Causes of arthrosis
Arthrosis develops due to metabolic disorders in the joint, which in turn leads to the fact that the cartilage begins to lose elasticity. This can be facilitated by the complete or partial loss of proteoglycans from the cartilage; this usually occurs due to rather deep cracks in the cartilage itself. Loss of proteoglycans can also occur for another reason: due to a failure in their production by joint cells.
According to experts, the reasons why articular cartilage may begin to deteriorate can be metabolic disorders, hormonal disorders, decreased blood flow to the joint, hereditary factors, old age, injuries, as well as diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and even psoriasis. And yet, the most common cause of arthrosis is abnormal load on the joints, while the cartilage cannot resist it.
In addition, the following reasons may affect the occurrence and development of arthrosis:
- Previous injuries. These can be dislocations, bruises, fractures, ligament ruptures and other injuries.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Excess body weight, leading to additional stress on the joints.
- The inflammatory process in the joints is acute purulent arthritis.
- Elderly age.
- Low quality food.
- Hypothermia.
- Autoimmune diseases - lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis.
- General intoxication of the body.
- Frequent colds.
- Specific inflammations - syphilis, tuberculosis, tick-borne encephalitis, gonorrhea.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Bleeding disorder (hemophilia).
- Perthes disease is a disorder of the blood supply to the head of the femur.
There are also several genetically determined causes leading to the development of arthrosis:
- If we consider arthrosis of the hand and fingers, then scientists have found that the so-called Bouchard and Heberden nodes, as a disease, can be inherited.
- Violation of the formation of joints and ligaments in the prenatal period, leading to dysplasia. Against this background, rapid wear of the joint occurs and arthrosis develops.
- Type 2 collagen mutations. When disturbances occur in the structure of the fibrillar protein located in the connective tissue, then rapid destruction of cartilage occurs.
Also at risk of getting a disease such as arthrosis in the near future are people whose professions include: bricklayer, miner, fisherman, blacksmith, metallurgist - and other areas of activity associated with increased physical labor.
Nutrition correction
It is extremely important to provide the tissues affected by arthrosis with the necessary substances that the body receives from food.
Collagen
A special protein, the main material from which cartilage tissue is built. A young body independently produces this substance, but with age this function fades, so you have to turn to external sources for help. One of them is jellied meat, but this dish cannot be consumed without restrictions: due to its high cholesterol content and calorie content, it can be eaten no more than once a week.
Symptoms of arthrosis
A symptom of arthrosis is pain when the joint is loaded, which subsides when the joint is at rest; decreased joint mobility, crunching, feeling of muscle tension in the joint area. Periodically, a joint affected by arthrosis may swell and become deformed over time.
Consider the following 4 large groups of symptoms of arthrosis:
- Pain. The presence of pain is the first sign of joint arthrosis. It can be assumed that with any damage, similar sensations arise, but with arthrosis, the pain has some features. Firstly, this is the occurrence of sharp pain or significant discomfort during movements. It will be localized in the place where the diseased joint is located. When a person stops moving and goes into a state of rest, the pain goes away.
At night, a person experiences virtually no unpleasant sensations, except when turning the body over, having found the optimal position, the patient calmly falls asleep. Pain appears during rest only at the stage of progression of the disease; it has some similarities with dental lumbago, when a person cannot fall asleep. They appear closer to the morning - around 5 o'clock.
So, at the beginning there is practically no pain, it can only be felt during load or palpation, over time the person’s suffering intensifies, and the joint requires more and more periods of rest. Then life completely turns into torture - the hyaline cartilage becomes thinner, the bone is exposed, and osteophytes begin to grow. Acute pain torments almost constantly, intensifying even more in bad weather and the full moon.
- Crunch. An equally indicative symptom of arthrosis is the presence of a crunching sound. It becomes audible due to the fact that the softness of rotation of the bones in the joint is reduced, they rub against each other, as a result of which a characteristic sound arises. Crunching can be heard in other diseases, and even when the joints are healthy. But it is the arthrosis crunch that is distinguished by its “dry” sound. The more the disease progresses, the brighter the sound becomes. Moreover, if a crunch is heard, pain will also be felt. This is what makes it possible to distinguish the sound made by joints with arthrosis from the usual harmless clicking.
- Decreased joint mobility is another characteristic symptom of arthrosis. At the initial stage, this phenomenon does not bother the patient, but with the progression of arthrosis, the germination of bone tumors leads to the fact that the muscles spasm, and the joint space almost completely disappears. This is the cause of immobility of the limbs at the site of the lesion.
- Joint deformity. Its modification is caused by the fact that osteophytes grow on the surface of the bones and synovial fluid arrives. Although deformation is one of the most recent symptoms, when arthrosis has already affected the joint to a significant extent.
The course of the disease is characterized by stages of exacerbation and stages of remission. This significantly complicates self-diagnosis of arthrosis, relying only on one’s own sensations. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor for clarification of the diagnosis.
When conducting an x-ray examination, he will be able to detect the following signs that allow him to determine the degree of progression of the disease:
- Stage 1 is characterized by the absence of osteophytes, the joint space may be somewhat narrowed.
- At stage 2, there is a suspicion of slight narrowing of the gap; osteophytes have already formed.
- At stage 3, the narrowing of the gap is clearly visible, there are multiple osteophytes, and the joint begins to deform.
- Stage 4 is characterized by an almost complete absence of joint space, multiple osteophytes, and significant deformation.
Degrees of arthrosis
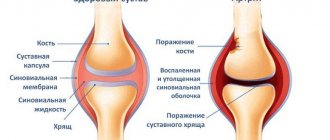
Arthrosis is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joints, which will haunt a person in the form of a chronic disease. The result of such destruction is damage to the cartilage of the joint, pathological changes in its capsule and synovial membrane, in ligaments and bone structures.
It is customary to distinguish between three degrees of arthrosis, which characterize different severity of the disease and have different symptoms.
1st degree of arthrosis
During the first stage of arthrosis development, serious changes in the morphology of the joint are not observed. Only the composition of the synovial fluid itself is disrupted. It supplies the joint tissue with nutrients less well, so the cartilage loses its former resistance to its usual loads. This leads to the cartilage tissue becoming inflamed and the person experiencing pain.
The patient may complain of slight stiffness in the joints, but most often he does not pay any attention to this feeling, attributing such health problems to weather changes, uncomfortable posture, etc.
Sometimes a faint crunching sound may be heard in the area of the affected joint. The pain manifests itself as slight tingling or may be aching. If the disease is diagnosed at this stage, then it will be possible to cope with it using conservative methods.
2nd degree arthrosis
The second stage of arthrosis is accompanied by the destruction of cartilage tissue. Bone growths appear along the edges of the joint. The more intense the load, the more the cartilage tissue of the joint will be destroyed.
A person experiences constant pain to which he gets used. The inflammation either subsides or worsens again.
The muscles surrounding the joints will lose their former functions, but most often such disorders are weak or moderate. Therefore, at this stage, a person may refuse to visit a doctor.
After a short period of strain on the legs, a person may experience fatigue. In this case, the aching pain in the joints becomes acute. The crunching noise increases during movement, which is explained by bone growths.
It is at the second stage of development of arthrosis that the deforming process begins in the joints, so you must definitely seek medical help.
3rd degree arthrosis
The third degree of arthrosis is the most severe. The articular cartilage of the affected joint is not only thinned, but has also begun to deteriorate, and the pathological lesions are already quite large. The joint is severely deformed, which affects the normal axis of the limb.
The ligaments that previously surrounded the joint lose their functional activity and become short, which affects the mobility of the arm or leg.
During this period, a person experiences contractures and subluxations. The muscles surrounding the joint are shortened and stretched, and they have difficulty contracting. The joint itself and nearby tissues suffer from insufficient nutrition.
A person suffers from severe pain, it is sharp and sharp. Even at rest, the patient experiences significant discomfort. The third degree of arthrosis is associated with the risk of complete loss of a person’s legal capacity.
Prevention
If you constantly perform certain actions and follow the recommendations, you can reduce the likelihood of developing arthrosis of the knee and hip joint.
- Excess weight plays a major role in the development of the disease, which creates excess stress on the surface of the knee and hip joint. For this reason, if you are overweight, it is worth normalizing it.
- Constantly on the move. A person should walk up to 7 km per day.
- Nutrition should be balanced and correct. The body should receive a sufficient amount of proteins, calcium, healthy fats, which are found in fish, lean meats, fermented milk products, and gelatin-based dishes.
Types of arthrosis
Depending on the cause of arthrosis, a disease with an unknown etiology is distinguished, that is, idiopathic arthrosis. It is most often diagnosed in people over 40 years of age. Secondary arthrosis is also distinguished, which occurs against the background of obvious causes (after an injury, inflammation of the joints, endocrine diseases, etc.).
In addition to the fact that arthrosis is classified depending on the cause of its occurrence, the following types of disease are distinguished:
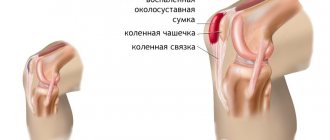
- Knee arthrosis or gonarthrosis. This is the most common type of disease. In this case, it is the knee joints that suffer. The pathology is most often diagnosed in people with excess body weight, against the background of metabolic disorders in the body, as well as due to stress. The disease develops over many years; at its later stage, the knee completely loses its mobility.
