Iodine is a chemically active element of the halogen group, which plays an important role in the human body:
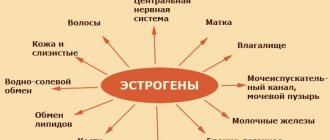
- Normalizes the functions of the thyroid gland;
- Regulates the functioning of the central nervous system;
- Supports and strengthens the immune system;
- Improves the functions of the cardiovascular system;
- Participates in the formation of tissues;
- Strengthens oxidative processes;
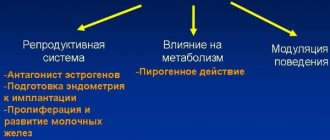
- Ensures normal cell metabolism, in particular, takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, as well as in water-salt metabolism;
- Influences the physical and psychological development of a person;
- Regulates heat exchange processes.
A safe daily dose of iodine is considered to be up to 500 mcg. If for medical reasons it is necessary to take higher doses, then treatment is carried out under strict medical supervision.
Compared to the iodine deficiency state, the phenomenon of excess iodine in the body is practically not common, but it also occurs. Most often, people working in production where iodine is mined or used suffer from an excess of this element. To ensure normal operation, according to sanitary standards, the concentration of vapors in the workplace should not exceed 1 mg/m3. If this indicator is in the range of 1.5-2 mg/m3, work becomes difficult, and at a dose of 3 mg/m3. – impossible.
Potential causes of pathology
There is an opinion that a deficiency of one or another element is a much more dangerous phenomenon than its slight excess.
But, as practice shows, an increased concentration of iodine is extremely dangerous for the entire body . And the reasons for this pathology are very banal:
- unbalanced diet, in which foods containing iodine lead;
- long-term residence on the sea coast;
- individual intolerance to the element;
- direct contact (oral consumption, overdose of iodine preparations, inhalation of iodine vapors).
ATTENTION! Very often, pathology is provoked by several factors at once.
It is important to know the amount of iodine consumed per day and the signs of iodine deficiency.
Actions of iodine
The content of the article
The most important effect of iodine is antimicrobial and it is used as an antiseptic. It has an irritating effect on the skin and mucous membranes.
By using iodine preparation internally, cholesterol is reduced, thereby it has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes, accelerating them.
Iodine affects the functioning of the thyroid gland on two fronts, namely, in hypothyroidism it takes part in the formation of thyroxine, and in case of hyperfunction in small dosages it inhibits the formation of thyroxine. Organic iodine compounds are used as radiocontrast agents.
Consequences of excess
If the microelement level is really elevated, then what does this pathology lead to ? In addition to the fact that the endocrine system suffers a real collapse...
- rapid breakdown of fats/carbohydrates (as a result: weight loss, despite good nutrition, increasing portions consumed);
- heat exchange disturbance;
- failure of the cardiovascular system;
- irritation of the mucous membrane/conjunctiva/salivary glands;
- decreased immunity;
- iododerma or skin lesions;
- iodism (acute/chronic iodine poisoning);
- development of Graves' disease, hyperthyroidism.
What are the dangers of using iodine with sugar?
As practice shows, this is a fairly common phenomenon not only in the “treasury” of traditional medicine recipes, but also among the ingenuity of schoolchildren who want to provoke an increase in body temperature in this way and skip classes. Pregnant women also sometimes experiment in order to get rid of an unwanted pregnancy by inducing an abortion at home.
But sugar and iodine are not a harmless combination, and what will happen if you eat a piece of such medicine will only be shown by the consequences in the form of severe poisoning, resuscitation and possible disability. After all, an artificial increase in body temperature is caused not by the mixture of sugar and iodine itself, but by a burn of the esophagus/stomach.
The patient will be lucky if the result of the experiment is only a rash, gastrointestinal upset, nausea/vomiting.
IMPORTANT! Unfortunately, often these same consequences are tragic, since the lethal dose of this element for a person is only three grams of solution. For a child's body, half of this dose will be enough. In the best case, the patient will survive, but his immunity will be impaired, and the thyroid gland will be completely disabled.
Artificially fortified foods with iodine
Since the problem of iodine deficiency has long acquired global proportions, familiar products fortified with iodine began to be produced: salt, drinking and mineral water, baked goods, milk, etc.
