Enterobiasis is a parasitic disease, one of the most common helminthiases. Enterobiasis is caused by pinworm worms. In Latin, pinworms are called Enterobius vermicularis, hence the name of the disease.
Pinworms are small round worms of a grayish-white color. The length of male pinworms is up to 5 mm, females are up to 13 mm. The living environment of pinworms is the human intestine (cecum, lower small intestine, large intestine). Pinworm eggs enter the human body orally (through the mouth). In the intestine, the eggs hatch into larvae that turn into sexually mature individuals. This process takes from 2 to 4 weeks. The fertilized female crawls out of the anus and lays eggs around it. For eggs to mature, a temperature of 34-36 °C and high humidity are required. The folds of skin in the perianal area ideally provide these conditions. The release of female pinworms most often occurs at night, when the anal sphincter muscles are relaxed. After this, the life cycle of the pinworm is completed. Thus, pinworms live no longer than a month.
Causes of enterobiasis
How does pinworm infection occur?
You can only become infected with enterobiasis from a person who is a carrier of pinworms. Pinworms do not live in the body of animals, and enterobiasis cannot be contracted from animals.
Self-infection is common. The female pinworm lays up to 13 thousand eggs, sealing them with acid, which causes severe itching. A person wants to scratch, and when he does this, the eggs get under the nails, on the fingers, and from them onto bedding, underwear, and household items. When living in a group, the spread of enterobiasis is very likely. If someone in the family becomes infected with pinworms, after some time enterobiasis can affect all family members.
Enterobiasis is predominantly a childhood disease
Most often, enterobiasis is detected in children aged 4 to 9 years. This is due to the fact that children at this age already take care of their hygiene on their own, but have not yet fully mastered all the necessary skills.
Life cycle of pinworm
Pinworm eggs are transparent, ellipsoidal, with asymmetry (the bottom is flattened, the top is slightly elongated). The shell of the eggs has many layers, it is smooth and has no color. Inside the egg, the larva is sometimes visible at various stages of its growth (Figure 2). The egg sizes are about 40-50 by 25-40 microns.
Figure 3 - Morphology of pinworm eggs
Infection usually occurs with a fairly large number of pinworms, sometimes there are several thousand. Helminths prefer to parasitize in the lower part of the small intestine and the upper part of the large intestine. Humans are the natural and sole host of pinworms and become infected as a result of ingestion of mature eggs containing a motile larva.
In the intestines, such a larva, under the influence of human digestive enzymes, is freed from the egg shells, with the help of a bulbus and vesicles it attaches to the intestinal wall and continues its development.
Figure 4 - Life cycle of Enterobius vermicularis
Young pinworms usually grow in the small intestine, and their sexual separation occurs there. After about twelve to fifteen days, the helminths become sexually mature individuals. In the cecum, males fertilize females. This process can also take place in the small intestine. Males die immediately after fertilization. The maturation of eggs in the reproductive apparatus of females occurs when the helminths are already located in the lower parts of the large intestine.
When the uterus fills with mature fertilized eggs, it puts its weight on the bulb, displacing it and causing it to detach from the mucous membrane. Thus, it is almost impossible for mature females to hold on to the intestinal walls.
Fertilized females with ready, mature eggs are detached from the intestinal walls and, with the course of peristaltic waves of the intestine, instantly descend to the final section of the large intestine.
In this zone, females, using body movements, crawl down the wall of the rectum, crawl out of the anus (anus) to the outside so that eggs are laid in the external environment. The female can lay several thousand eggs at a time.
When helminths move, an infected person experiences a sensation of itching and tickling in the rectum itself and in the circumference of the anus. For some time, parasites are able to crawl in the external environment, moving towards the genitals; at times they crawl onto the hips and lower back.
Most often, the female lays her eggs in folds near the anal ring, usually at the border between the skin and the mucous membrane, and sometimes on the walls of the genitals.
As females crawl along the rectal lining, some of them lose some of their eggs because their uterus is often full. Due to the fact that the larvae develop only in the presence of a sufficient amount of oxygen, unfavorable conditions are created for them in a normally functioning intestine.
Some clusters of eggs that the female lays on the surface of the skin are sometimes visible to the eye without the use of any special devices (magnifying glasses, microscope). They look like small white concentrations.
Females die immediately after laying their eggs. Therefore, the lifespan of these roundworms is approximately twenty to thirty days.
The eggs that the female lays contain an incompletely formed larva. In particularly favorable conditions (air humidity - from seventy percent and above, the presence of oxygen and the presence of a temperature close to the surface temperature of the human body), unformed larvae mature within four to six hours to the moving larval stage. Just in the perianal folds, on the skin of the perineum, on the fingers and under the nails, where they can get in the process of scratching itchy places, all the parameters correspond to those necessary for their development.
At the same time, eggs can be scattered across bedding and underwear. Thus, in the morning they already become invasive. Therefore, a person can become permanently infected with pinworms by swallowing or inhaling eggs with motile larvae.
With massive infestation, egg laying can occur at any time of the day (day and night), although this process is usually observed before sleep or at night, when the muscles of the anal ring relax due to the physiological characteristics of the nervous system.
Enterobiasis is transmitted to a healthy person from an infected person through contact (dirty hands) and through other objects (toys, linen, food, etc.) that may be contaminated with parasite eggs.
Therefore, children and family members are most often affected. In addition, organized children's groups, sanatoriums, camps, medical institutions and catering establishments are of epidemiological importance. There is no immunity to this disease, so there are known cases of long-term self-infection with pinworms due to non-compliance with hygiene rules.