- Ankle arthrosis. This type of disease affects the ankle joint. The disease develops against the background of injuries, sprains, due to existing dysplasia, gout, and diabetes. Sometimes the cause of the pathology is rheumatoid arthritis. Most often, ankle arthrosis is diagnosed in people whose work involves excessive stress on this area: dancers, athletes, women who wear high-heeled shoes.
- Shoulder arthrosis. The main cause of the pathology is considered to be congenital defects of the shoulder joint, or excessive loads on it. The risk group includes painters, plasterers and people who do heavy manual labor. This also includes arthrosis of the elbow joint.
- Arthrosis of the hip joint or coxarthrosis. This is one of the severe types of pathology. The main reason is considered to be age-related changes in joint tissues. The risk group includes people over 40 years of age.
- Cervical arthrosis or uncoarthrosis. Reasons that can lead to the development of this pathology: insufficient mobility of the cervical spine, obesity and previous injuries. The risk group includes people who are engaged in sedentary work. In addition to the main symptoms of arthrosis in the form of pain and limited joint mobility, patients experience dizziness, headaches, and sometimes even loss of consciousness. This is due to the involvement of the vertebral artery, which supplies the brain, in the pathological process.
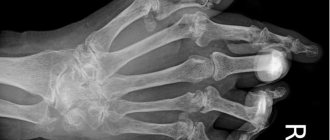
- Osteoarthritis of the hands and fingers. In this case, the wrist joint, interphalangeal joints, etc. are damaged. Most often, women who have entered menopause suffer from the pathology.
- Spondyloarthrosis, which affects the joints and cartilage of the spine. The disease most often develops in people over 65 years of age. Women suffer predominantly from spondyloarthrosis, which is explained by a decrease in estrogen levels after menopause. Spondyloarthrosis can be ankylosing, deforming, facet, polysegmental and degenerative.
- Polyosteoarthrosis or Kellgren's disease. This is a degenerative disease that affects peripheral joints, ligaments and tendons. The pathology may involve the joints of the spine with the development of discopathy.
Complications of arthrosis
If arthrosis is not given due attention and is not treated promptly and correctly, this can lead not only to the complete destruction of the diseased joint, but also to a change in the biomechanics of the spine, which can cause herniations in the intervertebral discs and the development of arthrosis in other, still healthy joints. . It is better to avoid complications of joint arthrosis.
The following pathologies are identified as the main complications of arthrosis:
- Joint destruction.
- Joint deformity.
- Inability to carry out movements.
- Disability of the patient.
- Violation of the biomechanics of the spine and other joints.
- Herniated intervertebral discs.
- Decrease in the patient's standard of living.
Drawing conclusions
It is difficult to diagnose stage 1 arthrosis due to the lack of pronounced symptoms. However, this is possible if you pay attention to your feelings and do not ignore even minor inconveniences. Early detection of the disease is extremely important for successful and effective treatment; the disease at this stage is quite easy to control. Compliance with the simplest rules - healthy eating and limiting exercise - allows patients to ensure a high quality of life.
Author of the article: Nivelichuk Taras, head of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, work experience 8 years. Higher education in the specialty “General Medicine”.
Diagnosis of arthrosis
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must interview and examine the patient. He will then order x-rays of the affected joints.
X-ray images are most often taken in 2 projections. The study makes it possible to visualize degenerative changes in tissues, damage to cartilage and adjacent bones. The joint space in patients with arthrosis narrows, the bone area is deformed, and bone growths and osteophytes can arise from it. Sometimes the joint itself becomes unstable, leading to subluxations.
The first sign of arthrosis, which can be visualized on an x-ray, is the presence of osteophytes. At first, the edges of the articular surface simply become sharp. Subsequently, they thicken, and then outgrowths and spines appear on them. The joint space becomes narrower as the pathology progresses.
Depending on the obtained x-ray picture, the doctor can make the following diagnosis (the Kellgren-Lawrence classification is taken as the basis):
- Arthrosis is doubtful. It is not possible to determine the degree of narrowing of the joint space, but small osteophytes are visible.
- Soft arthrosis, in which osteophytes are well visualized, but doubts remain about the narrowing of the joint space.
- Moderate arthrosis is diagnosed when the joint space is clearly narrowed and osteophytes are clearly visible. Sometimes bone deformities are found.
