Fibroids (fibroids) of the uterus are a benign tumor that is usually diagnosed in women between 35 and 46 years of age. Recently, there has been a trend toward “rejuvenation” of the disease, which is increasingly being found in young girls.
Until the neoplasm reaches an impressive size, beginning to put pressure on adjacent organs, fibroids can be asymptomatic. Malignancy of fibroids occurs in extremely rare cases.
What is fibroma and its types
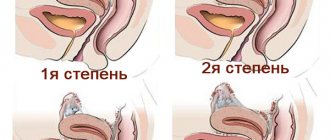
Uterine fibroid is a benign neoplasm that is formed from connective tissue and muscle fibers. Outwardly it looks like a small seal or knot. It can occur both inside and outside the cervix. The size of the tumor can vary - from 1 mm to 20 cm.
This benign tumor is a hormone-dependent neoplasm. This means that its occurrence and growth are associated with hormonal changes. That is why such a diagnosis does not occur in menopause, as well as in girls before puberty.
Depending on the location, the following types are distinguished:
- Submucosal or submucosal. Grows inside the uterine cavity.
- Interstitial - occurs in the thickness of the uterine wall.
- Subserous - forms under the outer lining of the uterus.
- Interligamentous - formed on the ligaments of the uterus or between them.
- Stalked - has a specific leg. Its torsion can lead to severe pain.
All these forms have their own characteristics, which determine the choice of treatment method.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
Before choosing a fibroid treatment method, you should know its size and location.
In addition, how to treat fibroids will depend on what the symptoms and signs of the disease are, the woman's age, whether the patient plans to give birth to a child in the future, and also on her general health.
There are two types of treatment for uterine fibroids:
- Medication.
- Surgical.
Drug treatment
Treatment of the disease with medications is prescribed when bleeding occurs, pain in the abdominal area, if the uterine fibroid has a diameter of no more than three centimeters, and also if there are contraindications for surgery or the woman refuses surgery.
Patients who are in the climatic period are offered observation, since when the synthesis of female hormones decreases, tumor regression occurs.
Drug treatment is designed to eliminate pain, anemia, which is the result of bleeding, and hyperplastic changes in the endometrium, which always accompany fibroids.
The doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, iron, analgesics, hormones that bring the menstrual cycle back to normal.
Treatment with hormonal drugs has its contraindications and side effects, and therefore the need to take and the choice of drug can only be determined by a qualified specialist.
Causes of pathology
The development of fibroids directly depends on the female hormone - estrogen. Therefore, the main reason for its formation is hormonal imbalance. But not every woman has hormonal disorders that lead to such a diagnosis. Why does this happen? This is due to the fact that for compaction to develop there must be fertile soil. Namely, pathological changes in the tissues of the uterine cavity. The following factors can cause them:
- abortion;
- damage to the cervix when installing or removing the IUD;
- childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the pelvic organs;
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine interventions, including diagnostic procedures.
Factors that can lead to hormonal imbalance include:
- endocrine pathologies;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- metabolic diseases;
- obesity;
- frequent stress;
- dissatisfaction with sex life;
- liver diseases;
- low physical activity.
Hereditary factors also play a role.
Medicines used in the treatment of fibroids
In conservative therapy, several groups of medications are used. Let's look at each in more detail.
Combined oral contraceptives
Combination of ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel:
- Mercilon;
- Marvelon;
- Novinet.
Combination of ethinyl estradiol with norgestrel:
- Ovidon;
- Rigevidon.
Treatment with contraceptive drugs containing combinations of 2 hormones is effective in reducing the severity of pain and bleeding. Therapy with such drugs can be expected to reduce the size of only those tumors that were initially up to 1.5 cm in size (more details: COCs (combined oral contraceptives)).
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
The action of these drugs is based on creating a temporary “artificial menopause” in a woman’s body. Under the influence of hormones, ovarian function is suppressed. Agonist drugs (analogues) of natural gonadotropin-releasing hormones (AGRH) inhibit the production of sex hormones of the pituitary gland, which affect the functioning of the ovaries.
Drugs in this group:
- Buserelin;
- Triptorelin (Diferelin, Decapeptyl, Decapeptyl-depot);
- Leuprorelin (Lukrin-depot);
- Goserelin (Zoladex).
