General information
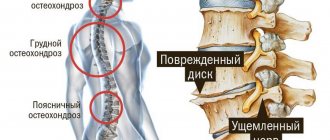
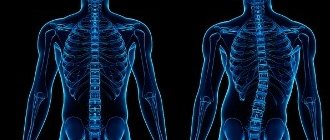
Lordosis is a condition of the spine in which its physiological or pathological bending with a convexity in front is noted.
Under normal conditions, physiological lordosis forms in the first year of a child’s life in the lumbar and cervical spine. The pathological form is also formed in these sections, but the degree of bending is much greater. The pathological form of this disease can appear in a person at any age. It is usually associated with pathologies of the vertebrae, both congenital and acquired, as well as pathological changes in the muscles of the back, hips and buttocks. The disease is characterized by poor posture and pain. If we are talking about a severe form, then the disease can negatively affect the functions of internal organs. As a rule, conservative methods are used in treatment. But sometimes, with severe forms of lordosis, the patient may require surgical intervention.
About the spine
The vertebral column is not a straight chord, as in lower vertebrates. The ability of a person to sit and walk on two legs led to the formation of 4 bends here:
- 2 curves - cervical and lumbar - are convexly directed forward, that is, these are lordoses;
- 2 bends - thoracic and sacral - bend backwards. They are called kyphosis.
This curved position allows the spinal column to better withstand loads, which include upright walking: when loaded, the spine is compressed like a spring, as a result the pressure decreases.
A child is born with a straight spinal column, and only when he begins to learn to sit does a curve in the lumbar region first appear, and then, for balance, all the other “concavities” appear. This curvature of the lumbar region, as long as it is within 150-170° (according to an x-ray, CT or MRI in a lateral projection) is physiological lumbar lordosis. As soon as this angle decreases or increases, lordosis is called pathological.
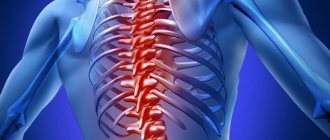
Pathological lordosis leads to the fact that the vertical load, first on the lumbar region, and then on the entire spine, increases. Compressed vertebrae change their shape (deform) and can easily move relative to each other even when performing normal work. Changes in several vertebrae at once lead to pinching of the nerves leaving the spinal cord, and this causes pain and dysfunction of internal organs.
The sacrum is 5 large fused vertebrae, convexly facing forward. Only the first, upper vertebra can separate from this structure, but all of them cannot bend in the other direction. Therefore, the term “lumbosacral lordosis” does not exist.
Pathogenesis
Lordosis and kyphosis are curves of the spine. Lordosis - with a convexity forward, kyphosis - with a convexity forward. In a normal state, there are four curvatures on the spine: lumbar and cervical lordosis, as well as sacral and thoracic kyphosis. Scoliosis , that is, lateral curvatures of the spine, should normally not exist at all.
Forward and backward bending is necessary to keep the body upright. Natural curves are a kind of shock absorbers that ease the load on the skeleton when a person walks, jumps or performs any other physical activity. Under normal conditions, the presence of such bends does not cause any discomfort. But if these curves become pathologically large, or form in uncharacteristic areas of the spine, this leads to a negative effect on the internal organs and the musculoskeletal system.
Immediately after the birth of a child, the first signs of physiological lordosis are observed, although during this period they are very weakly expressed. They become more noticeable when the baby begins to stand and walk. In a one-year-old child, the convexities of the spine are already more pronounced. But the spine is fully formed by adulthood, that is, by about 18 years. However, pathological bends can occur not only in adults, but also in adolescents and children due to pathological processes in the musculoskeletal system.
Pathological lordosis is characterized by certain changes. The vertebrae shift forward, and the vertebral bodies fan out. In the anterior sections of the spine, the bone structure becomes thinner and the intervertebral discs expand. Gradually, the spinous processes of the vertebrae adjacent to the affected ones become denser and closer together.
