Tinea versicolor - has several variant names, such as pityriasis versicolor versicolor; in everyday life it is also called sun fungus. Why sunny? Because it is believed that this skin disease most often appears in residents of countries with hot, humid climates and it manifests itself after exposure to the sun. In Russia, tinea versicolor, according to some statistics, affects only 5-10% of the population.
Pityriasis versicolor affects a certain group of people prone to dermatomycosis, and has the peculiarity of occurring in waves - with periods of subsidence and periods of relapse in the hot sunny season. This is not a dangerous disease that does not pose a threat to human health and is easily treatable, but it can cause a person psychological discomfort and a feeling of aesthetic deficiency or defect.
What it is?
Pityriasis versicolor is a fungal disease that affects the epidermis.
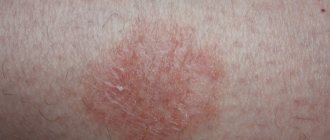
The disease manifests itself in the appearance of pigment spots on the skin, which over time can combine into large affected areas. The color of the spots can be yellow, pink, brown with characteristic peeling, there is no inflammation. Pityriasis versicolor gets its name from the scaling it typically exhibits. It is also called versicolor versicolor due to the different shades that appear during the disease.
The effectiveness of drug treatment
Treatment of versicolor versicolor requires patience from the patient, because in order to completely get rid of the rashes, it takes quite a lot of time.
Traditional methods of treatment, which involve the use of highly active drugs, are very effective, as they help eliminate the root cause of the disease and eliminate the external manifestations of the pathological process.
Important!
Treatment becomes effective only if medications are used correctly and the doctor’s recommendations are followed.
Reasons for development
The causative agent of pityriasis versicolor constantly lives in small quantities in the microflora of human skin. It manifests itself only when favorable circumstances arise for its increased reproduction. These conditions include the following factors:
- Hot climate with high humidity, increased sweating, taking antipyretics.
- Frequent stay in a stuffy room, hard physical work, habit of wearing very warm and synthetic clothes.
- Hereditary genetics.
- Frequent use of fats for skin treatment.
- Long-term use of steroids, antibiotics, some hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives.
- Diabetes mellitus, vascular problems, tuberculosis, oily seborrhea, rheumatism are another reason for the appearance of pityriasis versicolor.
The infection is recognized as non-contagious, so contact with the patient can be free. Transmission of “sun fungus” through household items is very rare. This type of dermatological disease does not actually affect children under 10 years of age and adults over 55, but can seriously complicate the course of other skin diseases.
Possible complications
Lichen versicolor, if left untreated for a long time or with the use of inappropriate medications, can provoke the development of minor complications:
- damage to large areas of skin by newly formed foci;
- the addition of an additional infection causing itching, discomfort, redness of the skin;
- high risk of the disease becoming chronic, characterized by frequent relapses and periods of exacerbation.
Due to the fact that the spots do not tan under the influence of sunlight, in the hot season the pathology causes cosmetic defects in the form of white spots against the background of tanned dark skin. Lichen versicolor is a fairly common disease, for which it is important to start treatment on time using antifungal drugs.
Otherwise, the disease may progress and spread to large areas of the skin. For preventive purposes, to exclude possible relapses, it is important to undergo a repeat course of drug therapy, maintain hygiene and avoid excessive sweating.
Symptoms
Typical symptoms of pityriasis versicolor in humans are:
- The appearance of pink spots with a yellowish color;
- A gradual change in their color to brown pigmentation, localized in typical places (primarily the décolleté area);
- Slight fine-plate peeling of rashes that appear on the skin;
- Intermittent itching of the spots, which is not very intense;
- The skin does not tan in the place where the rash is localized. This is explained by the functional inferiority of melanocytes - skin cells that produce pigment.
To determine if you actually have sunburn, visit a dermatologist. The doctor will check your skin with a lamp - the fungus has luminescent properties. If the skin glows pink or greenish-blue, a dermatologist will diagnose lichen.
In humans, the symptoms of pityriasis versicolor, in the form of itching and burning, are often not expressed. If the doctor suspects the presence of a fungal pathogen, he will send the patient for analysis of keratinized skin flakes.
When to see a doctor
At the first suspicion of the course of the pathology, you should contact a dermatologist.
Alarming symptoms that require consultation with a doctor:
- formation of pinkish or light brown spots in the neck, chest, back, neck;
- pronounced areas of peeling of the skin;
- noticeable growth of the resulting lesions;
- burning sensation, itching;
- the appearance of ulcers and papules in the area of the spots.
Discomfort and purulent processes in the presence of pityriasis versicolor indicate the addition of a secondary infection that has penetrated the skin through the affected stratum corneum.
