Enlarged liver, or hepatomegaly, is characterized by pathological enlargement of this organ. Medicine knows of cases where the weight of the liver reached 15 kilograms. If this symptom is not eliminated in a timely manner, then a life-threatening illness – liver failure – may develop. It should be noted that the presence of this symptom does not always indicate pathologies in the liver area. Quite often, the manifestation of this symptom may indicate the development of pathological processes in other organs and systems of the body.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
General information
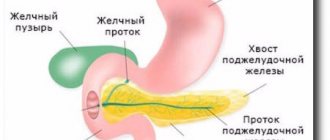
Pathological enlargement of the liver in medicine is called hepatomegaly .
This condition develops in many liver diseases, as well as in diseases of other organs and systems, chronic infections, parasite infection, tumor infiltration, etc. In liver diseases, this symptom is most often observed. In some cases, the liver can reach very large sizes and weigh more than 10 kg. However, when talking about what hepatomegaly is, it should be taken into account that an enlarged liver may indicate many pathological processes. Accordingly, the diagnosis of hepatomegaly means that the doctor must determine the underlying causes of this condition and provide adequate treatment. ICD diseases - K76 (other liver diseases). Why a person develops hepatomegaly, how this condition is treated, and what to do to prevent it will be discussed in this article.
Is partial liver removal a health risk?
The liver is able to restore its previous volume and function as soon as possible after resection
It is quite understandable for a patient who does not decide to undergo surgery, believing that the removal of part of this organ will entail lifelong health problems. It would seem that such an opinion is logical, but, fortunately, in reality it is wrong.
Liver tissue, like no other tissue in the body, has amazing abilities to restore both its original size and its functions. Even the remaining 30% of the liver tissue volume after damage or surgical removal is capable of complete recovery within a few weeks. Gradually it grows with lymphatic and blood vessels.
The reasons and mechanisms of such properties have not yet been fully studied, but they make it possible to expand the scope of surgical interventions. Thanks to the rapid recovery, partial organ transplantation from a living donor has become widespread practice. On the one hand, the patient does not lose precious time waiting for a cadaveric liver; on the other hand, within a period of 4-6 weeks, both the donor and the patient are completely restored to normal size.
Practice has established that even after removing 90% of the liver, with skillful management of the postoperative period, it completely regenerates.
Advice : it is not at all necessary to stay in a hospital for the entire period of organ recovery. It is also possible to restore the liver at home if you follow doctor’s orders and under his supervision.
Pathogenesis
Speaking about the pathogenesis of this condition, experts consider several possible options for its development. In this case, either a true enlargement of the liver may occur due to damage to the vascular bed, a neoplastic or infectious process, or other changes - intoxication, degenerative, traumatic, endocrine, autoimmune. Changes can also occur at the anatomical level.
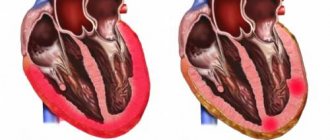
With the development of pathological processes, the liver increases in size and its structure becomes denser. In hepatosis, the process is caused by dystrophic changes in the liver cells, in acute hepatitis - by lymphomacrophage infiltration. If cirrhosis , nodes form in the liver and fibrosis occurs. If the veins of the liver are affected or heart failure , the enlargement of the organ is associated with blood stagnation. With tumors and abscesses focal changes occur.
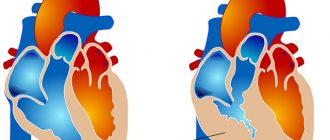
Hepatolienal syndrome
Pathological processes in the liver cause an enlargement of the spleen. The simultaneous enlargement of two organs is called hepatolienal syndrome. The condition is typical for children and is explained by physiological and anatomical features of development.
The development mechanism is determined by the presence of congenital defects and infectious diseases:
- various pathologies of the blood vessels of the liver and spleen, for example, thrombosis and vasculitis;
- with focal and diffuse liver lesions;
- due to excess iron accumulation;
- amyloidosis;
- Gaucher disease;
- hepatocerebral dystrophy.
Helminths and pathogens of various infectious diseases, together with the liver, also infect the spleen.
