≡ Home → Tumor diseases of the uterus → Cervical cyst →
Endocervical cysts are benign formations growing in the lumen of the cervical canal. They are filled with fluid and often occur against the background of chronic inflammation. They are diagnosed at any age, but more often in women after childbirth and undergoing surgical interventions on the cervix. Detected during ultrasound examination.
Single and multiple cysts of the cervical canal are amenable to conservative therapy. In some cases, surgical treatment is indicated. Therapy is justified in the development of severe clinical symptoms, concomitant pathology and before planning pregnancy. In other situations, wait-and-see tactics are allowed.
How do Nabothian cysts form?
The content of the article
The cause of these cysts is a blockage of the glands of the cervix (endocervix), which interferes with the outflow of fluid. As a result, mucus accumulates, forming bubbles filled with liquid contents. When several glandular ducts are blocked, multiple cystic lesions occur, making the cervix lumpy.
Violation of the outflow from the glands is provoked by:
- Inflammatory processes in the uterus and vagina, leading to the destruction of the squamous epithelium of the cervix and its replacement with cylindrical epithelium, which normally should not be there. Tissue cells that are not intended to come into contact with the moist, acidic environment of the vagina become irritated and inflamed. In them, the outflow of secretions is disrupted, leading to the appearance of cysts.
- Childbirth and surgical interventions accompanied by cervical trauma. The epithelium grows together incorrectly, and tissue that should remain inside ends up outside.
- Cervical erosion, which has almost the same mechanism of occurrence. Often these two diseases are combined. Sometimes cysts form after treating erosion with outdated methods, for example, electrocoagulation or surgery. After radio wave treatment of erosion, such complications do not occur.
Endometrioid cyst
How is it formed?
Endometriosis is a very common and at the same time little-studied disease. It is known for sure that for some reason, pockets of the inner layer of the uterine epithelium appear in various organs. That is, the layer that normally peels off and leaves the uterus in the form of menstrual bleeding. Most often, these lesions appear in the thickness of the uterus, ovaries and cervix. A few days before the usual menstruation, these areas begin to function as the endometrium, that is, they peel off and bleed. Blood can accumulate in the cervix, eventually forming endometriotic cysts.
Symptoms of an endometrioid cyst
- spotting appears a week before and a week after menstruation
- pain during the premenstrual period, especially during sexual intercourse and during gynecological examination
- infertility and chronic pelvic pain due to extensive endometriosis
Diagnostics
Endometrioid cervical cysts are rarely isolated, since endometriosis is a hormonal disease. Therefore, several methods are used for diagnosis:
Examination of the cervix using speculum. During a gynecological examination, it is very often possible to see a cavitary red-brown formation with liquid contents that extends beyond the cervical canal. They are very different from nabothian small cysts, which are light yellow in color. We must remember that cysts on the cervix are rare; usually endometriosis looks like small red-brown lesions that bleed during menstruation.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. With an ultrasound examination, you can see cysts and foci of endometriosis on the cervix, in the thickness of the uterus, endometrial cysts in the ovaries and other areas of the woman’s pelvis. This allows you to accurately diagnose endometriosis and begin treatment.
Biopsy. This is the most accurate, but rarely used method of diagnosis. During a biopsy, a section of the cervix with a cyst is removed for examination under a microscope. If the appearance of the cyst differs from typical endometriosis, then a biopsy must be performed to rule out cancer. Depending on the histology results, the doctor determines how to treat the cervical cyst.
Hormonal treatment
Endometriosis is a hormonal disease, so there are several treatment methods, often used together.
Despite the variety of theories about the occurrence of endometriosis, science has clearly established one thing: the direct cause of the appearance of endometriotic lesions, including cervical cysts, is an increased level of estrogen in the blood. Therefore, all treatment is aimed at stabilizing this level.
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs). All COCs consist of 2 components: estrogens and gestagens. The first component may differ in quantity in different preparations. Knowing that endometriosis is an estrogen-dependent disease, you need to choose drugs with a minimum content of this hormone. Such drugs include monophasic Jess, Logest, Janine and other drugs. It is important to remember that COCs help only in the initial stages of the disease, preventing its progression. If, in addition to the cervical cyst, there are other foci of endometriosis, then oral contraceptives will not help. In addition, after discontinuation of drugs, there may be an increase in the symptoms of the disease, so prescribing COCs for severe endometriosis should be done with caution (see the harm of oral contraceptives).
- Progestins. Preparations containing progestins reduce the relative level of estrogen, allowing you to get rid of foci of endometriosis. These drugs include Visanne.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are a reliable method of controlling endometriotic lesions, as they block estrogen synthesis at the highest level. Due to side effects, it is used when other treatments are ineffective or there is severe pain.
