Pain in the forehead, decreased sense of smell, and nasal congestion can signal the development of frontal sinusitis - inflammation of the frontal sinuses. This disease is less common than sinusitis, but is much more severe. Lack of adequate therapy or incomplete cure of frontal sinusitis can lead to serious complications, including the development of meningitis.
Treatment of this disease is carried out mainly by conservative methods. If it does not bring the desired result, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention.
Symptoms and signs of frontal sinusitis
Depending on which frontal sinus is inflamed, frontal sinusitis can be unilateral or bilateral. More often it is the left- or right-sided form, when the left or right sinus is affected. In this case, pain and swelling appear only on one side of the face. For unilateral frontal sinusitis there are other characteristic signs:
- body temperature 37.3-39°C;
- mucopurulent and mucous discharge from the nose;
- deterioration of nasal breathing and sense of smell;
- moderate headache in the superciliary area;
- a feeling of pain and discomfort in the inner corner of the eye.
With bilateral frontitis, the patient feels much worse than with unilateral frontitis. He is deprived of free breathing from both nostrils at once. Because of this, pain is more pronounced, as well as a feeling of fullness in the forehead. Discharge also occurs from both nostrils.
In mild forms of frontal sinusitis, predominantly local symptoms appear. In the case of a moderate course, signs of intoxication appear: the temperature rises, weakness and malaise appear, loss of appetite and worsening sleep are observed. With severe frontal sinusitis, more severe symptoms occur:
- severe, sometimes unbearable pain in the forehead;
- reactive swelling of the eyelids;
- swelling and redness of the skin in the projection area of the frontal sinus;
- puffiness of the face;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation.
Painful sensations
Pain in the forehead increases when tilting or moving the eyeballs. It can radiate to the temporoparietal region. If the patient sleeps on his back, then in the morning he experiences sharp exacerbations of pain. This is due to the accumulation of inflammatory masses in the frontal sinuses.
Discharge
Initially, the patient experiences a thin, mucous discharge. They are transparent, but over time they become viscous and acquire a yellow tint. The development of a purulent process is indicated by green discharge with an unpleasant odor. With unilateral frontal sinusitis, they come out of only one nostril, and with bilateral sinusitis, they come out of both nostrils at once.
Acute frontal sinusitis
Acute frontal sinusitis is characterized by a sharp onset and persistence of symptoms for up to 12 weeks. If the patient receives high-quality treatment, then complete recovery without residual signs is possible. The main symptoms of acute frontal sinusitis include:
- pressing or aching pain in the forehead (intensified by tapping);
- discharge of purulent sputum from the nose in the morning;
- sharp pain in the inner corner of the eye when pressing;
- feeling of fullness in the area between the eyebrows;
- elevated temperature.
Chronic frontal sinusitis
The transition of frontal sinusitis to a chronic form is associated with the lack of treatment or incorrectly selected therapy. A chronic process is said to occur when a person does not recover for more than 12 weeks. Symptoms characteristic of acute frontal sinusitis become less pronounced in the chronic form. The patient is concerned about the following manifestations:
- malaise that prevents you from doing your usual things;
- sometimes the temperature rises to 37°C;
- nasal congestion in the morning;
- persistent cough that is not helped by antitussive medications;
- swelling of the walls of the eye sockets in the morning;
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- feeling of heaviness behind the eyes.
Breathing problems in chronic frontal sinusitis are associated with the growth of polyps in the nasal cavity. Discharge in chronic frontal sinusitis may be absent. The first sign of an exacerbation of the disease is a feeling of “heat” or “flush” in the forehead. Only then does pain appear in this area. It intensifies with bending over and physical activity, and is sometimes accompanied by pulsation.
Catarrhal
The term “catarrhal” means “superficial.” This type of frontitis is accompanied by pain in the area of the brow ridges, which often torments the patient at night and 1 hour after waking up. It radiates to one or both eyes and jaw. Around lunchtime the pain goes away.
The catarrhal form is considered the first stage of the inflammatory process in the frontal sinuses. In addition to pain, the disease causes the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- photophobia;
- sleep problems;
- increased tearfulness;
- decreased performance and fatigue;
- swelling of the mucous membrane of the sinuses themselves, which leads to nasal congestion.
Purulent
One of the most dangerous forms of the disease is acute purulent frontal sinusitis. It can quickly lead to inflammation of the periosteum, cellulitis and osteomyelitis. This is due to the fact that the source of inflammation is located near vital organs. The purulent-necrotic process can spread to brain tissue and craniofacial nerves, which is dangerous for the development of sepsis, meningitis, and sometimes even death. Purulent frontal sinusitis can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- temperature 39-40°C;
- purulent nasal discharge;
- throbbing pain in the forehead, which intensifies when tilting and turning the head;
- cough at night and in the morning;
- Strong headache;
- photophobia;
- severe nasal congestion;
- tearfulness;
- tension and swelling in the bridge of the nose.
Possible complications –
Complications arise, as a rule, only as a result of the patient’s self-medication and late consultation with a doctor. The most harmless complication will be the transformation of acute frontal sinusitis into chronic purulent or polypous, with the need for surgical intervention. More serious complications may include: brain abscess, orbital abscess and loss of vision, thrombophlebitis of facial veins, sepsis... We hope that our article on the topic: Frontitis symptoms and treatment at home was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author's education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience in maxillofacial surgery and surgical dentistry, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Guide to maxillofacial surgery” (Timofeev A.A.), 5 "Surgical dentistry and maxillofacial surgery" (Kulakov A.).
Causes of frontal sinusitis
Frontal sinusitis rarely develops as an independent pathology. In most cases, it develops against the background of other diseases, most often of the ENT organs. This group of causes of frontal sinusitis includes the following pathologies:
- tonsillitis;
- sinusitis;
- pharyngitis;
- adenoids;
- chronic, allergic or vasomotor rhinitis;
- tubootitis.
With such diseases, there is a potential source of infection in the body, which can spread to the frontal sinuses. The causes of frontal sinusitis also include immunodeficiency states due to AIDS, malignant tumors, and if the patient receives radiation therapy.
Inflammation of the frontal sinuses is caused by various traumatic injuries or operations in the skull area, if they lead to deformation or blockage of the excretory duct or narrowing of the frontal sinus. Traumatic causes also include:
- deviated nasal septum;
- deformation of the ethmoid labyrinth and middle turbinate;
- other anomalies of the structure of the nose;
- fractures or displacement of the nasal septum.
Even improper nose blowing, when a person blows both nostrils at the same time, can act as a trigger for the onset of inflammation. Depending on the cause, frontal sinusitis is divided into several types:
- allergic;
- bacterial (the disease is caused by staphylococci, hemophilus influenzae, streptococci and other bacteria);
- viral (inflammation of the frontal sinuses occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, measles, rubella, damage by adenoviruses, etc.);
- fungal;
- mixed.
In children, frontal sinusitis may occur no earlier than 5 years of age. Until this age, the child’s frontal sinuses are not yet fully developed. They cannot become inflamed, and therefore frontal sinusitis does not develop. In childhood, the disease most often occurs due to an allergic runny nose or foreign bodies entering the nasal cavity. Also, frontal sinusitis in children can be caused by the same factors as in adults.
What it is?
Frontitis is an inflammation of the frontal paranasal sinus. Over the past decade, sinusitis (inflammation of the sinuses) has been considered one of the most common diseases in the world. Today, about 10-15% of the population suffers from them. A tenth of patients with sinusitis are diagnosed with acute or chronic sinusitis. Over the past 5 years, the incidence of frontal sinusitis has tripled and continues to increase.
In Russia, the number of people suffering from manifestations of frontal sinusitis reaches 1 million people per year. Among those hospitalized, there are more males, and among those treated on an outpatient basis, females are more common.
Diagnosis of frontal sinusitis
To make a diagnosis, the patient is subjected to a comprehensive examination. At the first stage, the doctor carries out:
- physical examination. The doctor notes the characteristic symptoms of frontal sinusitis: swelling, pain and redness in the bridge of the nose. The specialist applies pressure to this area to see if the pain gets worse;
- examination of the nasal cavity. The test is called rhinoscopy. It is necessary to detect purulent exudate in the nose, which drains from the front of the nasal passage. The doctor also notes that there is redness and swelling of the mucous membrane.
If necessary, the nasal cavity can be examined using an endoscope. This is a special device with a flexible tube, which is inserted into the nose to examine the mucous membrane. Additionally, frontal sinusitis diagnostics includes:
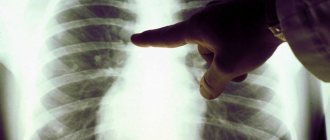
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses. This diagnostic method is considered the leading one in detecting frontal sinusitis. To get the most complete picture of the condition of the paranasal sinuses, doctors take x-rays in 3 projections;
- computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses. If the X-ray does not produce results, then doctors do a tomogram. On it you can clearly see all the changes in the bone structures and the entrance channel of the sinuses;
- bacteriological research. It is necessary to detect the causative agent of the disease. Before bacterial culture of the patient, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics to the patient, and after receiving the test results, he adjusts the therapy by prescribing a medicine against a specific pathogen. For research, samples of sinus tissue obtained by puncture or nasal discharge are used.
In acute frontal sinusitis, making a diagnosis is not difficult. The difficulty may lie only in detecting the pathogen. That is why specialists study the patient’s nasal discharge.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures include strengthening the immune system to prevent the development of acute respiratory viral infections and complications of these infections. To do this you need:
- harden;
- avoid physical inactivity;
- get enough vitamins and microelements from food. To lose weight, do not use mono-diets, but eat a variety of vegetable and meat dishes, regulating calorie content;
- dress according to the weather, avoiding hypothermia and overheating;
- undergo preventive examinations with a dentist, gynecologist (urologist), and have fluorography;
- promptly treat detected diseases.
Author:
Krivega Maria Salavatovna resuscitator
Treatment of frontal sinusitis
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. The treatment regimen depends on the severity of the disease and the cause that caused it. Treatment can take place at home. Only those with severe bilateral frontal sinusitis are sent to the hospital.
The main goal of treatment is to provide drainage, i.e. outflow of inflammatory contents from the frontal sinuses. Additionally, measures are taken to restore normal breathing and prevent complications. At the first stage of treatment, medications are used:
- antibiotics: Amoxiclav, Sumamed, Doxycycline, Ceftriaxone. A specific drug is prescribed taking into account the causative agent of frontal sinusitis;
- local antibiotics: Bioparox, Polydexa. They are produced in the form of a spray, and are used to act on bacteria directly at the place of their reproduction - in the nasal cavity;
- local antiseptics, for example, Miramistin. It can be used to rinse the nose. The drug will help wash away bacteria from the mucous membrane and remove the contents of the nasal cavity out;
- antihistamines: Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil. Prescribed for allergic nature of the disease;
- for nasal rinsing: Aqua Maris, Afrin, Quicks. They cleanse the nasal cavity of purulent contents, moisturize the mucous membrane and facilitate breathing;
- vasoconstrictor drops: Galazolin, Naphthyzin, Nazol. They are necessary to restore normal nasal breathing;
- antipyretics: Panadol, Paracetamol, Nurofen. Used when the temperature rises above 38.5°C;
- homeopathic remedies: Sinupret, Cetirizine, Tavegil. They help relieve swelling and inflammation, ensure the opening of the sinuses and normal breathing.
Physiotherapy methods are used in combination with drug treatment. Several procedures show good results for frontal sinusitis:
- laser therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- quartzization of the nasal cavity;
- irradiation with a Sollux lamp.
Surgery
If the disease cannot be controlled with the help of medications, then doctors perform surgery. There are several types of operations performed.
1. Puncture of the frontal sinuses. The procedure is also called a puncture. It takes place in several stages:
- the patient is given local anesthesia, after which a special needle is inserted into the nose;
- along its end, which remains outside, purulent contents flow out of the nose;
- when all the liquid comes out, the specialist applies an antiseptic inside to rinse the cavities;
- if there is a lot of discharge or it is purulent, then the doctor can insert a catheter through the needle, which will remain there for a while. Through the device, secretions can come out, and washing is also carried out through it.
2. Sinoplasty. An endoscope is inserted into the nasal cavity, and a special balloon is inserted through it. The latter is inflated to widen the anastomosis. Through the wide opening, secretions can easily flow out.
3. Open. Radical interventions are rarely performed, since they severely injure the tissue. Open surgery is performed through an incision above the bridge of the nose, a hole in the bone at the bottom of the frontal sinus, and sometimes through the nose.
The operation is also performed when frontal sinusitis was caused by a deviated nasal septum, adenoids or polyps. Intervention helps to get rid of these defects.
