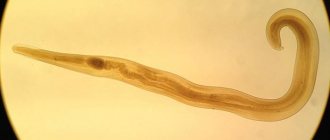
The most common diseases in children, especially young children, are helminthiases. Every third person in Europe is affected by helminths. Only official data for Russia discloses figures of about 2 million cases of helminthic infestations among the population. According to many experts, as well as the number of anthelmintic drugs sold annually, this figure is much higher than the official figure, amounting to 22 million people, 80% of which are children. In total, 342 types of worms are known, and only 70 of them most often infect Russians. When worms appear in children, the symptoms are not always clear and specific, accurately indicating that the child is infected with parasites. How to determine that a child has worms - this is what our article is about.
Causes of worm infection in children
Due to their natural mobility and curiosity, children often come into contact with the world around them and everything that inhabits it. The list of common causes of infection is quite impressive.
Contact with a contaminated surface
Worms and their eggs can survive up to two weeks without food.
The most
common places where a child can become infected with worms:
- playground or outdoor soil that contains worms or eggs;
- communication with animals or contact with their excrement infected with worms.
Consuming worm-infested food or water
It is very important to wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly before eating, as they contain worm eggs.
Raw or undercooked food also carries a risk of worm infestation. Contaminated water is a very common source of infection.
Contact path
Worms are transmitted to humans from humans. Pinworms usually spread in this way, so in children's groups there is a very high risk of helminth infection.
Insect bites
Mosquitoes are often carriers of infection.
Presence of worms in mother
You can infect a child even during pregnancy, when infection occurs in the womb.
Helminth larvae enter the bloodstream of the fetus through the placenta or during childbirth through the birth canal. Parasite eggs reach the child from the surface of the pacifier, toys and other objects. Helminthic infestations are more common in children than in adults. Worms in children under one year old are not as common as in children 1.5 - 3 years old, who actively explore the world, taste various objects and become infected much more often.
Helminth infections are dangerous at any age. Worms in a one-year-old child are a special case, because the baby’s body is not yet strong, the immune system is weak, and the presence of worms in children can cause frequent acute respiratory diseases, a tendency to allergies, and diseases of the internal organs.
The presence of worms in infants is a big health problem, since worms feed on substances required for the growth and full development of the baby.
Sources and methods of invasion
Prevention of helminth infection in children is possible if you understand information about the routes of transmission of worms. In reality, there are several possibilities for their penetration into the human body. Most of it reaches humans through contact, household or nutritional means.
Many people believe that strict adherence to the principles of personal hygiene will protect against helminthiasis. Unfortunately, this opinion is wrong. Children are most at risk of infection due to close contact with those responsible for the disease. Each source of invasion has its own characteristics:
- in the contact-household route, larvae penetrate the body through infected people, through things, from animals;
- with the alimentary method, the culprits are unwashed palms, water of questionable purity, and infected food supplies;
- in the transmission route, worms come from blood-sucking insects;
- with active (percutant) - the testicles of worms overcome the connective tissue or skin from the soil or from bodies of water during the bathing process. Sometimes larvae in the air enter the respiratory system along with dust particles.
Despite the variety of species of worms, children become infected with them in approximately the same way. Eggs, larvae, part of the body or the whole parasite, when it reaches a person, begin feeding and reproducing; their number increases rapidly in the absence of therapy. The health of an infected person worsens, and he becomes the culprit of transmitting the infection to others.
The eggs of the most common helminths - ascaris, pinworms, covered with an adhesive capsule, are firmly attached to the surface and held there. The spread happens quite quickly. Once on the palms and fingers, the eggs accumulate under the nails, from where they are transferred to everyday things that a person uses. This is how all family members and immediate surroundings become infected.
Certain types of worms are capable of penetrating the placenta and infecting the fetus in utero. Receiving an invasion from a mother suffering from enterobiasis is possible during childbirth. An infant can become infected from sick relatives, although the disease is not transmitted through mother's milk. There are also unusual cases of transmission of worm eggs from an infected person: through sexual contact or kissing, and contraception in this case is useless.
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from helminthiasis: their larvae live everywhere. However, there is a possibility of reducing the threat of disease for those who comply with hygiene requirements, eat heat-treated food, and regularly undergo preventive treatment for worms.
