- Conservative treatment
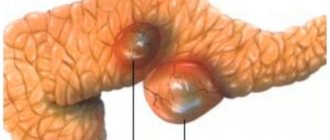
A spleen cyst is a neoplasm that is a pathological cavity in the parenchyma of the organ. The cystic formation is separated from healthy tissue by a capsule, the cavity is filled with liquid contents. According to statistics, this pathology occurs in approximately 1% of the population.
In approximately 50% of cases, a cystic formation is discovered accidentally during a routine medical examination or diagnosis for another reason.
There are several types of spleen cysts, the treatment approach depends on the type
Classification
Several different thickenings can form on the spleen. Due to education, they distinguish:
- true (disturbance of intrauterine development of the fetus, formed even before birth, can spontaneously resolve);
- false (after surgery, injury to the spleen, infections);
- parasitic (appear when parasitic larvae penetrate an internal organ).
A true cyst on the spleen can be solitary, dermoid, retention, multilocular cystadenoma. False ones are classified as inflammatory or traumatic.
Modern method of operations
The most effective method of surgical intervention today is laparoscopy. It allows not only to completely cope with the disease, but also to minimize the process of rehabilitation of patients. This operation is carried out within two hours, using ultra-precise instruments and a special camera. After surgery, only 3 small incisions remain on the patient’s body, onto which only 1 cosmetic suture is applied. After just a few months, the scars disappear almost completely.
Causes
There are several reasons for the appearance of neoplasms:
Violation of intrauterine development.
- intrauterine development disorder. This can be affected by taking medications during pregnancy, smoking, alcohol, toxic damage to the tissues of the woman carrying the child;
- suppuration of the spleen or its infarction. A void appears in this place, which is subsequently filled with liquid contents;
- surgical intervention to which an internal organ has undergone. A cyst appears when part of the spleen is removed, a purulent abscess is opened, etc.;
- mechanical injuries, abdominal bruises, which cause rupture of the internal organ and provoke the formation of a cyst;
- inflammatory changes, severe infections (typhoid fever). A cavity occurs in the place where internal tissues have been damaged;
- Parasitic cysts of the spleen are formed when infected with larvae of pork tapeworm and echinococcus.
Symptoms of a spleen cyst
The appearance of characteristic signs is influenced by the size of the thickening and location. Until the cyst reaches 2 - 3 cm, there are no symptoms in most cases. It is difficult to make a diagnosis even when examined by a doctor.
Subsequently, with a strong increase in the benign tumor, the following symptoms appear:
The pain is localized in the left hypochondrium.
- painful sensations are localized in the left hypochondrium;
- the temperature rises (with an increase in the diameter of the cyst to 7 cm and above);
- nausea or vomiting;
- deterioration of health, weakness;
- after lunch or dinner there is an unpleasant feeling of heaviness in the stomach, belching;
- Shooting occurs in the chest area when inhaling air;
- some patients suffer from shortness of breath and cough.
Upon examination, the doctor notes an enlargement of the organ. Splenomegaly is detected when the size of the spleen increases over 12 cm.
Odrex Patient History
“I work as a mechanic in the merchant navy. Minor injuries and bruises are commonplace on a boat, so when I fell on my stomach and hit my chest, I didn’t think anything of it. Moreover, at that moment nothing bothered me.
I saw a doctor on land, about a year after that fall. From time to time I felt pain and discomfort in my left side, and the time was approaching for a scheduled examination before leaving for the next flight. Through insurance, I turned to Odrex to the surgeon Anastasia Sergeeva . She inspired my confidence, and I decided to have the operation.
I was surprised how quickly I got back on my feet. Almost immediately I was able to continue living a full life. I am grateful to Anastasia for her professionalism and responsiveness,” Oleg Strekul , patient.
Possible complications
Education cannot be left unattended as the consequences can be quite serious. When a tumor appears, suppuration in the capsule is possible. If the cystic formation opens spontaneously, this threatens the penetration of pus into the abdominal cavity. Internal bleeding is possible.
As a result of opening a benign tumor, acute peritonitis develops.
As a result of opening a benign tumor, acute peritonitis develops and the body becomes intoxicated with decay products. In the most severe cases, this is fatal.