Effect on pregnancy
Pregnant women, when this pathology is identified, are interested in the question of whether pityriasis versicolor poses a threat to the health of her unborn child. For a baby, lichen is not dangerous. It is important that fungi do not penetrate the placenta and are not dangerous to the fetus. Pityriasis versicolor does not change the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth. The main thing is to identify the problem in a timely manner and competently begin to eliminate it.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor in pregnant women involves the use of antifungal and antiviral drugs.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor is made on the basis of the characteristic appearance of the spots, as well as several tests that make it possible to distinguish the disease from others with similar clinical manifestations, such as vitiligo, pityriasis alba or pink, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, dermatophytosis of the trunk, eczema, cutaneous syphilis.
Currently, the following diagnostic tests are carried out to clarify the diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor and distinguish it from other diseases with similar manifestations:
- Microscopy of scrapings from spots - when examining under a microscope the scales pre-treated with a 20% KOH solution, in pityriasis versicolor, threads of the fungal mycelium and the yeast cells themselves are visible in the form of a characteristic picture with the figurative name “navy pasta”. This means that the mycelium of the fungus appears as long strands, between which are dark, round yeast fungal cells. That is, in total, white strands and dark rounded pieces between them are visible in the microscope, which is reminiscent of the appearance of the dish “naval pasta”;
- Iodine test - spots and surrounding skin are treated with a 5% iodine solution and after a few minutes the intensity of the color is recorded. Pityriasis versicolor spots are dark brown, and their color is much more intense than the surrounding normal skin;
- Examining the spots in the light of a Wood's lamp - with pityriasis versicolor, the spots glow reddish-yellow or greenish-golden;
- Positive “chips” symptom (Bernier’s sign) – when the spot is scraped, peeling appears. The exfoliating particles are very small, similar to flour.
In the vast majority of cases, to diagnose pityriasis versicolor, it is sufficient to study the spots in the light of a Wood's lamp and an iodine test.
How to treat pityriasis versicolor
During the treatment of pityriasis versicolor in humans, the body must be kept clean. At home you need to take a hygienic shower twice a day. Use special antifungal gels for washing. Linen is washed at the highest possible temperatures, treated with steam or a hot iron. Successful treatment of the disease can be achieved through the correct selection of medications. They use drugs containing components to which the pathogen is susceptible.
For effective treatment, the following groups of antimycotic medicinal products for the disease are used for local application to the skin:
- Medicines containing the substance terbinafine. They destroy the membrane structures of fungi, inhibit the growth of colonies, and prevent further spread of stains. Terbinafine-containing drugs are produced in the form of a spray or cream. Treat the skin with the drug twice a day.
- Imidazole derivatives. The drugs block the activity of fungal enzymes. They stop the synthesis of membranes and destroy pathogenic lichen cells. The category of medications under consideration includes Ketoconazole, Miconazole, Clotrimazole, Bifoconazole. They produce drugs in creams and ointments. The body should be covered with the medicinal substance twice a day. For antimycotic treatment of fungus in cases of damage to the scalp, special shampoos with Ketoconazole are used.
- Preparations containing pyroxolamine derivatives. These are drugs such as Ciclopirox, Tolcyclate. Their action is aimed at preventing the penetration of substances necessary for the normal development of colonies into fungi. As a result, the reproduction and functioning of the pathogenic provocateur on human skin is suspended. Preparations in the form of creams or ointments are applied to spots 1 – 2 times a day.
- The drug Nizoral. The duration of the therapeutic course is three weeks. Apply the product to areas affected by fungi twice a day.
- Salicylic-zinc ointment. It is advisable to use the drug at the initial stages of the disease, when there is minimal damage and a small number of spots on the skin. Treatment with the drug continues for 7 days.
For pityriasis versicolor, exfoliating preparations are also used during treatment. They help get rid of scales and stains faster. It is recommended to wipe the skin with a mild solution of salicylic acid and rub in Vilkinska ointment. Demyanovich's technique is also used. Its meaning lies in the sequential treatment of unhealthy skin spots, first with an aqueous solution of thiosulfate 60%, then apply externally a solution of 6% hydrochloric acid.
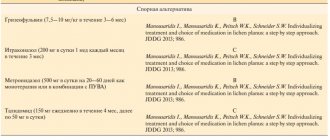
Large-scale fungal infection and frequent relapses of lichen are considered an indication for treatment with drugs that act systemically. Antimycotic drugs such as Orungal, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole are used internally.
The development of lichen in a woman during pregnancy does not pose a direct threat to the fetus. Drugs used to treat fungus can have a teratogenic effect. Many doctors do not advise taking this into account for the treatment of lichen in women during the gestational months. Often, lichen after childbirth goes away on its own, without drug treatment.
Approximate treatment plan for pityriasis versicolor
- Fluconazole – 2 capsules 1 time per week – course 2 weeks.
- Nizoral shampoo - wash your hair and body every evening for the first week. And every other day - 2 and 3 weeks.
- Instead of Nizoral, you can use Thermikon spray for the body - apply once a day to the affected areas for 3 weeks.
- Salicylic acid – lubricate the affected areas once a day in the morning.
