The main symptom of pancreatitis is the occurrence of pain due to inflammation of the pancreas. The symptom develops against the background of an ongoing pathological process, directly in the pancreas. As a rule, the pain symptom occurs on the left side, directly under the ribs.
As soon as pain occurs, you should immediately consult your doctor. You should not think that if you eliminate the pain of pancreatitis at home, the symptoms will not appear for some time, then you have gotten rid of pancreatitis.
No, this disease requires complex therapy; you cannot simply take antispasmodic medications.
It is the symptoms of pain during pancreatitis that are the root cause of a significant deterioration in the general well-being of patients with this type of pathology, as well as a predisposing factor for an indispensable visit to a doctor.
Read more about pain due to pancreatitis
The nature of the pain, its intensity, localization and duration depend on the stage of the pathology, the fullness of the stomach, even the time of day, and other factors.
When an exacerbation begins, the patient may be plagued by aching pains that usually occur at night. When the development of the pathology coincides with the acute phase of a duodenal ulcer, the nature of the pain becomes cutting, burning, the pain begins to occur in the morning, and it is localized mostly in the area of the diseased organ. Also, with pancreatitis, hunger pains are often felt.
In the acute course of the disease, the patient often cannot determine the exact location of the spasms, which is explained by the blurred clinical picture - girdling pain is felt not only in the abdomen, but also in the lower back.
Risk factors
The following factors significantly increase the risk of pancreatitis:
- Alcohol abuse. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body. The amount of alcohol that can lead to the destruction of pancreatic cells varies from person to person. On average, medical experts suggest that men should drink no more than two glasses of strong alcohol per day, and for women this norm should not exceed one glass;
- Gallstones. Gallstones can lead to blockage of the pancreatic duct, and as a result, the flow of digestive juices will be impaired;
- Increased levels of triglycerides in the blood;
- Deviation in the structure of the bile or pancreatic ducts, and congenital pathology, when the pancreas is divided and has two main channels.
It is important to know! You should seek medical help immediately if you experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting for several hours, or minor pain for several days. It is not necessary that such symptoms indicate diseases of the pancreas, but a number of tests must be performed to exclude the diagnosis. You should not endure for a long time and wait for the symptoms to go away on their own. This is especially true for severe abdominal pain, since this condition can seriously threaten a person’s life.
How pain occurs
The occurrence of pain can be affected by the following processes occurring in the pancreas:
- failure of tissue microcirculation (ischemia);
- obstruction of the gland ducts;
- inflammatory and dystrophic changes.
The dominance of any transformations is explained by the nature of the pathology - chronic or acute form.
In the acute course of the disease, the first place for provoking reasons is inflammatory changes in the tissues of the gland itself. You can observe classic signs of the inflammatory process:
- swelling;
- pain;
- dysfunction;
- redness.
The swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation adds to the negative effect - it puts pressure on the pancreas tissue.
The manifestation of dystrophic and necrotic areas in an acute course is considered an individual sign and can be either a single lesion or become total pancreatic necrosis.
When this pathology appears, the resulting violation of the unity of the lobules of the gland parenchyma is accompanied by an exit of the duct of its enzymes beyond the anatomical boundaries. Because of this, pain during pancreatitis increases even more.
In the chronic form of the disease, inflammatory changes are not so intense. Ischemic processes and replacement of glandular connective tissue occur more often. Cysts and areas of calcification appear in certain areas of the pancreas.
As a result of such transformations, compression of areas of tissue that are viable occurs, and a disruption occurs in the process of outflow of digestive enzymes from the pancreas. With pathology, the pain becomes stronger.
With a prolonged course of chronic pancreatitis, pathological transformations of sensitivity can be observed - pain appears in response to small stimuli (allodynia).
Diagnosis of inflammation
To establish a diagnosis, the doctor conducts a visual, physical examination and questioning of the patient. The patient has a coated tongue, rapid heartbeat, and low blood pressure.
What tests are done for pancreatitis?
- clinical analysis of blood, urine;
- blood chemistry;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA);
- glucose level test;
- stool analysis.
Diagnostic results:
- The results of a clinical blood test reveal an increase in ESR and an increased concentration of leukocytes.