To carry out therapy, it is necessary to identify the common cause that provoked the development of hepatolienal syndrome.
Classification
When making a diagnosis, the condition is classified from an anatomical and morphological point of view. The following types of damage are distinguished:
- bile ducts;
- parenchyma;
- connective tissue;
- vascular network.
In addition, during the diagnostic process it is noted whether hepatomegaly is combined with jaundice , enlarged spleen or ascites .
Hepatosplenomegaly is an enlargement of the liver and spleen. This condition can occur in a number of diseases and conditions. These are liver diseases, infectious and parasitic diseases, metabolic diseases, etc. Since an enlarged liver and spleen is a typical manifestation of many diseases, it is very important to promptly identify this condition and conduct additional examinations.
Taking into account the degree of liver enlargement, the following types of hepatomegaly are distinguished:
- Moderate – the size and structure are slightly changed. Moderate hepatomegaly is the easiest to treat.
- Pronounced - the organ is enlarged by 10 cm relative to the norm.
- Diffuse – an increase of more than 10 cm.
Partial hepatomegaly is distinguished separately, which is characterized by an uneven increase - the process affects only a part or one lobe.
Depending on the reasons for the development of such a pathological process, the following forms are distinguished:
- Drug injury – develops as a side effect when using certain medications.
- Toxic damage - occurs as a result of the influence of toxins - household (polluted air), natural (consumption of poisonous mushrooms), industrial (work in hazardous enterprises).
- Alcoholism is a very common form. fatty liver , alcoholic hepatitis , fibrosis , and cirrhosis can develop .
- Viral infection - occurs due to infection with hepatitis B and C.
- Infectious lesions - characteristic of mononucleosis , hepatitis A.
- Immune damage is a consequence of malfunctions in the immune system, when antibodies “erroneously” act on the liver.
- Cancerous lesion is a consequence of oncological processes. It can develop with ineffective treatment of hepatitis and cirrhosis .
- Dystrophic damage is a consequence of changes in the volume of liver cells and the accumulation of fat in them. This type of injury is called hepatic coma and can be fatal.
Modern interventions, robotic liver surgery
Today, liver surgery is no longer limited to a scalpel and laparoscope. New technologies have been developed and used, such as ultrasound resection, laser, and electrical resection. Operating robotics are widely used.
Thus, FUS (high-frequency focused ultrasound) technology is used to remove areas affected by a tumor. This is a Cavitron device, which destroys and simultaneously aspirates (suctions) the tissue to be removed, while simultaneously “welding” the crossed vessels.
A high-energy green laser is also used, which is most suitable for removing tumors and metastatic nodes by vaporization (evaporation). More recently, the electroresection (IRE) or nanoknife method has been introduced, based on the removal of diseased tissue at the cellular level. The good thing about this method is that you can remove a tumor even near large vessels without fear of damaging them.
Finally, the know-how of modern surgery is robotics. The most common use of the da Vinci surgical robot. This operation is performed minimally invasively, by the “hands” of a robotic surgeon, under the navigation of a tomograph. The doctor monitors the process on the screen in a three-dimensional image, controlling the robot remotely. This ensures maximum accuracy, minimum errors and complications.
The modern level of medicine and surgical technology makes it possible to safely perform operations on such a delicate organ as the liver, up to the removal of large volumes of it, with subsequent restoration.
We recommend reading: intestinal resection with anastomosis
Causes of liver enlargement
Liver enlargement can be caused by various reasons. In adults and children, this organ may enlarge due to the influence of one or more factors.
Most often, the causes of enlargement of the left lobe of the liver or the right lobe are associated with the following diseases and conditions:
- Neoplastic processes - the development of tumors, mainly metastatic, as well as hemangiomas or adenomas .
- Disturbances in the vascular bed - the hepatic and portal veins can be affected due to the formation of a blood clot. Also, such disorders may be a consequence of pathology of the hepatic artery, Budd-Chiari syndrome .
- Degenerative lesions - non-alcoholic steatohepatitis , steatohepatosis .
- The influence of substances toxic to the liver - alcohol abuse, taking medications.
