Bursitis of the knee joint is an acute, subacute or chronic inflammation of one of the bursae (joint capsule) located in the knee area. It can be aseptic (non-infectious) and infectious, i.e. caused by pathogenic microflora.
Bursitis of the knee joint - inflammation of the joint capsule
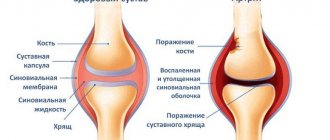
The bursa, or periarticular bursa, is a small sac located between tendons, muscles, and protruding areas of bones. The cells of the inner lining of the bursa synthesize fluid that facilitates the sliding of anatomical structures. In fact, the bursa is a kind of shock absorber that helps protect the tendons from significant friction or pressure. The amount of fluid in the bursa cavity is normally small, but with the development of the inflammatory process, the cells begin to synthesize fluid in a larger volume, which leads to an increase in the bursa cavity and clinically manifests itself as a tumor-like formation. There are about ten bursae in the knee joint, but in clinical practice inflammation of the anserine, infrapatellar and prepatellar bursae is most often observed.
Most often, bursitis of the knee joint is observed in people whose professional activities involve increased stress on the lower limbs, for example, roofers and athletes. In men, this pathology is diagnosed several times more often than in women.
Bursitis: what is it?
Bursitis is an inflammation of the synovial bursae (they are called bursae - small cavity formations) located in the joint area, which is accompanied by the accumulation of inflammatory fluid in them.
As a result, a swelling occurs, the size of which in some cases reaches ten centimeters. To the touch, the joint capsule is quite dense, sometimes touching causes pain, but it is worth noting that the functionality of the joint itself is not limited.
Bursitis most often occurs in the shoulder, elbow, or knee in men under 35, especially athletes. The hip, wrist, or ankle may also be affected. This is usually an occupational disease, but it also occurs in people who are overweight or wear ill-fitting shoes.
Usually the disease lasts 1-2 weeks and does not pose a threat to the patient’s life. But secondary trauma can cause the development of chronic bursitis, the treatment of which is very difficult.
In addition to the fact that the patient experiences persistent pain, he is also limited in movement, as the mobility of the joint is impaired. The risk group for bursitis includes athletes (skiers, golfers, tennis players), and people whose profession involves heavy physical labor (builders, miners, loaders).
What is a bursa?
The name of the bursa comes from the Latin word bursa, which translates as “bag”, “purse”. It is a flattened cavity containing fluid (it is produced by cells lining the inside wall of the synovial bursa).
The function of the bursa is to soften the mechanical impact on the joint elements, resulting in better mobility, as well as protection of the joints from adverse factors. The bursa can be articular or periarticular.
Consequences
The most severe consequences can be caused by post-traumatic purulent bursitis. In case of delay or unsuccessful treatment, it can provoke phlegnomas (spread of pus into the tissues surrounding the joint), sepsis, lymphadenitis (accumulation of pus and subsequent inflammation of the lymph nodes), arthritis (changes in the structure of the joint), calcification and loss of joint mobility. The most severe consequence may be tissue necrosis.
It is critically important not to miss bursitis in a child and to immediately consult a doctor, since in children under 14 years of age, the bones are not fully formed and are not strong enough, and any inflammation can have a detrimental effect on the structure of the skeleton and the motor functions of the joints in the future.
Traumatic bursitis is included in the International Classification of Diseases, as it is widespread among joint diseases and requires medical care at any stage. Do not develop joint diseases, because joints are the basis of movement, and movement is life.
Classification
In traumatology and surgery, there are several classifications of bursitis:
- Taking into account the location (elbow, knee, shoulder joint, etc.) and the name of the affected bursa.
- Taking into account the clinical course: acute, subacute and chronic bursitis.
- Taking into account the pathogen: specific (bursitis with syphilis, tuberculosis, brucellosis, gonorrhea) and nonspecific bursitis.
- Taking into account the nature of the exudate: serous (plasma mixed with a small amount of blood cells), purulent (microorganisms, destroyed cells, disintegrated leukocytes), hemorrhagic (liquid with a large number of red blood cells) and fibrinous (high fibrin content) bursitis.
In addition, in clinical practice, aseptic (uninfected) and infected bursitis are often distinguished.
Causes
The cause of bursitis is usually an injury, bruise or abrasion, that is, infection through the blood or damage to the affected area. It is also possible for pus to enter from erysipelas, this happens with osteomyelitis, bedsores, boils, and carbuncles. Infection occurs through abrasions or severe bruises. The chronic manifestation of this disease occurs due to constant irritation of the source of inflammation.