Under the influence of AHRH, the ovaries “fall asleep”, ovulation does not occur, the uterine mucosa does not change cyclically - menstruation stops. This process is completely reversible; after discontinuation of the drugs, all functions are restored. Treatment lasts no more than 6 months. During this period, the size of the tumor can decrease by up to 50%, and the symptoms of fibroids become less pronounced.
Disadvantages of using drugs:
- Possible complete restoration of tumor size after cessation of treatment;
- Long-term (longer than 6 months) use of drugs is prohibited due to the high risk of osteoporosis and other complications of insufficient estrogen levels.
It is advisable to prescribe AGRH before surgery for uterine fibroids in order to reduce the size of the tumor.
Complete list of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
Antiprogestogens
Like GnRH agonists, drugs in this group are used before surgery to remove uterine fibroids. The drug commonly used is Mifepristone (RU-486).
Under the influence of hormonal therapy, myomatous nodes decrease in size, and the symptoms of uterine fibroids weaken.
Antigonadotropins
Drugs used:
- Danazol (Danogen, Danoval, Danol, Vero-Danazol).
- Nemestral (active ingredient - gestrinone).
The effect of antigonadotropins is to reduce the intensity of symptoms without reducing the size of the tumor. Often, when using them, undesirable side effects occur (increased hair growth on the face and body, changes in the timbre of the voice, the appearance of rashes).
Antigonadotropins are used to treat uterine fibroids quite rarely, only in the absence of effect from treatment with other hormonal drugs.
Gestagens
Today, the use of gestagens is becoming less and less justified. Some gynecologists consider the use of gestagens to be effective because... With a lack of progesterone, tumor growth occurs. Many doctors, on the contrary, are categorically against the use of any gestagens for the treatment of fibroids. The mechanism of tumor formation is not based on the amount of any hormone, but on the imbalance of the woman’s entire hormonal system.
Currently, the use of gestagens is prescribed for the combination of uterine fibroids and endometrial hyperplasia.
Drugs used:
- Linestrenol (Orgametril, Escluton);
- Nor-ethisterone (Norkolut, Primolut-nor);
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera, Depo-Provera).
Latest research into drug treatment for fibroids
Scientists at the University of Brussels conducted research at St. Luke's Hospital to understand how the contraceptive drug Esmya acts on uterine fibroids. The main active ingredient in Esmiya tablets is ulipristal acetate. And since in the process of development and growth of fibroids, the level of not only estrogen, but also progesterone, is important, it was decided to study the effect of the drug Esmya and gestagen blockers.
The experiment involved 550 women who were indicated for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids. All subjects were divided into two groups. One group was given a placebo as “treatment” for 3 months, the other was given Esmiya tablets.
At the same time, another study was conducted: a comparison of the effect of the drug Esmya and injections of gestagen hormone blockers.
The results of two experiments revealed the following:
- After using the drug Esmya, the size of uterine fibroids is reduced, the intensity of the symptoms of the disease decreases;
- 90% of the patients studied noted a positive effect from taking Esmiya tablets;
- In 50% of patients taking Esmya, there was no need for surgical treatment (the effect is similar to the use of injections of gestagen blockers);
- After taking Esmiya tablets, there are no such side effects as when using injections of hormone blockers - hot flashes, bone degeneration;
- After treatment for 6 months, no resumption of tumor growth was observed, whereas after stopping injections of hormone blockers, myomatous nodes began to grow again.
It is likely that thanks to the efforts of scientists, the problem of uterine fibroids will soon be solved much faster and easier than at present.
On this topic:
Hog uterus and red brush for uterine fibroids
Symptoms of the disease
Small formations are asymptomatic. The tumor can develop for years before the female body reacts to it with any symptoms.
The following manifestations should alert you:
- Change in the length of the monthly cycle.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Problems with pregnancy or conception.
- Abnormally heavy menstruation.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Bleeding during the “dry” period.
As fibroids increase in size, they can put pressure on nearby organs, such as the ureter. In this case, disorders of the urinary system occur. Due to pressure on the blood vessels, a woman may complain of cramps, especially at night.
Large blood loss causes weakness, fatigue, and dizziness. If you have such symptoms, you should definitely contact a gynecologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Symptoms
According to statistics, only every fourth uterine fibroid occurs with severe symptoms.