In children and adolescents with a pathological form of the disease, the chest may be deformed, as a result of which the organs of the chest cavity are compressed and their functions are disrupted. Other parts of the body may also become deformed. The severity of such changes depends on how early this disease manifested itself: the earlier this happened, the more pronounced the pathologies.
Experts define the concept of “lordly posture”. It's quite specific. As the disease progresses, the person's head and shoulders move forward, while the chest becomes flatter and extends into the abdomen. As a result, the stomach protrudes significantly. In this condition, the spine is significantly overstrained, the muscular-ligamentous apparatus is stretched, and this limits mobility and provokes pain.
In this condition, the functioning of a number of internal organs may deteriorate: lungs, heart, digestive system, etc. Often there is a feeling of tightness in the chest, which is characterized by the feeling that it is impossible to breathe deeply.
Lumbar lordosis is smoothed - what is it?
As a rule, pathological lordosis is a condition in which the lordosis of the lumbar spine is increased.
Strengthened and smoothed lordosis
A severe variant of the disease is a condition when the lumbar lordosis is smoothed. In this case, the back looks completely straight at the lower back, and the person is slightly arched back. With this condition, the patient cannot walk straight.
Straightening cervical lordosis - what is it?
Cervical lordosis is a condition in which the neck may be either abnormally concave or straight. If the cervical lordosis is straightened, then the patient looks as if he is aligned “on line.” In this regard, the flattened lordosis is sometimes called “military neck.” If the physiological lordosis is smoothed, the patient often experiences pain, stiffness, and discomfort in the neck. Smoothness is often associated with incorrect posture during sleep and wakefulness. If the lordosis is smoothed, this may be associated with a number of diseases, as well as with congenital pathology.
Hypolordosis and its varieties
Next, we will consider the concepts of physiological lordosis, smoothed or straightened, what it is and what it means. This is the same name for the disease hypolordosis: flattening or straightening of the spine. Natural curves are erased, reduced, and the distance from a flat surface to the lower back or neck is reduced. Such changes are noticeable to the naked eye, so at the first suspicion of hypolordosis, you should urgently consult a specialist.
Signs of hypolordosis:
- Pain in the neck or lower back.
- Inability to remain in a static position for a long time.
- Muscle tension in the affected area.
- Straightening the spine during palpation.
- Decreased spinal mobility in the affected area.
Classification
The disease is classified depending on a number of features.
Spinal curvature
Considering the reasons for its occurrence:
- Primary - this condition is a consequence of various pathological processes that develop directly in the spine. It develops, as a rule, as a result of pathological changes in the spinal column. This condition can be provoked by hernias, tumors, vertebral displacement, and inflammatory diseases.
- Secondary (compensatory, pathological) - this condition is of a compensatory nature and develops due to the need to maintain balance in conditions that are not physiological for the body. This condition can occur due to injuries to the cervical spine during childbirth , due to pathological dislocation of the hip, constant high load on the feet (in athletes, in women who are accustomed to constantly walking in high heels), and with flat feet .
Taking into account the localization, lordosis is determined:
- cervical spine;
- lumbar spine.
Taking into account the shape, it is determined:
- physiological;
- excessive pathological (hyperlordosis) ;
- straightening the bend (hypolordosis).
Considering the ability to restore a normal position to the body:
- unfixed - in this state the patient can make an effort and straighten his back;
- partially fixed – you can change the bending angle to a limited extent;
- fixed – the patient cannot return the body to its normal position.
How to treat lordosis?
Treatment of lordosis of primary etiology is carried out exclusively by surgery. Therapy for secondary lordosis consists of identifying the cause and eliminating it, using physiotherapeutic treatment, therapeutic massage, traction of the spinal column, and using various orthopedic devices to relieve stress from the spine. Painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain.
At home, the best treatment would be daily therapeutic exercises. The doctor selects a set of exercises taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Medication
The drugs are used to relieve pain and inflammation, and vitamin complexes are also prescribed.