Symptoms of worms in children
Signs of worms in children depend on the habitat and life activity of the worms in the child’s body. The most common worms - roundworms in babies, pinworms, tapeworms - live in the intestines, but some of certain parasites can move from organ to organ. For example, roundworms first penetrate the stomach, and from there they enter the lungs or liver with the blood. There they grow for three weeks, then re-enter the intestines or stomach.
Pinworms often live in the anus, causing severe itching. In girls, they can be found in the genitals, causing vulvovaginitis.
Opisthorchis parasites often live in the liver and pancreas. Echinococcus can affect muscles and bones, tapeworms even penetrate the brain. Also, some types of helminths are found in the respiratory organs, causing a persistent cough.
Symptoms of infection
The manifestation of the disease at the initial stage of infection is practically imperceptible, therefore, it is almost impossible to determine the presence of worms, except as a result of analysis in a medical institution. Therefore, it is very important to detect these parasites in time. While their number is small, their vital activity does not negatively affect the functioning of the child’s body. But if parents constantly monitor the psychophysical state of the child, then they may suspect at an early stage that something is wrong with the child’s body.
How do you know if your child has worms? To do this, you should pay attention to some signs. For example:
- Itching appears in the child's anal area, which the child may constantly complain about to his parents.
- The child does not show his former activity and behaves passively, while his skin color changes to pale.
- The child complains of general weakness and constant fatigue.
- The child has a poor appetite.
- The child develops a cough for no apparent reason.
- Frequent constipation or diarrhea is possible as a result of poisoning of the body.
- Excessive salivation associated with the gag reflex.
- Dark circles appear under the eyes, indicating that the child is tired.
- There may be redness in the anal area.
- A child may grind their teeth in their sleep.
- Girls may experience vulvovaginitis.
- Constant complaints of burning and itching in the anus.
- Complaints of stomach pain without good reason.
- In the stool you can see worm eggs, as well as live parasites.
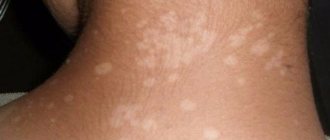
In addition to the above symptoms, allergic reactions of unknown origin are possible, which can lead to serious consequences.
Worms – School of Dr. Komarovsky
How to understand that a child has worms?
Depending on the location of the worms in children, the following signs of the presence of worms in a child may appear:
- Constipation. Large worms can block the intestinal lumen, causing problems with stool passage. Constipation may last more than 2 days.
- Diarrhea. Some parasites secrete a special substance that stimulates the body to excrete undigested pieces of food and large amounts of water.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. Helminths can cause inflammation in the intestines. This causes impaired absorption of nutrients and irregular bowel movements.
- Flatulence. Some types of helminths provoke fermentation processes in the small intestine, which causes excessive gas formation. If you do not get rid of the worms in time, flatulence can last for more than one month.
- Pain in joints and muscles. This occurs when parasites penetrate a joint or deep muscle tissue and destroy it.
- Allergy. The waste products of worms can activate special cells in the body that are responsible for the occurrence of allergic reactions.
- Worms can cause skin diseases. Acne, urticaria, papillomas and diathesis appear. Sometimes infection with worms leads to increased brittleness of hair and nails.
- Anemia. Some types of worms are able to adhere to the intestinal walls and receive from them not only nutrients, but also blood. Because of this, the child develops anemia, which is diagnosed using a clinical blood test.
- Change in body weight. As a rule, as a result of infection with worms, body weight decreases sharply, since the worms absorb more nutrients that enter the body with food. Having a helminth infection often causes loss of appetite due to toxins entering the blood. But often the child experiences an increase in body weight - this is a protective reaction to the spread of worms.
- Disorders of the nervous system. The child has capricious and irritable behavior. Schoolchildren and adolescents may develop depression due to helminthiasis.
- Sleep disorders. When a child wakes up every night, this may indicate an infection is in progress. At night, some types of worms leave the body through the anus, which is accompanied by severe itching that prevents the baby from sleeping.
- Jaundice. More common with tapeworm infections.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome. The child is constantly weak and gets tired quickly due to a lack of nutrients in the body. Memory problems arise, emotional stress and drowsiness develop.
- Immunity disorders. Due to helminthiasis, a child develops diseases of viral origin much more often, and an allergic reaction to ordinary foods appears. Dysbacteriosis and colitis often develop in the intestines, rashes, diathesis and herpes occur on the face.
- Problems with the respiratory system. They occur when worm larvae attack the lungs. With worms, children develop a cough and their body temperature rises. Bronchial asthma is an extremely dangerous complication of worm invasion.
Numerous symptoms of worms in children significantly complicate diagnosis. Therefore, parents should remember about routine preventive examinations, including tests to determine the presence of pinworms and roundworms.
Types of helminths
There are several types of parasites that can settle in a child's intestines. They differ in color, size, and the nature of their effect on the body. Moreover, the larger these parasites, the more dangerous they are for the body of a small child, since they release much more toxins.
Many parents assume that their child may only develop pinworms, but this is a misconception, since the child can also become infected with other, more dangerous parasites.
In children, the intestines may appear:
- Pinworms , which are small worms, up to 5 mm long, with females growing up to 12 mm in length. Pinworms are distinguished by their gray-white hue and rounded-elongated body shape. They prefer to live in the cecum and small intestine.
- Roundworms are already larger parasites, reaching a length of 25 to 40 cm, depending on gender. They are distinguished by a rounded body shape and pointed ends. As a rule, they live in the area of the small intestine.
- Whipworms are medium-sized parasites, up to 5 cm long. They are distinguished by a body divided into two parts: one part is wide, and the other is thread-like. These parasites live and reproduce in the large intestine.
Common types of worms in children
- Pinworms cause itching around the anus and painful urination.
- Roundworms. With ascariasis, diarrhea is observed, and worms in the child’s stool are visible to the naked eye. Fever and dry cough are detected within 4 to 16 days after exposure to roundworm eggs.
- Hookworm. The child develops a cough and wheezing. In case of severe infection, anemia and chronic fatigue develop.
- Tapeworms. They enter the body through contaminated food and water. Ingested worms travel from the baby's intestines, forming cysts in the tissues and organs of the body.
Types of parasites in a child’s body
| Group | Type of parasite |
| Roundworms | The most common group of parasites, which include:
Roundworms (nematodes) |
| Tapeworms | Chains:
And also broad tapeworm, echinococcus. Tapeworms (cestodes) |
| Flukes |
|
Helminths can affect not only the intestines - with the help of the circulatory system they easily move through different internal organs, causing a variety of symptoms.
How to identify worms in a child?
Abdominal pain, lethargy and diarrhea may be symptoms of other illnesses.
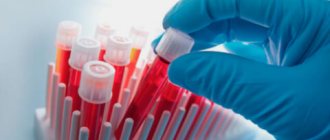
To make sure that they are signs of helminthiasis, it is necessary to perform some tests for worms in children: 1. Blood test for worms in children.
An enzyme immunoassay is prescribed for worms. As a result of the study, special antibodies and antigens are identified that indicate the presence of worms in the body. This analysis will show the type of worms present, their number, and ability to reproduce.
To diagnose worms, a general blood test is performed, which can reveal anemia or signs of inflammation in the body.
2. An accurate result is achieved using a histological coprogram.
It consists of a microscopic examination of feces. Thanks to this study, it is possible to clearly identify parts of the worm's body and their eggs. As a result, helminthiasis is diagnosed, as well as the type of worms.
3. X-ray and other diagnostic measures.
When there is a suspicion of the presence of worms in the lungs, an x-ray examination is prescribed. In addition, sputum examination is carried out. A CT scan or ultrasound scan is performed to identify parasites in the liver, brain, or kidneys.
Signs of other parasitic infestations
Opisthorchiasis (pathogen - cat fluke, or Siberian fluke) - disorders of the digestive system, hepatitis, enlarged liver, pain in the abdomen and right hypochondrium, skin rashes, allergy manifestations, myocardial dystrophy, enlarged lymph nodes, catarrhal syndrome, joint pain, low-grade fever , blood count abnormalities (increased ESR, eosinophil count, decreased hemoglobin).
Trichocephalosis (causative agent - whipworm) - symptoms in children are minimal, dyspepsia, diarrhea mixed with blood, alternating with constipation, bloating, vomiting may occur; with massive long-term infestation, children are diagnosed with retardation in mental and physical development.