Often the disease does not give clinical signs, even if the tumor has a large diameter (see photo above), and the disease can be detected by chance during a preventative visit to the doctor.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- heavy menstruation with blood clots;
- due to the fact that the tumor puts pressure on the bladder - frequent trips to the toilet;
- constipation due to compression of the rectum;
- feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- pain during menstruation, but in the last stages of the disease, aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back is constant;
- The size of the abdomen may increase, which may even require a change of wardrobe, despite the fact that the weight remains the same;
- with large sizes and a certain localization of fibroids, there may be a lack of pregnancy during planning, or failure to carry the fetus to term.
What complications can there be?
Large formations can lead to compression of the nerve endings of neighboring organs. Other complications of fibroids include:
- Partial or complete necrosis of the neoplasm. Leads to severe intoxication of the body. Characterized by intense pain and fever.
- Pinching or bending of the fibroid leg.
- Inversion of the uterus.
- Suppuration or infection of fibromatous formation.
- Rupture of tumor vessels is rare. Leads to intraperitoneal bleeding.
If a woman does not see a doctor for a long time, the risk of developing severe anemia increases. This condition not only leads to rapid fatigue and loss of performance, but can also be fatal.
Forecast
The tumor does not malignize, grows slowly and can be asymptomatic for a long time. Late diagnosis of the disease leads to the detection of large fibroids (10-20 cm).
It happens that a woman who has uterine fibroids attributes the reasons for heavy menstruation or bleeding to age-related changes or other diseases.
With timely diagnosis, fibroma does not cause concern and is treated conservatively, and operations on small tumors are less traumatic and do not cause complications.
Uterine fibroids are considered a disease whose causes are not fully understood.
It has a low risk of mangalization, and therefore, with slow growth and the absence of unpleasant symptoms, it is simply not observed.
Timely treatment will allow you to avoid such negative consequences as: severe anemia, leg torsion and necrosis.
Fibroma and pregnancy
About 35% of women with this pathology have problems conceiving. This is due not only to the fact that there are nodes in the uterine cavity. The main reason is disruption of the ovaries, which are responsible for the ovulatory phase of the cycle.
Small formations do not interfere with pregnancy. But under the influence of hormonal changes, a sharp growth of fibroids is possible. As it increases in size, it will begin to compress the uterus. The embryo will not be able to develop normally, which will lead to miscarriage or premature birth.
Also, low-lying nodes will interfere with natural delivery. In this case, there is a need for a cesarean section. During childbirth, damage to the fibroid is possible. This can lead to postpartum complications such as inflammation of the node, uterine bleeding.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis begins with a thorough collection of the patient’s history and complaints. During a gynecological examination, an enlarged uterus with a bumpy and dense surface is palpated. The initial examination does not allow differentiating fibroids from fibroids or sarcomas, so the doctor will prescribe an additional examination:
Pelvic ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is a highly informative and reliable diagnostic method and in 96% allows to confirm/detect fibroids, the size of nodes and their number, location and growth pattern, and deformation of the uterine cavity.
Hysterosalpingography
The introduction of contrast into the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes helps to assess the condition of the endometrium, identify submucosal nodes and their sizes, determine the size and deformation of the uterine cavity, the patency of the fallopian tubes and the presence of obstacles at their mouths.
Hysteroscopy
This method allows you to see the uterine mucosa and identify submucosal fibroids of even small sizes. If there are suspicious areas of the mucosa, a piece of tissue is taken (biopsy) followed by histological examination. Interstitial fibroma is defined as a bulge above the wall of the uterus and has a smooth surface and a pale pink color.
CT and MRI
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are performed to definitively confirm the disease and exclude uterine sarcoma or fibroma or ovarian cystoma (in the case of a subserous node).
Diagnostic laparoscopy
It is carried out in difficult cases when it is not possible to distinguish a fibroid tumor of the uterus from a tumor-like formation of the ovary.
Diagnosis and treatment methods for the disease
A tumor can only be detected during a gynecological examination. An accurate diagnostic method is ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may order the following additional studies:
- Metrography (x-ray of the uterine cavity).
- Diagnostic curettage.
- Bimanual (manual) examination of the uterus.