Drug therapy consists of:
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Movalis);
- B vitamins orally or by injection (Neurorubin, Neurovitan);
- in some cases, glucocorticoids (Prednisolone) are prescribed;
- drugs to relieve muscle spasms (Mydocalm);
- local treatment (Fastum gel, Diclofenac or compresses with Dimekid).
Physiotherapy
The use of physiotherapy methods allows one to achieve good results: relieve pain, strengthen the back muscles, and in case of functional pathology, together with exercise therapy and other methods of treatment, it is possible to return the spine to its normal position.
The main methods of physiotherapy include:
- water procedures;
- electrophoresis;
- heat treatment (paraffin baths, mud, ozokerite);
- acupuncture;
- the use of ultrasound;
- exposure to a magnetic field.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out in combination with other methods, this allows you to achieve the highest results.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics is the most important way to treat spinal pathology. With the help of exercises, you can significantly strengthen your back, reduce pressure from the spinal column and reduce the degree of curvature, or even eliminate it completely. You can get rid of lordosis with the following exercises:
- take a position lying on your back, arms along your body - raise your straight legs up and throw them as far behind your head as possible; performed in two sets of 6–8 times;
- remaining in the same position, you should pump your abs - hands behind your head, straining your abdominal muscles, you need to rise and return to the starting position; performed 6–8 times;
- in a standing position, feet shoulder-width apart, bend forward, trying to reach your toes; repeat up to 10 times.
Orthopedic procedures
Such procedures involve wearing special orthopedic products to correct posture, relieve tension from the spinal column, and, accordingly, pain.
Orthopedic factories produce various types of corsets, bandages and so-called correctors that improve posture. It is recommended that women wear a bandage during pregnancy to prevent the development of pathology.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy includes therapeutic massage and the impact of a specialist’s hands on the vertebrae, spinal column, muscles and joints. The procedure is performed only by a qualified, specially trained specialist.
Manual therapy improves blood circulation in the spine, relieves stress from the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, eliminates muscle spasms, and allows for the restoration of pathologically located vertebrae.
Spinal traction
This procedure is carried out by a physiotherapist, often in water. In some cases, dry traction is used, but this technique is more false and dangerous for the patient. The spine is stretched using weights and the patient’s own weight.
During the procedure, the goal is to reduce muscle spasm and return displaced vertebrae to their anatomical location. The course consists of 10–18 sessions, during which the person is prescribed to wear an orthopedic corset.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is prescribed exclusively in severe cases, with primary pathology or the absence of positive dynamics during conservative treatment.
The essence of the operation is to correct the pathological curvature of the spine using metal structures. The postoperative period consists of wearing a corset or bandage, prescribing vitamin supplements and performing exercise therapy.
Causes
Primary pathological curvature can develop due to a number of reasons:
- tumors;
- developmental pathologists;
- inflammatory processes in the vertebrae;
- muscle torsion spasms;
- spinal injuries;
- spondylolisthesis.
Secondary pathological curvature occurs due to the following reasons:
- immobility of the hip joint;
- flexion contracture of the hip joint;
- hip dislocation, pathological or congenital;
- systemic diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- polio;
- cerebral spastic paresis of the lower extremities.
Other factors that can trigger the development of this disease are also identified.
Lordosis may occur temporarily during pregnancy , but this condition disappears after the baby is born.
In such conditions, a person is forced to bend at the waist to maintain balance, as the center of gravity of the body shifts forward.
There are also a number of predisposing factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of developing this disease. This is a violation of posture, excess weight with the deposition of a large amount of fat in the abdominal area, as well as too active growth of the child in childhood and adolescence.
Lordosis in children occurs due to the fact that the development of the back does not occur symmetrically. As a result, temporary body asymmetry may occur. As a rule, this is a passing phenomenon. But in order to correct the situation, you need to take a number of corrective measures. We are talking about the use of special corsets, the use of physical therapy, etc.
