Hemangioma is the most common benign liver tumor that looks like a tangle of dilated blood vessels. It does not increase the risk of cancer, but it may lead to some other complications. According to various scientific studies, hemangiomas occur in 0.5–20% of the population. Most often they are asymptomatic, and a person may not know for the rest of his life that he has such a pathology.
Our expert in this field:
Ryabov Konstantin Yurievich
Chief surgeon, oncologist, endoscopist
Call the doctor
In most cases, hemangiomas are discovered by chance when being examined for another reason. The average age of patients at the time of diagnosis is 30–50 years. Women get sick 4–6 times more often than men.
Why do liver hemangiomas occur?
The exact causes of hemangiomas are unknown. It is believed to be a congenital disorder that occurs due to abnormal development of blood vessels. The liver tumor hemangioma is present in the human body from birth, but its growth appears to be enhanced by certain factors:
- Taking estrogen and steroid medications. For example, in one study that followed the condition of 94 patients for 7 years, it was found that hemangiomas grew in 23% of women receiving estrogen drugs, but in only 10% of women in the control group.
- Often tumors begin to grow during pregnancy. It is also believed to be due to hormonal changes.
- There are cases where hemangiomas were recorded in women during pregnancy after stimulation of the ovaries with the drugs clomiphene citrate and human chorionic gonadotropin.
Possible complications
Despite the optimistic prognosis, liver hemangioma can cause severe consequences, including death. Dangerous complications are:
- rupture of angioma (regardless of the cause) leading to massive internal bleeding;
- oppression of nearby organs with disruption of their functioning;
- necrosis of tumor tissue due to vascular thrombosis.
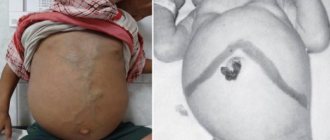
In addition, complications of vascular angioma include possible postoperative disorders, in particular, the formation of a hernia along the surgical scar.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
Liver hemangioma in adults most often does not cause symptoms. Typically, large (giant) hemangiomas with a diameter of more than 10 cm become symptomatic. The patient may experience the following complaints:
- Pain in the upper abdomen on the right (under the right rib).
- Fast saturation. After taking a small amount of food, a person feels full.
- Nausea and vomiting.
These symptoms are nonspecific. They occur in various diseases, and an accurate diagnosis cannot be made from them. Usually, if there is a suspicion of liver pathology, the first thing the doctor does is prescribe an ultrasound examination to the patient. The sensitivity and specificity of the method increases if ultrasound is combined with color Doppler sonography. In this case, it is possible to obtain more useful information and make a more accurate diagnosis.
A modern accurate method for diagnosing hemangiomas and other liver formations is ultrasound with contrast. This is a relatively new technique and is not used in all clinics.
To confirm the diagnosis, a computed tomography scan or MRI is performed. If CT is performed, it is advisable to perform it with dynamic contrast. Images are taken without contrast enhancement, then a contrast agent solution is injected intravenously into the patient and the images are taken again.
An even more informative diagnostic method is MRI. It can detect small hemangiomas that cannot be detected by ultrasound and computed tomography. The tumor is best seen on T2-weighted images. In order to make the images more informative, intravenous gadolinium contrast is used.
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to arteriography - an X-ray examination during which a solution of a radiopaque substance is injected into the artery.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Forecasts
The prognosis for liver hemangioma is favorable, since it is a benign disease that does not degenerate into malignant. It is important to follow all doctor's instructions to obtain the expected result.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital help patients get rid of hemangiomas using the most modern and effective methods. The conditions in the hospital will allow the patient to feel comfortable, and the friendly and qualified medical staff will do everything to make the stay in our clinic as comfortable and enjoyable as possible.
Make an appointment
In what cases should a patient with liver hemangioma be treated?
This is a complex question, and in order to get an answer to it, you need to contact an experienced medical specialist. As mentioned above, in most cases, liver hemangiomas do not grow and do not cause any symptoms; they are discovered by chance. Even if the tumor grows, it usually grows very slowly. This can only be noticed based on the results of examinations over time, over long periods of time. Moreover, even if the formation is large, this does not mean that it will cause symptoms or lead to complications.
In one prospective study, doctors monitored the progress of liver hemangiomas in 47 patients. After 1–6 years from diagnosis, the tumor increased in size in only one person. Not a single case of hemangioma transformation into a malignant tumor was identified. Other studies have not identified any contraindications for pregnancy and oral contraceptives in women with asymptomatic liver hemangiomas. In most patients, conservative measures can be used.
The question remains whether repeat X-ray examinations are needed after a person is diagnosed with liver hemangioma, and if so, how often. Some experts recommend repeat X-ray examinations after 6 and 12 months. If no changes in dynamics are detected, repeated x-ray examinations are not necessary. But there are exceptions, in some cases regular monitoring is recommended:
- If you have abdominal pain, the cause of which cannot be determined.
- In women - during pregnancy and taking estrogen medications.
- If the hemangioma has a diameter of 10 cm or more, the risk of complications is increased.
Diet
Any gastrointestinal disease requires a special diet, regardless of the chosen course of treatment. Failure to comply with nutritional rules threatens tumor growth or the development of side complications. The menu for liver hemangioma should primarily consist of:
- seasonal vegetables, fruits, rich in fiber and vitamin B12;
- sea and river fish;
- livers of animals and birds;
- lean meat;
- dairy products (kefir, cottage cheese, low-fat cheese);
- liquid dishes.
