13 May 2020
5096
0
3 out of 5
Back pain in the lumbar region is familiar to every person. According to statistics, it is the cause of 25% of all requests for medical help. Its appearance can be provoked by a lot of different factors, from banal fatigue to quite serious diseases. Therefore, you should not ignore the problem, especially if discomfort appears regularly and even worsens over time. In such situations, you should contact a therapist or a neurologist as soon as possible and undergo a comprehensive examination. This will make it possible to diagnose the disease in the early stages of development and take timely measures to stop its progression. But if on the eve of the onset of pain there was an injury or a bad fall, you should immediately make an appointment with a traumatologist or spinal surgeon.
What diseases cause back pain?
The causes of back pain can be different. Often this is damage to the muscles or ligaments of the back due to heavy lifting, sudden movements or injuries. The causes of back pain in the lumbar region can be a number of diseases:
- osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis;
- sprain, myositis, muscle bruise;
- scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis, kyphoscoliosis;
- osteomyelitis, epiduritis, ankylosing spondylitis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- intercostal neuralgia, diseases of the pelvic organs;
- spinal protrusion
- spinal stenosis, instability and spinal fractures;
- radiculitis, lumbago or lumbago, inflammation of the sciatic nerve;
- occasionally - spinal neoplasms, myeloma.
What to do if your lower back hurts
First of all, if you experience lower back pain, you need to visit a medical facility for diagnosis. Only after a diagnosis has been established can any measures be taken in consultation with the doctor.
If lower back pain occurs unexpectedly, you should warm your lower back with light heat to improve your well-being. To do this, you need to tie a woolen scarf or belt around your lower back. If there is no relief, you need to take a pain reliever and consult a doctor as soon as possible. It should be remembered that hot compresses cannot be used until a diagnosis is made.
You can try to improve the condition by adopting a position that allows you to relax your back muscles. To do this, you need to lie on your back on a flat, hard surface, raise your legs and bend your knees, and then place a pillow or blanket under them. You can choose a different position in each specific case. The main thing is to find a body position in which the pain will be less intense.
If aching discomfort is associated with weakness of the muscle corset, which provokes overstrain even with minor loads, then it can be relieved with the following exercises
:
- In a lying position, you should take turns raising your legs to a height of 10-15 cm. Each leg must be held in weight for several minutes.
- Lying on your back, you should bend your knees, maintaining an angle of 90-100 degrees and lift them to the maximum height. Bent legs should be tilted in different directions alternately, trying to touch the floor with them.
- While standing, perform smooth and slow bends in different directions. It is advisable to keep your back as straight as possible.
- In a position on all fours, swing simultaneously with your right leg and left arm and vice versa.
- Exercise "bridge". First, it must be performed leaning on a wall, or with the help of another person.
When should you consult a doctor immediately?
In most cases, back pain resolves without treatment within two weeks. If this does not happen, please consult a doctor. In rare cases, back pain signals a serious medical problem.
. Therefore, you should urgently seek medical help if:
- having problems urinating or defecating;
- there is a fever;
- pain spreads down the leg or radiates to both legs;
- the pain was caused by a fall, blow to the back or other injuries;
- the pain is intense and does not go away after resting and taking painkillers;
- pain is accompanied by weakness and numbness in the leg;
- pain is accompanied by sudden weight loss.
Individuals should also seek professional advice:
- over 50 years old;
- who have ever been diagnosed with cancer or osteoporosis;
- who take steroid hormones.
Physiological reasons
Lower back pain may occur if you:
- Are you overweight?
- Additional risk for women;
- You are pregnant or have recently given birth;
- Spend a lot of time driving a car or using a computer;
- Lead a predominantly sedentary (office workers) or standing (salespeople, waiters, street advertising employees, surgeons) lifestyle;
- Do dynamic physical labor with sudden changes in body position (especially if your specialty involves heavy physical activity);
- You overload yourself in the gym or fitness club. Be extremely careful if you have recently started training;
- Are you interested in gardening work?
- Have reached postmenopause, which is predisposing to the development of osteoporosis.
Which specialists should I contact?
If you want to be sure that you will receive high-quality medical care, contact the CELT Pain Clinic. Describe the nature, accompanying symptoms and causes of lower back pain - and, if necessary, you will receive a referral for examination to a specialist to solve a specific problem, without endless walking in circles. These may be doctors of the following specialties:
- traumatologist-orthopedist;
- neurologist;
- neurosurgeon;
- urologist;
- phthisiatrician;
- oncologist;
- rheumatologist;
- nephrologist;
In the area of the shoulder blades
A person can feel pain in the area of the shoulder blades in different locations.
