GastrituNet.ru » Stomach diseases » Diagnostics
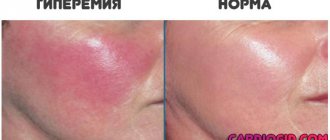
One of the main methods of examining the stomach is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). It is prescribed when symptoms of damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract appear. During the examination, the diagnostician has the opportunity to examine the inner lining of the stomach, and the expression “hyperemic gastric mucosa” sometimes appears in the description.
- 1 The gastric mucosa is hyperemic
- 2 Causes of hyperemia of the gastric mucosa
- 3 Classification of mucosal hyperemia
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Diseases with gastric hyperemia
- 6 Treatment methods
- 7 Useful video
- 8 Recommendations for nutrition in pathology
- 9 Possible complications and prognosis
- 10 Prevention measures
Diagnostics
Having looked at the statistics, we can conclude that almost 90% of people need consultation with a gastroenterologist.
To make a correct diagnosis, a specialist prescribes an examination, which is divided into laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. Laboratory methods include: studies of gastric juice, blood, urine and feces. With their help, you can determine the secretory function, bacterial composition of the gastrointestinal tract, enzyme activity and other important functions. But without instrumental methods, the analysis results are uninformative.
Instrumental methods include:
- gastroscopy or esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS) is a type of examination that is carried out using special equipment (gastroscope) with a flexible hose, equipped with viewing optics and a camera. Contraindications for manipulation are: heart disease, hypertension, mental disorders, severe respiratory failure. Before performing the procedure, the patient must refuse to eat food no earlier than 8 hours, and water 3 hours before, not take medications, smoke, or even brush their teeth;
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast agent. With its help, you can identify the condition of the gastric mucosa and diagnose improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation, intestinal obstruction, perforation of the stomach wall, or allergies to barium preparations. Before the procedure begins, the patient must take a contrast agent. A few days before the x-ray, completely abstain from legumes and dairy products; on the evening before the procedure, refrain from sweet products, raw vegetables and fruits;
- Ultrasound diagnostics or echography is a method that is based on the ability to reflect sound waves. This method is not very informative and is most often prescribed to young children. Using echography and ultrasound, you can determine the presence of tumors, ulcers, thickening of organ walls, etc.
FGDS is not the most pleasant, but informative method of research.
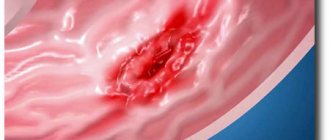
An experienced and qualified specialist will immediately recognize a swollen and reddened mucous membrane, since normally the inner layer of the stomach should have a pale pink color and transparent mucus. If there are any deviations from this norm, then a preliminary diagnosis of hyperemia of the gastric mucosa is made.
Functions of mucosal membranes
Mucous epithelium is found in all internal organs and systems of the human body.
It performs the following functions:
| Name | Description |
| Protective | The mucous layer protects the lower tissues from the negative effects of internal and external factors. The same applies to infectious agents, bacteria, pathogenic factors. |
| Sensory | The mucous membrane has temperature, pain and tactile receptors. Their irritation activates certain reflexes. |
| Secretory | The secreted mucus removes pathogenic flora from the surface of the epithelium and protects it from mechanical damage, for example, when swallowing solid food. The mucus also contains antimicrobial substances that prevent bacteria and viruses from accumulating on the surface of the shell. |
| Immune | Saliva in the mouth contains antibodies that are necessary in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Suction | In some places (oral cavity) the mucous membrane has a thin layer, due to which medicinal components are quickly absorbed and enter the blood. |
The mucous membrane also performs a thermoregulatory function in the human body, but it is not as important as other duties.
Recommendations for nutrition in pathology
Nutrition for gastric hyperemia
Very often, hyperemia does not need to be treated, because it means that your body is trying to restore itself, self-regenerating. Hyperemia accelerates metabolism in tissues, but such a diagnosis is only normal if it is arterial hyperemia, but more often redness and swelling are harbingers of gastritis.