Causes of joint bursitis:
- General weakening of the immune system and a decrease in the body’s protective properties due to various infectious diseases, neoplasms, AIDS, malignant neoplasms, liver cirrhosis, alcoholism and drug addiction, etc.
- Penetration of various pathogens into open wound surfaces during injuries and cuts.
- Excessive stress associated with professional activities or overexertion during sports.
- Deposition of salts in the synovial bursa. The likelihood of the disease increases with age.
- Obesity.
To summarize all of the above, the main causes of bursitis: in most cases, these are various injuries (chronic microtraumas, bruises, etc.), a little less often, these are metabolic disorders, infections, intoxications, autoimmune processes and allergic reactions
Surgical intervention
Bursitis of the knee joint, the treatment of which has had no effect, may require surgical intervention in the form of aspiration (suction) of the contents of the joint capsule and the injection of corticosteroids into it.
This procedure is performed using a thin needle under local anesthesia. After draining the joint capsule, the doctor may inject hormonal drugs into it - corticosteroids. This is necessary in order to stop the inflammatory process. Then it is necessary to continue wearing the elastic bandage and ensure long-term rest of the limb (usually 48 hours). This treatment is much more effective than treatment with medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), since tablet forms have a general effect on the body, often without penetrating into the joints.
In rare cases, treatment is ineffective, and the only option is surgical removal of the prepatellar joint capsule. Restoration of normal joint functions after such an operation occurs within a few days, and a return to a full life without restriction of physical activity can be achieved in 2-3 weeks.
Symptoms of bursitis + photos
Symptoms of bursitis include the definition of a rounded, limited, painful swelling, elastic consistency, fluctuating, at the site of the anatomical location of the bursa. This swelling can be about eight or ten centimeters in diameter.
Other symptoms of bursitis:
- Pain that is aching, shooting, sometimes strong and pulsating, intensifying at night, with irradiation (recoil) to the arm or leg, depending on the location of the pathological process;
- Edema, the development of which is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space;
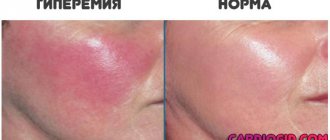
- Redness of the inflamed and swollen area (hyperemia);
- Limitation in the movement of the inflamed area, joint, which occurs as a result of the deposition of salts in the inflamed bursa;
- Increased or high body temperature, up to 40 ° C;
- General malaise, feeling of weakness and powerlessness;
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes located at the site of development of bursitis;
- Nausea.
| Features of the flow | Acute bursitis | Purulent | Chronic |
| Pain | Moderate | Strong | Minor |
| Swelling and swelling | Corresponds to the location of the bag | Pronounced over the entire joint area | Clearly limited in the form of a tumor |
| Skin redness | Minor | Strong | Absent |
| Limited mobility | Moderate | Expressed | Absent |
| Temperature increase | Minor (up to 38 degrees) | Strong (up to 39 degrees or more) | Not typical |
| Consequences and prognosis | Full recovery or transition to a chronic form | Recovery or occurrence of purulent complications (phlegmon, osteomyelitis) | Formation of a tumor-like formation without disturbance of movements |
Physiotherapy
The choice of physiotherapy method depends on the stage of the disease, bursitis of the knee joint.
During exacerbation of the chronic form or in the first 5–7 days of acute bursitis, the bursae contain a large amount of exudate. Therefore, treatment is aimed at relieving pain, reducing inflammation, increasing the number of enzymes and the number of cells that destroy microorganisms and inflammatory substances.
In the future, the disease can be treated with reparative-regenerative, vasodilating and fibromodulating methods (more details below). They completely eliminate exudate and improve tissue trophism.
Physiotherapy methods in the table:
| Physiotherapy method | Action provided |
| Electrophoresis of glucocorticosteroids, UHF therapy, microwave therapy | Anti-inflammatory |
| Electrophoresis of vitamins and metabolites, magnetic therapy, peloid therapy | Reparative-regenerative (stimulating tissue healing and restoring their functions) |
| Electrophoresis of vasodilators, paraffin therapy, ozokerite therapy | Vasodilator |
| Electrophoresis of analgesic drugs | Analgesic |
| Diadynamic therapy | Myostimulating (restoring the functions of muscle tissue) |
| Ultrasound therapy, ultraphonophoresis of fibromodulating drugs | Fibromodeling (restores the fibrous structure of connective tissue) |
Treatment of bursitis of the knee joint can take a long time (up to 2-3 months), which can be spent on an active full life. Therefore, pay attention to the most minor symptoms.
Complications
Complications that arise from untimely treatment:
- Purulent arthritis involving the knee meniscus and knee ligaments.
- Osteomyelitis of the tibia, fibula or femur.
- Fistulas of periarticular localization.