Iodized salt can be found in every home, but for it to be truly healthy salt, a number of conditions must be met:
- salt retains its beneficial properties only 3-4 months from the date of release;
- if the salt is wet or stored in an open container, some of the iodine will also evaporate;
- Iodine immediately leaves salt when it is boiled, so you need to salt already prepared and slightly cooled dishes;
- This type of salt cannot be used when pickling vegetables, since natural fermentation may not take place and the products will acquire a bitter taste.
The main signs of excess
The signs of pathology are quite obvious, but often they can be attributed to the clinical picture of other diseases:
- chronic inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane;
- rash of various types, which is accompanied by severe itching/burning;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (prolonged diarrhea);
- kidney dysfunction;
- decreased immunity;
- frequent diseases of the respiratory system;
- toxic hepatitis;
- chronic weakness, headaches, nausea, constant thirst, metallic taste in the mouth.
Iodism or poisoning
Iodine is vital for the entire body and its organs/systems. BUT! The optimal microelement concentration is very low:
- Adult patients - about 150 micrograms
- Children - 50-110 micrograms
- Pregnant women - up to 200 micrograms.
Even a slight increase in these numbers will provoke hormonal imbalance, cardiac dysfunction, damage to the nervous/respiratory/digestive systems, as well as the musculoskeletal system.
Is it possible to get poisoned by this chemical element? Yes, you can. This phenomenon is called “iodism”. Moreover, often a person does not even suspect that the body has received a lethal dose of a microelement. After all, the symptoms and signs of iodine poisoning (sometimes even with drug vapors) are quite vague/general, and the consequences are often fatal and simply do not wait for treatment.
Therefore, you should not find out in practice what will happen if you drink iodine, not a lot, even a drop with water or sugar. After all, poisoning in the traditional sense of the word is the minimum price for such carelessness.
Menstrual irregularities
An unstable menstrual cycle is a symptom of the initial stage of iodine deficiency, since the lack of iodine directly affects the functioning of the hormonal system. The state of iodine deficiency in women can be fraught with infertility and premature onset of menopause. Lack of iodine is no less dangerous during pregnancy: the lack of a vital element can have a detrimental effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus and lead to spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, and congenital pathologies.
Symptoms of excess iodine in the body
The symptoms of any disease are often individual and depend on many factors. Sometimes even the gender and age of the patient plays a role.
In men
In addition to the common symptoms of iodism (alternating diseases of the main organs/systems, rapid deterioration in health, skin rashes, hyperthyroidism, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes and nasopharynx), men often experience a significant deterioration in potency . Moreover, this is one of the main “alarm bells” of the disease, especially if there are other symptoms.
Among women
Symptoms of excess iodine in the body in women have more serious signs and consequences during an interesting situation.
Yes, it is vital for the normal course of pregnancy and intrauterine development of the baby, because the development of the baby’s brain/bone tissue directly depends on the concentration of this microelement.
But do not forget that its increased level in a pregnant woman can provoke miscarriage/premature birth or serious pathologies of fetal development. Read about iodine requirements for pregnant women.
This outcome can result from Graves' disease, hyperthyroidism, goiter, tachycardia, and other diseases of the cardiovascular/nervous/respiratory systems.
IMPORTANT! Symptoms of excess iodine in the body in women who are not “in position” are not much different from the signs and consequences of pathology in men. Is it possible that the female sex is more dependent on hormonal levels?
In children and adolescents
For a young organism, the required concentration of the element is determined in relation to age and weight category .
Even a slight excess of the norm can be accompanied by allergic reactions, weakness, emotional instability, weight loss, chronic acute respiratory viral infections, and impaired development of the musculoskeletal system.
Sources of iodine and consumption rates
Iodine enters our body only from the outside - with food and vitamin supplements, so it is always important to maintain a balanced diet.
The largest amount of iodine is contained in seafood - fish, crustaceans, algae and other sea inhabitants. There is much less of it in plant foods - cranberries, prunes, buckwheat, potatoes, rowan berries, etc. Considering the fact that in Kazakhstan there is a problem of iodine deficiency in the soil, the content in local products is negligible.
Over the course of a lifetime, a person needs only about 3–5 g of this substance. According to WHO, the recommended iodine intake for an adult is 150 mcg per day. This is approximately 70 g of seaweed or 100 g of pollock.
Of course, not all people love fish and seafood. Therefore, to compensate for the deficiency, experts recommend using iodized salt, nutritional supplements and medications. And this is where you need to be careful. If you don’t eat a lot of salt, uncontrolled use of medications and vitamin supplements can cause an overdose of iodine.
Risk group
The first places in the risk group for the development of iodism are rightly occupied by several categories:
- people who work in chemical plants;
- residents of coastal areas;
- patients/future mothers who have been taking medications containing iodine for a long time;
- people whose diet is dominated by foods high in this microelement;
- children with access to the drug solution.
CAREFULLY! The last category should be under the constant supervision of parents. Moreover, they must first of all remember the potential danger by limiting their child’s access to a home first aid kit.
Yodism and its causes
According to world statistics, more than 200 million people suffer from excess iodine, and almost a billion people are at risk.
The causes of iodism include:
- inhalation of iodized vapors (as a rule, this is the cost of harmful work);
- long-term use of drugs containing such an element;
- consuming iodine in quantities several times higher than the daily norm;
- iodine intolerance;
- sensitivity to iodine and iodine-containing drugs.
Diagnosis of the disease
Often the main factor that indicates an excess of iodine is the symptoms of the pathology. Yes, the doctor simply compares the patient’s complaints, the obvious clinical picture, his occupation, the medications he has taken recently, his place of residence and makes a diagnosis.
If signs/symptoms are insufficient, the patient may be referred for blood/urine testing.
This is interesting! Read the article about the importance of iodine for humans, its benefits and harms.
Treatment
Drawing up a therapeutic algorithm directly depends on the type of iodism:
- If the poisoning is acute, the ambulance team will begin to treat the pathology: the patient’s stomach is washed with sodium thiosulfate (5% solution), and the skin is cleaned.
- In case of chronic iodism, the doctor determines the routes of entry of the chemical element into the body and temporarily blocks them. At the same time, an algorithm for restoring the thyroid gland, digestive tract, and other affected systems is being drawn up.
But, unfortunately, sometimes minutes count, especially when it comes to children . Parents should remember what to do if their child drank iodine and react immediately before the baby loses consciousness. Namely:
- call an ambulance;
- give the victim several glasses of warm water to drink, inducing vomiting after each of them;
- after gastric lavage - activated carbon.
ATTENTION! How long it takes to be removed, how to remove it and how to reduce the excess of a microelement can only be answered by a qualified specialist, who should be contacted when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
When does an overdose occur?
- Taking medications and iodine supplements. There are quite a lot of pharmaceuticals containing potassium iodide. There is an even greater selection of dietary supplements containing this component. Tablets are standardly dosed at 100 and 200 mcg. When accidentally or intentionally taking 15–30 tablets at a time, a toxic amount of iodine enters the body.
- Unconventional use of iodine combinations. Unfortunately, some alternative medicine recipes contain dosage forms containing iodine that are not used for therapeutic purposes. This could be advice: take iodine solution orally, add it to mixtures for rinsing, inhalation, make iodine nets. Such recommendations are not consistent with the text of the official instructions.
A 5% iodine solution contains 5 g of this substance in 100 ml of alcohol solution, and there is only one way to safely use it - topically, on wound surfaces (this is also written on the packaging). At the same time, possible side effects are indicated that are observed with prolonged use and application to large wound surfaces. Despite this, some patients deliberately violate the instructions and are treated in an unconventional way.
It is easy to calculate that one drop of such a solution contains 2.5 mg of iodine. Two drops is already a toxic dose! Taking 60 ml of this drug solution can be fatal.
- Conditions associated with problems with microelement excretion:
- chronic kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, renal failure);
- chronic hyperkalemia, treatment with potassium-sparing diuretics and ACE inhibitors.
- Allergic manifestations:
- dermatitis herpetiformis;
- intolerance to iodine-containing products and substances.
- Iodine intoxication in workers of specialized industries. Employees of chemical extraction and processing facilities must wear gloves, respirators and protective clothing. Failure to follow safety rules and neglect of personal protective equipment leads to poisoning. The maximum permissible concentration of iodine in water is 0.125 mg/dm3, in air – 1 mg/m3.
- Working with radioactive isotopes of iodine . These components are synthesized, in particular, for radiation therapy of thyroid cancer.
Prevention
The best option for preventing pathology is to exclude a potential threat . We are talking about changing activities (if this is the reason), place of residence, discontinuing certain medications, adjusting the diet and minimum safety rules. Especially when it comes to young children.
And away with experiments. After all, it is better not to know in practice how iodine vapor affects a person, what a sip of brown liquid will entail, and what the dangers of excess iodine in general are.
5 / 5 ( 20 votes)
LiveJournal