Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Avelox; |
| 4. Macrolides and azalides – Erythromycin, Azithromycin. |
Anti-inflammatory drugs include ibuprofen, analgin, and indomethacin. Desensitizing drugs include diphenhydramine, tavegil, suprastin.
Therapy
Treatment of acute salpingoophoritis or during exacerbations is carried out in a specialized hospital. Therapy includes the prescription of antibacterial drugs, which is carried out taking into account the sensitivity of the flora to them and the type of causative agent of the disease. Simultaneously with antibacterial therapy, detoxification therapy is prescribed, during which special anti-inflammatory suppositories are used, which reduce temperature, relieve inflammation and have an analgesic effect on the affected pelvic organs.
After the inflammatory process is relieved, the patient is prescribed absorbable medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. They will prevent the appearance of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, reducing the risk of infertility and ectopic pregnancy in the future.
If conservative treatment does not produce results, then surgery is indicated, usually laparoscopy. The scope of the operation is determined individually. If an abscess forms, the fallopian tube is removed as a source of infection. To restore the patency of the appendages, adhesions are cut and rough scars are removed.
Chronic salpingoophoritis during periods of exacerbation is treated similarly to acute. During the remission phase, the use of physiotherapy is indicated. The appropriateness of prescribing a particular technique is determined by the attending physician, depending on the severity of menstrual irregularities, the presence of adhesions, and the symptoms of the disease. Treatment includes techniques such as ultrasound, magnetic fields, pulsed currents, reflexology, mineral waters, mud in the form of applications, irrigations, baths. These procedures have a beneficial effect on general and local immunity, improve blood supply to the pelvic organs, enhance regenerative processes, and restore hormonal balance.
Patients with inflammation of the appendages are not recommended to visit hot countries with a humid climate; it is better to give preference to balneological hospitals and local sanatoriums. If the pathology causes infertility, an IVF procedure is indicated. This technique allows you to give birth to a child even for those women who have a history of hormonal or tubal infertility. Pregnancy after IVF usually proceeds normally. Hormonal support is rarely necessary to prevent spontaneous miscarriage.
Local treatment
Local treatment involves irrigation of the vagina through a tube with two lumens. It is necessary to purchase herbs at the pharmacy that have an anti-inflammatory effect (chamomile, eucalyptus, acacia flowers). You need to make a decoction of herbs: pour 200 g of herbs into 1 liter of water. Then heat 10 liters of water to 40 degrees. Mix all ingredients. The procedure is carried out every day for 7-14 days.
Irrigation cannot be carried out during the menstrual cycle, since the permeability of the cervix for microbial pathogens is increased.
During pregnancy, irrigation is not prohibited, but it must be justified for some significant reasons. If you irrigate without a doctor’s advice, you can infect the fetus, as a result of which its physical formation will be disrupted.
Important! During menopause, some solutions are prohibited. It is imperative to consult a gynecologist so that he can assess the condition of the uterine mucosa and choose a drug for irrigation.
Surgery
At the initial stages of salpingo-oophoritis, laporoscopy is performed for diagnostic purposes. Surgeons rinse the abdominal cavity with antiseptic and antibacterial agents.
With the progression of adnexitis and the formation of tubo-ovarian abscesses, an operation is performed under general anesthesia to remove the formed purulent cavities, lavage of the abdominal cavity and placement of drainage tubes to completely drain the accumulated pus.
Treatment methods for acute salpingoophoritis
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the appendages in women are closely interrelated, since medical tactics are determined by the course of adnexitis. In the acute stage, the woman is hospitalized. In the hospital, conditions are created for her that provide physical and mental peace. The disease is fought using the following methods:
- medicinal: the attending physician may prescribe antibacterial, painkillers, anti-inflammatory and desensitizing drugs;
- surgical intervention;
- physiotherapy.
In acute cases of adnexitis, physiotherapeutic procedures are prohibited. However, when the disease takes a subacute course, the doctor prescribes such treatment. For adnexitis, the following are widely used:
- ultrasound;
- electrophoresis with magnesium, zinc or potassium on the lower abdomen;
- vibration massage.
It is highly not recommended to use traditional medicine recipes as the main therapy. If the patient does not receive timely and adequate treatment, then acute salpingoophoritis turns into chronic inflammation. This course is characterized by periodically occurring exacerbations.
Drug therapy
Treatment of adnexitis with antibiotics and suppositories is directed against the causative agent of the infection; the dose of the drug should ensure the maximum concentration of the active component in the inflammatory focus. The following groups of antibiotics are used:
- penicillins;
- fluoroquinolones;
- macrolides;
- cephalosporins;
- tetracyclines;
- aminoglycosides;
- nitroimidazoles;
- lincosamides.
If the disease takes a severe course and threatens the development of septic complications, the specialist prescribes antibacterial drugs in various combinations.
| Group of medicines | Drugs used | Their action |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Diclofenac, Ketorol, Indomethacin | Have a quick analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect |
| Antimicrobials | Candles Terzhinan, Hexicon | Have antiseptic properties |
| Absorbable drugs | Lidaza, Magnesium Sulfate | They have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, analgesic properties |
| Immunomodulators | Timulin, Lykopid, Echinacea extract | Allows for enhanced immune response |
| Vitamins | Complivit Multitabs, capsules with vitamins A and E | Have strengthening properties |
| Infusion devices | Solutions of glucose, dextran, water-salt solutions | Eliminate intoxication manifestations of the disease |
Such drugs are considered auxiliary. They are part of complex therapy along with an antibiotic. Drug therapy is effective when prescribed in a timely manner.