:
- The pain syndrome is localized under the shoulder blades. This nature of BS is observed in the presence of ulcers and erosions in the stomach. In this case, the main epicenter of negative sensations is concentrated in the epigastric zone, and the irradiation radiates under the scapula.
- Compression of the chest, aching and dull pain often cause osteochondrosis or myositis.
- When the back hurts between the shoulder blades, then with a high degree of probability we can assume the localization of intercostal neuralgia (if the pain occurs in the form of lumbago). If pneumonia develops, the pain intensifies when coughing and at the peak of a sigh.
- PS in the scapula most often manifests itself as a post-traumatic consequence. The symptoms of negative sensations intensify when moving the upper limbs.
Risk factors
Back pain can occur in absolutely anyone at any age, including children and adolescents. However, the following factors increase the risk of their occurrence:
- Age.
Most often, pain in the back and lower back appears at the age of 30; - Sedentary lifestyle.
Weakening of the back muscles due to low physical activity is one of the factors causing problems with the spine; - Overweight.
Extra pounds create additional stress on the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, leading to the development of diseases; - Accompanying illnesses.
Back pain occurs with a number of diseases, including cancer. - Psychological disorders.
People who suffer from depression or anxiety are at greater risk of developing back pain.
Intervertebral disc herniation
Intervertebral disc herniation is an equally rare cause, the clinical manifestation of which is pain in the lumbosacral back. The intervertebral disc (internal nucleus pulposus) with prolonged traumatic exposure, as well as with age, loses its elastic properties and elastic ability.
With continued exposure (excess weight, injury, progressive osteoporosis), the fibrous ring of the disc becomes thinner and defects form in it. Through these weak spots in the annulus fibrosus, the nucleus pulposus of the disc can shift and even protrude.
Diagnosis of back pain
In order to make a correct diagnosis, a number of studies are carried out at the CELT clinic.
MRI of the spine
The gold standard for diagnosing back pain is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Depending on the changes detected on the MRI, in conjunction with the clinical picture and neurological status, the doctor draws up a treatment plan for the patient. In addition, the MRI picture allows you to predict how the disease will progress.
Diagnostic blockades
Diagnostic blockades are highly informative for confirming the diagnosis in patients with a complex, unclear clinical picture. For example, the effectiveness of diagnostic blockade of the facet or sacroiliac joints confirms the axial nature of the patients’ pain and is an important criterion for setting indications for radiofrequency denervation of the corresponding joints.
In addition to their high diagnostic value, intra-articular blockades are a therapeutic procedure and have a pronounced analgesic effect with varying durations of action. For patients with radicular pain, diagnostic blocks can be performed when there is a need for additional diagnostics.
Diagnosis and treatment
If your lower back hurts after walking, only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment. He will conduct a survey and find out what type of pain you are suffering from, when it appears, and in what situations it worsens. Frequent research methods are MRI
or
x-rays
, which allow you to determine the condition of the spinal structures. MRI in this case is the safest and most informative method. Based on the results of such studies, the doctor will be able to tell exactly why your lower back hurts when walking for a long time, and will prescribe effective treatment. This may include taking medications, visiting a massage therapist, and doing physical therapy.
Treatment for back pain
Back pain is treated in different ways:
Pharmacological therapy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a pronounced effect, but the effectiveness of their use in the long term is relative due to the rapid development of addiction and the risk of side effects. Muscle relaxants have proven themselves well, especially when used in the acute period. Antidepressants and some anticonvulsants are used with good effect in the complex treatment of pain. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor individually for each patient, depending on the patient’s tolerance to the medications, individual sensitivity, and the severity of the therapy effect.
Therapeutic blockades performed under x-ray control
In the last decade, due to the rapid and pronounced analgesic and therapeutic effect, the use of minimally invasive procedures, including epidural and intra-articular blocks, has sharply increased. An epidural block is the procedure most often prescribed for radicular disease. If the diagnosis is correct and there are indications for this procedure, the effect is simply amazing! Pain relief is achieved for a period of 6 weeks to 6 months, which allows in many cases to avoid the need for surgical treatment.
Neurosurgical operations
The range of neurosurgical operations for back pain is wide. Techniques used include spinal cord decompression, discectomy, foraminotomy, intervertebral disc replacement, minimally invasive and microsurgery, as well as a number of other surgical techniques.
Radiofrequency denervation
Radiofrequency denervation (RFA) is one of the most optimal treatment methods to avoid or significantly delay surgical intervention. Thanks to it, you can not only quickly eliminate pain symptoms, but also minimize or completely eliminate the use of painkillers. Recovery after this procedure occurs quite quickly, which allows you to quickly return to your normal lifestyle.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Pain above the lower back
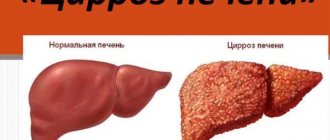
If the back hurts on the right above the lower back, liver pain can radiate, with any pathological changes in the liver - hepatitis, liver failure, taking toxic medications. The pain is most often localized in the right hypochondrium.
If pain is felt on the right or left just above the lower back, it is very possible that the cause lies in acute kidney disease. Many chronic kidney diseases, such as polycystic disease, malignant kidney tumors, chronic pyelonephritis, are accompanied by minor symptoms, since the renal capsule gradually stretches.
Degenerative pathologies
Degenerative changes occur in cartilage and bone tissue. Violation of the morphological structure causes dystrophy, which causes osteochondrosis, spondylosis or spondyloarthrosis.
Among the provoking factors of destructive changes are:
:
- metabolic disorders causing insufficient supply of nutrients to the intervertebral discs;
- limited intake of beneficial microelements into the body;
- heavy loads and previous injuries;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- bad habits, for example, smoking and excessive addiction to alcoholic beverages;
- physical inactivity and sedentary lifestyle.
Inflammatory diseases
Diseases leading to inflammation in the spine can occur either independently or as a result of complications of pathologies. They are recorded in rare cases, but pose a serious threat to the patient's health.
The source of inflammation can be localized in different parts of the vertebra
:
- in the anterior section, spondylitis, discitis or spondylodiscitis are most often diagnosed;
- localization in the posterior region provokes the development of osteomyelitis, spondyloarthritis or paravertebral abscess;
- if the spinal canal becomes infected, the inflammation is manifested by the development of an abscess or epiduritis.
In addition, spinal tissue can be affected due to tuberculosis, brucellosis, trichinosis (a type of helminthiasis).
This type of pathology is characterized by sharp pain attacks in muscle groups, which are difficult to eliminate by taking analgesics. The clinical picture may be supplemented by accompanying symptoms, for example, an abrupt increase in body temperature and loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the spinal column.
Muscle soreness
Pathological processes in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs change the structure of bone and cartilage tissue. Because of this, overstrain of the muscles and tendon fascia occurs. This leads to the body reacting with the occurrence of BS.
In some cases, it is noted that the back hurts after being in a draft for a long time or during hypothermia. These two factors contribute to the manifestation of myositis, in which pain is localized in the superficial muscles. Its distinctive feature is an increase in discomfort during palpation or when the patient tries to turn or bend the body. Sometimes its symptoms appear after sprains and bruises.
Painful syndrome in muscle groups often occurs due to intense training in athletes. In this case, overloaded muscle fibers lose their elasticity and compactions appear in them, which are revealed by palpation.
Symptoms
In order to consult a doctor in a timely manner and correctly describe your complaints to him, you need to have an idea of the symptoms. At the same time, the symptoms of back pain may differ somewhat, and if we take into account the fact that pain itself is a symptom, we should highlight its main manifestations, which vary in nature and location:
- By nature, painful sensations can be: sharp, dull, stabbing, cutting, aching, pulling, burning, etc.
- Painful sensations can be strong, moderate and weak; these indicators are individual for each person. However, they must be taken into account, for example, when determining treatments for chronic back pain.
- Back pain along the entire spine is quite rare. More often, painful sensations are either point-like or are assigned to a specific part of the spinal column (cervical, thoracic, lumbar).
- However, it also happens that pain in the upper part of the spine (or any other part) radiates. In this case, the pain syndrome affects other areas of the back; it is often called wandering.
- As a rule, acute pain in the spine brings the most discomfort and has the greatest impact on everyday life, but it often comes in waves and is easier to treat. At the same time, dull pain is less intense, but is constantly present, persists for a longer period and responds worse to therapy.
These are the general provisions regarding painful sensations in different parts of the back. But in addition to understanding the general symptoms of pain, it is also important to know that depending on the disease, the clinical picture may vary. So in one case, pain is felt between the vertebrae of the cervical spine, in another case it is localized in the lumbar region and has a different character.
For this reason, it is worth considering the symptoms of various pathological processes accompanied by back pain separately.
Osteochondrosis
If your back hurts in the spinal area, the most likely diagnosis will be osteochondrosis, since this disease is more common than others. It is also important to understand that doctors distinguish three types of osteochondrosis: cervical, thoracic and lumbar.
In each of these cases, pain between the vertebrae is associated with different parts of the spinal column. The disease itself involves the destruction of cartilage tissue in the intervertebral discs, while the pathological process also occurs in the vertebrae, because due to the reduction of the space between them, they are erased.
The main symptom of the disease is pain, but clinical signs from the nervous system may also be present, since the spinal cord is most likely affected and its roots are pinched.
Myositis
A rare disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the muscle tissues of the body, including the back. More often, myositis is accompanied by aching pain, but sharp pain or so-called shooting in the back is also possible.
The pain syndrome is localized directly in the place where the muscle tissue is inflamed, but the pain can radiate to nearby areas.
Spondylosis
If your spine hurts, one of the likely causes may be spondylosis. This pathology is characterized by proliferation of bone tissue of the vertebrae, as well as their degenerative changes. In this case, painful sensations appear during physical activity due to prolonged stay in one position, for example, during sedentary work.
Sciatica
The term refers to pinching of the sciatic nerve with its further inflammation.
The pathological process is accompanied by cutting, stabbing, sharp pains. With sciatica, pain is not felt constantly, it occurs suddenly and comes in waves. With sciatica, there is severe pain directly in the place where the pinching or inflammation occurred. However, due to the fact that the sciatic nerve is very long, pain is present in different areas, most often the legs hurt.
Osteoporosis
The disease develops due to calcium deficiency in the body. As a result, bone tissue along the entire spinal column loses its elasticity and rigidity, and microtraumas and cracks form everywhere.
With this pathological process, the entire spine hurts, especially in the later stages of the disease.
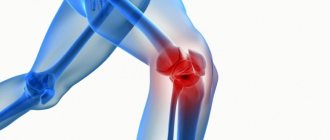
Herniated disc
Acute and severe pain in the spine may be evidence of a herniated disc. In this case, the pain syndrome is constant, but intensifies with physical activity, bending over, coughing, sudden or careless movements.
In most cases, a hernia forms in the lumbar spine, which is explained by the vulnerability of this area to excessive loads and heavy lifting. A hernia often occurs as a complication of osteochondrosis, which is due to the peculiarities of the course of this pathology.
In this case, a hernia is dangerous not only due to pain, there is a risk of pinching the nerve branches of the spinal cord and the development of neurological symptoms.
Excessive mobility of the spine
Otherwise, this problem is called vertebral hypermobility or spinal instability. A clear sign of pathology is pain, which intensifies with intense physical activity and lifting weights. Painful sensations in the back are fickle; they either subside or suddenly reappear.
The cervical spine suffers the most; if the disease progresses, it becomes difficult for a person to hold his head up.
Scoliosis
Oddly enough, but curvature of the spine is the direct cause of pain. One of the most common problems is scoliosis. Pain with scoliosis is more of a muscular nature. This is due to increased load on certain back muscles, while others are relaxed.
With scoliosis, due to the curvature of the spinal column, individual spinal discs are compressed and cartilage tissue is deformed. Painful sensations with scoliosis are constant, aching or pulling, their intensity is low, in rare cases the pain is severe and acute.
Spinal injuries
Of course, any mechanical damage, even minor, is painful. In this case, the more severe the damage, the more severe the pain, and sometimes even with a seemingly insignificant bruise, acute pain is felt, which may indicate severe internal damage. In this case, blows, bruises, sprains, and dislocations are taken into account, but the most severe type of injury is fractures.
It is noteworthy that old, long-healed injuries make themselves felt decades later. So back and neck pain can remind you of how you fell on the ice as a child.
Ankylosing spondylitis
This dangerous disease is also called ankylosing spondylitis. The pathology is characterized by a chronic inflammatory process in the joints, in other words – inflammation of the spine.