- Taking multivitamins (Complivit, Selmevit and others).
Folk remedies
You can use traditional medicine at home only after consulting your doctor, because there is a possibility of developing allergic reactions. You can treat pityriasis versicolor with ointments with herbs and bee products. The finished product should be stored in the refrigerator to avoid souring of the ingredients.
- Blackberry and calendula leaves, mixed in a 2:1 ratio and poured with a glass of boiling water, can cure the disease. To get rid of the symptoms of pityriasis versicolor, you should drink this decoction 3 times a day, half a glass.
- Ointment. For 10 days, lubricate the lichen with fresh sorrel gruel mixed with heavy cream or sour cream.
- Sorrel. A tablespoon of a mixture of horses and sorrel seeds should be boiled in 200 ml of water for 5 minutes and left for an hour, then to lubricate the skin affected by lichen with it or apply compresses to it.
- Beet juice. To prepare a medicine for pityriasis versicolor, use 200 grams of beets and 1 lemon. Juice is squeezed out of beets and juice, the resulting liquid is diluted with water, the total volume of the product should be 300 ml. For two weeks, the juice is taken three times a day, 100 ml.
- Treatment of pityriasis versicolor with vinegar is considered one of the most effective and at the same time simple folk methods. You need to lubricate the areas with ringworm with apple cider vinegar 4-6 times a day for 1 week.
- Garlic. It has antimycotic and bactericidal properties. Garlic juice is applied twice a day to lichen spots.
Additional recommendations
Since sun fungus is not a contagious disease, it can be treated at home. In the initial stages of development, there is no need to resort to the use of potent drugs; in such cases, it is enough to purchase an antifungal shampoo and use it for a certain period.
Shampoos for lichen for humans
The most effective shampoos available without a doctor's prescription include:
- "Mycozoral";
- "Nizoral";
- "Sebozole-ketoconazole";
- "Keto plus";
- "Fitoval" and others.
It is advisable to avoid using creams.
If you are in doubt about the choice of product or have any difficulties, contact the seller for help. Shampoos must be used strictly according to the instructions indicated on the packaging. It is also advisable to avoid using greasy skin creams during the treatment period, as this will slow down the healing process.
Pityriasis versicolor in children
In children under 10 years of age, pityriasis versicolor almost never occurs, since they have protective mechanisms against the negative effects of moisture and high temperature on the skin of the body. However, if a child’s skin is often lubricated with hard fats (for example, butter, cocoa butter, etc.), then he or she may develop pityriasis versicolor even before the age of 7–10 years.
Starting from about the age of 10 years, when children enter prepuberty and their body begins to undergo restructuring with the production of sex hormones, the skin acquires properties like that of adults, that is, it becomes sensitive to high humidity and temperature. As a result, starting from the age of 10 years, children also become susceptible to pityriasis versicolor, which develops in them in the same way as in adults - when an opportunistic fungus transforms into a pathogenic form under the influence of predisposing factors.
Pityriasis versicolor in children usually occurs in exactly the same way as in adults, without any fundamental differences or features. Only its spots on untanned skin in children are often painted in light colors, including white, reminiscent of those on tanned skin. Otherwise, there are no features or differences in the course and treatment of pityriasis versicolor in adults and children, so considering this disease separately in childhood does not make practical sense.
Kinds
The disease is classified into several types, which have a similar course and require the same approach to therapy. Depending on the location of the pathology, it is divided into the following forms:
- Erythematosquamous - appears on the shoulders, back, chest and upper abdomen. It is characterized by the absence of obvious itching.
- Follicular - develops against a background of weakened immunity and in the presence of concomitant pathologies, such as diabetes. It is distinguished by the formation of small pustules on the spots and severe itching.
- Inverted - diagnosed in the folds of the skin and in the groin area. Does not cause inflammatory symptoms.
Without proper treatment, any form of pityriasis versicolor spreads over large areas of the skin. Despite this, the disease is not considered dangerous. In some cases, it progresses for several years without causing complications other than aesthetic discomfort.
After recovery, pathological spots quickly disappear, leaving no scars or other marks.
Prevention
If we take into account the factor in the occurrence of lichen, which is a fungus located in the layers of the epidermis, it is necessary to remove the causes of its occurrence. The patient is prohibited from wearing clothing that caused the disease. He is given several disinfected items to wear.
For a more accurate diagnosis, an iodine test is performed. Apply an iodine solution to the skin, wipe the affected areas with alcohol and monitor the reaction. After this procedure, lichen spots turn dark brown. Also, to identify the pathological pathogen, the doctor prescribes a microscopic examination.
Prevention of pityriasis versicolor involves disinfecting the premises and all objects in order to prevent the spread of infection. If one of the family members is infected, the rest must be examined using a fluorescent lamp. Next, all clothes and bedding need to be washed and ironed on both sides with a hot iron. You should not stop visiting a dermatologist until he says that you are completely healthy.