Causes
The bladder can become infected in the following ways:
- Rising. The infection spreads upward from the urethra.
- Descending. Pathogenic microflora moves in the direction of urine flow during the inflammatory process in the kidneys.
- Hematogenous. Pathogens penetrate through the bloodstream from chronic foci of infection. The cause of such infection can be carious teeth, cholecystitis, tonsillitis, and furunculosis.
- Lymphogenic. The lymphatic vessels of the pelvic organs collect infection from the genitals and lower intestines.
- Straight. Occurs when ulcers located in nearby organs are opened.
Important! E. coli accounts for about eighty percent of cases of acute cystitis.
The following factors play a major role in the occurrence of acute cystitis:
- pregnancy. The enlarging uterus puts pressure on the urinary tract and provokes stagnation;
- prostatitis. Swelling and growth of the prostate gland disrupts the natural flow of urine;
- structural abnormalities of the urinary system;
- ICD;
- injuries;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- circulatory disorders in the pelvis;
- incomplete or untimely emptying of the bladder;
- vitamin deficiency, hypothermia, fatigue, weakened immunity;
- overactive bladder;
- reflux urine.
Acute cystitis can be caused by:
- Representatives of the intestinal microflora: Escherichia coli, Proteus, Enterococci, Enterobacteriaceae.
- Representatives of sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasma, yeast-like fungi, ureaplasma.
- Nosocomial infections: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, viruses, gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Reasons for the development of the disease
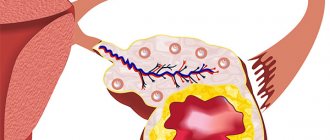
Acute cystitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder and urinary tract. As a rule, the disease is infectious in nature and occurs in 35% of people of both sexes aged 20 to 40 years, although it is often diagnosed in young children.
And yet, it is women who, due to the anatomical features of the structure of the genitourinary system, are 8 times more likely than men to suffer from cystitis.
Acute inflammation can be caused by bacteria, parasites and viruses. Most often these are E. coli, staphylococcus and mushrooms. The infection can enter the bladder either through the urethra or through the blood or lymph.
Bacteria are common causative agents of cystitis.
What are the causes of acute cystitis:
- Violation of personal hygiene rules and entry of bacteria from the anus into the urethra.
- Microtrauma of the bladder (in various studies).
- Long-term use of a catheter. The catheter is a carrier of infection, and the longer it is in the urethra, the higher the chance that an infection is intensively cultivated on its walls.
- Change of sexual partner.
- Hormonal changes.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- Hypothermia of the lower half of the body. It is enough to wet your feet a little, and the first symptoms of the disease may appear.
- Venereal diseases. Inflammation of the bladder can be caused by chlamydia and trichomonas.
- Disruption of the normal outflow of urine. This occurs in men who suffer from prostate adenoma, as well as in cases where a kidney stone is stuck in the urinary tract and cannot pass out on its own.
- Weakening of the immune system. It should be noted that despite the fact that cystitis is a very common and common disease, it is strictly individual in nature.
- Diabetes mellitus, a tendency to frequent diarrhea, and a number of other diseases.
- Elderly people and pregnant women are at risk.
And even in the presence of many of the factors described above, cystitis rarely occurs in people with strong immunity, but in people with weak immunity it flares up regularly - as soon as you get a little cold.
Symptoms
The manifestation of acute cystitis depends on three main factors:
- prevalence of the pathological process;
- depth of lesion;
- degree of blood vessel involvement.
Classic signs of acute cystitis include the following symptoms:
- frequent urge to urinate. If normally during the daytime a person walks “smallly” up to eight times, and at night - a maximum of two, then with inflammation the urge occurs every few hours, or even more often;
- excretion of a meager amount of urine;
- at the end of urination, cutting, burning and painful sensations occur, and sometimes blood appears;
- feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder;
- pain in the suprapubic region radiates to the groin and perineum;
- urine loses transparency, becomes cloudy and in severe cases takes on the appearance of meat slop.
When the bladder neck is involved in the process, urinary incontinence occurs. The development of a diffuse process is indicated by an increase in temperature and chills.
Classification
Acute cystitis in women is an uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection. It occurs when there are no concomitant diseases, malfunctions of the kidneys, and when the bladder functions normally.
Inflammation can affect the entire mucous membrane of the bladder (total cystitis) or parts of it (cervical, trigonitis). Based on the nature of the inflammation, the catarrhal form is distinguished, when the mucous membrane is swollen and filled with blood. Cystitis with blood in women, which is called hemorrhagic, develops when red blood cells enter the urine. In this case, blood in urine is visible to the naked eye.
Acute cystitis with blood
With hematuria, blood occurs not only at the end of urination, but also from the very beginning. The urine may turn pale pink or even dirty brown. This largely depends on the stage of the pathological process. Urine acquires an unpleasant odor. In some cases, entire blood clots are passed in the urine.
The following reasons can provoke hemorrhagic cystitis:
- if a person endures for a long time and does not empty the bladder. As a result, muscle fibers are overstretched and blood circulation is impaired;
- neurogenic conditions can negatively affect the contractile function of the bladder;
- the presence of a foreign body or a growing tumor.
One of the most dangerous complications of hematuria is blockage of the urethra with a blood clot. The bladder becomes distended because urine is produced but cannot be released. In addition, pathogenic microorganisms can easily enter the systemic circulation through damaged blood vessels. This is fraught with blood poisoning.
Complications
With poor treatment or lack thereof, the infection from the bladder rises higher. Pyelonephritis, or inflammation of the kidneys, occurs.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
- Temperatures 37.5°C and above.
- Chills, fever and increased heart rate.
- Increased fatigue and general weakness.
- Dehydration, nausea and vomiting.
- Frequent urination, painless or with burning pain.
- The presence of blood clots and a “fishy” odor in the urine.
- A nagging pain in the lower back or on the side of the affected kidney.
A similar condition during pregnancy and in children requires immediate hospitalization, since the body is poisoned by excretory products. In other cases, urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Timely treatment of pyelonephritis has a favorable prognosis, but one should not hesitate. Its complications include chronic form and renal failure, kidney abscess and sepsis.
Acute cystitis in women
Urologist: if you want to get rid of cystitis so that it doesn’t come back, you just need to dissolve Read more »
Features of the anatomical structure contribute to the prevalence of cystitis among the female population:
- short urethra;
- the external opening of the urethra is located close to the vagina and anus.
In most cases, pathogens first enter the urethra and then enter the bladder cavity. As a rule, cystitis is closely associated with colpitis and bacterial vaginosis.
Provoking factors
Microflora penetrates the bladder, multiplies there and causes inflammation under the influence of the following factors (one or more):
- Anatomical structure.
In 95% of cases, infectious agents enter the bladder, rising from the anus. This is where the greatest concentration of various microorganisms is. The female urethra (urethra) is short and wide (unlike the male one), and its ending is in close proximity to the anal area and vagina. For this reason, it is easy for microflora to penetrate the urethra and rise higher into the bladder. And this explains why inflammation occurs more often in women than in men. However, in some cases, the infection can also penetrate from the kidneys and other neighboring organs where there are foci of inflammation.
- The presence of concomitant diseases and especially sexually transmitted infections.
Very often, a urinary infection coexists with candidiasis (thrush), bacterial vaginosis, and colpitis. With these gynecological diseases, the balance of the vaginal microflora is disturbed towards an increase in the number of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Instrumental intervention.
Examination with instruments, installation of a catheter, presence of an implant.
- Hereditary predisposition.
The bladder has a protective layer that is capable of secreting special substances that prevent the attachment of bacteria. In some cases, they are produced in smaller quantities, and this disorder can be inherited.
