Hematocrit is a barely noticeable to ordinary people, but extremely important indicator of the state of the blood. The indicator, in simple terms, expresses the ratio of red blood cells (red cells) to a single volume of total blood (usually determined as a percentage). Based on the hematological parameter, we can conclude about the viscosity of the blood - the higher the hematocrit level, the thicker the biomaterial.
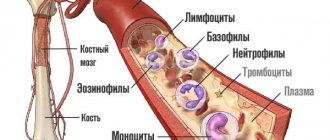
It should be mentioned that in rare cases, such an index shows the concentration of all formed elements along with platelets and leukocytes. These blood components are represented in a minimal amount compared to the same red blood cells, so the data obtained is not so different from the classical measurement.
Conducting a hematological study
In order to find out the value of hematocrit, doctors can remove a small portion of blood from both the finger capillary and the cubital vein. In laboratory conditions, a substance that prevents premature clotting - an anticoagulant - is added to the sample. The test tube is then placed in one of the centrifuge cells and the apparatus is activated.
The drum begins to accelerate around its own axis, and as a result of the centrifugal force, heavier blood cells (red blood cells) settle at the bottom, and a light liquid appears on the surface - translucent plasma. Other components (leukocyte cells, platelets) form a thin intermediate film.
After completing this stage, the specialist assesses the level of red blood cells in the blood using special markings and writes down information about the hematocrit on a form. Some clinics use modern devices to detect blood counts that perform the counting function automatically. The results of the study are most often given to the attending physician who referred the patient for the procedure the very next day.
The principle of establishing the level of hematocrit in the blood
Symptoms are not always pronounced
Blood, losing the normal level of red blood cells, will cause the development of primary symptoms. The patient complains of fatigue, weakness, and headache. Within 3-5 days, dry mouth and other symptoms will appear:
- tingling in fingertips;
- cold hands and feet;
- feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- depressed emotional state;
- drowsiness;
- loss of coordination of movements.
Secondary symptoms of high hematocrit include hypertension, fainting, nausea, and inability to concentrate.
On a note! Lack of proper attention to the problem on the part of the doctor leads to the formation of blood clots in the arteries, heart attack, acute oxygen starvation, and frequent bleeding.
What is accepted as the norm?
The hematological parameter depends mainly on 2 factors - gender and age:
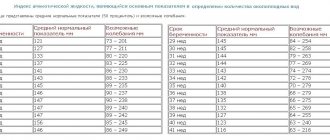
| Age category | Hematocrit content in blood (%) | |
| Among women | In men | |
| Up to a month | 40–67 | |
| 2–3 months | 32–44 | |
| 4–12 months | 35–44 | |
| 2 years–6 years | 36–41 | |
| 7–12 years | 33–44 | |
| 13–17 years old | 35–44 | 36–48 |
| 18–45 years old | 36–46 | 39–48 |
| 46+ | 35–47 | 40–50 |
The blood count increases to the maximum in infants, which is considered a completely biologically substantiated phenomenon. On forms, hematocrit may be referred to as HCT. As a rule, an index over 52–55% means a sufficiently increased concentration of red blood cells, so detection of such a hematocrit should be a reason for prescribing a repeat analysis and additional procedures.
If, against the background of increased blood viscosity, a person experiences swelling, dizziness, nausea, headaches, difficulty breathing and numbness of the limbs, then you need to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible. Such a clinical picture often indicates the beginning of pathological transformations in the body. A sharp deterioration in the condition of the nail plates, skin and hair can also manifest itself.
What values are considered elevated?
To identify the fact of increased hematocrit in patients, it is necessary to consult a table that indicates the normal values of this substance depending on gender/age. For example, in men, increased hematocrit is determined differently than in women and children.
| Normal hct values, % | |
| Women. | 36 – 46. |
| Pregnant women. | 33 – 36. |
| Men. | 40 – 48. |
| Elderly women (>65). | 31 – 45. |
| Older men (>65). | 30 – 49. |
| Newborns. | 45 – 60. |
| Children under 13 years old. | 38 – 40. |
Causes of low hematocrit
A decrease in hematocrit in a blood test may indicate the following anomalies:
- anemia (anemia);
- cystitis;
- bleeding (external and internal);
- hemolysis (rapid destruction of red blood cells);
- severe poisoning with toadstool or heavy metals (antimony, zinc, cobalt, mercury, lead);
- pathological self-destruction of blood cells in malaria and typhoid fever;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, disrupting the absorption of iron into the blood;
- Hodgkin's disease (malignant degeneration of lymphoid tissue);
- overhydration (excessive amount of fluid in the body).
Sometimes a low hematocrit in the blood is due to hyperproteinemia (excess protein). This disease sometimes accompanies chronic infections, sarcoidosis and autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid polyarthritis). Also, the hematological indicator may be lowered due to damage to certain organs that are directly related to the production or purification of blood:
- Bone marrow. Hemoblastosis, myeloma.
- Liver. Fatty degeneration, cirrhosis and hepatitis in the active phase.