- Infectious viral processes - infectious mononucleosis , viral hepatitis , nonspecific cholangitis , etc.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Amyloidosis.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Injuries.
In addition, experts identify some factors that increase the likelihood of developing hepatomegaly:
- Regular alcohol abuse.
- Long-term use of high doses of medications, vitamins, biological additives.
- Excess weight , unhealthy and irrational nutrition.
Types of liver surgery
Liver
The scope of interventions can vary from removal of a small area to complete removal of the organ (hepatectomy). Partial hepatectomy or liver resection can be economical (marginal, transverse, peripheral), and called atypical. In typical interventions, the anatomical segmental branching of the vessels is taken into account; a segment or the entire lobe can be removed - lobectomy. Their volume depends on the nature of the pathological focus.
For example, in case of cancer metastases, a lobe is completely removed - right or left. For cancer that has grown into the pancreas along with the left lobe, resection of the tail of the pancreas is performed. In cases where there is extensive tumor or cirrhosis, a total hepatectomy (complete removal) is performed and an orthotopic liver transplant is immediately performed - a transplant from a donor.
Two methods of intervention are used:
laparotomy or open - through an extensive incision in the abdominal skin; laparoscopic or minimally invasive - by introducing a laparoscope with a video camera and special instruments into the abdominal cavity through small skin incisions.
The choice of method is carried out individually. For example, laparoscopic removal of a small benign liver tumor can be performed, but if it is affected by cancer and metastases, a laparotomy is required.
Symptoms of liver enlargement
Signs of hepatomegaly are associated primarily with true enlargement of the liver. It is diagnosed if the size of the organ along the right midclavicular line is more than 12 cm, or its left lobe is palpated in the epigastric region. In normal condition, the liver is soft and can be easily felt under the ribs.
It is also important to take into account the fact that there are no nerve endings in the liver, so even with the development of pathological processes, symptoms may not appear. Often, in the initial stages, adults periodically experience only minor discomfort or pain at the location of the organ. Only during an ultrasound examination can characteristic echo signs be determined.
Symptoms of liver enlargement
Consequently, signs of liver enlargement in adults, and sometimes in children, are often diagnosed already in the later stages, when the pathological process is already actively developing. Then a more pronounced clinical picture is observed. If the liver is enlarged by 2 cm or more, the following signs may be observed as the pathological process develops:
- Discomfortable sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium. They may worsen after eating and physical exertion.
- A feeling of heaviness after consuming a small amount of water or food.
- Periodic heartburn .
- Belching with an unpleasant odor.
- Disorders of the digestive system - constipation , diarrhea , nausea, periodic vomiting. Possible vomiting of bile.
- Discolored stool that may contain particles of undigested food.
- Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, yellowness of the sclera of the eyes. The skin may also take on a sallow tone.
- Itchy skin.
- Sudden mood swings, irritability.
- Drowsiness or insomnia .
- Tachycardia.
- Heavy sweating.
- High blood pressure .
- Pain in the chest area, feeling of tightness.
- When palpating the liver at a doctor's appointment, a person may feel pain.
Normal liver size in adults
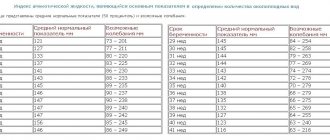
Speaking about the size of an organ, it is necessary to stipulate by what methods they are assessed. When determining parameters by tapping (percussion), their normal values are 9x8x7 cm. They can vary depending on the patient’s height. For values above average, liver measurements may be 1 cm larger. With small growth, they decrease by 1 cm.
When palpated in a state of absence of disease, this parenchymal organ is located in the right hypochondrium and does not extend beyond the boundaries of the costal arch. If the edge is found lower, this may be a sign of hepatomegaly or organ prolapse due to enteroptosis or diseases of the chest organs (emphysema, etc.). To clarify the reasons for the protrusion of the liver edge below the ribs, it is necessary to use percussion, ultrasound or chest x-ray.
The normal parameters of the organ when examined using an ultrasound device in the anteroposterior direction are 12.5 cm when measuring the right lobe and 7 cm when measuring the left lobe. The transverse size is 20–22 cm. The size of the vascular bundle of the liver is also important.