To treat and prevent the disease, folk remedies use herbal remedies and diets, as well as the diet of the Soviet scientist M. I. Pevzner. The Pevzner diet is a system of therapeutic tables that are differentiated according to various types of diseases. Pevzner's diet No. 1 is intended for people suffering from gastritis and ulcers. It is also prescribed during the recovery period after surgery and for duodenal ulcers.
Hard-to-digest foods, as well as foods that actively irritate the mucous membranes, are completely excluded from the diet. Those who adhere to this diet eat a menu consisting of berries and fruits, condensed milk and cream, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, fish and poultry. All products included in this dietary table must be used either stewed or steamed. In any case, it is forbidden to eat fatty meat, salted fish, fresh baked goods, hot dishes and dairy products that increase acidity.
Symptoms
Diffuse changes in the tissues of the thyroid gland are detected accidentally during routine medical examinations and palpation of the organ. Parenchyma is significantly different from stroma, which consists of only one type of tissue. Changes in it are accompanied by deterioration of the skin and nails, chills, and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
In adults there are:
- decreased libido;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- obesity not related to diet.
In children, pathological conditions are expressed in hyperactivity, retardation in psychophysical development, constant aches in muscles and joints, and a tendency to viral infections. Chronic fatigue is combined with deterioration of memory and attention.
Signs of thyroid disease vary depending on the nature of the disease. In the early stages there may be no symptoms.
In mature women, thyroid lesions may be accompanied by signs of hormonal imbalances - lack of menstruation, the appearance of benign tumors in the mammary glands.
Prevention of hyperemia
Prevention of hyperemia includes compliance with the following rules and recommendations:
— Avoid hypothermia, frostbite or overheating of the body;
— Do not leave untreated diseases to chance, especially cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive and other systems, skin diseases;
— Wear comfortable clothes and shoes, preferably made from natural fabrics;
— When working with aggressive substances (detergents, etc.), be sure to use protective equipment;
— Stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Try to move more;
— Observe the rules of personal hygiene;
— Follow the regime – work/rest/sleep;
- Avoid stress;
— Try to eat foods enriched with vitamins and microelements.
Therapy of a pathological condition
Treatment of mucosal hyperemia directly depends on the use of vasoconstrictor and antibacterial medications.
The main treatment for hyperemia involves rinsing the nasopharynx on a daily basis, irrigating with a solution of 0.9% sodium chloride with a drop of iodine. You can also use Dolphin , a product available in many pharmacies.
In a situation where hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa manifests itself slightly, vasotomy, ultrasonic disintegration and laser destruction are prescribed.
In a situation where hypertrophy is clearly expressed, conchotomy is performed in a gentle manner, osteoconchotomy, as well as amputation of the edge of the nasal concha.
In conditions of persistent runny nose within 7 days, it is important to consult a specialist for additional examination and determination of further treatment methods, since the advanced form threatens the development of sinusitis, bleeding, purulent rhinosinusitis and other diseases.
Diagnostic methods
A gastroenterologist will help diagnose the problem. He first examines the patient and collects anamnesis.
After a medical examination, a gastroscopy is performed. It is performed using a special device - an endoscope. It is equipped with viewing optics and a camera.
This diagnosis is an unpleasant and painful procedure, but it allows you to accurately determine the condition of the organ, identify the causes of hyperemia, thanks to which the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment tactics. In addition, using this method, a biopsy is performed, i.e., tissue is taken for examination.
Timely diagnosis is a chance to prevent consequences
Gastroscopy is the main method for diagnosing the disease.
Hyperemia of the gastric mucosa is established through a comprehensive examination, which includes laboratory and instrumental methods. This pathology is dealt with by a gastroenterologist who examines the patient and finds out the medical history. The main diagnostic method for determining hyperemia is gastroscopy. The procedure is performed using an endoscope on which a camera and microscopic optical instruments are located. The manipulation is extremely unpleasant and often causes discomfort in the patient. With the help of a gastroscopic examination, it is possible to find out how much hyperemia the gastric mucosa is.