- Adhesive capsulitis. Inflammation of the entire shoulder capsule with the formation of adhesions and scars.
- Hygroma. With a protracted process, an isolated cystic cavity filled with fluid may form.
- Sepsis. With reduced immunity, purulent contents are carried through the bloodstream throughout the body, causing a severe general reaction.
- Necrosis. Death of the tissue of the bursa wall occurs in a number of cases and is an absolute indication for surgical intervention.
Exercises
Special exercises play an important role in the treatment process:
- Static contractions of the inner head of the quadriceps muscle
Tighten your quadriceps muscle by placing a towel roll under your knee joint and trying to straighten your leg. Place your palm on the inside of your thigh to feel the muscle tension as it contracts. Next, fix your leg in this position for 5 seconds, then relax. The exercise should be repeated 10 times, straining the leg as much as possible, but without causing pain.
- Flexion and extension of the leg at the knee
Without causing pain, it is necessary to bend and straighten the leg at the knee with the maximum range of motion. The exercise should be repeated 10-20 times, if during the execution there is no increase in the symptoms of the disease.
Crossing legs, repeated bending of the knee joints, squats and other similar exercises should be excluded from the training program.
Diagnostics
Simple tests help diagnose bursitis:
- The doctor asks the patient to try to place his hand behind his head as when combing his hair.
- The patient should squat for a while.
If pain and limited movement are detected, the likelihood of illness increases. The farther the inflamed bursa is located from the surface of the body, the more difficult it is for a specialist to make a diagnosis. But no matter how deep the focus is hidden, when pressure is applied the patient will definitely feel pain.
Initially, the doctor interviews the patient and palpates the affected joint. Bursitis can be diagnosed using the following examination methods:
- radiography;
- arthrography;
- bursography;
- puncturing the joint and taking a biopsy, in this way the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibacterial drugs can be established;
- ultrasound examination;
- MRI.
Diagnostic methods used to make an accurate diagnosis
In case of traumatic bursitis, the victim is referred to a traumatologist. The doctor collects the medical history of the patient and his family; this disease has a genetic predisposition. To make a diagnosis, you will need to conduct some instrumental examinations. As a result of a fall, bruise or traffic accident, the patient may have a crack or hidden fracture. It is important to examine the limb well enough. Doctors use the following imaging methods:
- examination of the affected joint using an ultrasound machine;
- X-ray examination method;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
After analyzing the victim’s medical history and the images obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Treatment of bursitis
Regardless of the location of the pain, the main components of the fight against the disease are rest and immobility of the joint. How to treat bursitis depends on the type of inflammation, but in any case it will be complex therapy. What does it include:
- Drug treatment.
- Massage.
- Physiotherapy.
Recommendations:
- The most important criterion in the course of treatment is the rest of the joint.
- The patient should remain in bed to reduce pain in the joint, while preventing the spread of the inflammatory process.
- The doctor may place a cast on the affected joint to prevent the patient from causing any movement in it.
- Bursitis can be treated both in the hospital and at home.
As a rule, treatment of acute bursitis is carried out on an outpatient basis. During the first five to seven days, complete rest is recommended, during which a plaster cast is applied and treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed. Treatment with rest should not last more than ten days.
With chronic bursitis, various complications develop. Treatment for such forms of the disease is only surgical. In the first case, a bursectomy operation is performed (surgical removal of a pathologically altered synovial bursa). If there were no infectious contents inside, the postoperative wound will heal in 7-10 days. If a fistula is present, complete surgical excision is performed with further treatment of the purulent wound.
Medicines for bursitis
Medicines can be used both for oral administration or injections, and for local therapy (ointments, gels, compresses). As a rule, drugs from the group of analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They suppress the inflammatory process, help reduce or completely disappear the main signs of bursitis (pain, swelling, fever).
In addition to general medications, orthopedic doctors always prescribe local remedies to patients with bursitis, such as ointment, warm compress, and the like.
Local treatments for bursitis include:
- "Solcoseryl";
- "Levomekol" (has a resolving effect and promotes rapid subsidence of residual effects of inflammation);
- "Dimexide" for the treatment of bursitis (used in the form of compresses);
- ointments based on chondroitin sulfate (Teraflex ointment, as clinical studies have shown, has a positive effect after the first month of use);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments;
- homeopathic and herbal ointments.
Physiotherapy
Treatment for bursitis may also include the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- UVT – acoustic wave treatment;
- Inductothermy (use of a magnetic field);
- Electrophoresis (administration of medication using current);
- Paraffin-ozokerite applications.
All these actions are aimed at activating the body's metabolic processes. They are prescribed strictly individually, in accordance with the symptoms of the disease.