Cyst in the spleen in a child
If the expectant mother has bad habits, the risk of tumor formation increases significantly.
In most cases, the pathology in children is congenital. A splenic cyst in a newborn develops during fetal development. If the expectant mother has bad habits or uses medications prohibited during pregnancy, the risk of developing a benign tumor increases significantly. Even severe toxicosis can cause deviations in the development of an internal organ.
In children, it is more difficult to detect thickening, since they cannot always complain about the malaise or explain its nature. It is necessary to show the child to the doctor if he is capricious a lot, loses weight, sleep has become intermittent and the baby often feels sick.
Choosing the right course of therapy is difficult, since surgical intervention is used only in rare cases. When performing surgery on young children, there is a risk that the spleen will not retain its functions and will need to be removed. Intervention is prescribed only when there is a strong increase in the size of the cyst, an inflammatory process, or a threat of spontaneous opening.
Upon reaching 2 years of age, the thickening may resolve on its own.
In other cases, doctors take a wait-and-see approach and watch how the formation develops. Upon reaching 2 years of age, the thickening may resolve on its own. However, it is necessary to exclude participation in traumatic sports, as well as follow the doctor’s recommendations on organizing proper nutrition.
Psychosomatics
The spleen is the keeper of the energy of the physical body. Sometimes a person is visited by thoughts associated with anger, fear, and anxiety. Bad thoughts are introduced into the blood due to evaporation processes. Plasma particles appear, which are captured by the mental elements and, together with other products - waste - begin to destroy the vital functions of the body. The elements spread throughout the body and turn the body into a “crypt”.
Emotional isolation
Diseases of the spleen indicate that a person is constantly worried and does not receive joy from life. He feels useless and empty. He does not find the strength to solve the problems of everyday life.
Internal insulation
The body wants to help strengthen the spirit. But there are people for whom life is nothing but experiences. Because of this, they torment themselves. The spleen serves to ensure that the integrity of the blood is not compromised. You should take care of unity within yourself and resist outside influence. You shouldn’t consider yourself weak, it’s better to try to realize your desires.
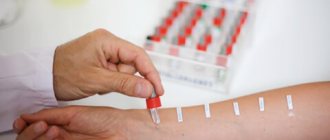
Diagnostics
Doctors can detect pathology by chance, during a routine examination. Only when it reaches a large size do symptoms of the resulting tumor appear. If the development of a benign neoplasm on the spleen is suspected, the therapist prescribes the following types of examinations:
Ultrasound is the main way to clarify the diagnosis.
- examination by a surgeon. During the visit, the doctor feels the abdominal cavity, finds out what symptoms the patient is experiencing, and gives directions for other studies;
- Ultrasound examination of the organ of the internal cyst of the spleen. Ultrasound is the main way to clarify the diagnosis. During the procedure, the type of cyst, its size, and location on the internal organ are identified;
- MSCT of the spleen is a relatively new examination method. The procedure allows you to diagnose the location of the thickening, size and features more accurately than other methods.
Additionally, blood and urine tests are prescribed, but they cannot be used to detect the exact presence of a cystic formation. Tests only help determine whether there is an inflammatory process in the body or whether parasites are present.
Prevalence
The incidence of splenic cysts is very low: 0.5-1% in various age groups. However, in recent years, more and more patients with this pathology have been identified. This is due to the widespread use of ultrasound diagnostics, CT and MRI. They diagnose even asymptomatic small cavity formations.
Primary cysts are predominantly found in children and young people. In women, secondary cysts are more often diagnosed (60%). Parasitic ones are mainly recorded in South America and the Mediterranean region.
Treatment of pathology
When treating splenic cysts, doctors prefer not to prescribe surgery if it can be avoided. If the lump does not exceed 3 cm in diameter, a wait-and-see approach is followed. Twice a year the patient is sent for a routine ultrasound, which allows monitoring the process.
Only if the benign tumor increases in size, with multiple cystic lesions, can a decision be made to perform surgery. The patient is additionally referred to undergo a CT scan to exclude the formation of a malignant form.
Surgical removal is used for the parasitic nature of the pathology. Removal of parasitic foci is indicated.