Tests and diagnostics
To determine the presence of hepatomegaly and the causes of such manifestations, the examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The doctor conducts a detailed survey of the patient about complaints and examines the medical history.
- Next, palpation is performed to determine the size, boundaries and density of the liver.
- It is important to determine the results of a general and biochemical blood test. Using the data obtained, it is possible to determine the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes and assess the level of liver enzymes . A general urine test is also performed.
- Markers of viral hepatitis are determined.
- An ultrasound of the liver is performed. This is a fairly informative method that allows you to determine the condition of the liver, portal vein, and hepatic artery.
- Informative studies are CT and MRI.
- If necessary, the doctor prescribes a laparoscopic examination.
- According to indications, a puncture is performed and material is taken for a biopsy .
In the normal state of the organ, its length is 14-20 cm, its cross-sectional size is 20-22.5 cm, in the sagittal plane - 9-12 cm. The length of the right lobe is 11-15 cm, the thickness of the left lobe is approximately 6 cm, and its height is less than 10 cm. Deviations can be no more than 1.5 cm.
Hepatomegaly is diagnosed if the size of the organ exceeds 12 cm or an increase in the left lobe of the liver is noted (in this case it is palpated in the epigastric region). During the diagnostic process, liver prolapse and the location of other tissues in the right upper quadrant (this could be tumors, an enlarged gallbladder) are also excluded.
When is liver resection necessary?
Liver resection of various volumes is performed in the following cases:
in case of damage with crushing of the liver tissue; for benign tumors; for cancer (carcinoma); with cancer metastases from other organs; for various liver developmental anomalies; with echinococcal cysts (helminthic infestation); for the purpose of transplantation (organ transplantation).
A thorough examination of structure and function is carried out before any intervention is carried out. If necessary, a diagnostic liver puncture is performed using ultrasound (under the control of an ultrasound scanner). Only then are the indications for intervention and its method determined.
Advice : if after an examination a specialist offers surgical treatment, you should not refuse it or hesitate to make a decision. A long period of reflection does not work in favor of the patient, because during this time the disease progresses.
Treatment with folk remedies
For hepatomegaly, any folk remedies should be used very carefully and in no case should they replace the main treatment. Before using any traditional method, you should consult your doctor about the advisability of its use. In addition, traditional methods also have certain contraindications.
- Milk thistle tea . This medicinal plant protects liver cells and promotes the regeneration of new ones. Also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. The main active component of the plant is silymarin, which is part of a number of hepatoprotective drugs. To prepare milk thistle tea, you need 1 tsp. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the seeds of the plant. After half an hour, strain and drink warm in two doses.
- Infusion of immortelle . The inflorescences of this plant contain a lot of flavonoids that have hepatoprotective activity. The use of products with immortelle helps restore the detoxification function of the liver. To prepare an infusion of immortelle, add 10 g of flowers to 250 ml of water and heat the container in a water bath for half an hour. After 10 minutes, strain and squeeze. Add water so that the total amount of product is 250 ml. Drink in 4 doses throughout the day.
- Rose hip decoction . Rose hips also contain many flavonoids. Rosehip helps eliminate spasms of the bile ducts, has a beneficial effect on the digestion process, and produces an anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare a decoction, add 200 g of berries to 1 liter of water, bring to a boil and cook for 15 minutes. Strain, drink 150 ml 4 times a day.
- Collection of herbs . This collection may include oregano, nettle, chamomile, calendula, centaury. Herbs should be mixed in equal proportions and an infusion should be prepared by pouring 2 tsp. mixture 250 ml water.
- Beetroot, pumpkin . These vegetables should be included in the menu more often, preparing a variety of dishes from them. Raw pumpkin is beneficial, as is freshly squeezed beet juice.
Why is pathology dangerous?
Hepatomegaly is only a consequence of underlying diseases. With inadequate treatment of infections, helminthic infestations, and tumors, life-threatening complications arise:
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- portal hypertension;
- liver failure;
- encephalopathy;
- cysts in the parenchyma;
- abscesses;
- hepatic coma.
Against the background of an enlarged liver, accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum (ascites, or abdominal dropsy) is possible. Its formation leads to compression of internal organs. Iron also performs a neutralizing function in the body. Violations in its work are fraught with poisoning, toxic shock, and death.
Prevention
The essence of prevention is to prevent diseases that lead to liver enlargement. To do this, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- Eat right and do not abuse unhealthy foods, control your intake of carbohydrates and fats.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Avoid uncontrolled use of medications, carrying out drug treatment only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Follow all hygiene rules to avoid parasitic or viral infection.
- Those who have suffered from liver disease should undergo regular preventive examinations with a doctor.
- Practice regular physical activity, but it should not be excessive.
Features of hepatomegaly during pregnancy
An increase in liver volume can be observed in women during pregnancy. The growth of the uterus promotes displacement of the liver. Compression of the organ leads to poor flow of bile and disrupts blood circulation.
Changes in hormonal levels lead to malfunctions of the liver, which is reflected in the appearance of pigment spots on the skin. A blood test shows an increase in cholesterol and triglycerides.
The pathogenesis of hepatomegaly is due to:
- Toxicosis, which is accompanied by prolonged vomiting. 2% of pregnant women in the early stages of pregnancy suffer from its manifestations. The condition leads to electrolyte imbalance, weight loss and dehydration.
- Stagnation of bile, which occurs due to genetic predisposition.
Hepatomegaly in a pregnant woman
Enlargement of the liver during pregnancy occurs against the background of exacerbation of chronic diseases:
- fatty hepatosis;
- diabetes;
- GSD – cholelithiasis;
- biliary dyskinesia - BDL.
In children
Hepatomegaly in a child may be associated with neonatal jaundice. In a small child, it develops due to birth injuries, as well as dysfunction of the mother’s endocrine system. As a rule, liver enlargement in newborns does not require treatment and goes away within a month.
Minor hepatomegaly, which is determined by palpation or ultrasound in a child under 7 years of age, is also considered a physiological phenomenon. It is normal if the liver protrudes beyond the edges of the ribs by 1-2 cm. The condition, as a rule, normalizes as the child grows. However, if an increase in the right lobe of the liver or its left lobe is detected, it is better to undergo additional studies to exclude the development of diseases.
An enlargement of the left or right lobe of the liver in children may be associated with the following diseases and conditions:
- inflammatory processes;
- toxic damage;
- congenital TORCH infections;
- dysfunction of the biliary tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- tumors, metastases.
A particular cause for concern is the situation when hepatomegaly in children is combined with other alarming symptoms: fever, vomiting, rashes, weight loss, poor appetite, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes. In this case, you should immediately consult your doctor.
What is moderate hepatomegaly?
Moderate hepatomegaly means a slight increase in the metric parameters of the liver, not exceeding 20 mm, which can only be diagnosed using instrumental imaging methods. Clinical signs of moderate hepatomegaly are usually minimal, making early diagnosis of this condition difficult. Clinical manifestations of moderate hepatomegaly appear only with a long course and organic damage to the parenchyma, accompanied by dysfunction of the organ. Thus, moderate hepatomegaly tends to progress and provoke significant health problems for the patient.
Typical signs of moderate hepatomegaly are general intoxication manifestations in the form of unmotivated weakness, rapid fatigue, which have nothing to do with a person’s physical activity. Moderate hepatomegaly almost never causes intense pain in the abdominal cavity, however, some patients suffering from this pathology note the periodic appearance of unpleasant sensations of heaviness in the epigastrium on the right, heartburn and loss of appetite in the form of a decrease in appetite. The appearance of even such nonspecific manifestations of moderate hepatomegaly should be the reason for further instrumental examination of the patient in order to eliminate the cause of its occurrence. The initial link in the diagnosis of moderate hepatomegaly is an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity, however, it should be taken into account that in some patients echography may be difficult, and therefore, an additional computed tomographic examination of the abdominal organs should be performed.