What are the signs of pathology?
The presence of spinal pathology is additionally indicated by the following symptoms:
- lower back pain that gets worse when bending over;
- muscle tension in the back and lumbar region;
- pain in the lower limb;
- numbness in the lumbar region or back of the leg;
- weakness in the foot, limitation of leg movements.
The presence of such symptoms may indicate diseases of the spine even with preserved lumbar lordosis.
Therefore, in such cases, doctors often resort to additional research methods: radiography, CTG or MRI.
Symptoms
This condition is characterized by lordotic posture , in which there is a strong curvature in the lumbar spine. With such a curvature, the stomach protrudes strongly, which is noted not only by the patient, but also by those around him.
In this state, a person feels discomfort, and his internal organs may not function properly. As a result, the following manifestations are possible:
- pain in the affected part of the spine, intensifying after exercise or uncomfortable positions;
- sleep disorders;
- severe fatigue;
- deterioration of metabolic processes;
- nervousness;
- restrictions when performing a number of physical activities.
Children with such disorders may often complain of pain in the neck or lower back. However, parents often do not pay attention to such complaints. In order not to miss the disease, it is important to pay attention to its external manifestations: protruding high shoulder blades, an overly pronounced lumbar curve, a protruding abdomen.
External signs of the disease depend on the characteristics of pathological changes:
- Kypholordotic posture - in this case, all curves increase. In this condition, lumbar lordosis and thoracic kyphosis are enhanced. The shoulder blades protrude, the stomach is protruded forward, the shoulder girdles are raised, the head moves forward.
- Kyphotic posture – thoracic kyphosis is significantly increased and lumbar lordosis is decreased. The center of gravity is shifted back, the head tilts forward, and the angle of the pelvis is reduced. The chest sinks, the stomach protrudes forward. The arms may hang slightly forward from the body.
- Plano-concave back - with this condition, the cervical lordosis is flattened, and the thoracic kyphosis is reduced. Lumbar lordosis is normal or increased. The chest is sunken, the shoulder blades stick out, the chin is down.
- Flat back - all natural curves are reduced, flattening of the lumbar lordosis is very noticeable. The chest moves forward, the shoulder blades stick out, and the lower abdomen protrudes.
Treatment
Lordosis usually does not cause any discomfort or serious problems and often does not require any special treatment. However, in cases of excessive lordosis (hyperlordosis), the excess curvature can lead to severe pain in the neck or more commonly in the lower back, which requires treatment. Treatment depends on the genesis of lordosis and the severity of the curvature. If the cause of lordosis is diseases such as infections, osteoporosis, then, first of all, the underlying disease is treated. In case of obesity, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic measures aimed at reducing weight. Conservative treatment of lordosis disease includes the use of medication (NSAIDs, muscle relaxants), physiotherapy and, most importantly, exercise therapy. Physical exercises, by strengthening the muscle corset, make it possible to compensate for impaired biomechanics of the spine. Exercises should combine both strength training and stretching exercises (for example, if you have problems with the hip, when stretching the flexor muscles is necessary). Corseting is possible in cases of severe lordosis caused by serious organic lesions of the vertebrae or during pregnancy.
Severe lordosis can lead to serious health problems, and therefore, in such cases, surgery may be required (for example, in cases of severe spondylolisthesis, vertebral fixation is necessary).
Tests and diagnostics
Pathological lordosis is diagnosed after examination and obtaining information after radiography. During the examination, the specialist determines the characteristics of posture, conducts special tests to determine whether the patient has fixed lordosis, and whether he has neurological disorders. The doctor also palpates the back muscles and examines the organs of the chest cavity.
If an expert suspects that a patient has developed pathological lordosis, he must undergo an X-ray examination of the spine. X-rays are carried out in two projections - frontal and lateral. The extent of the disease can be determined by taking lateral radiographs in a position where the back is maximally bent and extended. During the X-ray process, the mobility of the spine is assessed - it can be normal, increased, decreased. This study also makes it possible to determine violations of the shape, structure and relative position of the vertebrae.