Additionally, in case of hyperemia, a biopsy can be performed, in which damaged tissue is taken for laboratory testing.
Return to contents
How to treat
Arterial hyperemia is not treated in 85% of cases. In such a situation, intensive blood supply to tissues begins as a consequence of independent regeneration of damage. The cells of the stomach receive the necessary amount of oxygen and nutritional components, due to which metabolic processes are accelerated. As a result, cells begin to divide rapidly, and healthy tissues replace damaged structures. In the arterial form of the pathology, doctors only prescribe proper nutrition and help balance the diet.
In the remaining 25% of cases, active hyperemia, as well as venous blood filling, indicate the presence of gastritis. In case of inflammation of the mucous membrane, complex treatment is carried out. The patient must follow a strict diet, take antibiotics to suppress the growth of Helicobacter pylori and other medications to accelerate tissue regeneration. You are allowed to drink herbal infusions and eat honey.
Possible complications and prognosis
Prolonged irritation and damage to the mucosa are harbingers of gastritis. If you do not pay attention to this in time, plethora leads to the development of microthrombosis, hypoxia and the progression of damage to epithelial cells.
If hyperemia is detected, the patient should be observed by a doctor to avoid the development of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer. With adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable, since normally the surface epithelial layer is renewed every 7–10 days.
Treatment of the stomach with hyperemic mucosa
Actually, hyperemia does not need to be treated in any way. This is a beneficial process, indicating that the body is trying to heal itself.
Hyperemia helps accelerate metabolic processes, which leads to tissue restoration and healing.
In some cases, doctors even artificially induce blood flow to a diseased organ in order to speed up its recovery.
These are cups and mustard plasters, with the help of which you can cause a rush of blood to the inflamed bronchi and lungs, thus speeding up their recovery.
Most often, redness of the mucous membrane indicates one or another form of gastritis. This disease is a consequence of errors in nutrition or the result of colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by pathogenic bacteria of the Helicobacter genus.
Treatment of gastritis consists of a set of measures: a special diet and medication, including antibiotics (if Helicobacter pylori infection is detected).
When the cause of the redness of the epithelium is discovered, the doctor will prescribe treatment aimed at eliminating the disease itself.
After curing gastritis, ulcers or other ailments, the gastric walls will independently acquire normal color and thickness.
Hyperemic epithelium can be a consequence of not only inflammatory processes. The mucous membrane turns red due to problems in the person’s mental state.
Chronic stress, prolonged depression and fear cause a rush of blood to the stomach walls, causing them to become red and swollen.
Gastroenterologists warn that often problems with the gastrointestinal tract do not have an anatomical or infectious basis, but are only a consequence of a person’s severe psycho-emotional state.
You can find out that the walls of the stomach are red and swollen from the inside only after a special examination - gastroscopy.
Such equipment allows the doctor to see on the monitor screen everything that is happening in the gastrointestinal tract, and, if necessary, to take a sample of the epithelium for analysis or carry out local therapeutic measures: remove a polyp, inject medicine into the affected area of the organ.
Gastroscopy is a painful and unpleasant examination for the patient, but it is absolutely necessary, as it allows the most accurate diagnosis to be made.
The patient needs to strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment, only in this case can one count on its success.
Very often they try to treat stomach ailments on their own, using traditional methods, relying on herbal remedies, honey, special diets, etc.
Indeed, traditional medicine has accumulated vast experience, but it should only complement the treatment prescribed by a specialist, and not replace it.
Before starting any herbal treatment, you should always consult your doctor.
Video:
As for diets, for hyperemic mucous membranes it is best to adhere to the therapeutic diet developed by Professor Pevzner: if necessary, the gastroenterologist will definitely recommend one of his diets.
Errors in nutrition and stress have long become the norm for modern city dwellers.
So is it any wonder when the doctor writes on the examination form that the epithelium in the stomach is hyperemic, that is, red and swollen? This means that the patient will have to be treated for gastritis or some other stomach ailment.
Signs
The main manifestations of arterial hyperemia include:
- redness of the skin area;
- an increase in volume and a local increase in temperature of the hyperemic area;
- expansion of arterial blood vessels, as well as an increase in the number of active vessels in a certain area;
- increased pressure in the arterial vessels of the hyperemic area;
- reducing the difference between the oxygen content in arterial and venous blood vessels;
- acceleration of blood flow;
- increased lymph formation;
- pulsation in blood vessels where there is usually no pulsation.
Neurotonic arterial hyperemia is manifested by redness of the skin of the face in response to the influence of an emotional factor.
With neuroparalytic arterial hyperemia, there is a disruption in the oxygen supply to blood vessels and tissues due to paralysis of the neuromuscular system, after which blood begins to flow to this area, which leads to a sharp dilation of arterial vessels. If ischemia develops when vessels are compressed by ascitic fluid during its rapid release, neuroparalytic arterial hyperemia occurs in the mesentery, which can cause the patient to faint.
With the development of venous hyperemia, blood circulation slows down and venous blood stagnates. The hyperemic area increases in volume and becomes cyanotic in color, while its temperature decreases.
With the development of cerebral hyperemia, pronounced redness of the mucous membranes, tachycardia, and tachypnea are usually observed. Body temperature may increase or remain within normal limits; a local increase in temperature is detected by palpating the head. Patients complain of a feeling of pressure in the head, dizziness, lethargy, drowsiness, apathy, dullness of consciousness up to fainting, visual and hearing disorders, weakened reflexes, and gait disturbance. Reaction to pain and sound stimuli decreases.
Source: morehealthy.ru
Skin hyperemia most often occurs in women over 40 years of age and usually appears on the face. In this case, red or purple spots appear on the skin, the temperature of the affected areas rises, and blood vessels dilate at the site of redness.
Preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of hyperemia depend on the underlying disease that caused it.
During examination of the oropharyngeal region, when the patient develops hyperemia of the throat, redness of the mucous membranes is accompanied by swelling of the tonsils, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes is often observed. Patients complain of sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and hoarseness.
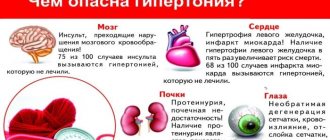
With the development of hyperemia of internal organs, patients may experience swelling of the torso, face, upper and lower extremities, rapid increase in body weight, urination problems, headaches, shortness of breath, palpitations, and spatial orientation disorder.
Conjunctival hyperemia is redness of the mucous membrane of the eye, especially pronounced near the transitional fold. The pathological process is accompanied by lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, and photophobia.
Folk remedies
Despite the fact that most doctors now know how to treat inflammation of the duodenum using traditional methods, patients still trust centuries-old herbal complexes. The most commonly used medications are the following, which are easy to prepare:
1. Pour boiling water over 1 tsp. flaxseed, after which everything is left for 20 minutes. The prepared drink is consumed in small sips on an empty stomach. The medicine is taken for a month without interruption.2. Chamomile, lemon balm, licorice and marshmallow root, buckthorn bark, lavender, and shepherd's purse are mixed in equal parts. Next 1 tsp. The prepared mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and sent to a water bath. Strain and drink everything 30 minutes before eating.3. Crush 0.5 kg of sea buckthorn and pour in 0.5 liters of sunflower oil. This composition is infused for a week in a closed container. Next, the mass is ground and taken, if inflammation of the duodenal bulb is observed, 1 tbsp. l. every day for a month.4. An aqueous solution of St. John's wort is prepared and in moments of exacerbation several sips are taken every day.5. The juice is squeezed from the leaves and stems of the large plantain, after which a little honey is added. The resulting mixture is drunk 1 tsp. before eating food.6. Rhubarb sprigs are soaked in clean and warm water, then they are applied as a compress in moments of inflammation on the stomach area.
Treatment of hyperemia in adults, children
The mucous membrane is hyperemic - this means that you need to go to the hospital and be examined. Therapy for small and adult patients is drawn up taking into account the results obtained after a comprehensive diagnosis. Children are prescribed gentle medications, taking into account the area of the inflammatory process and the individual characteristics of the small organism.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial agents | Augmentin, Amoxiclav | The adult dosage is 1 tablet (250-500 mg/125 mg) 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 5-14 days. |
| Antihistamines | Tavegil, Suprastin | The drug is taken orally in the morning and evening, 1 tablet. |
| Antiseptics | Cholisal, Furacilin | Medicines in the form of sprays or tinctures are used to treat the affected mucous membrane. Some products are applied topically 2-3 times a day. The medicine is applied to the affected area and rubbed in with light massaging movements. |
| Immunostimulating drugs | Immunal, Amiksin | The tablets are taken orally with a sufficient amount of water. The adult dosage is 1 tablet 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 1-8 weeks. |
| Antifungal | Daktarin, Miconazole | To rinse the mucous membrane, it is recommended for an adult patient to use 0.5 scoop 4 times a day. The cream is applied to the affected areas and rubbed in with light massage movements. The course of treatment lasts 7 days. |
| Antiviral agents | Acyclovir, Serol | The medicine is taken orally 200 mg 5 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 5 days. |
In addition to drug treatment, patients are advised to attend physiotherapeutic procedures after the exacerbation period has subsided. It is also recommended to take a course of vitamins to increase the body's defenses.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the thyroid parenchyma
Therapeutic measures should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Self-medication is not only ineffective, but also dangerous to the life and health of the patient.
Subsequently, the therapeutic regimen undergoes several adjustments.
Since diffuse lesions of the thyroid gland are accompanied by a disruption in the production of hormones, replacement therapy cannot be avoided. Such treatment is a vital necessity for chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. The amount of thyroid hormones in this case exceeds the maximum permissible values.
If there are moderate signs of damage to the thyroid gland, treatment involves changing the diet and taking iodine-containing medications. If the pathology is accompanied by hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormones are used.
If the pathology is accompanied by hypothyroidism, the doctor recommends taking synthetic thyroid hormones.
For diffuse nodular lesions of the thyroid gland that contribute to the development of compression syndrome, emergency surgical intervention is prescribed. After the operation, the patient must regularly visit the endocrinologist and undergo all necessary tests. With proper treatment, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Without treatment, dangerous complications may develop.
How dangerous?
In order to cope with gastric hyperemia, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of its occurrence. After which the swelling and redness will go away on their own. If the pathology is not stopped in a timely manner, serious complications arise:
- formation of multiple benign tumors on the organ wall;
- internal bleeding;
- cancerous tumor;
- lack of iron in the body, leading to anemia;
- chronic hypertrophic polyadenomatous gastritis;
- chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- cholecystitis.
As inflammation of the mucous membrane progresses, an ulcer of the digestive organ may develop.
As gastritis progresses, a stomach ulcer often develops, which in severe cases leads to the death of the patient. The development of hyperemia of the organ mucosa has a negative impact on the condition of the nail plates, skin and hair. It is possible to prevent serious consequences if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and eliminate the causes of the disorder.
Return to contents
Additional information about pathology
The presence of this gastric pathology requires treatment. If the affected areas, which are expressed in redness, are not diagnosed in time, an ulcer or erosion of the mucous membrane may develop. Hyperemia is a protective reaction. Blood flow to the vessels occurs only if any provoking factor occurs.
This is possible, but not always. It is persistent hyperemia that requires treatment. If the presence of mucosal pathology leads to vasodilation, the risk of bleeding increases. The main provocateurs of the development of hyperemia are:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- autoimmune diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- an abundance of fatty, spicy, smoked and spicy foods;
- prolonged exposure to a stressful situation.