An important point in making a diagnosis is the woman’s age. In 80% of cases, fibroids are diagnosed after 35-40 years.
Small formations that do not cause discomfort to the woman are subject to dynamic monitoring. Treatment in this case is not required. An independent decrease in the node is observed during menopause, when the ovarian function fades.
Conservative therapy
For minor pain, as well as problems with conception, the doctor may prescribe hormonal treatment (progesterone injections intramuscularly for 7-10 days).
It is possible to take a course of androgen medications. They reduce estrogen production in the ovaries, which leads to tumor shrinkage. An effective method is to install a special intrauterine hormonal system. However, such methods are used only for small nodes.
In exceptional cases, it is possible to perform radiotherapy on the area of both ovaries. This type of treatment leads to a stop of the menstrual cycle, so its use is undesirable for women planning a pregnancy.
Surgical treatment
The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- rapid growth of fibroids;
- prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding;
- severe anemia;
- node necrosis;
- infertility;
- suspicion of transformation of fibroma into sarcoma (malignant tumor);
- large tumor size, which negatively affects other organs.
In most cases, organ-preserving surgery is performed using a gentle laparoscopic method. It allows you to remove formations while preserving the uterus. Manipulations are carried out through small punctures in the lower abdomen. The rehabilitation period is short, since there is no classic peritoneal incision.
It is also possible to perform a procedure such as embolization of the uterine arteries. The purpose of the operation is to introduce a special substance into the arteries, which disrupts blood circulation in this area. This leads to obstruction of the vessels that feed the fibroma.
A modern method is also ultrasound ablation (USA). With its help, the formation is “evaporated” without injuring the uterus. The operation is performed under MRI guidance.
The effectiveness of traditional medicine
Many women are afraid of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures and try to treat the disease with folk remedies.
At the same time, uterine fibroids do not decrease in diameter and do not stop growing. And no infusions or herbal decoctions will cure the tumor, so you should stick to traditional methods of treatment and consult a doctor.
Nevertheless, it is still possible to use traditional methods of treatment, but only to reduce the symptoms of the disease. Eg:
- a decoction of nettle or oak bark reduces the amount of uterine bleeding
- douching with chamomile reduces inflammation of the genital organs, which often accompanies the disease.
Treatment with folk remedies not only does not produce an effect, but also delays taking medications or undergoing surgery.
Often, in order to avoid hormonal therapy, patients choose homeopathy.
Despite the fact that the drugs should also be selected by a specialist, their effectiveness has not been proven.
Homeopathic remedies:
- Mylife;
- Wild Yams;
- Aurum;
- Calcium;
Prevention of uterine fibroids
To maintain women's health, it is enough to visit a gynecologist annually. You should also follow these simple recommendations:
- Do not take hormonal medications without consulting your doctor.
- Installation of intrauterine devices should only be performed by an experienced doctor. The structure must be removed strictly within the prescribed period.
- Use protection if you are not planning a pregnancy.
- Treat all infectious diseases.
- After childbirth, do not ignore preventive examinations with a doctor.
- Don't give up breastfeeding. This is a natural method of preventing mastopathy.
Try to maintain peace of mind. The female reproductive system is sensitive to emotional experiences and stress.
Why are uterine fibroids dangerous?
Uterine fibroids pose a danger to a woman’s health in terms of the development of complications of the disease. With regular monitoring by a gynecologist and careful attention to her health, a woman can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Therefore, you should be aware of possible potential problems:
- Massive uterine bleeding is dangerous both in itself, a threat to life, and the development of anemia;
- Torsion of a myomatous node on a thin stalk. It is fraught with the development of an “acute abdomen” picture. Requires immediate prompt assistance;
- Necrosis of myomatous node. Necrosis of fibroid tissue. More often it occurs during involution (contraction) of the uterus after childbirth, before the 40th day. Immediate surgical attention is also required;
- Malignancy of a myomatous node is the degeneration of a tumor from benign to malignant. According to research, it occurs in 1.5 - 3% of all cases, which does not detract from the danger of complications;
- The birth of a myomatous node with submucous myoma occurs with inversion of the uterus;
- Violation of a woman’s reproductive activity - development of ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriages, premature and complicated births, infertility;
- Development of purulent processes in the myomatous node and surrounding tissues. Inflammatory processes without medical attention can lead to severe septic complications.
Women diagnosed with uterine fibroids should be regularly monitored by a gynecologist. At the slightest change in your health, you should seek medical help to avoid all of the listed complications.
On this topic:
Uterine fibroids during pregnancy - why are they dangerous? How to treat?
Diagnostic scheme: how the problem is identified
A fibroid node on the uterus is clearly visible during an ultrasound. Screening studies are carried out once a year for all women, starting at the age of 25 years. If a tumor is detected, it is recommended to repeat ultrasound every 6 months.
With the introduction of organ-preserving operations into practice, it is of particular importance to determine not only the size of the node, but also its location. For this purpose, more accurate diagnostic methods can be used: CT or MRI. Computed tomography is also used to monitor the condition of nodes after uterine artery embolization (UAE).
In modern clinics, ultrasound examination is necessarily supplemented by Doppler ultrasound - assessment of blood flow in the vessels feeding the tumor. These parameters are important when developing treatment tactics, in particular when determining indications and contraindications for UAE.
Other diagnostic methods:
- Hysteroscopy – examination of the uterine cavity under magnification. Allows you to identify submucosal fibroids, as well as concomitant pathologies. Nascent submucosal nodes can be removed immediately during the diagnostic procedure;
- Laparoscopy is the best method for identifying subserosal, intraligamentary, peduncular and parasitic fibromas. A diagnostic procedure can also turn into a therapeutic one.
Laparoscopy is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing all types of benign neoplasms.
Other examinations are also prescribed according to indications:
- Blood test for hormones (relevant for infertility);
- Test for tumor markers.
How to treat?
The method of eliminating uterine pathology depends on the type of fibroid, its size, location, as well as the woman’s age and plans for pregnancy. If education does not increase and does not affect the girl’s well-being, observation is indicated. Treatment is carried out in case of rapid growth of fibroids, compression of nearby organs, or suspected malignancy.
Treatment for fibroids is:
- Conservative. Involves taking medications, using physiotherapy and alternative medicine.
- Operational. Perform surgeries (minimally invasive, abdominal).
Drug treatment
Indications for drug therapy: bleeding, abdominal pain, fibroid size from 3 cm. The use of the method helps eliminate discomfort, anemia, and hyperplastic changes in the endometrium. Analgesics, painkillers, and vitamins are prescribed. For girls with vegetative-vascular pathologies, treatment with sedative medications is indicated. Venotonics are used to normalize the menstrual cycle. In case of severe bleeding, antianemic therapy is carried out. In order to increase defenses, immunomodulatory treatment is used.
The basis of the conservative method is the use of medications that reduce the effect of female hormones on the formation of the uterus. Prescribed use:
- Antigonadotropins (Danol, Nemestrana). They provide a decrease in estrogen production and a decrease in the replenishment of the node.
- Gestagenov (Yarins). Restore the cycle.
- Intrauterine device (Mirena).
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (to reduce estrogen concentrations).
Surgery and non-invasive procedures
When drug treatment for uterine fibroids is ineffective, surgery is prescribed. The radical method is used in case of rapid growth of a nodular formation, degeneration into cancer, or deterioration of the condition. The choice of method depends on the diameter and location of the formation. Hysterectomy and myomectomy are often prescribed. The difference between the two methods is that the second is considered organ-preserving. The woman will be able to bear and give birth to a baby.
But more often, doctors try to resort to minimally invasive manipulations - operations with minimal damage.
Carrying out UAE (uterine artery embolization)
Treatment consists of stopping the feeding of fibroids. During manipulation, a thin tube is inserted into the femoral artery (to identify the characteristics of the blood supply to the uterus). The veins are then filled with small particles that block blood flow to the fibroids. As a result, the node decreases in size.
FUS ablation
Treatment of tumors with this method is common because it is safe and bloodless. After the procedure, reproductive function is preserved. It involves the effect of ultrasound on fibroids. The unit is heated and destroyed.
This method is used for single small formations. It can be replaced by cryomyolysis (freezing of formation), electromyolysis (exposure to the fibroid with current).
Physiotherapy
Treatment of fibroids on the uterus without surgery is effective for small fibroids. Provides improved well-being, normalization of the cycle, and reduction in the size of the formation. The specific method is selected by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s age and tumor type.