Diphyllobothriasis (caused by the wide tapeworm Diofillobotrium latum), provoked by the consumption of fish that has not undergone full heat treatment, is manifested by intestinal disorders, allergies, anemia with vitamin B12 deficiency.
Hymenolepiasis (pathogen - rat or dwarf tapeworm) - has no specific symptoms, but can be manifested by gastrointestinal disorders (pain, heartburn, alternating diarrhea and constipation, nausea, decreased appetite), allergic and vasomotor rhinitis, increased fatigue.
Toxocarosis (causative agent - toxocara, transmitted to children from infected cats and dogs) - pronounced manifestations of allergies (cough, choking, facial swelling, fever, skin rash), eye damage (keratitis, ophthalmitis, choriretinitis), enlarged liver, lymph nodes, X-rays show infiltrates in the lungs.
How to get rid of worms in children?
To effectively treat worms in a child, contact a parasitologist and follow his recommendations.
Self-medication with anti-worm drugs is unacceptable for children, as they are quite toxic. Also remember that when invading different types of worms, individual courses of treatment are required, which are built in accordance with the life cycle of the worm. When calculating the dose, the specialist must take into account the age and body weight of the patient.
Your doctor may prescribe deworming medication, which is available in syrup form for babies or tablets for older children.
- Mebendazole. Used to treat various helminth infections in children;
- Pirantel. Another safe deworming agent for children;
- Zentel is prescribed to children from two years of age;
- Zentel anti-worm suspension for children. This is a syrup for worms for children under two years of age;
- Vormil - anti-worm suppositories for children. The active ingredient of the drug is albendazole. Contraindicated for children under two years of age. Effective against adult worms, larvae and eggs.
deworming medicines for children
Deworming tablets for children usually kill worms without harming the owner, in this case the child. The treatment period is usually short and lasts no more than a few days. Sometimes one dose of Mebendazole is enough to rid the baby of worms.
But many drugs are ineffective against worm larvae and eggs. In addition, there is a fairly high risk of repeated self-infection with pinworms in young children. Therefore, after 2 - 3 weeks the treatment course should be repeated.
If a child has worms, in parallel with etiotropic drugs, a specialist may recommend a choleretic drug if there is a suspicion that worms live in the gallbladder. Laxatives are often prescribed to quickly eliminate helminths and sorbents to absorb toxins. Antihistamines can reduce allergies and improve the health of a young patient.
Treatment of helminthiasis in infants is very difficult. Almost all deworming medications are not used for children under two years of age because they are very toxic and have many side effects. The damage to the body caused by the consumption of such drugs can be significant even with the slightest dose overdose. Therefore, self-medication of helminthiasis in children is absolutely prohibited.
If there is any suspicion of worms in an infant, it is necessary to contact a specialist who will determine the degree of infection and develop a treatment regimen that is valid in this case. In some situations, the doctor may even suggest delaying treatment for a short time so that the child grows up.
Do not rely on over-the-counter medications as they may not be suitable for babies and young children. Always visit a doctor and follow the dosage and treatment regimen to rid your child of worms. It is recommended to use deworming tablets for children once every six months for prevention. Talk to your doctor about what to give your baby to prevent worms; a specialist will determine the dosage and frequency of preventive deworming.
Drug treatment
There are many means that can be used to treat a child for worms. It is worth taking into account that all of them have a toxic effect, due to which worms and larvae die. However, they have an adverse effect not only on worms, but also on the child’s body. Therefore, anthelmintic medication should be selected depending on its effect on the child. Popular medications used for baiting helminths in children are as follows:
Albendazole
Albendazole
It is used to treat children from 2 years of age. Before this age, with great caution and in cases where other anthelmintics are ineffective. The drug works well against nematodes and cystodes. Available in the form of capsules, tablets, suspensions. Helps with large and small invasions. It is better to take it with fatty foods for maximum effect. The dosage and course of treatment depend on the specific nature of the infection and the patient’s weight. Side effects include pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, heartburn, vomiting, stomatitis, urticaria, dizziness, and confusion. It should not be taken during pregnancy, lactation, or hypersensitivity to the components.
Vermox
Able to get rid of round and tapeworms and mixed infections. For children from 2 to 10 years of age, tablets are prescribed under the supervision of a doctor. Contraindications: ulcerative colitis, liver failure, allergic reactions. Concomitant use with other anthelmintic drugs is not recommended to avoid intoxication. The majority of the drug is taken once. After two days, the worms die and are excreted along with the feces. Vermox causes side effects: nausea, vomiting, liver problems; in case of overdose, anemia, hair loss, dizziness, leukopenia, rash. The drug is able to reduce the level of insulin requirements, which must be taken into account when treating children with diabetes.
Dekaris
It has a wide spectrum of action, but produces a strong intoxicating effect on the children's body. Contraindicated in children under 3 years of age, pregnant women, nursing mothers, and patients with liver and kidney failure. The tablets are used once. The dosage is calculated depending on the patient's weight.
Dekaris
Piperazine
A low-toxic drug in tablet form that can be used in children over 3 years of age and pregnant women. Affects only the class of nematodes in small infestations. Removes adult worms in feces. Contraindicated for kidney and liver diseases. The dosage depends on the age of the patient; the need for repeated courses is determined by the doctor. If the dosage is observed, there should be no side effects. Sometimes nausea, vomiting, dizziness, abdominal pain, and mood swings are observed.
Pirantel
A modern drug that can be given to children from 6 months to 3 years. Side effects and contraindications of the suspension correspond to Piperazine. The medicine is given to children once, if necessary repeated after 2-3 weeks. Sometimes parents do not want to give their children medications using homemade recipes against worms. But in most cases, folk remedies are used in conjunction with pharmaceuticals.
Folk remedies for worms for children
Along with medications, treating worms in children with folk remedies will help relieve discomfort due to worms in the body.
A natural dewormer will not necessarily get rid of worms in your child, but it will help treat and prevent the infection. Let's consider folk remedies:
- Garlic is a natural anthelmintic for children. This remedy is known to be effective against parasitic worms. Raw garlic contains amino acids and sulfur, which will help kill parasites and rid the body of them. Eating three cloves of raw garlic on an empty stomach will help in comprehensive deworming.
- Papaya is the best remedy for health. Unripe papaya has an enzyme called papain, which acts as an anthelmintic agent to kill worms in the intestines. Additionally, papaya seeds are used to expel worms from the stomach. Grind the papaya seeds and stir a tablespoon of the mixture in warm milk or water. Ask your child to drink the drink in the morning, three days in a row. Mix one tablespoon of raw papaya and a tablespoon of honey in warm milk or water. Drinking this drink on an empty stomach helps drive away intestinal worms.
- According to research, pumpkin seeds help in expelling intestinal parasites. The seeds contain cucurbitacin, which paralyzes pests and makes it difficult for them to survive in the body. Offer your child a spoonful of pumpkin seeds with honey. Boil a spoonful of peeled and crushed pumpkin seeds in three glasses of water. Let the drink brew for half an hour. Offer to the child when the liquid has cooled.
- Chinese bitter gourd. Although it has a slightly sour taste, it is very effective in combating worms living in the intestines. Mix a cup of bitter gourd juice with water and honey and give it to your child twice a day.
- Carrots contain vitamin A, which boosts immunity and allows the body to fight any intestinal worms before they have completely colonized the body. Eating carrots on an empty stomach will help neutralize stubborn parasites in the body and also prevent re-infection.
- Turmeric is a natural antiseptic and helps in eliminating all types of intestinal worms. It is necessary to give a glass of warm water mixed with one spoon of turmeric to the child for worms once a day for five days.
- Coconut has strong anti-parasitic properties, making it effective in treating worms. You can use fruit or oil to kill worms. Let your child eat a tablespoon of grated coconut daily with breakfast. Continue using this home remedy for a week. Concentrated coconut oil contains medium chain triglycerides, which will help remove worms from your baby's body. If your baby takes four to six teaspoons of coconut oil every morning for a week, it will boost immunity and prevent recurrence of worm infestation.
- Cloves kill existing intestinal worms and their eggs, and prevent future infestations. Add a teaspoon of cloves to a glass of hot water and let steep for 20 minutes. You need to drink this water three times a week to avoid infection.
- Onion juice helps in the fight against roundworms. Take an onion and chop it well, drain the juice from the onion mixture. Use it in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Indian lilac has anti-parasitic properties and can kill a variety of intestinal worms. Mix powdered leaves in warm milk and honey. Offer to your child twice a week.
Traditional home remedies will help relieve the infection, but will not cure it completely. They are not a substitute for prescription medications.