Signs of moderate hepatomegaly can most often be partial in nature, that is, the enlargement of the liver does not occur diffusely, but due to changes in limited areas of the liver parenchyma, echo signs of which are the detection of areas of structural homogeneity in the form of abscesses, tumors, and metastases.
Moderate hepatomegaly is most often provoked by a disease such as fatty hepatosis, the pathomorphological basis of which is the degeneration of hepatocytes into fat cells. The main etiopathogenetic factor in the development of moderate hepatomegaly caused by fatty hepatosis is nutritional obesity, that is, a person’s consumption of large amounts of simple fats. Fatty hepatosis refers to a slowly progressive form of hepatomegaly and there are several stages in the pathogenesis of its development.
Diet
Diet for an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles. in Week
Diet is one of the important components of complex treatment of this condition. If the increase is insignificant, sometimes only nutritional correction can normalize the condition of the organ.
First of all, it is important to limit the amount of salt to 6-7 g per day and the amount of sugar to 50 g per day. You should drink up to 2 liters of water daily. You need to eat fractionally - up to 6 times a day in small portions.
For hepatomegaly, it is recommended to include the following foods and dishes in the diet:
- Low-fat dairy products.
- Vegetables – fresh, as well as stewed, baked and boiled.
- Lean meat, fish.
- Vegetable soups.
- Vegetable oils.
- Fruits.
- Marmalade, dried fruits, honey, biscuits.
- Cereals.
- Egg white.
The following foods should be excluded from your diet:
- Spicy, fried, salty dishes.
- Smoked meats and canned goods.
- Fatty meat and fish.
- Mushrooms.
- Egg yolk.
- Legumes.
- Sorrel, spinach, radish, onion.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Muffins, baked goods, cocoa, nuts.
- Alcohol.
- Soda, coffee, sour juices.
How to treat liver hepatomegaly
Treatment of hepatomegaly depends on the type of underlying disease. Therapy includes several areas:
- dietary nutrition;
- pharmacotherapy;
- operation.
For oncology, chemotherapy and radiation techniques are prescribed. Benign tumors in the liver are simply removed surgically.
Diet and lifestyle
People with liver pathologies are recommended to follow the Pevzner diet, table No. 5.
To reduce the load on the affected organ and improve digestion, it is recommended:
- eat small meals, up to 7 times a day;
- completely give up alcohol;
- limit confectionery products on the menu;
- include boiled and stewed vegetables in your diet;
- eat only lean fish and meat.
In case of hepatomegaly, legumes, canned food, seasonings, and whole milk are strictly prohibited. You should also give up coffee and hot chocolate in favor of natural juices and herbal tea.
For patients with severe liver hypertrophy, smoking, excessive physical activity, and working in hazardous industries are contraindicated. To prevent congestion in the abdominal organs, take daily walks in the fresh air.
Drug therapy
Pharmacotherapy involves taking medications that combat the manifestations of the underlying pathology. To prevent liver enlargement, take:
- hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Artichol) – protect liver cells from the negative effects of toxins;
- cardiac glycosides (Korglikon, Digoxin) – stimulate contraction of the myocardial muscle, eliminate symptoms of circulatory failure;
- antibiotics (Augmentin, Doxycycline) – destroy bacteria that cause intoxication of the body and inflammation of the parenchyma;
- choleretic agents (Allohol, Hofitol) – stimulate the removal of bile into the intestines, restore digestion;
- cytostatics (Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin) – disrupt the growth and division of cancer cells in oncological pathologies.
Painkillers, antiemetics and other drugs are used to relieve symptoms.
Surgery
If surgical intervention is necessary, the following is performed:
- drainage of abscesses in the liver;
- removal of tumors;
- ligation of blood vessels.
Patients with acute thrombosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and severe hepatomegaly are indicated for organ transplantation. Untimely surgery can lead to liver failure and death.
Other methods
Hepatomegaly due to cancer is treated with chemotherapy and ionizing radiation. When eliminating provoking factors, physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, plasmapheresis, ultraviolet radiation) are indicated. They cleanse the blood of toxins, accelerate the restoration of normal liver size, and prevent complications. The choice of treatment method depends on the cause of the disease and the presence of contraindications.