The following products are contraindicated for liver hemangioma:
- fatty spicy foods;
- carbonated drinks and strong coffee;
- canned foods;
- pickles and other foods high in salt;
- sugar and products containing it;
- smoked food.
By following a diet and following all the doctor’s recommendations, you can get rid of hemangioma in a short time.
Surgical treatment of liver hemangioma
There are four main groups of indications for surgical treatment of liver hemangiomas:
- If the patient is bothered by severe symptoms.
- If the hemangioma grows very quickly.
- If the results of the examination cannot determine whether the tumor is a hemangioma or a malignant neoplasm.
- If complications arise, for example, spontaneous rupture of a hemangioma.
Most often, the surgeon removes only the tumor (enucleation - peeling away from surrounding healthy tissue) or the part of the liver in which it is located (resection). In very rare cases, when the tumor is gigantic, inoperable, or causes serious complications, a liver transplant has to be resorted to.
There are also minimally invasive interventions:
- Embolization is a procedure during which a special drug consisting of microscopic particles is injected into the hepatic artery. They clog the lumen of the vessels feeding the hemangioma, which leads to its death. At the same time, healthy liver tissue does not suffer due to the “spare” blood supply routes.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) involves inserting a needle-electrode into the tumor, to which radiofrequency waves are applied. Due to this, pathologically altered tissues heat up and die.
- Microwave ablation (MWA) is a procedure similar to RFA, but during it, waves in the microwave range are applied to the electrode. This is a more modern method; it allows you to destroy larger formations compared to RFA.
- Cyberknife is a device that generates X-rays, they are focused at the location of the tumor and destroy it, practically without affecting the surrounding healthy tissue. This method refers to stereotactic radiosurgery.
- Radiation therapy to the liver is currently practically not used due to the risk of serious complications and the availability of safer treatment methods.
Is it necessary to operate on a person who has a large liver hemangioma? How high are the risks of dangerous complications in such cases? Doctors and scientists often discuss this topic; there is no clear answer. In each situation, the decision must be made individually.
Treatment tactics
If medical intervention is necessary, the optimal treatment is determined - conservative or surgical. There are no general rules; all appointments are made on an individual basis.
- Drug and non-surgical treatment. Therapy is traditionally carried out with hormonal drugs: the patient takes medications in the form of tablets according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. In addition to medications, modern non-invasive techniques are used, including microwave and radiotherapy, electrocoagulation, laser and cryotechnologies.
- Surgery. If the tumor grows beyond 5 cm, surgical intervention is recommended. The significant size of the tumor interferes with the functioning of the gland, compresses nearby tissues and organs, and the risk of its rupture increases significantly.
Surgery, the only radical treatment for the disorder, can be performed:
- planned, when during the operation the hemangioma itself and all its structural units are removed (if the tumor is multiple);
- urgently - in case of rupture or threat of damage to the tumor membrane, which will lead to massive internal bleeding, dangerous to the patient’s life.
If surgery is necessary, the intervention is carried out using the method that is optimal in each individual case (taking into account the size of the vascular angioma and its location).
Basic removal methods:
- resection – excision of part of the gland;
- enucleation – desquamation of the hemangioma itself.
Today, minimally invasive (laparoscopic) methods have begun to be used in surgical practice, when the operation is performed through small approaches. This intervention has its limitations; serious preoperative preparation is required, but the recovery period is significantly reduced.
Conservative therapy
The possibilities of conservative therapy in the treatment of liver hemangiomas are very limited. Until recently, no medications were known that could stop tumor growth. In recent years, there have been reports that targeted drugs may help:
- In 2008, a case was described of a decrease in the size of a liver hemangioma in a patient who received the drug bevacizumab (Avastin) for colon cancer. This medicine blocks VEGF, a substance that stimulates the growth of new blood vessels that feed tumors.
- Another case involved a 20-cm hepatic hemangioma in a 76-year-old patient. Using the targeted drug sorafenib, a multikinase enzyme inhibitor, the tumor volume was reduced from 1492 ml to 665 ml.
Classification
In world medical practice, there are several varieties of this tumor:
- cavernous hemangioma of the liver, which is several free cavities connected into a single one;
- capillary hemangioma of the liver forms a large number of small cavities, each of which houses a blood or venous vessel.
Along with the most common ones, venous, cluster-shaped hemangioma, and hemangioendothelioma can also occur.
Diagnostics
Studies that are carried out during diagnosis:
- Ultrasonography . Ultrasound is used, which is absolutely harmless to the patient.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) . Thanks to magnetic fields, an accurate image of organs and internal anatomical structures of the human body is created. This is absolutely harmless to the patient.
- CT (computerized axial tomography) . It shows the organs and internal structures of the human body very accurately, but exposes the patient to a minimal dose of x-ray radiation. The images shown are flat.
- Computerized single photon emission tomography (SPECT/SPECT) . It is similar to a CT scan, except that the images are in three dimensions (3D) and use ionizing gamma radiation.
Since in most cases liver angiomas are asymptomatic, their identification is often accidental and in many cases the result of some other diagnostic test carried out for problems of a different nature.
Prevention
Since vascular angioma of liver tissue is a hereditary disease and it appears in utero, no preventive measures have been developed against its occurrence. As preventive measures, a healthy diet, an active lifestyle and giving up bad habits (alcoholism, smoking) are recommended, as this helps reduce the likelihood of the disease.
The disease can be completely asymptomatic and, when detected, does not always require treatment. In addition, there are cases of spontaneous disappearance of hemangioma for no apparent reason. But, of course, once a tumor is detected, the best way to prevent its further growth is to live a healthy lifestyle and not overload your liver.