Massage and therapeutic exercises
When bursitis goes into remission, doctors advise using therapeutic exercises and manual massage. You can also massage the damaged area yourself, but remember that this must be done carefully - an incorrect massage can only worsen the patient’s condition. Massage the inflamed area at night using plant oils - eucalyptus, petroleum jelly and lavender.
Therapeutic exercises are especially important for bursitis. It helps improve blood flow and, as a result, tissue nutrition, and restore motor function of the joint. Exercises are selected individually, taking into account the patient’s age and type of bursitis. As a rule, the initial exercises are very simple - just swing your arm back and forth.
The entire treatment period for bursitis takes on average from 1–2 to 4–5 weeks. The prognosis is almost always favorable. Relapses of the disease with timely and complete treatment (including surgery) occur in 2–3% of cases.
Conservative treatment of pathology
Conservative treatment consists of the use of painkillers. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are most often prescribed. Medicines relieve pain in a short time, stop inflammation, if present, and also remove swelling from surrounding tissues. For traumatic bursitis, local treatment is recommended. Therapy with drugs for external use relieves pain a little more slowly; ointments should be used 2-3 times a day or as needed when severe pain begins.
Folk remedies for bursitis
All traditional methods of treating bursitis should be used after the permission of your doctor.
- Kalanchoe. Take 3 large Kalanchoe leaves, wash them and put them in the refrigerator overnight. In the morning, make a paste out of them and apply it as a compress to the inflamed area.
- Apple vinegar. A drink based on water (200 ml), 15 ml of natural vinegar and a tablespoon of bee honey is taken twice a day on an empty stomach. Course - 2 weeks.
- Celery for bursitis. Tea made from celery seeds increases the body's resistance and helps fight inflammatory processes in any tissue, including joints. A tablespoon of dry celery seeds is poured into ¼ liter of boiling water, covered, left for 2 hours, filtered and drunk 100 ml twice a day. The course of treatment is 15 days.
- Cabbage leaves, or more precisely, compresses made from them, have an excellent anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Preparing such an application is very simple: you need to take a clean cabbage leaf, remove all the rough veins from it with a knife and lightly beat it with a wooden mallet until the juice appears.
- For bursitis, compresses are also made using propolis. To do this, pour propolis (10 g) with vodka (100 g) and leave to infuse in a dark place for 5 days. Apply a compress to the swollen joint until it goes away.
- The main component of the following compress is castor oil, which is recommended to be used directly on the affected area. A white cotton cloth should be soaked in castor oil and squeeze out excess. Wrap the affected area, cover it with a thick cloth, such as a towel, to prevent oil drops from spilling, and wrap the entire compress in cellophane.
Further recovery
The recovery period, especially after surgical procedures, is a fairly long process, which must be accompanied by proper rehabilitation therapy.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have also proven themselves quite well
After surgery, a splint or brace is applied for several days. If there are no complications, then it is removed after 3-5 days.
Physical therapy will allow the patient to gradually return the joint to its previous functions and get used to the load.
People usually return to their normal lives after a few weeks. However, if the activity involves strenuous physical activity, you should give yourself a few more months to rest to avoid complications.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have also proven themselves quite well, judging by the reviews of many patients.
The most commonly used rehabilitation therapy is:
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- ultrasound therapy;
- massage;
- hydrotherapy;
- magnetic therapy.
Massage is most often used as a restorative therapy.
Prevention
Prevention of bursitis includes following the following recommendations:
- People predisposed to bursitis (athletes, some workers, etc.) should take precautions, give joints timely rest, and wear special protective bandages.
- It is necessary to promptly treat wounds in the joint area and prevent them from becoming infected.
- Timely treatment of any infectious diseases, pustular skin lesions.
- For sports, you need to choose comfortable shoes that fit.
- Before intense loads on the joints, you need to perform “warm-ups”.
- In no case should athletes train excessively or violate the instructions of the sports doctor and coach.
Stages
The course of this disease includes several stages, distinguishable from each other by the time of manifestation and symptoms:
- spicy. In this case, there is a rapid progression of inflammation in the bursa, which is accompanied by hyperthermia, chills, severe pain, as well as a disturbance in general well-being;
- subacute Gradually the patient's condition stabilizes. Swelling in the affected area, as well as hyperthermia, subside. The intensity of the pain syndrome decreases, and the pain becomes dull;
- chronic. The range of movement of the limb is somewhat limited, as the bursa membranes thicken and tissue fibrosis is observed. If bursitis of the knee joint is not treated on time, the existing bursa cavity will divide into several separate cavities in which necrotic areas will form;
- recurrent. It is characterized by a wave-like course, which means that periods of exacerbation of symptoms are followed by periods of their subsidence.