- Features of behavior and sexual life.
Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, lack of urination after sex, frequent sexual intercourse, use of vibrators, wearing thongs - urologists consider these factors to be of paramount importance in the development of the disease.
Acute cystitis in children
The acute process quite often develops in children and the treatment process is not fundamentally different from the treatment of adults. In the first year of life, both boys and girls get sick with the same frequency, but the disease is most common among girls seven to eight years old.
The causes of childhood cystitis may include the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- past infections;
- developmental anomalies of the urinary system.
The following pathogens can cause childhood cystitis: chlamydia, streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli. A child can become infected with chlamydia in a family where basic personal hygiene rules are not followed, as well as when visiting a swimming pool or bathhouse.
In young children, the presence of acute cystitis can be judged by the following signs:
- irritability, moodiness;
- cry when urinating;
- refusal to feed;
- hyperthermia.
Inflammation of the bladder in pregnant women
The development of cystitis during pregnancy is often observed, both in the early and late stages. The course of this disease during pregnancy is in itself considered complicated, since the use of many medications is contraindicated. Cystitis during pregnancy should be treated only in a hospital setting, since the risk of the inflammatory process spreading to the kidneys is very high, and this is fraught with the development of unfavorable conditions for the development of the fetus.
The main reason for the development of cystitis during pregnancy is compression of the walls of the bladder by the growing uterus, as a result of which some of the urine is retained in the body and creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of bacterial microflora.
A woman must understand that she is responsible not only for her health, but also for the life of the growing fetus in the womb, therefore the detection of the first symptoms of cystitis should be a reason to immediately contact your obstetrician-gynecologist.
Acute cystitis during pregnancy
WHAT DO THE DOCTOR'S SAY?
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation and Honorary Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Anton Vasiliev:
“I have been treating diseases of the genitourinary system for many years. According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, cystitis in 60% of cases becomes chronic.
The main mistake is delaying!
The sooner you start treating cystitis, the better. There is a remedy that is recommended for self-treatment and prevention of cystitis at home, since many patients do not seek help due to lack of time or shame. This is Ureferon. It is the most versatile. It contains no synthetic components, its effect is mild, but noticeable after the first day of use. It relieves inflammation, strengthens the walls of the bladder, its mucous membrane, and restores general immunity. It is suitable for both women and men. For men there will also be a pleasant bonus - increased potency. " READ THE FULL INTERVIEW"
Approximately ten percent of pregnant women experience acute cystitis and this is due to the following reasons:
- chronic foci of infectious process;
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- mechanical compression of the organ;
- hormonal changes.
Important! Even overwork can cause acute cystitis in a pregnant woman .
Cystitis during pregnancy can be allergic in nature. Allergens may include:
- decorative cosmetics;
- Food;
- shower gel;
- bath foams and more.
Most medications are prohibited during pregnancy due to toxic effects on the fetus. For this reason, herbal medicines form the basis of the healing process. Herbal treatment continues until urine tests normalize.
Antibacterial therapy is a last resort measure that is prescribed if the development of pyelonephritis is suspected. In this case, inpatient treatment is indicated. Pregnant women are prescribed a dairy-vegetable diet.
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis (simple bladder ulcer) is a special form of inflammatory lesion of the bladder wall.
The etiology of interstitial cystitis has not been fully elucidated. The inflammatory process, starting in the submucosal layer, gradually affects all layers of the bladder wall, accompanied by progressive fibrosis and a decrease in its capacity (wrinkled bladder); disturbance of trophism leads to the formation of ulcers. Women aged 45-50 years are more likely to get sick. The course of the disease is protracted and progressive. Characterized by pronounced dysuria (see), terminal hematuria (see).
Cystoscopy reveals a round, sharply painful ulcer with a diameter of no more than 20 mm at the apex of the bladder or on its side wall. Inflammatory changes along the periphery of the ulcer are usually not pronounced. As a rule, only one ulcer is detected at a time, and after healing, another one forms.
Differential diagnosis is made with tuberculosis and bladder tumor. The absence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the urine, normal function of both kidneys, and the absence of signs of scarring in the pelvis and ureters allow us to exclude tuberculosis. Endovesical biopsy plays an important role in the differential diagnosis of interstitial cystitis and bladder tumor.
Treatment is conservative, complex. Prescribe sedatives, hyposensitizing, antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory drugs, instillation of hydrocortisone into the bladder in combination with antibiotics and anesthetics, presacral novocaine blockades (see), and physiotherapy.
Improvement can only occur in cases of intensive treatment started in the early stages of the lesion. The progression of the disease leads to irreversible changes in the bladder with disruption of its function, resulting in the need for intestinal plastic surgery (see).
Complications of acute cystitis
Acute cystitis is dangerous due to its complications:
- interstitial cystitis. The process involves not only the mucous layer, but also the muscular layer of the bladder. This threatens the organ’s shrinkage and loss of functional activity;
- hematuria. Blood discharge can be so profuse that it leads to significant blood loss;
- pyelonephritis. The infection spreads along the ascending tract and reaches the kidneys. In severe cases, pyelonephritis is life-threatening;
- reflux of urine. There is a reverse flow of urine towards the kidneys;
- During pregnancy, the disease threatens premature birth or the birth of a low-weight baby.
Radiation cystitis
Radiation cystitis is a complication of radiation therapy (see), developing depending on the radiation dose and the sensitivity of the irradiated tissues, at different times: during the course of radiation therapy, immediately after it, several weeks, months or years. The wedge, manifestations and changes in urine are the same as with chronic cystitis. In the later stages, cicatricial and ulcerative changes in the bladder wall are characteristic. For radiation cystitis, in addition to symptomatic and antibacterial treatment, instillations of fish oil, methyl uracil, and intravesical injections of corticosteroids are used. If there are extensive lesions of the bladder and there is no effect from conservative treatment, resection of the affected area or intestinal plastic surgery is performed. The prognosis is relatively favorable only with treatment in the early stages.
Prevention consists of rational planning of radiation therapy, taking into account the radiation sensitivity of tissues and organs (see Radiosensitivity), as well as the use of protective devices (see Radiation damage, prevention).
See also Bladder.
Bibliography:
Arsanukaev M.A. and Starchuk N.I. Postoperative cystitis in children, Urol. and nephrol., No. 6, p. 14, 1980; Doletsky S. Ya. et al. The use of supratonal frequency current in the complex treatment of cystitis in children, ibid., No. 6, p. 35, 1982; Dukhanov A. Ya. Urology of childhood, p. 199, M., 1968; Klimenko B.V. The role of trichomoniasis in the occurrence of cystitis in men, Urol. and nephrol., No. 6, p. 44, 1976; Lavrovskaya L.K., Barybin A.S. and Mezentsev A.I. The use of dimethyl sulfoxide in the complex treatment of early and late radiation cystitis, in the book: The use of radioactive isotopes in diagnosis and treatment, ed. A. I. Mezentseva and V. D. Tarasenko, p. 60, Sverdlovsk, 1973; Lyulko A.V., Volkova L.N. and Sukhodolskaya A.E. Cystitis, Kyiv, 1983; Pugachev A.G. and Eshmukhambetov S.N. Chronic cystitis in children, Alma-Ata, 1983; Romanenko A. M. Chronic cystitis in the aspect of their belonging to precancer, Arch. pathol., No. 12, p. 52, 1982; Tiktinsky O. L. Inflammatory nonspecific diseases of the genitourinary organs, p. 193, L., 1984; Aubert J., Dore B. La cystite a eosinophiles, J. Urol., t. 89, p. 65, 1983; Aubert J. ea La cystite incrustee h urine alcaline, Aspects cliniques et traitement, ibid., t. 88, p. 359, 1982; Buckwold FJ ao Therapy for acute cystitis in adult women, J. Amer. med. Ass., v. 247, p. 1839, 1982; Doyle PT ao Abacterial cystitis, Brit. J. Urol., v. 49, p. 647, 1977; Dunn M. a. O. Interstitial cystitis, treated by prolonged, bladder distension, ibid., p. 641; Fall M., Garlsson C.-A. a. Erlandson B.-E. Electrical stimulation in interstitial cystitis, J. Urol. (Baltimore), v. 123, p. 192, 1980; Mufson MA a. BelsheR. B. A review of adenoviruses in the etiology of acute hemorrhagic cystitis, ibid., v. 115, p. 191, 1976; WorthP.HLa Turner-Warwick R. The treatment of interstitial cystitis by cystolysis with observations on cystoplasty, Brit. J. Urol., v. 45, p. 65, 1973.
A. V. Lyulko.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of acute cystitis is not difficult. Usually the clinical picture clearly indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the bladder. Additional research will help confirm the doctor’s assumptions.
A general urine test is of great diagnostic value. Microscopy of sediment reveals the following changes:
- increased levels of red blood cells and white blood cells. If normally these elements are present in single values, then in acute inflammation they can cover the entire field of vision;
- a large amount of mucus;
- presence of bacteria.
To identify the pathogen, bacteriological urine culture is performed. For analysis you will need a morning urine sample. Before collecting biomaterial, you must wash yourself. Urine is collected in a sterile container, which is best purchased at a pharmacy.
Important! Correct collection of biological material is the key to accurate diagnosis. Women are strictly prohibited from taking a urine test during menstruation.
An ultrasound examination is performed with a full and empty bladder. This will help rule out neurogenic dysfunction.
The doctor conducts a differential analysis of acute cystitis with the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis;
- appendicitis;
- paraproctitis;
- neoplasms;
- ICD.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you have a question about what to do with acute cystitis, it means that the first symptoms have already appeared. It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics. Cystitis is diagnosed by blood tests, general and bacteriological examination of urine.
Thanks to the tests, the specialist determines nonspecific signs of the inflammatory process and the causative agent of inflammation - bacteria, parasites or viruses. Then it determines sensitivity to antibiotics and then selects the appropriate drugs.
Urine and blood tests cannot always answer all questions regarding the causes of the disease. If there is a suspicion of the presence of a stone or a protrusion of the walls of the bladder (diverticulum), to clarify the picture, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys, X-rays and CT (X-ray radiation).
Important! Only after these measures can a medical history be formed and a course of treatment prescribed.
Treatment
Several factors influence the choice of treatment tactics:
- age;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- presence of pregnancy.
Important! Most often, treatment of acute cystitis is carried out on an outpatient basis. The doctor may decide to hospitalize in case of severe intoxication and suspicion of acute pyelonephritis.
General principles of treatment
Treatment of acute cystitis includes following these recommendations:
- compliance with bed rest;
- drinking enough fluids;
- refusal of foods that irritate the bladder mucosa: spicy, fried, alcohol, coffee;
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene;
- for the period of treatment, abstain from sexual intercourse;
- monitor bowel movements.
Drugs
Treatment of acute cystitis includes the use of the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- antispasmodics;
- herbal medicines;
- corticosteroids;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- non-steroidal drugs.
Antibiotic therapy is an important element of the treatment process for cystitis. It affects the very cause of the disease, completely eliminating it. For acute cystitis, the following antibiotics are prescribed:
- nitrofuran series – Furadonin;
- fluoroquinolones – Ofloxacin, Norfloxacin;
- macrolides – Monural;
- cephalosporins – Cefixime.
The treatment course lasts seven to ten days. Warming home procedures should never be carried out at high temperatures. Taking a hot bath is prohibited! It is allowed to place a warm heating pad on the suprapubic area.