Surgical treatment of cervical cysts
For single cysts, their complete removal is possible in several ways:
- Mechanical removal of cervical cysts by conization. If the cysts are large, cause a lot of inconvenience and prevent pregnancy, then conization of the cervix is performed, that is, cutting off its inner layer. This procedure is quite traumatic, but completely eliminates the symptoms. After the body has recovered, you can plan a pregnancy.
- Laser removal. Laser treatment is less traumatic than others; it allows targeted action on the smallest lesions.
- Cryodestruction (exposure to low temperatures). Coagulation (cauterization of the cyst).
All these methods involve the removal or destruction of foci of the disease, including cysts. But without subsequent drug treatment with hormones, the return of the disease is guaranteed. Therefore, after surgical treatment, the gynecologist prescribes appropriate drug therapy.
What are the symptoms of Nabothian cysts?
The disease is often asymptomatic and is detected during a gynecological examination. Sometimes, due to mechanical impact, for example, during sexual intercourse, Nabothian cysts rupture with the release of copious white mucus accumulated in the glandular ducts.
A large number of cysts leads to deformation of the cervix and its extensive inflammation, manifested by yellowish-purulent discharge and pain in the lower abdomen. The inflammatory process is provoked by microbes accumulated in cystic formations.
Untreated cysts can reach a size of 2.5-3 mm, causing discomfort during sexual activity and leading to painful menstruation. Large cysts disrupt the patency of the cervical canal, preventing the flow of menstrual blood.
There is no likelihood of cancerous degeneration of endocervical cysts - so far no such cases have been recorded.
Causes
Cystic capsules of the endocervix develop due to the following reasons:
- Inflammation of the genital tract. Any such process in the vagina, cervix, uterine mucosa, ovaries or fallopian tubes can lead to the formation of a benign defect.
- Erosion. During healing and scarring, the glandular ducts narrow, secretions accumulate, which is why a retention cyst occurs.
- Leukoplakia. Pathology leads to keratinization of the skin, the appearance of a white coating that blocks the outflow of mucus.
- Ectopia. Here, blockage occurs when there is abnormal growth of the epithelium of the cervical canal or reflux of cells.
- Endometriosis. The uterine mucosa spreads into the cervix, the ducts become compressed, the outflow worsens, and cavities appear.
- Various damages. Childbirth, abortion, the use of chemical contraceptives, and intrauterine devices lead to a variety of injuries that cause nabothian vesicles.
The disease often develops against the background of acute viral or sexually transmitted infections. The first include HPV and cytomegaloviruses, which destroy cells of the mucous membranes. No less dangerous are pathologies transmitted during sexual intercourse.
Examination before treatment
The causes of cysts are identified by hardware and laboratory research methods. The gynecologist will prescribe:
- blood test for biochemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- blood for sex hormones;
- analysis for tumor markers;
- smear to check the purity of the flora;
- cytological examination;
- smear for STI infections,
- Ultrasound of the pelvis, etc.
You should not refuse tests, since cysts are accompanied by other gynecological diseases or become their complication.
Diagnosis
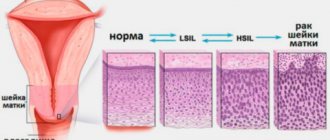
Diagnostic methods are necessary to distinguish a nabothian cyst from other abnormal formations, including cancerous tumors, and also to discover the causes that caused its development.
Use instrumental methods:
- Examination by a gynecologist. It allows you to detect only nodules localized on the vaginal (outer) part of the uterine cervix.
- Ultrasound of the cervix is a more in-depth method that makes it possible to assess the size, changes in structure, and localization of formations.
- Colposcopy is the most reliable method in which the cervix with endocervical cysts is examined under multiple magnification.
- Biopsy (sampling of a microfragment of tissue) and histological examination, which makes it possible to identify probable malignant changes.
Lab tests:
- general blood and urine examination;
- blood and smear for genitourinary infections;
- oncocytological examination of a smear from the endocervix in order to exclude cancerous degeneration (the procedure is carried out in the second phase of the monthly cycle);
- PAP smear for the earliest symptoms of malignant cell changes;
- blood test for hormones and tumor markers;
- PCR method for identifying specific types of infectious agents in biomaterial;
- bacterial culture of secretions to determine pathogens and their sensitivity to antibiotics.
After using diagnostic methods, the doctor determines the cause of the formation of cystic nodes on the uterine cervix, the question of the need for their surgical removal, treatment of the causative disease, and the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs or hormones is considered.
Do you use folk remedies?
Not really
Nabothian cysts of the cervix and pregnancy
Large cysts interfere with the penetration of sperm into the uterus, causing female infertility. When pregnancy occurs, due to hormonal changes in the body, leading to an increase in the intensity of mucus secretion, the size of the “bubbles” increases. The formations are not removed during this period, so as not to provoke a miscarriage. Treatment is delayed until after the baby is born.
In the first months of pregnancy, Nabothian cysts do not affect pregnancy, but later problems begin. Large formations that deform the cervical tissues can provoke early opening of the cervix and premature birth.
During labor, when the cystic cervix opens, ruptures occur due to decreased tissue extensibility. The blisters burst, and long-term non-healing wounds form - an open gate for pathogenic microbes. Therefore, endocervical cysts need to be disposed of at the stage of pregnancy planning.
What's happened
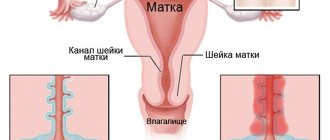
The surface of the inner lining of the female genital tract consists of columnar epithelium, which is responsible for the production of mucous secretions. The endocervix is part of the covering that is located in the cervical canal. Hormonal levels directly affect the thickness of the cell layer, the amount of mucus produced and its viscosity.
Under normal conditions, the endocervix changes due to pregnancy, abortion, and after childbirth. Because of this, women who have given birth multiple times often suffer from a small formation with jelly-like contents on the cervix.
Most often, minor paracervical cysts occur, which do not adversely affect health in any way. Most often, the pathological process develops on the transitional epithelium between the canal and the pharynx, since this area is most susceptible to damage during childbirth.
These formations are not prone to self-resorption and therefore require immediate therapy. The presence of multiple defects on the cervix often leads to serious health problems.
Treatment of nabothian cysts
By themselves, these formations do not resolve or disappear, so nabothian cysts, especially large ones, are removed, getting rid of the source of infection in the genital tract. In addition, with this pathology, an intrauterine device cannot be installed.
It is pointless to treat Nabothian cysts with folk remedies. On the contrary, the introduction of tampons into the vagina and uncontrolled douching lead to the growth of old and the appearance of “fresh” tumors.
Before removing Nabothian cysts, the cervix is punctured to allow the contents to drain out. Residues are removed using laser or radio wave coagulation (sealing of blood vessels), which does not cause pain, severe tissue trauma or bleeding.
Such cellular formations are removed using modern methods:
- electrocoagulation (electric current);
- cryocoagulation (cooling with liquid nitrogen);
- laser excision;
- endoscopic method (microinstruments equipped with a microscope and illumination);
- radio wave therapy is the latest technique.
The gynecologist decides how exactly to remove the nabothian cyst. The doctor selects the method individually, taking into account the size of the formation and the characteristics of the body. If you have a choice, it is better to prefer a radio knife, since there are no bleeding or complications after it. The technique is suitable even for nulliparous women.
Since the cervix does not contain nerve endings, the procedure is painless. A small number of patients with sensitivity in the cervical area are given local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
The procedure is carried out after the end of the next menstruation. The epithelium is restored before the next menstrual cycle.
After surgery, you need to take medications: antibiotics, antiseptics, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Can it develop into cancer?
Nabothian cavities are benign. In this case, the disease never degenerates into a cancerous tumor.
However, the processes that cause the appearance of endocervical cysts create favorable conditions for malignant lesions of the cervix, so the bubbles must be treated in a timely manner.
Although there is no risk
Signalization of neoplasms, large defects are dangerous with other serious complications. Some of these consequences can even be fatal.
Diagnostics
Endocervical cysts on ultrasound (ultrasound)
There are different methods for diagnosing this disease. The most accessible and simplest method is ultrasound examination. Extended colposcopy is also considered a fairly informative method. The procedure involves an examination using a special microscope. This allows you to carefully examine the cervix for various neoplasms.
If a doctor, during an ultrasound examination of a patient, suspects the presence of a cyst, then she is referred for an extended colposcopy in order to clarify the diagnosis.
To clarify the diagnosis, an oncocytological examination of a smear can be performed, which will give more accurate results if carried out in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
Another fairly effective research method is the Pap smear, which can be used to determine the initial stages of precancerous changes in the cervix. A similar smear is made using special fixatives and paint compositions. It would be better for a woman to go through all stages of the examination, as this will help her know the exact state of her health.
Why do they arise?