YAMIK method
This is a non-surgical treatment similar to "cuckoo". It can be used in children from 5 years of age, but requires the purchase of an expensive catheter and is therefore expensive.
A YAMIK catheter is a rubber tube with 2 channels inside, ending in two separate outlets. In addition, there are 2 cylinders on the tube. The catheter is inserted into the nasopharynx, then balloons are inflated using syringes, and this blocks the nasopharynx, in which negative pressure is then created. Under its influence, the contents come out of the sinuses. And if you then change the pressure to positive, you can spray the medications without puncture directly near the affected sinus.
The YAMIK catheter is inserted with the patient in a sitting position, after preliminary lubricating the mucous membranes with a mixture of lidocaine and adrenaline solutions (to anesthetize and at the same time narrow the blood vessels, removing swelling and reducing the risk of bleeding). Treatment using this method is contraindicated for diseases of the blood coagulation system and for severe polyposis of the mucous membrane, which will prevent the contents from coming out.
Indications for frontal sinusitis
To speed up recovery, with frontal sinusitis the patient should adhere to some recommendations:
- regularly ventilate the room in which the patient is located;
- humidify the air daily;
- observe bed or semi-bed rest;
- provide plenty of warm drinks and easily digestible food.
During frontal sinusitis, it is very important to regularly rinse your nose so that you can breathe normally and the nasal cavity is not filled with inflammatory contents. A regular syringe without a needle is suitable for rinsing. A solution is drawn into it, which is then poured into one nostril.
It is better to carry out the procedure over a sink. The head must be turned to the side. The solution is poured into the nostril, which, when tilted, turns out to be the top. The fluid should come out of the other nostril. A sea salt solution is considered a classic solution for washing. For a glass of boiled water, 1/3 teaspoon of salt is enough.
It is important that its crystals completely dissolve, otherwise the mucous membrane can be injured. You can rinse your nose up to 5-6 times a day. If the nose is stuffy, then before the procedure it is necessary to instill vasoconstrictor drops, otherwise the solution will not be able to pass through the nasal passages.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods are used already at the stage of remission of the disease, when the temperature has returned to normal and there are no signs of intoxication. The procedures help speed up recovery and strengthen the immune system. The following physiotherapy methods are useful for frontal sinusitis:
- Low-intensity ultra-high frequency (UHF) therapy. It involves exposing the body to electromagnetic fields with a wavelength of 1–10 m. To do this, special capacitor plates are placed on the frontal sinuses. Due to the thermal effect, blood circulation improves, swelling decreases and recovery is activated.
- Quartzization of the nasal cavity. This procedure helps to destroy pathogenic bacteria that caused the disease. The special lamp is turned on for 5 minutes to warm up. It has a special nozzle that is inserted into each nostril for 30–60 seconds. During this time, the nasal mucosa is irradiated with ultraviolet light.
- Endonasal probing. 2 cotton swabs soaked in antibiotics are inserted into the nasal passages. One of the electrodes is connected to them, and the second is applied to the forehead area. Next, weak current discharges are passed through the body. Under their influence, the medicine penetrates the mucous membrane. The course includes 10–12 procedures.
- Flushing using an electric pump (“cuckoo”). This method is completely painless. The medicine is injected into one nostril, and the contents are sucked out through the other using an electric pump. To prevent liquid from getting into the mouth, the patient must say “ku-ku” during the procedure.
Contraindications for frontal sinusitis
Warming up during frontal sinusitis is not only not useful, but in some cases even dangerous. Heat exposure can only increase swelling. Warming up also creates favorable conditions for further growth of bacteria. Also, the patient may accidentally warm up the lymph nodes, which will also increase inflammation and even lead to complications.
Thermal procedures for frontal sinusitis are allowed only if the patient does not have a fever or purulent nasal discharge. But even here it is important that the treatment occurs under the supervision of a doctor. Only he will be able to determine whether warming up will do any harm at a specific stage of the disease.
What else should not be done if you have frontal sinusitis:
- continue to go to work and maintain your usual lifestyle. In the acute form, it will be difficult for the patient to do this due to severe weakness, but in the chronic form, patients often neglect bed rest. This often leads to complications;
- smoke. It is necessary to give up cigarettes at least for the duration of treatment of the disease. Cigarette smoke irritates the mucous membrane, which only increases its swelling and delays recovery;
- use vasoconstrictor drops for a long time. They can be used for no more than 7-10 days. It is advisable to instill only before bedtime in order to get a good night's sleep. With the constant use of such drops, addiction develops, and the nasal mucosa also grows, which only worsens the course of frontal sinusitis.