Medicinal decoctions that have diuretic and antiseptic effects are used as herbal medicine:
- bear ears;
- kidney collection;
- lingonberry leaves.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of acute cystitis, it is necessary to adhere to some rules:
- Monitor your diet, as good nutrition supports the body’s immune defense, in particular humoral immunity.
- Maintain personal intimate hygiene.
- Monitor weather conditions, as a common cause of cystitis is hypothermia due to improperly selected clothing.
- Use barrier methods of contraception when having sex.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
How to relieve an attack of acute cystitis
In case of severe pain, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before the team arrives, you can do the following:
- lie down;
- to warm up, make foot baths;
- wear warm socks and wrap yourself in a warm blanket;
- drink warm tea based on medicinal herbs.
You can relieve an attack using traditional methods of struggle:
- Place a hot stone in a bucket and warm it up over the bucket. Granite is best suited for this. You need to sit on the bucket and wrap yourself in a blanket. The procedure lasts fifteen minutes;
- Brew dry eucalyptus leaves in a liter of water and let it brew for two hours. Use a ready-made remedy in the form of douches, this will help relieve an attack of pain. This recipe is even suitable for hematuria;
- A decoction of rosehip roots contains a large amount of ascorbic acid. Vitamin C is known to help the body better fight infection. Twenty minutes before meals, drink half a glass of broth.
If this is not the first time you have had an attack and it was provoked by an exacerbation, then you can soften the symptoms with the help of antimicrobial agents: Furadonin, Monural, Nolitsin. As an emergency, take two Furadonin tablets.
The drug has not only antimicrobial properties, but also a diuretic, so at the same time drink enough liquid. After the first urination, the pain will subside. After an hour, be sure to eat, because these medications can have side effects.
Monural is taken once, 2 g of the drug is diluted in water. As for Nolicin, it is taken one tablet twice a day for three days.
Drugs
An adult patient can choose a medicine with few side effects. For children, you need to look at the manufacturer's instructions to determine whether the tablets are allowed to be used in infancy.
The doctor may recommend medications from the following list:
- "Monural" is a good quality antibiotic in the fight against bacterial infection.
- "Nolitsin" is a drug with a wide spectrum of effects, antimicrobial.
- Nitroxoline is an antibiotic that kills both bacteria and fungi.
- "Palin" is an antibiotic, used in both acute and chronic phases.
- “Furagin” is an antibiotic; pathogens remain sensitive to it for a long time.
- "Nevigramon" is a uroantiseptic agent with a bactericidal effect.
- "Rulid" is a widely used antibiotic.
- "Furadonin" is an antimicrobial agent used exclusively in the fight against bacterial infections.
Treatment of acute cystitis at home
The following pharmaceutical drugs will help relieve spasm and pain at home:
- Analgin;
- No-shpa;
- Spasmalgon;
- Rectal suppositories: Ketorol or Diclofenac.
At home you can use herbal preparations:
- Monurel. It contains cranberry extract. The product strengthens the body's defenses;
- Phytolysin. Available in paste form. The composition of the drug includes plant extracts. Phytolysin has anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and diuretic effects;
- Canephron, like Phytolysin, reduces inflammation and eliminates dysuria.
Chronic cystitis
If treatment of acute cystitis was not started in a timely manner or the patient independently stopped taking medications prescribed by the doctor, then cystitis passes into the chronic stage. In this case, acute manifestations of the disease, as a rule, subside, and the patient mistakenly believes that a cure has occurred. However, after some time, under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors (hypothermia, rough sex, abuse of alcohol and spicy foods), the disease worsens with renewed vigor, with more pronounced clinical symptoms that are already difficult to respond to antibacterial therapy. This is due to the development of resistance of the pathogenic infectious agent to the antibiotic. Thus, cystitis will occur more and more often, and it will be more and more difficult to cure it.