It is especially important to take into account the last provoking factor. People who have an unstable psyche are often nervous and irritated, exposing themselves to pathologies such as hyperemia of the gastrointestinal tract
The defect can appear in any organ. The stomach is most often affected by this disease, because stressful situations contribute to the release of gastric juice, which in large quantities begins to irritate the mucous membrane.
Increased blood flow also occurs due to frequent irritation of the mucous membrane with bile or hydrochloric acid. This is possible in the presence of gastric hypersecretion and non-calculous cholecystitis. The gallbladder fills with secretion and releases it. When it enters the stomach, damage to the mucous membrane occurs, especially if there is no food in it.
The focal form is characterized by other signs. The mucous membrane becomes thinner, which is a favorable factor for the development of ulcerative processes. If there is Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the organ, the hyperemic areas become pronounced.
Pain occurs in advanced stages, and symptoms increase as inflammation develops. The burning sensation mainly occurs on an empty stomach and at night. Hyperemia in the initial stages of its development can be successfully cured with the help of diet.
Healing of the defect occurs gradually. If redness spreads over a significant surface area of the stomach, then reverse development is possible only with an integrated approach to treatment. In this case, you must follow all doctor's orders.
In most cases, the pathology is temporary. Under favorable conditions, the defect quickly disappears. When making a diagnosis, a specialist is based on data from an endoscopic examination. It is not difficult to determine the source of the lesion.
Main causes
Hyperemia of the mucous membrane occurs due to the following diseases:
- peptic ulcer;
- duodenitis;
- gurgle;
- gastritis.
In addition, the following factors can provoke this condition:
- mechanical damage to an organ with a sharp object;
- improper and irrational nutrition;
- measles infection, scarlet fever;
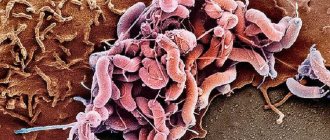
- entry into the body of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- renal failure;
- depression for a long time;
- stressful situations.
In some cases, the mucous layer may turn red due to an inflammatory process in the walls of the organ.
Chronic form
A chronic state of hyperemia can be observed with a prolonged runny nose, frequent relapses of rhinitis, prolonged exposure to chemical, mechanical, thermal irritants, and work in hazardous industries. Less commonly, swelling of the nasal mucosa is a consequence of cardiovascular pathologies, diseases of the endocrine system, nephritis, emphysema, and bronchiectasis. In children, chronic hyperemia can occur with enlarged adenoids.
In the chronic form, patients usually complain of nasal congestion, poor sleep, constant nasal discharge, decreased sense of smell, headache, and fatigue. They also experience a change in the color of the turbinates; they become pale, sometimes bluish in color. In most cases, the anterior and posterior ends of the inferior and middle conchae are affected.
Drug-induced (reactive) rhinitis
Reactive hyperemia is a response to drug treatment for a runny nose. As a rule, it occurs against the background of long-term use of vasoconstrictor drugs. Drops, sprays based on naphazaline, tetrizoline, oxymetazoline, xylometazoline.
With drug-induced rhinitis, the normal movement of the vascular walls is disrupted, mucosal cells degenerate, cilia are lost, which complicates the process of cleansing the epithelium. In addition, patients have enlarged mucous glands, as a result, mucus secretion increases. Drug-induced rhinitis is difficult to treat.
Types and symptoms of pathology
Hyperemia of the gastric mucosa is divided into several types, each of which is characterized by a special clinical picture. With the passive type, there is an excessive flow of blood. The stomach stops working and becomes further damaged due to lack of oxygen. The second type is arterial hyperemia in the stomach, characterized by impaired blood flow from the walls of the internal organ. With this form of hyperemia, the likelihood of complete recovery is much higher than with superficial hyperemia. The mucous membrane can be diffusely and focally hyperemic, which depends on the localization of the pathological process.
How to recognize the symptoms?
In a healthy patient, the gastric mucosa has a pale pinkish tint. When the organ is swollen and reddened moderately, the clinical picture may take a long time to manifest. If hyperemia occurs against the background of bulbitis, then thickening occurs in the antrum of the stomach and the duodenal bulb of the intestine. In this area, swelling occurs and the mucous membrane becomes motley. Hyperemia occurs with general symptoms:
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! Right now you can find out a cheap way to get rid of stomach pain. FIND OUT >>
- severe epigastric pain;
- heartburn;
- attacks of nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- problems emptying the bladder;
- constant desire to sleep;
- swelling of the legs and face;
- tachycardia;
- loss or gain of body weight;
- impaired coordination.
A common cause of gastric hyperemia is an inflammatory reaction that occurs in several forms:
- Moderate. Hyperemic mucosa is characterized by swelling, which looks like a foam-like coating on the top layer. Hyperemia may be accompanied by one focus or the mucous membrane is damaged unevenly. Such signs indicate mild inflammation of the stomach.
- Local. The folds of the mucous membrane turn pale and become thin, and blood vessels are visible. Such manifestations signal atrophic gastritis.
- Phlegmous. The mucous membrane is significantly swollen, which is associated with mechanical trauma to the stomach with a sharp object.
- Fibrous. Hyperemia covers several foci that turn red and fester. A dangerous symptom of this form is vomiting blood.
Preventive actions
To avoid atrophy of the gastric mucosa and other complications, as well as to completely get rid of unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first signs of a clinical picture to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the causes of the development of the pathology.
Twice a year it is recommended to undergo diagnostics using gastroscopy to avoid recurrence of the disease. Take preventive measures prescribed by your doctor in a timely manner. Do not neglect your health, follow all the recommendations of your doctor and do not ignore unpleasant symptoms. If the disease is recognized in time, serious consequences and long-term treatment for advanced pathology can be avoided.
The gastric mucosa is hyperemic, what does this mean?
Regular visits to a gastroenterologist should become normal if a person experiences symptoms of gastritis. It should be understood that the examination helps to see the extent of damage to the gastric mucosa. Based on the results of the study, the specialist can make a conclusion about how hyperemic the gastric mucosa is and what caused this lesion.
Depending on the endoscopy result, the doctor can determine the severity of the disease and prescribe treatment. Before talking about endoscopic criteria for the gastric mucosa, you should know its normal state.
As a rule, the healthy mucous membrane of the stomach is a pink, shiny layer of epithelium, which, when examined, well reflects the light incident from the endoscope. The thickness of the folds is 0.5-0.8 cm. When air is blown into the stomach, the folds straighten.
In the outlet section of the stomach, the mucous membrane is slightly lighter than the mucous membrane of the body of the organ. The folds in most cases have a slight thickening closer to the pylorus, and if there are no other signs indicating pathology in the development of the organ, this is not considered a deviation from the norm.
Some patients have a yellowish tint to the mucous membrane with a distinct villous pattern.
Diseases characterized by hyperemia of the gastric mucosa
In most gastrointestinal diseases, hyperemia of the mucous membrane is observed. As a rule, the type of disease can be determined by its condition.
Superficial gastritis
Superficial gastritis is characterized by a moderately hyperemic mucous membrane. Moreover, inflammation can be both focal and widespread. In this case, its swelling occurs, foamy white mucus forms on the walls of the stomach, the folds have tortuous thickenings, and do not completely straighten out when air is insufflated.
Atrophic gastritis
With atrophic gastritis, thinning of the mucous membrane occurs in one of the sections of the stomach. The atrophy zones have a pale membrane with a clearly defined vascular pattern and thin folds.
Fibrinous gastritis
It occurs due to a severe infection and has hyperemic mucosa with purulent manifestations. Often fibrinous gastritis is caused by measles or scarlet fever.
In this case, the patient usually experiences frequent vomiting of blood. Thus, fragments of the purulent film are rejected, which can cause pain in the patient.