- Kidneys. Glomerulonephritis, renal failure, paresis and stenosis (narrowing of the lumen) of the renal artery.
Poor nutrition and adherence to a strict diet can lower the hematocrit in the blood. The body does not receive enough vital substances (B vitamins, iron), as a result, erythropoiesis (the process of formation of red blood cells) slows down significantly.
With a low hematocrit in the blood, the patient experiences malaise, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, pale skin, lethargy, drowsiness, aching headaches and increased fatigue
It is not often that a low index indicates that there are parasitic life forms in the human body that feed on blood or weaken red blood cells. Uninvited guests may include:
- protozoa (unicellular): malarial plasmodium, toxoplasma, hemosporidia, trypanosome, dysenteric amoeba;
- helminths (worms): guinea worm, mansonella, tapeworm, opisthorchis, whipworm, echinococcus, roundworm.
In medical practice, there are cases of false results in the form of an underestimated hematocrit. In completely healthy people, it can be observed if blood thinning was previously carried out.
Vessels that are too compressed with a tourniquet during the removal of a blood sample or the procedure is performed with the patient in a supine position also contribute to a decrease in the corresponding indicator. For those who stubbornly fight a malignant tumor, the blood sometimes becomes thinner after chemotherapy and the use of cytostatics.
What causes a high rate?
Pathologies in which the hematocrit in the blood is increased include:
- diabetes;
- burn disease;
- pneumonia;
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- chronic obstructive bronchitis;
- tuberculosis;
- leukemia (malignant lesion of the hematopoietic system);
- ischemic kidney and heart disease;
- bronchial asthma;
- intestinal obstruction;
- state of shock;
- peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum);
- Vaquez disease or erythremia (benign formation that enhances the synthesis of blood cells).
High parameters are also characteristic of some renal diseases - acute or chronic polycystic disease, Wilms tumor and hydronephrosis. The latter anomaly is a pathological dilation of the calyces and pelvis, which leads to kidney dysfunction.
Severe dehydration (loss of fluid) contributes to blood thickening, requiring urgent medical intervention. In the absence of emergency care, the patient may die from dehydration. Illnesses accompanied by prolonged diarrhea, profuse sweating and vomiting can cause such a harmful reaction.
At a critical level of water in the body, protective mechanisms are activated to force fluid to be removed from the bloodstream. Thus, the plasma reserves in the blood are sharply depleted, the number of red blood cells remains unchanged, and the concentration of these cells is greatly overestimated. Blood thickening occurs.
The amount of hematocrit is especially affected by long-term use of several groups of medications - diuretics (diuretics), anabolics and glucocorticosteroids. The hematological parameter may be elevated if a person has developed anemia, which provokes swelling and an increase in red blood cells. Among such deviations is megaloblastic anemia.
Prolonged overstrain of the central nervous system (for example, sustained stress) also increases the hematocrit content in the blood
Non-pathological causes of an increase in viscosity index are represented mainly by the following factors:
- deficiency of iron-containing foods in the diet;
- menstrual cycle;
- adherence to the pastel regime for a long time;
- the presence of morbid obesity;
- age-related changes in elderly people.
Thick blood is observed in heavy smokers and citizens who abuse alcoholic beverages. At significant elevations, the volume of oxygen cannot be called sufficient for the full functioning of the body. It follows that a completely understandable increase in hematocrit can be detected in those who:
- flies regularly on airplanes;
- works in high mountain areas;
- engages in rock climbing and mountaineering;
- lives in the mountains.
Divers who constantly dive to depths with special equipment also sometimes have a slightly elevated blood count.
Preparing for diagnosis
Preparing for a blood test involves few restrictions. So, a day before the procedure, a taboo is established on fast food and food with a high percentage of fat content. Alcohol is excluded. Any type of physical activity should be avoided.
The study is carried out on an empty stomach, so you should refrain from eating food for at least 6-7 hours. You should drink water only when necessary. When using medications that change blood viscosity (anticoagulants, non-steroidal analgesics), you must inform your doctor in advance.
For 2 hours before the analysis, it is recommended to monitor your mental balance and under no circumstances smoke. It is undesirable to donate blood for hematocrit during and immediately after an acute viral infection, menstruation, and large blood loss as a result of injury. These conditions can distort the patient's diagnostic picture.
Prevention
In order to avoid serious consequences, you should take a blood test from time to time, especially if you feel tired or dizzy. The procedure of donating blood is also useful. According to statistics, this can be done 4 times a year with an interval of 12 weeks. However, the patient may be referred for analysis after a detailed examination and consultation with a doctor. The procedure is useful in that the body gets rid of excess iron, which can cause atherosclerosis, the arteries become stiffer, and the risk of cardiovascular diseases is eliminated.
Proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, drinking enough fluids and exercising are all ways to prevent an increase in hematocrit.
Features of the indicator in children
A high hematocrit in the blood of a child under 1 year of age is normal. If, after the baby’s first birthday, the tendency for this parameter to increase continues, then parents should take care of making an appointment with a pediatrician to determine the reasons. In some situations, a high content of red blood cells in the blood is typical for children under 13–16 years of age, whose height seriously exceeds the average for their age category.
Many cases of deficiency or excess of hematocrit in a child are explained by individual characteristics, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle or constant dieting (teenage girls are especially guilty of this). Otherwise, their pathological causes are similar to those of adults.
The most common diseases in children are mild anemia and helminthic infestation. Those. all of the above problems that are responsible for changes in blood composition are completely reversible, although this does not mean that fluctuations in hematocrit should be ignored.
Why does the state of the blood change during pregnancy?
The viscosity index in pregnant women is almost always slightly lower than standard indicators - about 30–35.5%, with the generally accepted norm being 36–46%. This phenomenon is associated with a natural increase in the amount of plasma against the background of a constant level of red blood cells. Exceeding the parameters, in turn, may indicate insufficient water intake, prolonged bowel disorder and chronic stress.
Often, excess hematocrit in the blood of pregnant women appears due to daily abuse of salty foods and sodium chloride (table salt)
Since hematological abnormalities can signal serious disorders (late toxicosis, hormonal imbalance, abnormal kidney function), if a high hematocrit is diagnosed, you should immediately visit your doctor.
How to lower hematocrit in the blood?
If an overestimated parameter appears due to an unbalanced diet, you should change your usual diet. Approximate requirements for drawing up a complete therapeutic diet are reflected in this table:
| Types of food | Recommended Products | Prohibited or strictly restricted products |
| Fruits and berries | That's it, a special place is given to citruses and sour berries | Bananas, careful use of currants, lingonberries, viburnum, blackberries and mangoes |
| Vegetables and greens | Yellow, orange and red fruits (especially carrots, pumpkins, zucchini and tomatoes) | Green plants (broccoli, cabbage, spinach, zucchini, arugula) |
| Fermented milk and dairy foods | Low-fat sour cream and cottage cheese, Varenets, fermented baked milk, kefir | Powdered and whole milk, sour cream with a high percentage of fat content, butter, cream and cheese |
| Cereals, legumes | Barley, barley, millet, oats in the form of oatmeal, brown rice, corn | All legumes and buckwheat |
| Meat and fish | Fatty varieties of sea fish (mackerel, salmon, trout, tuna) and lean meat (turkey) | Lard, ham, liver, goose, duck, lamb, pork and beef |
| Mushrooms | — | All |
| Seafood | Everything, including seaweed | Black and red caviar |
| Sweets and baked goods | Honey, rye bran bread | — |
| Convenience foods and fast food | — | All |
| Preservation and smoked meats | — | All |
| Spices | Cinnamon, ginger | — |
| Beverages | Pure water, juices without added sugar, herbal teas based on sage, licorice, sweet clover and hawthorn | Soda, coffee, alcohol, black and green tea, pomegranate juice |
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe medications that reduce hematocrit and normalize blood viscosity. Often among them appear:
- anticoagulants (Heparin-Agrikhin 1000, Warfarex, Clexane, Sinkumar);
- antiplatelet agents (Curantil, Ticlopidine);
- NSAIDs (Aspirin).
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to special medical procedures such as erythrocytopheresis. In addition to the above, it is worth noting that the positive result will be more noticeable if you start doing physical exercise every day (even walking will do) and get rid of dangerous bad habits - alcoholism and smoking.
Treatment of pathology and possible complications
The essence of correcting pathological deviations from the norm is eliminating the root cause. Sometimes it is enough to give up bad habits, walk a lot, regularly ventilate the room, correctly calculate the drinking ration (40 ml of water per 1 kg of weight), and stop taking uncontrolled medications.
In other cases, additional medical intervention is required, the essence of which is to thin the viscous blood. To do this, replace biological fluid with solutions that reduce its viscosity, bloodletting (up to half a liter of blood/day), and medications: Interferon, Busulfan, Hydroxycarbamide.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to eliminate the root cause.
Do not forget about a special diet enriched with foods that can make the blood less viscous. These are: fermented milk products, herbs, vegetable oils, nuts, tomatoes, carrots, seeds, fatty fish, seafood, offal.
Traditional medicine can also make its contribution to correcting the situation. You can normalize the indicator by taking a smoothie made from currants, peach, apple, pomegranate, tomato or carrot juice, and baked apples. An infusion of yarrow, meadowsweet and budra (50% of the total collection) with leaves of celery, parsley, immortelle helps: a couple of spoons of the collection in two liters of boiling water, infuse in a thermos for a couple of hours and drink in 4 doses daily. The drink normalizes kidney function.
An infusion of garlic and honey in a 2:3 ratio is also effective; the ingredients are crushed, mixed, left for a month, and taken a tablespoon three times a day, half an hour before meals.
As for complications, they are all associated with a violation of the blood clotting system, the loss of normal rheological properties by the biological fluid. The most dangerous, of course, are AMI and stroke. Gangrene of the limbs with amputation and acute respiratory failure can lead to death or disability.