Diet
Diet for acute cystitis is no less important than drug therapy. Proper nutrition helps you achieve good success:
- remove intoxication. To do this, experts recommend arranging several vegetarian days. Animal proteins can only aggravate intoxication. Use pureed boiled carrots, zucchini, beets or cauliflower. Drink more liquid, it can be anything: jelly, compote, fruit drink, tea, juice. The liquid helps eliminate toxic substances and relieve intoxication;
- stop the active reproduction of pathogens. Lingonberry and cranberry juice can help with this;
- reduce irritation of the bladder mucosa. Hot seasonings and spices can irritate the affected organ: horseradish, mustard, pepper. Also prohibited are those products that contain a large amount of essential oils: smoked meats, mushrooms, broths, radishes, radishes, garlic;
- prevent stone formation. If amorphous urates have been detected, then it is necessary to eat food that will provide the body with the required amount of alkali: milk, fruits, vegetables, berries. If phosphates are present, it is better to give preference to fish, seafood, meat, and eggs. If you have oxalates, you should avoid citrus fruits, greens, cocoa and anything that contains oxalic acid;
- enhance the effect of antibiotics. The activity of some drugs depends on the acidity of the urine. Therefore, adding or excluding certain products can affect the effectiveness of such products.
Recommendations
Acute cystitis in women with timely treatment has a favorable prognosis. However, it is equally important to carry out appropriate prevention:
- Treat genital infections promptly.
- Be sure to urinate after sexual intercourse and perform water procedures before and after intimacy.
- You cannot tolerate or deliberately delay emptying. This weakens the urinary immunity.
- During treatment and after, for the purpose of prevention, drink more fluid (at least 2.5-3 liters per day). In addition, high fluid intake is the first prevention of bladder cancer.
- Don't wear thongs. Such underwear makes it easier for E. coli to enter the urethra.
When treatment is completed and the symptoms of acute cystitis have disappeared, a repeat general analysis and urine culture are not performed. If within 2 weeks after treatment signs of the disease reappear, a bacteriological culture must be prescribed to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. In this case, the doctor recommends another drug, but for a longer course.
Did you like the article?
Prevention
Cystitis is mainly an infectious disease, therefore preventive measures should be aimed primarily at preventing the penetration of pathogenic microflora and strengthening the body's resistance.
Let us highlight the main recommendations that will help reduce the risks of acute cystitis:
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene. After each act of defecation, you should wash yourself. The stream of water should be directed towards the anus, and not away from it. Avoid intimate hygiene products and vaginal tampons;
- wearing underwear made from natural fabrics;
- using a condom during casual sexual intercourse;
- rehabilitation of chronic foci of infection and timely treatment of somatic diseases;
- compliance with the drinking regime;
- try not to get too cold;
- Avoid radical diets; the daily diet should be balanced.
Diagnosis and treatment of cystitis
The key to quick and effective treatment of cystitis is correct diagnosis and timely administration of appropriate therapy. Our center carries out all the necessary examinations for this disease: urological and gynecological examinations, ultrasound of the genitourinary tract, urine and blood tests and cystoscopy. Experienced urologists will help you get rid of the disease as soon as possible. The main thing is to contact a specialist at the first signs of the disease, so that cystitis does not become your “eternal companion.”
Reading reviews on the Internet about the treatment of cystitis, you may come across methods of treating cystitis using folk remedies or, for example, the widely advertised drug Monural. But self-medication in this matter is absolutely unacceptable! Only a urologist will be able to select the correct treatment regimen for you, including effective drugs for the treatment of cystitis, and will also prescribe the necessary follow-up examination after cystitis to prevent relapse.
We know how to treat cystitis! The method of treatment of cystitis in the multidisciplinary clinic "MedicCity" is selected individually by a urologist, taking into account the characteristics of each patient and examination data. Treatment of cystitis should be aimed both at suppressing the source of infection, and at increasing the body’s immunity and restoring normal vaginal microflora in women with cystitis.