- During a biochemical study, high levels of amylase, lipase, trypsin, increased activity of C-reactive protein, and a decrease in the amount of albumin are detected.
- In acute pancreatitis, amylase is also present in the urine . An increased concentration of sugar in the blood indicates damage to the cells of the islets of Langerhans, a lack of insulin and the development of diabetes mellitus. If the inflammatory process affects the urinary system, urea, protein, and red blood cells are found in the urine.
- To assess the condition of the pancreas, bile ducts, and gallbladder, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is performed.
To accurately localize degenerative areas, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is prescribed.- Gastroscopy is required to examine the stomach and duodenum. If a cancerous tumor is suspected, a fragment of gland tissue is taken for histological examination.
- X-rays of the pancreas are performed to identify stones in the parenchyma and ducts.
- When making a diagnosis is difficult, laparoscopic examination is performed . Differential diagnosis is carried out with acute cholecystitis, appendicitis, perforated ulcer, myocardial infarction, intestinal obstruction, bleeding, mesothrombosis.
How and where does it hurt
The nature and exact location of the pain depend not only on the course of the inflammatory process, but also on the personal characteristics of each person.
In acute cases, pain is often located in the upper abdomen. Most often this is the epigastric zone, but sometimes it can shift to the left or right hypochondrium. Pain during the acute course of the pathology can sometimes resemble the pain that is characteristic of angina pectoris. They can be burning, baking, and spread to the arm, the left half of the lower jaw, and the back.
In a chronic course, the pain does not have a clear location; it can also be of varying intensity:
- In the form of a left half-belt or a full belt in the lumbar area.
- In the back area without further spread.
- In the area of the lower sternum (lower ribs).
- In the middle or upper abdomen.
In chronic pancreatitis in adult patients, pain is directly related to drinking alcohol, eating spicy, fatty, fried foods. The first attacks of pain are observed after eating half an hour.
Ulcer-like pain (pain on an empty stomach) is quite rare. After periods of improvement, there are sometimes periods of increasing pain.
When the pain disappears, especially if it was very strong, you should not calm down, since its sudden disappearance may indicate the development of necrosis.
Pain during pancreatitis can be divided according to localization zones:
Belly . The most severe pain is in the abdominal cavity, since this is where the inflamed pancreas is located. The pain can spread throughout the entire upper abdomen, painful spasms are accompanied by pain in the stomach and lower abdomen, and may sting in the right side. Such symptoms indicate the initial stage of exacerbation of pancreatitis.
Intestines . The processes occurring in the intestines are the cause of most discomfort, the predominant of which is pain. Poorly digested food accumulates in the intestines, which contributes to irritation of the organ mucosa and acts as a provocateur of inflammation. Consequences in the form of dysbacteriosis force a person to lose a lot of weight.
Back . With an exacerbation of pancreatitis, swelling of the pancreas and its ducts occurs, which causes the tissues adjacent to the diseased organ to be pinched. Along the surrounding nerve fibers, pain spreads to other parts of the body, most often radiating to the perineum and lower back.
Anus . Exacerbation of pancreatitis contributes to disruption of the digestive process. Inadequate processing of food causes an inflammatory process in the lower intestines, and signs of diarrhea or constipation form. Bowel movement is accompanied by pain; it can also occur after defecation, localized in the anus. Painful spasms can be very strong, and the patient may involuntarily begin to resist the urge to defecate, only making the situation worse.
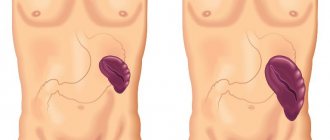
Subcostal area . Pain can be felt in the right or left side, and in some cases radiate to the chest, it depends on which area of the pancreas the inflammation process covers. When pain is felt only on the right, this means that the inflammatory process has affected the head of the pancreas, when on the left - the tail of the organ.
If the inflammatory process affects the entire body of the pancreas, pain can affect the entire epigastric zone: a triangle whose apices are located on the chest and hypochondrium. Similar sensations can occur during a heart attack.
Limbs . Problems in the gastrointestinal tract can affect the general health of the patient. With pathology, there is an acute lack of useful vitamins and microelements, calcium and other important minerals are washed out of the body, which results in problems with the joints - arthritis and arthrosis can occur. Pancreatitis can often cause pain in the knee or elbow joints, which is a result of the destruction of bone tissue.
Head .
Violation of the functionality of the pancreas can cause general intoxication of the body. Pathological transformations that affect the nervous and circulatory systems appear due to putrefactive processes occurring in the intestines and a constant lack of nutrients. For this reason, a large number of patients diagnosed with pancreatitis complain of sudden jumps in blood pressure and severe headaches - migraines, attacks of which can last for two or three days.
Treatment of pancreatitis
What to do if you are diagnosed with pancreatitis? Treatment of this disease is carried out comprehensively. Diet, giving up bad habits, and a healthy lifestyle are of great importance. Diet for pancreatitis is a separate and important treatment method. Since alcoholism is one of the most common causes of pancreatitis, the patient may undergo treatment for alcohol addiction.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis
How to treat acute pancreatitis? Acute inflammation of the pancreas may require multi-stage treatment using surgical and conservative methods. In the initial stages, the patient is prescribed complete fasting to avoid stress on the diseased organ. To maintain energy balance, nutrients are administered through a tube.
It is important to establish the causes of acute pancreatitis.
Surgery. Treatment of complicated forms of the disease may require emergency intervention on the abdominal organs. Trauma to the pancreas and complications of acute pancreatitis may require removal of the organ. If there are reasons that impede the outflow of pancreatic secretions, endoscopic operations are performed: stones are removed from the excretory ducts of the pancreas, structures that expand the lumen of the duct are installed, and the walls are stretched with special balloons.
Severe pain is treated with analgesics; sometimes opioid medications may be required due to the high intensity of the pain.
Also, according to Russian recommendations, the following drugs and treatment methods are used:
- cold on the stomach;
- pumping out gastric contents;
- intensive detoxification therapy;
- antacids in the form of solutions (H-2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors);
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antispasmodics;
- antibacterial agents (in case of infection).
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis is aimed at:
- getting rid of habits that can provoke the disease (alcoholism, unhealthy diet);
- providing conditions for pancreatic restoration (diet);
- pain control;
- restoration of complete digestion of food (taking enzymatic preparations);
- restoration of hormonal balance (taking hormonal medications).
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis begins with the administration of enzyme preparations at every meal. The result of therapy is normalization of digestion, reduction of inflammation in the pancreas, and improvement of the patient’s well-being. If the disease is in the acute phase, hospitalization may be required. Detoxification and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. Treatment of chronic pancreatitis is unthinkable without a strict diet. Without this measure, all attempts to cure the patient are reduced to zero. Alcohol consumption is prohibited, fatty, salty, spicy and spicy foods are excluded, and smoking cessation is recommended.
Surgery for chronic pancreatitis is very rarely necessary. It is carried out only if surgery is the only effective method of treatment. The need may arise when:
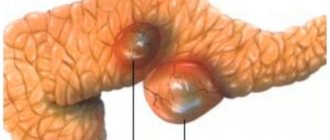
- detection of pancreatic pseudocysts;
- abscess (a cavity filled with purulent contents);
- fistula;
- ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity);
- narrowing or blockage of the excretory duct.
Symptoms accompanying painful spasms with pancreatitis
An attack of pancreatitis often resembles manifestations of diseases of the hepatobiliary system, kidneys, stomach and duodenum. The patient suffers from vomiting, nausea, and dyspepsia. Acute pancreatitis is distinguished from all pathologies of the digestive tract by the suddenness of the onset of an attack.
Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by painful manifestations, usually without nausea and vomiting - sometimes the stomach just hurts, at times it hurts very badly, but there is no nausea and vomiting. The pain with pancreatitis is very intense, it quickly covers all the insides. In acute pancreatitis, rapid exhaustion occurs, repeated vomiting does not provide relief, bile and a greenish liquid are observed in the vomit.
In especially severe cases, the patient may vomit feces with bile, and later blood clots. There is also a complete stop of intestinal functionality; the doctor may observe a complete absence of peristalsis sounds. With this disease, a rapid heartbeat is observed. The patient's breathing is heavy, intermittent, and there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Often the pathology is accompanied by a headache caused by general intoxication and dehydration.