Stomach gurgle
Caused by damage to the duodenal bulb, and is manifested by hyperemia, swelling, thickening of the folds of the intestinal mucosa. Stomach bulbitis occurs due to infection or due to an incorrect lifestyle.
Phlegmous gastritis
Formed due to suppuration due to a foreign body entering the stomach. Often, even an unsuccessfully swallowed fish bone can serve as a provocateur of the disease, which, moving along the esophagus, injures the mucous membrane. Phlegmous gastritis can also be caused by certain sexually transmitted infections.
Necrotizing gastritis
With necrotic gastritis, a burn of the mucous membrane occurs, caused by aggressive chemicals - alkali, acid, ethyl alcohol. As a rule, with this disease, the deep layers of the mucous membrane are affected, with necrosis of individual tissue sections occurring, ulcers and erosions forming.
Hyperemia of the mucous membrane can also occur with other diseases of the digestive system. For example, gastroduodenitis also contributes to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
The doctor’s task is to determine the extent of damage to the diseased organ and establish the correct diagnosis. The hypertrophic form of the disease has hyperemic mucosa, and plaque forms on the walls.
Often in this condition, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, multiple erosions appear, which have fibrinous content.
Typically, hyperemia of the gastric mucosa may indicate specific problems associated with one or another form of gastritis.
After undergoing a series of examinations, the patient is prescribed complex treatment, the effectiveness of which depends on timely treatment and punctual implementation of all doctor’s recommendations.
Intoxic is an anthelmintic that safely removes parasites from the body. Intoxic is better than antibiotics because: 1. It kills parasites in a short time and gently removes them from the body. 2. Does not cause side effects, restores organs and reliably protects the body. 3. Has a number of medical recommendations as a safe remedy.
4. Has a completely natural composition.
Diseases due to gastric hyperemia
In gastroenterology, mucosal hyperemia is associated with stomach diseases such as gastritis and peptic ulcers. In various forms of gastritis, in addition to focal hyperemia, the following signs are observed:
- Spicy . It is characterized by severe hyperemia and swelling of the folds, petechiae, erosions, and copious amounts of thick mucus.
- Chronic . The mucous membrane is pale, dull, grayish in color. Sometimes there are thinned areas (atrophy) with translucent vessels. This is the so-called false hyperemia.
- Superficial gastritis is characterized by diffuse hyperemia, the formation of foamy white mucus, swelling of the folds that do not level out when inflated. Submucosal hemorrhages are sometimes observed.
- Hypertrophic gastritis is characterized by thickening and pronounced diffuse hyperemia of the folds; they acquire a cherry color. Proliferative processes (nodules, warts) are revealed on the surface.
Hyperemia is also present in other forms of gastritis (phlegmonous, necrotic), as well as ulcers. It indicates an inflammatory process. When infected with Helicobacter Pylori, hyperemic manifestations are more pronounced.
Diagnostic methods
Hyperemic changes can only be diagnosed using endoscopy. For diagnosis, fibrogastroduodenoscopy or endoscopic video capsule is used. ultrasound , radiography , CT , MRI visually determine the appearance of the inner layer only indirectly, by identifying swelling of the mucous membrane.
Diet for inflammation of the duodenum
Patients suffering from duodenitis need to adhere to the correct diet, which will promote recovery. First of all, you need to give up rough food, which injures the already damaged mucous membrane. Boiled, grated, stewed and steamed dishes are recommended for consumption.
You need to stop eating salty, spicy, sour and fried foods; marinades and smoked foods are also unacceptable. It is necessary to replace fresh baked goods with bread and crackers. Hot chocolate, alcoholic drinks, lemonade and coffee are completely contraindicated.
Enveloping and gentle foods should take precedence in the diet; these can be casseroles, porridges, purees, jelly, meatballs, cutlets, vegetable and cereal soups. It is very useful to consume low-fat fermented milk products. It is also necessary to observe the rule of fractional and regular diet. The water diet is not the least important: you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day.