Conservative therapy
If the cyst is small in diameter, it can be treated with medication. Treatment without surgery includes the use of several groups of drugs prescribed by the doctor:
Tumors of small diameter can be treated with medication.
- antibacterial agents to prevent the development of the inflammatory process;
- enzymes and probiotics;
- drugs that activate the immune system;
- vitamin and mineral complexes, etc.
If a cyst has formed on the spleen due to the penetration of parasites, additional agents are prescribed to detoxify the body. Drug treatment involves taking medications that improve a person’s condition and eliminate attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Types of surgical interventions
Abdominal surgery involves performing surgery for several indications. If the cyst has increased to 10 cm and constantly causes pain to the person, then the doctor decides on surgical intervention. The indication is a purulent abscess, a rupture of the thickening.
The operation cannot be performed if the spleen has increased to 25 cm, if the patient has serious cardiovascular diseases, malignant tumors, or concomitant infectious diseases.
Several methods of surgical intervention are used.
In the absence of contraindications, the following types of surgical removal of the cyst are prescribed:
- peeling the capsule along with the liquid contents;
- puncture. The procedure involves pumping out fluid, as well as introducing a substance into the cavity that promotes gluing of the tumor walls after removal of the secretion. This method is most often used to identify a solitary cyst, the diameter of which does not exceed 5 cm. It is convenient to remove it if it is located on the surface of the spleen;
- resection. This intervention method involves removing the capsule along with part of the spleen. A laparoscopic type of operation is used. It involves a small incision through which the affected tissue is removed;
- splenectomy. Tissues that have undergone pathology, or the entire internal organ, are completely removed. Laparoscopy is also used, since large incisions in the abdominal cavity take a long and difficult time to heal and contribute to the development of complications.
Complete removal of an internal organ is done in extreme cases, since without it the human immune system will not work at full strength.
After completion of the procedure, the contents are sent for histological examination to exclude the development of malignant processes.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures include:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene (to avoid infection with helminths);
- undergoing medical examination (for timely detection of the disease).
With timely detection and treatment, the outcome is favorable. Large cysts, if untimely and incorrectly treated, can lead to health-threatening conditions.
Recovery period
The duration of the recovery process after surgical removal of a tumor on the spleen depends on the size of the cyst, where it was located, and what type of surgery was used. Laparoscopy promotes an accelerated tissue healing process. The advantage of the method is its low invasiveness and small incision.
An ultrasound should be performed every six months to exclude relapse.
After any operation, the patient must be observed by the attending physician (usually a hematologist or surgeon) for several weeks. Physical activity, during which the abdominal cavity can be injured, is excluded for up to several months. An ultrasound should be performed every six months to exclude relapse.
A cyst formed on the spleen requires mandatory medical supervision. It is especially important to monitor neoplasms that occur in newborns or young children. If the thickening is small, a wait-and-see approach is used to monitor the development of the pathology. If the cavity greatly increases in size or causes constant discomfort to the patient, a decision is made to surgically remove it.
What does a neoplasm look like and why is it dangerous?
A splenic cyst is a focal process in the parenchyma of the organ. In most cases, round in shape, filled with liquid contents.
Cavity exudate can be of two types:
- hemorrhagic;
- serous.
Statistical data:
- It is observed quite rarely, only 1% of the world's population.
- It affects the working population, on average 35-55 years old.
- Women are more susceptible to developing cysts.
Initially, symptoms of the disease may not appear. As the tumor grows, the corresponding symptoms also increase, up to the development of serious pathologies not only of the organ, but also of the body as a whole.
ICD 10 (international classification of diseases) code D 73.4 is a separate code in the category of spleen diseases.
A small cyst (up to 1 cm), which appears as a result of inflammation, can regress on its own (dissolve) when it is eliminated.
Anatomy of the spleen
The spleen or lien (in Latin) is a lymphoid organ that has a well-defined blood supply network and is involved in the formation of immunity. It is located in the left hypochondrium (IX-XI ribs), between the stomach and the diaphragm.
The size of the spleen can vary from one person to another. The increase or decrease of the organ directly depends on the filling of the blood vessels.
Average sizes of the spleen of an adult:
- length 120 mm;
- width 80 mm;
- thickness 30-40 mm;
- weight up to 200g.