Electrophoresis
A method of treating pathology in which the medicine is administered through the skin and mucous membranes using direct current. This supply of drugs ensures an active increase in their activity. To treat fibroids in the body of the uterus, electrophoresis of zinc and iodine is used on the lower abdomen. Application of the method helps in eliminating inflammation and pain, and also:
- decreased estrogen production;
- restoration of the menstrual cycle.
Magnetotherapy
The use of this method in complex therapy of uterine fibroids promotes regression of the pathology. The anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and restorative effects of the technique are known. The procedure ensures:
- inhibition or stabilization of fibroid growth;
- improving the functioning of the endocrine system;
- normalization of the cycle.
Iodine-bromine and radon baths
The positive effect of the procedure is due to the entry into the tissues of the inert gas radon and its decay products. The radiation that appears stops bleeding and also helps slow the growth of fibroids in the uterus and restore hormonal levels. The procedure has a relaxing, calming effect, lowers blood pressure and normalizes blood flow.
Treatment with iodine-bromine baths is no less effective. Bromine released from medicinal waters accumulates in the brain, and iodine in the thyroid gland. The procedure restores the balance of pituitary and ovarian hormones.
Unconventional methods
It is recommended to use folk remedies for the treatment of uterine fibroids. Medicines and herbal teas speed up the healing process, restore strength, strengthen the immune system, and also eliminate discomfort. Compositions are used as an auxiliary method. Doctors recommend use for fibroids in the uterus:
- infusion of oak bark or nettle (to stop bleeding);
- douching with chamomile decoction (removes inflammation).
No less effective are compositions from boron uterus, chestnut, lemongrass, and aloe. Treatment of fibroids with folk remedies should be agreed with a doctor.
Features of therapy for menopause
During menopause, pathology does not develop. If symptoms or signs appear during menopause, this means that the pathology did not progress before and was hidden. Women with a tumor that does not appear are not treated. Regular examination and observation is indicated. If there are any changes (increased growth, painful symptoms), surgery is prescribed to remove the formation. If malignancy is suspected, the tumor is excised along with the uterus and sometimes the appendages.
Often fibroids regress during menopause. This is due to decreased production of hormones and loss of reproductive function.
Reasons and factors
To date, it has not been possible to definitively determine the nature of this formation. There are many hypotheses, among which experts give priority to malfunctions in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, and, accordingly, to the resulting imbalance of estrogen in the female body. Among gynecologists, there are hypotheses about the correlation between the level of the disease process and the amount of estrogen, the jump of which occurs at the beginning of puberty, and decreases about 3 times by the menopausal period. Thus, most often fibroma is diagnosed no earlier than 35 years of age, and surgical intervention is most often performed in women 40–45 years old; small nodular formations do not make themselves felt for a long period of time, but if there are factors that adversely affect the body , perhaps the beginning of their progressive growth. These include:
- hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of tumor processes;
- absence of childbirth in a woman over 30 years of age;
- no breastfeeding by age 30;
- long-term uncontrolled contraception using hormonal medications;
- many abortions and diagnostic curettages;
- excess weight;
- lack of intimate life or, conversely, regular promiscuous sex;
- inflammatory processes in the uterus, appendages, ovaries;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation for a long period of time;
- pathological processes in endocrine organs - adrenal glands, thyroid gland, etc.;
- ovarian pathology affecting the hormone-producing function (including cystic formations);
- hemodynamic disorders detected in the pelvis;
- postpartum complications accompanied by a traumatic outcome.
Tactics for suspected fibroids
To identify a tumor, the following is carried out:
- Examination by a gynecologist. During a bimanual examination of the uterus, the doctor pays attention to its enlargement and the presence of nodes. For small tumors, no significant changes are observed;
- Laboratory examination for fibroids is not indicative. The doctor may recommend a blood test for hormones to identify concomitant pathologies, determine tumor markers if sarcoma is suspected;
- Ultrasonography. On ultrasound, fibroids are visible as a hypoechoic formation. During the examination, areas of connective tissue occupying up to 50% of the tumor are determined;
- Hysteroscopy. Allows you to identify submucosal nodes, distinguish them from polyps, take aspirate from the uterine cavity, and conduct diagnostic curettage;
One of the types of diagnostics of tumors in the uterus is hysteroscopy, with which you can see pathological changes and take a tissue sample.
- Laparoscopy. Indicated for subserous formations, compression of the pelvic organs by a tumor;
- Histological examination of macro- and microspecimens is carried out after removal of the node. Allows you to identify the type of tumor and distinguish malignant from benign.
On a note
Uterine fibroids are often accompanied by other pathologies of the reproductive organs (polyps and endometrial hyperplasia, adenomyosis, ovarian cysts). Also, examination often reveals mastopathy and pathology of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism).
Clinical picture: leading symptoms to recognize the disease
The first signs of pathology appear when the tumor reaches a size of 2 cm. Until this point, fibroids are considered clinically insignificant. They do not cause concern, do not disrupt the menstrual cycle, and do not interfere with conception and birth of a child. Such nodes can be detected accidentally during a routine ultrasound.
As the disease progresses, the following symptoms occur:
- Menstrual irregularities: menometrorrhagia - heavy, prolonged and painful menstruation;
- Uterine bleeding on any day of the cycle and postmenopause;
- Chronic pelvic pain: pulling and aching sensations in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, radiating to the sacrum, coccyx, perineum - depending on the location of the node;
- Disturbance in the functioning of adjacent organs: bladder and rectum - discomfort when urinating, chronic constipation.
In the early stages, fibroma makes itself felt by moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen and back. Unpleasant sensations occur mainly during menstruation. As the node grows, the pain becomes more intense, and menstruation becomes longer and more abundant. The larger the size and number of nodes, the higher the likelihood of breakthrough uterine bleeding and other complications.
The growth of fibroids is often accompanied by pain in the lower back or lower abdomen, uterine bleeding, and disruption of the functioning of adjacent organs.
On a note
Uterine fibroids are often combined with other pathological changes in the genital organs: endometrial hyperplasia, polyps, endometriosis. In this situation, the symptoms are blurred and do not fit into the typical clinical picture of the disease.
Modern techniques and diet
New technologies are now being used to eliminate the disease. One of them is to eliminate the tumor using ultrasound. The beam is directed to the location of the tumor. Subsequently, it is advisable to do tomography to monitor the postoperative process occurring in the uterus.
This manipulation makes it possible to remove the tumor without loss of blood, the use of anesthesia, or tissue injury. Childbearing function is also preserved. With this method of eliminating a tumor, there is no pain, fever, intoxication, or other side effects. Doctors rule out relapses of the disease after the procedure.
It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right, which normalizes metabolic processes in the body. Physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated. It is worthwhile to cure all existing genital infections as soon as possible, eliminate anemia, and normalize the menstrual cycle.
Myoma and fibromyoma
Since the uterus contains not only smooth muscles, but also connective tissue, it is customary to distinguish fibroids from myomas. However, in reality, many specialists, to understand patients, combine the concepts of fibroma, myoma and fibromyoma into a single whole. In the tissue layers of the uterus, if stromal cells predominate in the tumor process, and smooth muscle fibers are in the minority, they speak of fibromyoma of the uterine body. If the predominance of myometrial cells is pronounced, and there is very little connective tissue, the doctor has the right to diagnose myofibroma. When only connective tissue structures are found in a tumor, it is called fibroma.
What is common in the characteristics of these neoplasms is that any benign process in the uterus involves a large number of blood vessels, proliferating tissues and maintains characteristic symptoms. A thorough cytological examination revealed that there are still more of them in fibroids. A tumor consisting exclusively of smooth muscle cells is softer to the touch.
Is it possible to get pregnant with fibroids?
If a small uterine fibroid has been diagnosed, this will not be an obstacle to pregnancy and gestation. But the location of the tumor is sometimes important.
If the fibroma is located at the mouth of the fallopian tubes, which lead to the ovaries, then there is a mechanical obstacle to the advancement of the egg and associated infertility.
A fibroid located near the cervix (cervical fibrosis) can cause miscarriage or difficulty during childbirth and may cause heavy bleeding.
Large interstitial or submucosal fibronodules can compress the embryo, interfere with its development, prevent it from taking the correct position, which will complicate childbirth and force a cesarean section.
Considering all these reasons, you should carefully monitor the course of pregnancy. The issue of delivery is considered in each case individually.