The reasons for the appearance of such formations have not yet been fully established, but there is every reason to assume that the formation of endocervical cysts is facilitated by chronic infectious and inflammatory processes: colpitis, cervicitis, salpingitis or adnexitis. In addition, mechanical injuries and cervical leukoplakia can lead to the occurrence of this pathology. Nabothian cysts often appear during the healing process of erosions. There is evidence that cytomegalovirus and human papillomavirus can provoke the development of endocervical cysts. There is a high risk of the formation of cystic cavities with endometriosis, since pathological growing endometrial tissue can penetrate the cervical canal, disrupting the outflow of cervical secretions from the glands.
Special mention should be made of hormonal disorders, since changes in the concentration of sex hormones on different days of the menstrual cycle lead to changes in the functioning of the endocervical glands. Observations show that Nabothian cysts occur more often in women with hormonal disorders. In addition, there is evidence that the intrauterine device can provoke the formation of cysts.
Necessary diagnostic tests
Cervical cysts are primarily detected by a doctor during a gynecological examination. So, on the mucous membrane of the cervix, the doctor may notice a whitish formation (retention cyst) or a red lesion (endometrioid cyst).
If a cervical cyst is detected, a woman will need to undergo a number of tests. This is necessary, first of all, in order to clarify what this formation actually is: an ordinary cyst or a tumor?
So, to diagnose a cervical cyst, doctors prescribe the following studies:
- Transvaginal ultrasound;
- Colposcopy;
- Cytological examination of a smear;
- Bacteriological examination of a smear.
How to treat correctly
Patients diagnosed with an endocervical cyst are wondering how to treat the tumor without harming reproductive function. The treatment regimen is drawn up by the attending physician based on the diagnostic results: a small cystic cavity is eliminated with the help of drug therapy, while a severe cystic cavity is eliminated through surgery.
Medicines
Treatment of a benign tumor with medication is based on the complex use of the following medications:
- Antibacterial drugs - Tetracycline or Ampicillin. Incorrect use of antibiotics precedes the manifestation of side symptoms (nausea, fever, itching of the skin, vomiting, swelling), therefore, when using them for medicinal purposes, you must follow the dosage determined by your doctor.
- The antiseptic agent Tsimezol has a disinfectant effect and accelerates the process of growth of connective tissue. The advantage of Tsimezol is the absence of contraindications to its use and side effects.
- The Nutrimax vitamin complex is aimed at activating the body's defenses and strengthening the immune system.
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, the patient limits the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Folk remedies
To prevent the growth of a benign tumor, treatment with folk remedies is used. Stopping the growth of the cyst is provided by an infusion of medicinal herbs. To prepare it, you need to mix equal quantities of rose hips and sea buckthorn, chamomile flowers, and plantain leaves, grind the components and pour a liter of boiling water over them. In order for the drug to acquire beneficial properties, it must be infused for 8 hours, and then taken twice a day, 10 ml.
Egg drink has a healing effect on the mucous membrane of the cervix. The preparation recipe is as follows: 8 boiled yolks are crushed to obtain a powder consistency, mixed with 20 g of pre-crushed pumpkin seeds, after which the raw material is poured with 500 ml of sunflower oil. The resulting liquid should be placed in a water bath for 15 minutes: one tablespoon of the drink is drunk on an empty stomach daily.
For topical use, it is recommended to use natural suppositories. To prepare them, you need to mix butter and honey in a 3:1 ratio, form a candle from the viscous mass and place it in the refrigerator so that it hardens and takes shape. Inserting a suppository into the vagina is recommended every evening before bed. The duration of the treatment course is seven days.
Surgical therapy
If the hollow capsule on the uterine cervix reaches a diameter of 3 cm, becomes inflamed or begins to accumulate pus, the pathology is treated surgically. The most common method of surgery is the removal of a cyst using radio waves, during which the doctor pierces a dense node, extracts a viscous liquid from it and cauterizes the remaining walls.
A tumor that has formed deep in the cervical canal is removed using cryotherapy, during which the doctor treats the benign formation with liquid nitrogen. Being under the influence of a low-temperature substance, the parenchyma of the cyst loses its strength and begins to gradually collapse.
It is advisable to get rid of the hollow capsule, which is localized at the beginning of the uterine cervix and clearly visible with mirrors, using laser exposure. The advantage of laser removal is the absence of postoperative sutures, which ensures rapid rehabilitation of the patient.
Removing a cyst through surgery is contraindicated for pregnant girls, nursing mothers, and patients during menstrual bleeding. In addition, it is not recommended to operate on the cervix in the presence of a sexually transmitted infection, the development of ectopic endometriosis and the formation of polyps.