Other methods such as CT and MRI can also be used in the diagnostic process.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is not made at home. Even a traumatologist does not have the right to do this based on examination alone: radiography, CT or MRI is required to see the pathological lordosis and assess the angle of bending. And if radiography only helps to establish a diagnosis and determine the type of lordosis, then tomographic methods can help find the cause of this condition.
The doctor can only suspect this disease. To do this, he asks the patient to stand with his back to the wall, pressing his buttocks and shoulder blades against it. If there is a lot of free space left in the lumbar region (more than 5 cm at the deepest point of the bend), this indicates pathological lordosis.
In addition to determining the lordosis itself and its type, studies are carried out (tests and instrumental diagnostics), the purpose of which is to determine the cause of this condition.
Prevention
To prevent the development of this disease, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- It is important to constantly monitor your posture.
- Avoid serious back strain.
- Control your body weight and avoid gaining excess kilograms.
- Use vitamin-mineral complexes periodically to prevent deficiency of elements important for the body.
- Practice proper and nutritious nutrition.
- Exercise regularly, practice swimming and other types of physical activity.
- Use special orthopedic devices during pregnancy.
- Treat in a timely manner diseases that provoke the development of lordosis - osteochondrosis , arthritis , disc protrusion , etc., by consulting a doctor if you have complaints of back pain.
Diet for lordosis
Diet for osteochondrosis
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1450-1780 rubles per week
Diet for arthritis
- Efficacy: Therapeutic effect after 2-6 months
- Terms: 2-6 months
- Cost of food: 1780-1880 rubles per week
You don’t have to adhere to a special diet for this disease, but it is important to eat in such a way that food easily passes through the gastrointestinal tract, is absorbed and does not cause constipation .
- It is important to drink a lot of liquid per day - at the rate of 30 ml per 1 kg of weight.
- Every day the menu should include a lot of fiber-rich foods - fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs.
- Reduce the amount of sweet and starchy foods.
- Minimize or completely eliminate fried, spicy, fatty, smoked, and alcoholic drinks.
- You can follow diets that are recommended for arthritis and osteochondrosis.
Complications
If no measures are taken, a number of serious complications may occur with lordosis:
- Impaired respiratory function due to the fact that the diaphragm is deformed.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Chronic constipation.
- Too much mobility of the vertebrae.
- Deforming arthrosis of the joints between the articular processes of the vertebrae.
- Deterioration of disc stability between vertebrae.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Discs falling out.
- Problems with kidney function, leading to frequent urination , pyelonephritis , etc.
- Compression of the spinal cord, leading to impaired urination and defecation, immobilization of the legs, and infertility .
Why is it dangerous?
Without treatment, a pathological bend can provoke the development of many serious complications, among which the most common are the following:
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- excessive mobility of the vertebrae;
- destruction of joints and cartilage occurs;
- neurodystrophic syndrome;
- spinal cord compression;
- disorders of the pelvic organs (complications during labor, spontaneous urination, constipation, etc.).
To prevent serious consequences that can cause disability, it is recommended to follow some simple rules to prevent the development of the disease. First of all, you need to give up bad habits, follow a healthy diet with enough vitamins, monitor your weight, visit the pool and pay attention to physical activity every day.
If you experience discomfort and pain in the back, limited mobility, you should seek professional help from a therapist, orthopedist or vertebrologist for further examination and correct therapy.
(
3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Forecast
The prognosis for this disease in adults may vary, but it is generally favorable. Pathological processes proceed slowly, so it is possible to diagnose the disease and treat it before critical complications appear.
A worsening prognosis is likely under the following circumstances:
- Previous spinal diseases or injuries.
- Spinal pathologies that appear in older people.
- Advanced stage of the disease.