Surgery
When the disease takes a purulent form, surgical treatment of the pathology is performed. Currently, gentle operations are used. They shorten the rehabilitation period and are less traumatic.
During laparoscopy, several punctures are made on the abdominal wall. Through them, instruments are brought to the pelvic organs. During the intervention, the surgeon removes the pus and irrigates the inflamed tissue with antiseptic and antibacterial agents.
A woman should take easily digestible food, consume an adequate amount of fluid in the form of alkaline drinks, fruit drinks, teas or water, and monitor the excretory function.
To evacuate the contents of the saccular tumor, a puncture of the vaginal vault is performed, after which antibiotics are administered locally. If the appendages have melted under the influence of pus and severe complications have developed, complete removal of these organs (adnexectomy) is indicated. This measure will save the woman’s life.
Gynecological massage
Gynecological massage is carried out for preventive purposes. It is carried out in the gynecologist's office, on a couch or in a gynecological chair. More often it is carried out by nurses and midwives, less often by doctors. The woman is seated in a gynecological chair. The nurse disinfects his hands, puts on gloves, and disinfects the patient's gloves and genital tract.
One hand is inserted into the vagina, and the second is placed in the abdominal area. The procedure begins with light massaging movements. After warming up, the nurse makes stretching, pressing and other types of movements. Patients may feel discomfort and pain. Duration of massage is from 4 to 15 minutes.
The positive effects of massage are the restoration and improvement of microcirculation of the vessels of the lower floor, the acceleration of metabolic processes and the prevention of gynecological diseases.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures are aimed at improving the general condition and increasing the effect of the therapy provided. Physiotherapy methods are selected individually for each patient.
Some of the significant methods are:
- Magnetotherapy involves the effect of magnetic fields on the human body, providing a metabolic and regenerating effect.
- Therapeutic gymnastics allows you to improve your condition, improve blood circulation and metabolism of the body.
- Electrophoresis carried out during remission of the disease. The method is based on the subcutaneous administration of drugs under the influence of an electric current. It has an anti-edematous effect.
- Water therapy. Water baths with herbal infusions have anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effects.
Prevention
Prevention of salpingoophoritis includes measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of an infectious process of any location, especially an infectious-inflammatory reaction in the genital tract. The normal immunological resistance of the body prevents an infectious agent from entering the body.
That is why all patients are recommended to improve their immune status. Proper sexual activity guarantees the absence of STDs, and annual preventive gynecological examinations make it possible to identify any pathology of the urogenital tract at the initial stage. Sanitation of foci of infection localized in other organs is also of practical importance. Particular attention is paid to preventing hematogenous spread due to pathology of the gums and teeth, urinary tract and lungs.
ethnoscience
In addition to drug and surgical treatment, a special role is given to traditional methods of medicine:
- Herbal infusions of plantain, flaxseeds, mint. Pour 300 ml of hot water in the same ratio of 5 g. It is necessary to insist for 1-2 hours. Afterwards, strain and mix with 20 g of honey. Divide the resulting liquid into 3 doses and take 3 times a day.
- Anise and honey. Mix 50 g of anise powder and 200 g of honey until smooth. Take 1 tsp daily. three times a day.
- Herbal collection from the boron uterus. It is necessary to pour sage, boron uterus and chamomile into 1 liter of hot water. Leave for 24 hours. Take 1 glass three times a day.
- Compresses with ichthyol ointment. It is necessary to form a tampon from a bandage, onto which to apply ichthyol ointment. You need to apply the tampon to the painful area of the abdomen. Then wrap the area with a scarf. Compresses are best done at night.
- Tampons with sea buckthorn oil. Apply sea buckthorn oil to a sterile tampon and insert the tampon into the vagina. It is recommended to carry out the procedure at night for 4-7 days.
Complications
If not diagnosed in a timely manner and treated adequately, this disease can lead to complications.
It can be:
- pelvioperitonitis;
- tubo-ovarian abscesses;
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- disturbance of the ovarian-menstrual cycle;
- decrease or disappearance of libido.
Symptoms that arise that are similar to the clinical picture of the pathology should force the woman to consult a gynecologist. Early treatment and confirmation of diagnosis allows you to prescribe effective treatment that will prevent the development of complications of salpingoophoritis and ensure the restoration of all impaired functions in the body.
Author of the article: olga6870 (Olga Morozova)
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Stages and types
Salpingo-oophoritis is a common inflammation that affects women of any age category, but the majority are young patients who are sexually active. Based on the nature of the clinical course, there are three stages of adnexitis :
- Acute, characterized by pronounced symptoms. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease takes on a more complex form.
- Subacute salpingoophoritis, occurring with vague symptoms. The process develops in the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Chronic, lasting over 2 months, accompanied by exacerbations and remissions. A dangerous condition that provokes serious disruptions in the functioning of the female reproductive system.
The duration and intensity of each stage of pathology depends on the individual characteristics of the organism and the presence of factors contributing to the growth of pathogenic flora. In addition, doctors classify the disease into types, depending on the location of the infection:
- right-sided - the focus of inflammation is concentrated on the right uterine appendages;
- left-sided - occurs when the left fallopian tube and ovary are affected;
- bilateral - observed when the appendages are infected on both sides of the uterus.
The most severe forms of the disease include chronic bilateral salpingoophoritis. Its specific symptom is considered to be enlarged fallopian tubes. The progression of this type of adnexitis greatly complicates the process of conceiving a child. Pregnancy can occur only after complete recovery, so it is recommended to immediately consult a gynecologist. Advanced cases of the disease are treated surgically.