Ankylosing spondylitis is accompanied by severe pain, and the intensity of the pain syndrome is high from the very beginning of the pathological process and only intensifies in the future. In this case, the pain intensifies after rest and depending on weather changes, but it is well relieved with NSAID drugs and physiotherapy.
Oncological diseases
Cancer is the most dangerous pathology, the obvious sign of which is pain. In this case, pain syndrome appears in both benign and malignant neoplasms, if they are localized not far from the spinal column and put pressure on it.
An even more dangerous manifestation of oncology is metastases. In this case, the pain is constant and severe; it haunts the person always and everywhere, regardless of body position or any actions. The back hurts just as much even in a lying position.
Kidney diseases
The causes of pain in the lumbar region do not always lie in back problems.
Due to the anatomical location of the kidneys, pathologies affecting them also cause severe pain in the lumbar region. The pain can be dull and drawing or sharp stabbing, the intensity varies depending on the disease and the degree of its progression. It is important to understand here that pain can be on both sides or only on one, which indicates which kidney is involved in the pathological process.
Cardiovascular pathology
The opinion that in diseases of the cardiovascular system pain occurs exclusively in the thoracic region is erroneous. For example, with coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction, the painful sensations are girdling and radiate to the back in the thoracic region. They are characterized as sharp, stabbing, and occur abruptly.
Pathologies of the cardiovascular system include aneurysms of the aorta, in which acute sharp pain occurs near the spinal column in the thoracic region.
Pathology of the digestive tract
Diseases of the digestive tract also often provoke back pain, however, in such cases there are always a number of distinctive clinical signs. In addition to pain, there are stomach upsets, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or diarrhea, as well as general malaise.
Infections
Among infectious diseases accompanied by back pain, the most severe and dangerous is bone tuberculosis. The disease is accompanied by severe pathological processes in the bone tissues, the entire spinal column hurts. The pain is different in nature, sometimes nagging, sometimes stabbing, but always constant.
Respiratory diseases
The lungs occupy most of the thoracic region of the body, so pulmonary pathologies are often accompanied by back pain. Among such ailments are pneumonia, pulmonary tuberculosis, pleurisy, etc.
With such pathologies, pain intensifies during coughing, sneezing, deep breaths, and yawning. In addition, the clinical picture is enriched by cough, shortness of breath, and other similar symptoms.
Congenital pathologies
The factor of congenital anomalies is extremely rare, but still occurs. In this case, the main suspicions fall on a congenital excess or insufficient number of vertebrae in the spinal column. This affects the muscles and ligaments, the structure of the body, and threatens protrusion of the spine or compression, which is invariably accompanied by pain.
Pregnancy and childbirth
Pregnancy is also one of the causes of painful back symptoms.
Pain in the spine and other problems of a similar nature appear more often by the third trimester, which completely depends on the growth of the fetus and the increased load on the spine. In such cases, the pain is usually dull and nagging; it subsides or temporarily disappears after a short rest when the expectant mother lies down.
Inflammatory processes
A lot of different inflammatory processes lead to the development of pain, some of which we have already talked about. Take, for example, spondyloarthritis (Bechterew's disease). This pathology originates in the lumbosacral region, then inflammation, and with it aching pain in the back, rises up the spinal column.
Myofascial syndrome
Myofascial syndrome is characterized by a chronic course with the formation of compactions in the muscle tissue in the form of pain (trigger) points. This not only causes severe discomfort, but also leads to a decrease in physical activity, as a result of which the patient quickly gets tired even from minor physical activity.
The likelihood of developing myofascial syndrome increases significantly in the following situations:
:
- osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, injuries and bruises;
- in case of diagnosis of scoliosis or flat feet;
- if the work involves the repetition of stereotypical movements;
- in case of disturbance of the psycho-emotional state (if this occurs with increased muscle tension).
In clinical practice, the condition of trigger points is of great importance. They can be active or latent.
Taking this into account, they are classified as follows
:
- Acute form. Trigger points are active and cause a feeling of discomfort when trying to make any movement.
- Subacute. Negative manifestations disappear in a state of rest.
- Chronic. The latent condition causes only minor discomfort in the affected area.
In addition, in order to make the correct choice of therapy, neurology has adopted a classification based on the etiological principle
:
- primary trigger points are formed due to muscle damage;
- secondary ones are registered when the functionality of joints and somatic organs is impaired.