What danger does helminthiasis pose?
Long-term infestation with parasites can cause serious damage to the body. The presence of helminths in the intestines makes it difficult for food masses to pass through and can lead to obstruction. When there is a buildup in the appendix, appendicitis develops.
Enterobiasis is often accompanied by urticaria, lesions of the genital mucosa, and urinary incontinence.
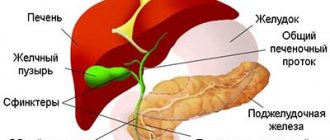
With opisthorchiasis, the main impact falls on the liver and pancreas, as a result of which pancreatitis and cholecystitis are possible.
All types of helminths provoke weakening of the body in children, which occurs due to intoxication. Anemia often develops. Parasites worsen the quality of life, cause other diseases and damage to various organs.
Prevention of worms in children
Children who play in dirt, sand, grass and other open areas are more likely to become infected with worms. Although worms can be eliminated through deworming, it is best to prevent infection as much as possible.
Hygiene is critical here. Teach your children basic hygiene habits and educate them about how worms get into their body and make them sick.
Prevention against worms involves the following actions:
- Do not give raw water to your child from springs or wells. This water must be filtered and boiled before use.
- Hands must be washed thoroughly with soap after contact with the ground.
- It is also worth washing the vegetables, herbs, fruits and berries that the child and other family members eat.
- It is important to thoroughly heat process meat, fish and poultry.
- Do not offer your child dried, salted or raw foods that have not been cooked.
- It is necessary to take a shower after swimming in ponds. Do not allow pets to lick your child's hands or face because their tongue may contain worm eggs.
- After each contact with animals, you must wash your hands well.
These precautions do not eliminate the possibility of helminth infection, but reduce it to a minimum.
Traditional methods of fighting parasites
When choosing traditional methods for removing parasites from children, you need to remember that they kill helminths, which means they are not entirely safe.
Garlic is a good remedy for any parasites. This infusion is prepared for children. Squeeze 2 cloves onto a glass of heated milk. Leave for half an hour, filter. Drink a glass a day, take 1/3 of it before meals.
To drive out parasites, the child is given flaxseed oil. You should drink a teaspoon in the morning and evening before meals.
An enema with soda helps with pinworms. For 250 milliliters of water take ½ teaspoon of soda. Do it 2-3 times a day.
Before using any products, please consult a pediatrician.
Preventive measures
A child should be taught cleanliness and hygiene from an early age. Hands should be washed more often: after returning from the street, playing with animals, going to the toilet, before eating.
Parents need to closely monitor their child and his health. Trim your nails regularly, change your underwear, avoid eating outside, and monitor the health of your pets.
Prevention includes developing correct behavior skills on the street and in public places - not putting your hands in your mouth, not eating in questionable places.
Even the most caring parents can have children infected with parasites. Therefore, you should not skip the recommended medical examinations and tests. It is possible to identify helminths at an early stage, preventing serious damage to the body.
If there is a high risk of infection, prophylactic use of antihelminthic drugs is possible. You cannot treat children on your own; a visit to a doctor is a prerequisite for getting rid of parasites.
Poor appetite in a child and abdominal pain due to worms
Appetite may decrease due to the fact that the body constantly has to fight parasites, lethargy and drowsiness appear. The disease can provoke not only a decrease in appetite, but also its increase. All these manifestations depend on the type and type of parasite, its life cycle, and location in the body.
An example is pinworms - they require a large amount of nutrients from the host's body for their reproduction, which occurs en masse and quite actively. Therefore, appetite increases significantly. They settle in the duodenum. At the same time, a person eats a lot, but his body weight does not increase; he may even lose weight. This sign is quite reliable in determining the disease.
Take a test for worms
In opisthorchiasis, worms primarily affect the liver and bile ducts. They can cause the formation of malignant neoplasms due to their carcinogenic effects. In addition to organ damage, parasites cause general weakness, loss of appetite, and vomiting after prolonged nausea.
As a conclusion, we can say that, like any disease, helminthiasis is easier to prevent than to treat .
Helminthic infestations are difficult to identify, quite dangerous, and treatment is accompanied by a large number of adverse reactions. One of these reactions may be an allergy, the manifestations of which are unpredictable and can be quite varied.