With the advanced chronic course of the disease, the intestines hurt. An attack of pancreatitis is often accompanied by jaundice - the sclera of the eyes and the surface of the skin turn yellow. This happens when the ducts are blocked by stones or when the flow of bile is disrupted. The so-called Mondor triad - the presence of pain, severe vomiting and bloating can guarantee with almost 100% certainty that the patient is having an attack of acute pancreatitis.
During an acute attack, subcutaneous fat in the area of the projection of the pancreas is depleted. Facial features become sharper, and pinpoint hemorrhages measuring 1-4 mm in diameter begin to appear on the skin of the buttocks and abdomen. They occur due to the release of pancreatic enzymes into the blood.
Causes of the disease
The main reasons for the development of pancreatitis:
- Prolonged and excessive consumption of alcohol. Ethyl alcohol increases the saturation of pancreatic juices and provokes a spasm of the sphincter, which regulates their flow into the duodenum. Statistics: 40% of patients with pancreatitis are alcoholic; 70% – periodically abuse alcohol.
- Gallstone disease - a gallstone can cause blockage of the efferent ducts and cause inflammation of the glandular tissue. Statistics: 30% of patients have a history of gallstones.
- Disorders of lipid metabolism associated with overeating and obesity lead to increased production of enzymes, which provokes the risk of inflammation. Statistics: 20% of cases are accompanied by excess weight and lipid metabolism diseases.
- Viral infections, including hepatitis, tuberculosis, chickenpox, mumps, measles, typhoid fever, etc.
- Calcium metabolism disorder – hypercalcemia. Leads to sclerotization (hardening) of gland tissue with disruption of secretory function and spasm of the ducts.
- Autoimmune diseases - some types of allergies can provoke autoimmune aggression of antibodies to the pancreas’s own cells.
- Parasitic infestations - a cluster of large parasites, such as roundworms, that can block the efferent ducts of an organ.
- Damage to the ducts due to injuries and during operations.
- Poisoning or intoxication of the body leads to an overload of enzyme systems with excessive production of digestive juices.
- Endocrine diseases - directly or indirectly affect the functioning of all endocrine and exocrine glands. Disorders of the thyroid gland and diabetes mellitus have a particularly detrimental effect on the pancreas.
- Pathologies of the structures of the digestive system - enterocolitis, colitis, duodenitis, diverticulitis, peptic ulcer, Reye's syndrome (fatty degeneration of the liver).
- Long-term use of certain medications - steroid drugs, certain types of diuretics, antibiotics, sulfonamides.
- Vascular pathologies (arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis) with impaired blood circulation in the pancreas, as well as complications during pregnancy in women.
- Hemolytic diseases - including hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
- Hereditary pathologies (most often cystic fibrosis). The associated thickening of internal secretions, including pancreatic juices, leads to disruption of their outflow.
The causes of pancreatitis can occur independently or in combination. This determines not only the etiology of the disease, but also the degree of its manifestation, severity and therapeutic prognosis.
Repeated attacks of acute pancreatitis provoke the transition of the disease into a chronic form. Due to frequent inflammation, the organ becomes covered with scar tissue (fibrous degeneration) and loses the ability to produce the required amount of enzymes. If the areas that produce insulin (the islets of Langerhans) are damaged, an insulin-dependent form of diabetes mellitus develops.
How long do the pain last and what is its nature?
The acute phase of chronic pancreatitis can be accompanied by painful attacks that have varying intensity, intensifying after eating, and stopping within 3-4 hours. If the diet is not followed, the pain can increase and the attack time increases. As a result, the patient requires hospitalization and inpatient treatment. If the pathology is ignored, abdominal pain will accompany the patient constantly.
Pain can occur from eating or from physical fatigue. Relief from pain comes with rest. Body position also influences the manifestation of pain. During exacerbations, it is difficult for the patient to sit; a feeling of a driven stake appears in the stomach and back. Pain occurs of various types:
- aching;
- pulling;
- piercing;
- drilling;
- spicy;
- stupid.
Disturbance from them can last for weeks. The duration of the attack depends on how much the gland swells or on the area of necrosis.
With timely assistance, pain relief occurs quite quickly, and a painful attack can be relieved within a day. In case of complications and dangerous development of the situation, it can last up to three days. Depending on the duration of the painful attack, pancreatitis can be divided into the following types:
- type A. With this type of painful attack, the pain lasts 7-10 days, the exacerbation phases are replaced by phases of “calm”;
- type B. This type of pain lasts from one to three months. Usually characteristic of alcoholic pancreatitis;
- incessant pain. Requires surgery.
Any type of pain due to pancreatitis requires immediate pain relief.
Alcohol is the cause of 55% of cases of acute pancreatitis and 60-70% of chronic pancreatitis.
Nutrition is an important factor in the development of pancreatitis. A diet with a predominance of fatty and fried meat foods negatively affects the health of the pancreas.
The following types of chronic pancreatitis are distinguished depending on the etiology according to the TIGAR-O classification:
- toxic (as a result of exposure to alcohol, tobacco smoking, hypercalcemia, drugs and various toxins);
- idiopathic (without an obvious cause, it accounts for 20-30% of cases);
- hereditary;
- autoimmune;
- obstructive (due to a violation of the outflow of secretions).
First aid at home
An attack of pathology can occur anywhere, unexpectedly. It is very important not to give in to panic, and for those around you to do everything to help the patient get rid of such an attack:
- An ambulance is immediately called.
- At this time, the patient needs to create a calm environment (emotional and physical) and be placed in an isolated room, closer to the bathroom and toilet.
- Ask to take a sitting position, leaning forward a little - this will ease the pain a little. Shallow breathing, followed by short periods of retention, also helps.
- If the patient feels nauseous, you can try to induce vomiting. If simple effort is not enough, you need to press on the root of the tongue with your fingers.
- Even with severe pain, refrain from using analgesic medications - most of them can only worsen the patient’s condition and prevent the correct diagnosis.
- In order to calm a strong spasm, you can inject “Papaverine”, “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”. Refrain from taking pills, as this may only intensify your gag reflex.
- The patient should be given a large amount of water at room temperature, without gas - one-fourth of a glass every 30-45 minutes.
It is strictly forbidden to apply a heating pad with ice to the stomach during an attack. The influence of cold can increase vascular spasms and worsen the condition of the tissues of the damaged organ.
Symptoms of pancreatic inflammation
The most obvious symptom of inflammation of the pancreas is quite severe pain in the left hypochondrium or in the upper abdomen. Sometimes the pain radiates to the lower back and is girdling in nature. When you take a sitting position or bend slightly forward, the pain gradually subsides and becomes insignificant.
Symptoms also include:
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Increased sweating;
- State of shock;
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin;
- Back pain, however, this symptom is sometimes provoked by diseases such as peptic ulcer, appendicitis, cholecystitis, intestinal obstruction, diverticulosis.
How to relieve pain attacks
You can quickly get rid of pain in acute pancreatitis by taking:
- "Fentanyl";
- "Novocaine";
- "Omnopon";
- "Ketanov";
- "Tramadol".
In addition to painkillers, it is advisable to take antidepressants, tranquilizers, and antipsychotics - they are needed to alleviate the emotional state of the patient.
Taking painkillers is carried out together with taking antibiotics, antispasmodics and others. When taken in combination, they quickly help get rid of pain and improve overall health.
Pain syndrome that appears due to exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is relieved by:
- "Baralgina";
- "Diclofenac";
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Metamizole";
- "Paracetamol."
They are also used in cases of chronic pancreatitis. The dosage of each drug is determined individually, taking into account the patient’s age, concomitant pathologies and other factors.
Also, pain significantly decreases when following a diet. The optimal choice for pain during an exacerbation is a three-day fast. During fasting, you are allowed to drink only weak tea with a spoon of honey and still mineral water.
To get rid of pain, it is prohibited to take various alcohol tinctures, since they not only do not alleviate the patient’s condition, but can, on the contrary, aggravate his condition.
Yoga and the use of traditional medicine can help, but prior consultation with a doctor is required.
The complex therapy of chronic pancreatitis includes the following groups of drugs:
Pancreatic enzymes (Pancreatin). It improves digestion processes and helps reduce the load on glandular tissue, which helps relieve pain or reduce its intensity.
The hormone somatostatin and synthetic compounds with it . Somatostatin reduces the body's sensitivity to pain. An analogue of the synthetic drug is Octreotide. The drug has a long duration of action, which is why even a 3-day course helps to achieve a long-term effect. But this drug has a wide range of side effects and contraindications, so its analogues are not applicable to all categories of patients.