Development mechanism
The development of frontal sinusitis begins as an acute process due to a viral or microbial infection, or as inflammation as a result of injury to the frontonasal canal and frontal bone.
With frontal sinuses, swelling and blockage of the passage in the area of the frontonasal canal develop. The normal communication between the nose and sinus is disrupted, inflammatory fluid or pus accumulates in it, and the mechanisms of local immune defense are disrupted.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the inflammation subsides and becomes chronic; other sinuses may also be affected. Inflammation can worsen with any cold, which significantly affects the quality of life of patients.
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
Everyone who comes to the clinic of JSC "Medicine" undergoes an examination in accordance with medical standards. This helps to accurately identify the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment. By contacting JSC “Medicine”, you can be confident in the provision of quality services. Each patient here receives:
- Personal access to medical history via the Internet.
- A personal curator who will accompany the patient throughout the entire therapy, even if other specialists take part in it.
- An accompanying person for quick movement around the clinic.
- Explanation in clear language about treatment and prescribed medications.
- Possibility of receiving all necessary services on the day of treatment.
- The wait for an appointment is no more than 20 minutes, subject to prior registration.
- Providing examination results on a CD.
The Clinic of JSC "Medicine" is always ready to discuss in case of justified claims. If you were not provided with certain services properly, you can receive financial compensation.
The administration considers any requests, since JSC “Medicine” works on the principle that only the client evaluates the quality of the services provided. This is what became the key to the clinic’s success in providing medical care. Each patient leaves us not only healthy, but also completely satisfied with the services provided.
Kinds
Acute frontal sinusitis can occur in two forms - catarrhal and purulent. In the first case, the mucous membrane swells greatly and is saturated with liquid - exudate. It fills the main part of the sinus, displacing air. The cilia covering the surface of the epithelium disappear. Immune cells accumulate around the vessels.
Catarrhal sinusitis, in contrast to purulent sinusitis, is not accompanied by damage to the entire thickness of the mucous membrane. The purulent form causes damage to all layers of the mucosa and involvement of the periosteum. The tissues are saturated with immune cells, most of which are white blood cells. Capturing pathogenic microorganisms, they die, forming pus.
When the periosteum is damaged, chronic frontal sinusitis develops. It can occur in exudative, productive, alterative and mixed forms. A chronic variant of the pathology is said to exist if the manifestations of frontal sinusitis do not subside within 4 weeks. Predispose to chronicity of the process:
- improper or short-term treatment of acute inflammation in the sinus;
- constant violation of the free passage of the canal between the sinus and nasopharynx;
- enlargement, proliferation of the nasal wall or changes in the shape of the nasal septum.
If chronic frontal sinusitis has features of exudative inflammation, the patient has a predominant discharge of a mucous or mucopurulent nature; This option also occurs in the allergic process. The productive variant includes hyperplastic formations (tissue growths) and polyps. With alteration, atrophy of the sinus walls or osteomyelitis develops, and the development of intracranial complications is possible.
Preventive measures
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and a balanced diet is important for keeping your immune system healthy and reducing the risk of sinus infections. It is required to increase the daily consumption of vegetables and fruits high in antioxidants. Grapes, berries, and nuts are full of antioxidants that strengthen the immune system.
It is necessary to quickly treat a runny nose and allergies to avoid a secondary infection developing in the sinuses. Reduce nasal congestion using a nasal spray. Drinking plenty of fluids during illness promotes the outflow of mucus.
Maintaining personal hygiene is necessary to reduce the risk of inflammation. Common allergens such as smoke and dust should be avoided as they cause respiratory reactions. Smokers and those exposed to cigarette smoke are susceptible to developing the disease.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Drugs with anti-inflammatory effects complement the treatment regimen and inhibit the production of substances that promote the development of inflammation. These products can be used internally or locally. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the chain of biological reactions, reducing swelling and pain. Normalize the function of the mucous glands, restore communication between the frontal sinus and the nasopharynx. The drugs affect symptoms of bacterial and viral nature.