- Severe arthrosis is accompanied by significant narrowing of the joint space and the formation of large osteophytes. The joint will be deformed.
If the doctor needs more information about the condition of the joint, he may refer the patient to undergo a CT scan, arthroscopy or MRI. To assess the quality of synovial fluid, joint puncture is performed.
Treatment methods
It is better to treat diseased joints at an early stage; the treatment itself should be pathogenetic and comprehensive. The essence of treatment is to remove the causes that contribute to the development of this disease; it is also necessary to eliminate inflammatory changes and restore functions that were previously lost.
Complex treatment of arthrosis includes medications that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, and physiotherapeutic procedures that have an analgesic effect on the joints should also be performed. If the treatment is carried out at a sanatorium, it consists of climatic conditions that have a beneficial effect on the joints, as well as the use of mineral waters and mud.
The treatment of arthrosis is based on several basic principles:
- Damaged joints should be relieved of excessive stress. If possible, during treatment it should be kept to a minimum.
- Following the established orthopedic regimen.
- Physical therapy classes.
- Completion of a course of physical therapy, which includes magnetic and electrotherapy, shock wave, and laser therapy.
- Sanatorium treatment. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment at specialized resorts once a year, on the recommendation of a doctor.
- Saturation of the joint with oxygen, or so-called intra-articular oxygen therapy.
- Drug therapy.
- Intraosseous blockades, as well as decompression of the metaepiphysis.
- A rational approach to nutrition.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
You can cope with arthrosis using physiotherapeutic methods of treatment.
These include:
- UVT.
Shock wave therapy makes it possible to get rid of osteophytes, which are bone spurs. They are the main cause of pain. The waves soften these growths and after some time they resolve. At the same time, joint nutrition improves and metabolic processes are normalized. This procedure is effective only in the early stages of the disease. In addition, only a doctor can prescribe it, since it has many contraindications.
- Myostimulation.
The method is based on muscle stimulation with electrical impulses. The procedure is indicated for the treatment of bedridden patients who are forced to adhere to bed rest after suffering an injury. This method is not very often prescribed for arthrosis, although it allows you to normalize blood flow in the problem area and increase muscle tone, which makes it possible to speed up the recovery time of the joints.
- Phonophoresis.
With this method of treatment, the joint is exposed to ultrasonic waves and medications. The effect of medications is increased, since they will be delivered “exactly to the destination”, and the cells will absorb them better.
- Ozone therapy.
This method involves injecting a gas mixture into the joint. The patient’s pain disappears, inflammation decreases, joint mobility normalizes, and blood circulation improves. Treatment is carried out in courses. Their duration depends on the severity of the pathology.
Other treatment methods include:
- Physical therapy complexes are one of the effective methods of combating arthrosis. Performing exercises allows you to normalize blood flow in the problem area, as well as make the muscles stronger. You need to start practicing with simple exercises, gradually increasing the load.
- Manual therapy and massage, namely lymphatic drainage, are aimed at reducing pain and improving blood supply and nutrition to the sore joint. These treatments can be implemented even when the patient is immobilized.
- Mechanotherapy can complement physical therapy complexes, increasing their effectiveness. Simulators are used for this purpose. They make it possible to increase the load during training, but the joint will not be damaged. Mechanotherapy allows you to increase blood circulation in the joint and increase muscle tone.
- Using special devices, you can practice joint traction. The procedure takes 20 minutes. At the same time, the load is removed from the diseased area, which helps slow down the progression of the pathology. To feel the desired effect, you need to undergo 10-12 procedures, which are performed once every 6 months.
- To prevent the disease from progressing, you must adhere to a diet. This is an auxiliary measure that allows you to increase the efficiency of other procedures.
- In general, patients are advised to change their lifestyle. It is important to choose the right shoes from an orthopedic point of view and sleep on an orthopedic mattress. It is necessary to give up bad habits. The load on the joints must be adequate. Sometimes patients are advised to wear an orthosis. You can increase the effectiveness of treatment if you regularly visit the pool.
Surgical treatments
When it is not possible to cope with the disease using conservative methods, the patient is referred for surgery.
Methods of surgical intervention include:
- Performing a puncture.
This is not only a therapeutic, but also a diagnostic method. During this procedure, a needle is inserted into the joint, removing a small amount of fluid. Subsequently, it is sent for analysis. This method allows you to relieve stress from the joint and also deliver medications, such as corticosteroids, into it.
- Arthroscopy.
In this case, an arthroscope is inserted into the joint, for which several small incisions are made in the skin. This procedure makes it possible to assess the condition of the joint from the inside. During arthroscopy, the doctor can remove unnecessary cartilage, thereby relieving the person of pain.
- Periarticular osteotomy.
The operation boils down to the fact that the bones of the joint are filed and fixed in the desired position. This allows you to reduce the load on the affected area, as well as relieve the person from pain. Although the procedure is quite effective, it is rarely used, since it is performed under anesthesia and requires a long recovery period.
- Replacing your own joint with a prosthesis.
Endoprosthesis replacement is used when the joint is severely deformed and cannot be restored. This is a complex operation that costs a lot of money. The prosthesis itself is made from materials such as metal, ceramics, and plastic. After the intervention, the person recovers for a long time and may suffer from pain. Although it is often impossible to help patients with other methods, otherwise the person can be completely immobilized. A high-quality prosthesis can last for 20 years. All this time the person will not experience any problems with movement.
Differences in treatment depending on the type of arthrosis
Treatment for arthrosis varies depending on its type. Although different types of arthrosis have similar symptoms, the methods for eliminating them vary. For example, applying medicinal ointments to the skin for arthrosis of the hip joint does not make sense, since the fat layer will not allow the medicinal substance to reach its destination. While for arthrosis of the knee or elbow joint, doctors recommend using local remedies.
- Arthrosis of the hands and fingers.
To reduce pain, drugs from the NSAID group and corticosteroids are prescribed. These medications help reduce inflammation. To stop the process of destruction of cartilage tissue, patients are advised to massage, stretch their fingers and take chondroprotectors.
- Arthrosis of the shoulder joint.
Therapy comes down to massage and exercise therapy. To reduce pain, intra-articular injections and antispasmodics are prescribed.
- Arthrosis of the elbow joint.
The patient is prescribed methods of physiotherapeutic treatment, application of compresses with ointments from the NSAID group.
- Arthrosis of the hip joint.
To reduce pain, the patient is prescribed injections, taking tablets and capsules, as well as applying compresses based on anti-inflammatory solutions.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint.
UVT gives a good effect; you can stretch the joint and do exercise therapy. Patients are advised to apply NSAIDs in the form of ointments and creams to the affected area.
- Arthrosis of the ankle joint.
Patients with arthrosis of the ankle joint are prescribed bed rest, medicinal baths, and visits to the office of a massage therapist and physiotherapist.
Video: treatment of joints quickly and reliably, forever. Recipes and methods from Frolov Yu.A.:
Drug treatment
Let's take a closer look at drug treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. By starting comprehensive therapy for arthrosis, you can slow down the course of the disease and significantly improve your quality of life. It is worthwhile to dwell in more detail on some points of treatment. In particular, drug therapy includes, at the initial stage, pain relief, as well as the elimination of inflammatory processes occurring in the joints. For this, all doctors use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Experienced doctors do not recommend their oral use, since these drugs significantly irritate the walls of the stomach. Therefore, depending on the drug chosen, either intravenous or intramuscular administration is used. Sometimes NVSP is used as an auxiliary agent in the form of ointments, but their absorption is extremely low, so a significant effect cannot be achieved.
- Hormonal corticosteroids. When arthrosis is at the acute stage, it is advisable to take hormonal corticosteroids. They are injected into the joint, using drugs such as hydrocortisone or diprospan. Externally, you can use a special patch, ointment or tincture, which are made from hot pepper.
- Chondroprotectors aimed at restoring cartilage and improving the qualitative composition of synovial fluid will also not be superfluous. The most common agents in this group are glucosamine or chondroitin sulfate. The course lasts for quite a long period of time until improvement occurs. However, if the expected effect does not appear within six months of use, the drugs should be discontinued. Also, intra-articularly, along with chondroprotectors, it is advisable to use drugs made on the basis of hyaluronic acid. They contribute to the formation of the membrane of cells responsible for the formation of joint cartilage. What chondroprotectors are best for arthrosis?
- Diacerein. The treatment regimen can be supplemented by taking diacerein, which promotes the regeneration of cartilage tissue. But you should not expect an immediate effect; as a rule, improvements occur two weeks or even a month after the first dose.
If the case is particularly severe, then narcotic analgesics may be prescribed. But they are used extremely rarely, when other means have not brought the desired effect.
Preventive measures
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Following simple rules and regular examination will help reduce the chance of developing various types of arthrosis.
It is recommended to avoid excessive stress, but do not forget about preventative warm-ups. It is better to choose gentle sports as a sport. Walking, swimming, and light jogging are ideal. It is worth giving up bad habits and leading a healthy lifestyle. If you are overweight, adjust your diet and introduce foods rich in vitamins and minerals into your diet. If you have problems with the endocrine system, do not neglect treatment, but visit an endocrinologist.