H2-histamine receptor blockers . “Functional rest” for the pancreas is created not only by directly inhibiting the secretion of pancreatin enzymes; for this, you can take H2-histamine receptor blockers or proton pump inhibitors. Among the former, Famotidine is the most popular. It has antioxidant activity, has a minimum of side effects, and helps improve the rheological characteristics of the blood.
Proton pump inhibitors . These include:
- "Esomeprazole";
- "Rabeprazole";
- Lansoprazole.
They have the least number of side effects, which indicates the safety of their use. Individual prescription allows you to take them for quite a long time.
In adults, an attack of chronic pancreatitis can in some cases be prevented. This is easier to do than to anesthetize an attack that has already begun. When planning a feast or eating unusual food, leaving the diet, etc. together with the beginning of the meal, you need to take “No-shpu” (2 tablets) along with an enzyme preparation (“Panzinorm”, “Mezim”, “Festal”). In the absence of cholelithiasis, you can take one of the choleretic drugs - “Karsil”, “Allohol”.
Painkillers for home use
The pain from inflammation of the pancreas is so severe that a person can lose consciousness and even die from painful shock. It is important to be able to provide first aid before the ambulance arrives. It is also useful for those who suffer from the chronic course of the disease to know how to relieve pain during an attack of pancreatitis.
Attention! The patient is helped to take a comfortable position, access to fresh air is provided, and ice is placed on the stomach in the navel area. Ice is needed to reduce swelling of the diseased gland. Antispasmodics, analgesics and NSAIDs are used as painkillers for pancreatitis.
Antispasmodics
This group of drugs includes No-shpa, Baralgin, Buscopan, Papaverine, Platyfillin, Spazmalgon. They eliminate spasm of smooth muscles, restore normal flow of juices and thereby relieve pain.
Moreover, for pain relief for pancreatitis, you need to give injections, so the drug will act faster than if you take it in tablets.
In acute pancreatitis, it is impossible to take painkillers in tablets due to vomiting and disruption of normal digestive function. You need to know how to relieve pain correctly.
Injections are given intramuscularly, slowly injecting the medicine. The drugs are combined so that they complement and enhance their properties. Papaverine is administered together with Platyphylline or No-shpu (Drotaverine) with Papaverine. If it is impossible to give an injection, you can drink the painkiller by breaking the ampoule and drinking a small amount of water.
Attention! Treatment at home is only possible for chronic cases of the disease.
Analgesics
Analgesics can also help relieve pain at home. Analgin and Pentalgin are able to anesthetize a mild or moderate attack without any side effects.
NSAIDs
An injection of Paracetamol or taking Nimesil will relieve inflammation and relieve pain. The use of Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin will effectively relieve pain and relieve inflammation. The most effective remedy in its group is Ketorolac; inflammation is relieved instantly even in severe cases.
Important! Drugs from the NSAID group are acceptable at home as an emergency measure of pain relief. NSAIDs negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys, so they should not be used uncontrollably at home.
An attack of chronic pancreatitis in adults can in some cases be prevented. This is much easier to do than to relieve pain after inflammation has started.
If you are planning a feast, or eating unusual food (when coming out of hunger, diet, fasting), simultaneously with the start of the meal, you must take 2 tablets of no-shpa with an enzyme preparation (Mezim, Festal, Panzinorm).
If chronic pancreatitis is not accompanied by cholelithiasis, you should take a choleretic agent - Karsil, Allochol.
Attention! These measures will serve as protection against an attack. However, you should not rely entirely on medications; restrictions on the amount of food and its fat content are much more effective.
An attack of pancreatitis can also be avoided by eating small meals regularly at one time. This is the best preventive measure, coupled with avoiding alcohol and fried foods.
How to get rid of pain in hospital
In case of severe pancreatitis, the patient must be urgently hospitalized. In the hospital, narcotic analgesics are used to relieve pain. Usually used:
- "Tramadol";
- "Omnopon";
- "Ketanov";
- "Promedol."
In particularly difficult situations, such analgesics are combined with antidepressants, tranquilizers, and antipsychotics, since these drugs enhance each other’s effect on the body.
Nutrition for inflammatory processes
In the first days of exacerbation of pancreatitis need to abstain from eating, you are only allowed to drink warm water and rosehip decoction. Therapeutic fasting should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Later, you can use mucous decoctions, pureed milk porridges without sugar.- Starting from days 6–7, other dishes low in animal fats and carbohydrates are added to the diet .
- After 3 weeks, patients are transferred to treatment table No. 5; for chronic pancreatitis, it is necessary to follow the 5 P diet.
- You should eat in small portions, 5–6 times a day . The dishes must be served warm and ground. Meat and fish must be steamed, stewed or baked with vegetables in the oven. You can add a little vegetable oil (olive, flaxseed) to salads.
- The patient should consume 80 g of fats and proteins per day , of which 60% should be products of plant origin. The permissible amount of carbohydrates in the diet is 400 g, table salt is no more than 10 g.
- It is important to maintain a drinking regime ; daily you need to drink 1.5–2 liters of clean, still water.
- The daily energy value is 2400–2600 kcal.
- For people with excess body weight, caloric intake is reduced to 1800-2200 kcal/day.
- The duration of the diet depends on the patient’s condition and is determined individually. It is necessary to adhere to the correct diet for at least 3–6 months; in severe forms of chronic pancreatitis, dietary restrictions must be observed for life.
| Authorized Products | What should you not eat if you have pancreatitis? |
|
|
Diet for pain
After a 3-day abstinence from food, the patient must follow a strict diet that excludes the consumption of spicy, fried, fatty foods, large amounts of spices and salt. Allowed to use:
- Semi-liquid and liquid porridges, which are prepared with water or low-fat milk;
- Chicken bouillon;
- Meatballs, steamed cutlets, meat soufflé;
- Boiled fish and poultry;
- Vegetable puree;
- Baked fish and meat dishes (without crust);
- Sweet fruits (baked and pureed).
Patients with this diagnosis are advised to follow the principles of fractional nutrition: eat small portions of food 4-6 times a day.
List of references: https://www.kp.ru/guide/zabolevanie-pankreatit.html https://www.alfazdrav.ru/zabolevania/zabolevaniya-podzheluzhochnoy-zhelezy/pankreatit/ https://www.kp.ru/ guide/pankcreatit.html https://aif.ru/boostbook/boli-v-podzheludochnoi-zheleze.html https://www.gmsclinic.ru/gms/press/articles/art-pancreatitis https://doctor.ru /question/10789/ https://medportal.ru/enc/gastroenterology/pancreas/2/ https://www.rlsnet.ru/mkb_index_id_4823.htm poliran.ru/hirurgija/pankreatit-simptomy/ https://ru. wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatitis med.vesti.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/simptomy-zabolevanij-podzheludochnoj-zhelezy/ https://aif.ru/health/life/30182 Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Prevention
Preventive measures for any type of pancreatitis are simple. To prevent inflammation, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Get rid of bad habits. Minimize or completely stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Lead an active lifestyle, engage in light sports (for example, breathing exercises).
- Coffee lovers are allowed to drink no more than 1 cup per day. Preference should be given to natural products.
- Follow a daily routine, do not eat at night and before bedtime.
- It is worth limiting your consumption of fast food, fatty, smoked, spicy, fried foods.
- Consume sugar-containing foods in moderation.
- You need to eat fractionally, in small portions, and eat freshly prepared meals.
- Before the feast, you need to take enzyme medications (Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal).
Course of the disease
Before starting treatment or getting rid of an attack of pancreatitis, it is important to understand the essence of the process occurring in the body at this moment.
The disease is non-infectious and is characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The factors that contribute to this are different, but they all lead to increased production of enzymes by the organ.
Due to the fact that the enzymatic composition becomes more concentrated, digestive juice begins to be produced stronger and in larger quantities, and the body’s own tissues are digested.
If measures are not taken to eliminate the disease for a long time, then there is a risk of necrosis, i.e. death of tissue areas of the digestive system.
If any organ has undergone necrosis, even if the current occurs only in a small part, then its normal functioning ceases.
The disease is divided into two forms:
If a patient suffers from chronic pancreatitis, his attending physician must treat or maintain the body in normal condition. If the patient is overtaken by an attack, then it is important to know what to do in such a situation.