Symptoms of enterobiasis
The main symptom of enterobiasis is severe itching in the anus. Typically, itching begins 12-14 days after infection, when the first female pinworms crawl out to lay eggs. Enterobiasis is characterized by itching (or intensification of itching) at night.
Intensive scratching can lead to dermatitis and secondary infection.
At the same time, very often a child suffers from enterobiasis without the parents noticing. If there are no other symptoms besides itching, the child may scratch himself without considering it a problem and not complain about anything. Therefore, enterobiasis is often detected only during preventive examinations of children.
Other symptoms of enterobiasis:
Abdominal pain
If there are a lot of parasites in the intestines, abdominal pain and flatulence may occur.
Stool disorder
The presence of pinworms in the intestines leads to disruption of its functioning, dysbiosis develops, and stool disorder is observed (alternating diarrhea and constipation).
Allergic manifestations
Pinworms secrete toxins that poison the body and cause a response in the form of allergic manifestations. With enterobiasis (especially in children), headaches, dizziness, increased fatigue, and decreased performance are possible. Children can become capricious and excitable; It is difficult to put such children to bed; their sleep is easily interrupted. In their sleep, they can scream, cry, and grind their teeth.
Diseases of the genitourinary system in women
In women, pinworms, when migrating, can leave the anal area and enter the vagina. At the same time, intestinal microflora (in particular, E. coli) can be introduced into the genital tract, which can lead to the development of inflammation - colpitis, urethritis.
Structure and physiology of pinworms
The human pinworm is the causative agent of enterobiasis. These helminths parasitize the human intestines, but the eggs need to be released into the environment to fully mature. Pinworms have the same structure as other roundworms.
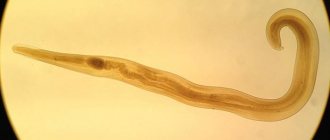
The body of the helminth is round in cross-section and elongated in shape. Adults vary in sex. The rear end of the female is pointed, while that of the male is curled on the ventral side. That's why these parasites got their name. On the sides of the caudal end there are growths of the cuticle, which are called caudal wings. Females are usually larger than males and measure between nine and twelve millimeters. Males are only two to five millimeters in size (Figure 1).
Figure 1 - Male pinworm under formaldehyde
At one end of the body there is an opening for the mouth, framed by three folds resembling lips (one of them is located on the side of the “belly”, the other two are on the back). Behind them is a special swelling of the cuticle, which is called a vesicle. Thanks to it, pinworms are retained in the intestines of the host. The anus is located at the end opposite the opening of the mouth and is located on the abdomen.
The helminth is covered with a special skin-muscular sac. This is a complex cellular formation, the first layer of which is the cuticle, the second is the muscles, which are represented by longitudinal ribbons, and the third is the hypodermis, which forms ridges between the muscles. The cuticle has a complex biochemical structure. Its main function is to provide a barrier with the environment; it prevents the penetration of various substances into the helminth, ensuring its internal constancy of the environment (homeostasis). Also, the cuticle is a specific skeleton, since muscle fibers are attached to its cells.
The hypodermis lies under the cuticle. It looks like compacted ridges located throughout the body of the pinworm. The hypodermis takes part in the barrier function and in the formation of the cuticle, and many useful microelements also accumulate in it.
Figure 2 - Structure of pinworms
Immediately below the hypodermis there is a layer of longitudinally arranged muscle fibers. The space under the skin-muscle sac is a cavity filled with a toxic liquid that has a complex biochemical composition. It is a hydroskeleton that functions as a support.
The digestive system is well developed and is represented by a straight tube stretching from the opening of the mouth to the anus. Behind the mouth opening is the esophagus. Its initial compartment is separated from the final one by a deep constriction. The esophagus works like a pump. It is followed by another extension, the so-called bulbus. It is also involved in parasite attachment. Thus, food moves through the helminth’s intestines in one direction and is better absorbed.
The excretory system consists of cervical glands, from which long canals extend. They are located inside the hypodermal ridges. The channels of the right and left halves of the body merge into one duct that opens on the abdomen. The function of the excretion system is to excrete waste as well as maintain internal pressure.
The female genital organs are double. They are represented by two ovaries, which flow into two oviducts, followed by double uteruses. They merge and form a short vagina, which opens with a slit in the anterior quarter of the body, located transversely. The male genital organs are always unpaired. First comes the testis, after it is the vas deferens, which turns into the ejaculatory canal. Behind it a complex copulatory organ is formed. The circulatory and respiratory systems are not developed. Breathing is carried out using the integument, and sometimes only through chemical processes.
Methods for diagnosing enterobiasis
Diagnosis of enterobiasis is made based on the results of laboratory tests. Analysis of stool for eggs of pinworm helminths, as a rule, does not detect. This is due to the fact that pinworm eggs do not pass into the feces. To identify pinworm infections, scrapings from the folds of skin around the anus are used (scraping for enterobiasis).
Scraping for enterobiasis
A scraping for enterobiasis in a child can be done in the treatment room of any of the Family Doctor clinics. The procedure is carried out quickly and does not cause any discomfort in children.
The biological material is transferred to the Family Doctor’s own laboratory for microscopic examination.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Treatment methods for enterobiasis
Treatment of enterobiasis is carried out by pediatricians, and in adult patients - by gastroenterologists.
For treatment success, it is important that all family members are treated at the same time. Careful personal hygiene is also necessary. When treating children, parents need to pay special attention to the child’s hygiene.
Anthelmintics
Anthelmintic drugs are used in the treatment of enterobiasis.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating