An umbilical hernia is a protrusion of internal organs covered by peritoneum through the umbilical ring. There is practically no fat layer in this part of the abdominal wall, and the umbilical ring itself is covered from the inside only by connective tissue. It, unlike muscle tissue, can stretch, but not contract. Therefore, with a prolonged increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the umbilical ring becomes a “weak spot” through which internal organs, usually the intestinal wall, begin to protrude. In children, umbilical hernias account for up to 15% of all possible hernias, in adults - about 8%.
Umbilical hernia - what is it and what does it look like?
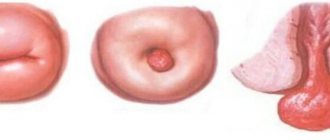
This is a protrusion of the anterior abdominal wall in the peri-umbilical region of various sizes: from a small coin to several tens of centimeters. With the development of this disease, prolapse of the abdominal organs occurs through a defect in the navel area.
In addition to the visual defect, the patient may be bothered by pain in the abdominal area, a general deterioration in health up to critical when a hernia is strangulated and the development of necrotic changes in the internal organs.
This is a disease that requires mandatory medical supervision and treatment; it cannot be left to chance. The disease can develop in utero, form during the newborn period, or in adulthood under the influence of certain factors.
general description
A pathology in which there is prolapse of internal organs through the umbilical ring is called an umbilical hernia.
The disease is manifested by the formation of a bulge in the form of a ball in the area near the navel, which appears with abdominal tension, nausea, and pain in the epigastric region. The diagnosis is made by a surgeon based on examination of the patient, palpation of the abdominal area, and instrumental studies.
Treatment for children under five years of age is conservative. In the absence of positive dynamics, surgical removal of the hernial protrusion is indicated for children over five years of age, as well as adults.
Causes
The etiology of the development of this type of hernia directly depends on the period when they formed. When considering the causes of this pathology, one should touch upon their classification depending on the age of the patient.
There are the following forms of umbilical hernias:
- Embryonic
The reason for their formation is intrauterine underdevelopment of the abdominal fascia or other defects in the formation of internal organs. A newborn is born with already formed pathology.
- Occurred in childhood
This disease is more typical for children in the first six months of life. The reasons for the formation of a hernia in tender infancy are weakness of the muscles and fascia of the abdominal wall, a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure with prolonged screaming and crying.
Abnormal bowel movements and constipation can also cause excessive straining. In infants, muscle tone has not yet been formed and tissue turgor is reduced, which is a predisposing factor in the formation of umbilical protrusions.
Diseases such as whooping cough, phimosis, dysentery can cause high pressure inside the abdominal cavity in babies, expansion of the umbilical ring and protrusion of internal organs through it.
- Formed in adults
Among the adult population, this pathology accounts for 3 to 5% of all external abdominal hernias and is more common in women.
Predisposing factors to its development include excess weight, pregnancy (repeated or multiple), weakness of the abdominal muscles due to neglect of exercise and gymnastics, excessive physical effort, heavy lifting, chronic constipation.
A rare but common cause of the formation of a hernia in the navel area is metastases of stomach cancer.
At-risk groups
The pathology occurs in adults and children. At the same time, considering risk groups, each group has its own specifics.
Umbilical hernia in adults
The following categories of adults are at particular risk:
- People with a hereditary predisposition. If someone in your family has already had umbilical hernias (especially direct relatives), it is important to remember: a decrease in tone, weakness (dysplasia, determination) of the connective tissue in the abdominal area should not be allowed. Therefore, exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles should be done daily.
- Women whose first birth was quite late - after 35 years.
- People with poor metabolism (metabolic disorders lead to changes in connective tissue).
- Those who engage in strength sports. Umbilical hernias in athletes occur less frequently than inguinal hernias, but at a critical level of stress, athletes are a very typical risk group in the context of the problem of the development of umbilical hernias. A sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure and sudden movements when working on weight training equipment or when lifting a barbell can provoke protrusion of part of the abdominal wall outward, forming a hernial sac.
Important! It is extremely important to maintain balance. In patients with a genetic predisposition, hernia results in a weak abdominal wall; in professional athletes, on the contrary, the pathology develops due to strong stress on the abdominal cavity.
Umbilical hernia in children (newborns)
- Premature babies with low weight are more prone to pathology. Umbilical hernia is diagnosed in 30% of premature babies.
- In children whose parents suffered from an umbilical hernia in childhood, an umbilical hernia is diagnosed much more often than in children whose parents themselves did not encounter this disease.
- The risks of expansion of the umbilical ring and prolapse of internal organs are higher in children suffering from rickets, malnutrition or other diseases in which muscle tone decreases.
- Children who started walking earlier than their peers are also included in the risk group. Here we are talking mainly about those children whose muscles are not strong enough, but whose activity is very high.
- Statistics show that umbilical hernia occurs more often in girls than in boys.
Note! For a long time, it was generally accepted that an umbilical hernia could be caused by improper tying of the umbilical cord. But experts confirmed: there is no direct connection. The technique of tying the umbilical cord is not associated with the expansion of the umbilical ring
Umbilical hernia in pregnant women
Potential risk groups include pregnant women:
- Multiple births often lead to umbilical hernias. Women who are carrying twins, and especially triplets, are under special control.
- Another factor that provokes an umbilical hernia in pregnant women is polyhydramnios - an excess of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid in the uterus). If there is a suspicion of a deviation in the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus of a pregnant woman, the doctor establishes control over it. It is important that, on the one hand, there is enough amniotic fluid for its direct function - protecting the fetus, and, on the other hand, the fluid should not provoke conditions for squeezing the umbilical cord. Amniotic fluid is collected through the vagina or through the abdominal wall under ultrasound guidance.
- Women whose fetus grows very quickly are also at risk.
The presence of a hernia affects both the management of pregnancy and childbirth. The tactics of labor management (natural/caesarean) are selected individually. If the hernia is large, but the gestation period is short, they most often resort to hernia reduction and cesarean section. If the hernial sac is empty, then wearing a special bandage and natural childbirth are practiced.
Clinical picture and possible complications
Characteristic signs of the disease are:
- Abdominal pain;
- A protrusion in the navel area that disappears with pressure (with an unstrangulated hernia);
- Expansion of the entrance gate - the umbilical ring;
- Nausea (sometimes).
The prolapse of contents through the ring of the anterior abdominal wall (intestinal loops, parts of the omentum) can increase with physical exertion, coughing, and therefore the bulge in the umbilical region increases.
In small children, when lying on their back, the formation may disappear, but when crying, sucking, or moving, it appears again.
The severity of the clinical symptoms of this pathology depends on the size of the hernia, the presence or absence of its complications.
Dangerous complications are:
- Incarceration of the contents of the hernial sac (intestinal loops or omentum)
- Inflammation of the umbilical membranes
- Rupture of the membranes, their purulent melting
- Formation of intestinal fistulas
These are life-threatening conditions that can lead to the development of acute intestinal obstruction or peritonitis.
Stages and degrees
An umbilical hernia (differential diagnosis is necessary for an accurate diagnosis and treatment) develops in several stages:
- First of all, the muscle tissue of the umbilical ring weakens.
- Further, as a result of too much sudden or constant tension of the peritoneum (laughter, hysterical coughing, crying, blows to the stomach, as well as lifting weights), an increase in intra-abdominal pressure occurs.
Degrees of umbilical hernia in children - Due to increased pressure, the loops of the small intestine fall out and a tumor-like formation is formed - a hernia. It consists of 3 sections: the hernial orifice (a loop or loops of intestine exit through this opening), the hernial sac (a section of the peritoneum that protrudes due to the pressure on it from the internal organs) and its contents (the extended walls of the organs, or the omentum - part of the peritoneum).
- As the hernia grows, even more organ parts enter its sac. Part of the stomach, large intestine, and part of the liver may be affected.
Strangulated umbilical hernia
This is a sudden compression of the hernial contents in the area of the exit gate. Occurs in 7% of cases among all carriers of this pathology.
In a strangulated condition, a piercing, sharp, unbearable pain develops in the area of the hernial sac, its contents cannot be reduced, the protruding part of it on the anterior abdominal wall becomes tense, swollen, and an increase in body temperature over the protrusion is possible.
If a patient in this condition hesitates to see a doctor, symptoms of intoxication develop: general weakness, fever, nausea, vomiting, confusion. Coprostasis and peritonitis may develop. Without timely surgical treatment, these conditions will end in death.
If you suspect the development of a strangulated hernia in the navel area, namely:
- As pain increases;
- Inability to push the contents inside the umbilical ring;
- Enlargement of the hernial sac and development of its tension.
You should call an ambulance immediately! A patient with such symptoms will be hospitalized in the surgical department and operated on as soon as possible.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Is it necessary to remove an umbilical hernia? The formation of a hernial protrusion in the navel area is in most cases associated with a predisposition of the body. Many of those who are actively involved in sports and have trained abs rule out the development of such a disease. This is an erroneous judgment. Developed muscles and muscles do not always protect against the onset and progression of the disease. Moreover, elastic, inflated muscles can aggravate the condition. The hernia will become almost invisible, but it will not go away and can cause strangulation at any moment. Unfortunately, there is no cure for umbilical hernia. It cannot be treated with folk remedies, and therapeutic exercises are also powerless. All these methods are effective only for improving the general condition and relieving some symptoms, but you can only get rid of the pathology by removing it. If this is not done, the hernia will grow, and the risk of complications increases.
How to determine an umbilical hernia in an infant? Even an inexperienced parent finds it difficult not to notice an umbilical hernia in a baby. After the umbilical cord falls off, a slight protrusion of the navel is considered normal. This is an anatomical predisposition and you should not be afraid of it. The protrusion increases when the child cries or strains. The navel can be pushed back into place without the baby experiencing any discomfort. The reason for a visit to the pediatrician should be symptoms such as non-reducible hernia, vomiting, nausea, discoloration of the formation and swelling in the navel area.
How is an umbilical hernia removed in adults? Two options are used to access the area of the hernial sac: through an incision or laparoscopically, that is, by puncture method. The last method is considered the most optimal. The doctor sutures the hernial orifice, cuts off adhesions and strengthens the abdominal walls. Large incisions are made for large hernia formations. Sometimes the umbilical ring needs to be removed, which the doctor must inform the patient about in advance. To avoid relapses, a special mesh is placed during the operation.
Is it possible to treat an umbilical hernia without surgery? This is unlikely. Those who seek medical help at the first signs of illness have a chance. Such cases are very rare; most people come to doctors when pain begins to bother them and the protrusion reaches a large size.
Reducible and irreducible umbilical hernia - what is the difference
The main difference between these conditions is that with reducible protrusion of the internal organs, they can be carefully and effortlessly returned to the abdominal cavity by lightly pressing on the hernial sac.
Irreversible hernias are characterized by either incarceration of intestinal loops or omentum sections that have prolapsed into the umbilical ring, or the formation of an adhesive process.
This is a dangerous condition that disrupts the work and functioning of internal organs and requires immediate surgical intervention.
Irreversible protrusions are a rare occurrence in children of the first year of life. As a rule, their disease does not occur with this type of complication, but it cannot be completely excluded.
Every parent should be aware of the signs of a strangulated hernia, and also understand that if these signs appear, the child should be immediately hospitalized.
Kinds
Hernia has several types of classification:
| By origin | |
| Congenital | They arise due to improper formation of the tissues of the umbilical ring and abdominal wall during intrauterine development. |
| Purchased | They occur due to injuries, weak abdominal muscles, and high intra-abdominal pressure. |
| According to the type of protrusion of the walls of organs | |
| Oblique | The exit of the organ walls has an oblique direction. |
| Direct | Direct protrusion of organ walls is a progression of oblique protrusion. |
| According to the degree of protrusion of organ walls | |
| Reducible | The hernia can be corrected by hand pressure - its contents are easily reduced into the peritoneal cavity (in this case, the formation itself is not eliminated - it simply becomes invisible). |
| Irreversible | The hernia becomes irreducible when the inflammatory process develops or when the contents of the hernia grow together with the hernial sac (adhesions form). |
Diagnosis of the disease
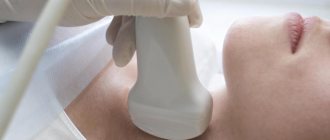
Diagnosis of this pathology is not very difficult and is based on the characteristic clinical picture, laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
If a child or an adult experiences a characteristic protrusion in the navel area that decreases in volume in a horizontal position, pain in the abdomen, or nausea, you should consult a surgeon. The doctor will prescribe:
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity, stomach and duodenum;
- FGDS;
- Ultrasound of hernia formation;
- Herniography is a research method based on the introduction of a contrast agent and a subsequent series of x-rays.
The doctor’s task is to establish the correct diagnosis and identify concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The tactics for treating the pathology depend on the patient’s age, the size of the hernia defect, and the presence or absence of complications.
According to the doctor's indications, a laparoscopic examination can be performed for diagnostic purposes, which combines not only diagnosis, but sometimes treatment.
Laparoscopy refers to minimally invasive surgical interventions using special video devices inserted through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall under anesthesia.
Thanks to this research method, it is possible to visualize on the monitor screen the entire “picture” that occurs in the abdominal cavity, perform the necessary medical manipulations, and even eliminate the hernia defect.
Causes
The main causes of a hernia are weakness of the umbilical ring muscles coupled with increased intrauterine pressure.
The following factors can also lead to the development of pathology:
- genetic predisposition (congenital weakness of the peritoneal tissue, the presence of a hernia in the father or mother);
- abdominal obesity (with the accumulation of a large amount of fat on the abdomen, the umbilical ring is stretched);
- sudden and severe weight loss;
- surgical manipulations in the navel area, sutures and scars on the navel;
- ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity);
- diseases of the respiratory system (mostly chronic), accompanied by frequent and severe cough;
- frequent constipation;
- diastasis;
- injuries of the abdomen and abdominal organs;
- tumors in the abdominal region;
- complicated childbirth;
- pregnancy (especially multiple pregnancy);
- sedentary lifestyle.
In children, pathology can appear as a result of prematurity, heavy lifting, intestinal problems, frequent and severe crying. In children under 5 years of age, the development of a hernia is often due to a slow process of closure of the umbilical ring. Normally, the umbilical ring tightens after the umbilical cord falls off, but in some cases the process slows down and a hernia occurs.
It does not cause discomfort and very often goes away on its own, but after 5 years the child needs to be shown to a surgeon - he will decide whether surgical intervention is necessary.
Symptoms and treatment of umbilical hernia in adults
The first and most obvious sign of how to recognize the disease will be a protrusion in the navel area of various sizes: from a pea to a chicken egg.
If the process is not complicated by strangulation and the internal organs protrude freely through the entrance hernial orifice, in the lying position the formation will decrease in size or disappear altogether.
When straining, coughing, laughing, crying, defecating, the protrusion reappears in its original place.
Abdominal pain of varying intensity is another symptom that often worries patients. The intensity of pain can be moderate, insignificant, or increasing, unbearable.
If an irreducible hernia develops, intestinal obstruction, coprostasis, ischemic or necrotic changes in the wall of the organ strangulated in the umbilical ring are formed.
In pregnant women, the expansion of the umbilical ring is often a harbinger of pathology. It can be detected by an excessive increase in the diameter of the navel, its stretching and some bulging.
If the hernia has not yet formed, gynecologists and surgeons recommend that such women wear a bandage, which serves as a kind of support for the abdominal muscles and an additional fixation.
Significant symptoms indicating a hernial strangulation that require immediate medical attention include:
- Formation of a dense, painful, irreducible bulging formation in the navel area;
- Increasing intensity of abdominal pain up to unbearable;
- The appearance of nausea, vomiting;
- Increasing symptoms of intoxication: increased body temperature, weakness, sweating.
Prevention
The main measures to prevent the disease are:
- properly tying the baby’s umbilical cord and caring for the navel so that it heals properly;
- Infants should be placed on their stomach several times a day, this will help strengthen the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- Do not swaddle the baby too tightly, do not keep him in an upright position for a long time;
- Pregnant women are advised to wear a bandage and lead a healthy lifestyle;
- proper nutrition;
- timely treatment of diseases that can lead to the development of a hernia;
- compliance with safety rules, refusal to lift heavy objects and engage in strength sports - it is especially important to follow this recommendation for people who have undergone surgical interventions on the abdominal organs in the past;
- refusal of a sedentary lifestyle, physical education (without fanaticism and weight lifting);
- weight control, preventing the development of obesity;
- refusal to go on diets that lead to sudden weight loss;
- compliance with safety rules, avoidance of abdominal injuries;
- Immediately contact a doctor when the first possible symptoms of an umbilical hernia appear - this will help to start therapy on time and avoid the development of complications.
Good health to you!
How to treat an umbilical hernia
This disease is treated by a surgeon. Treatment tactics vary depending on the age of the patients.
Surgeons recommend conservative treatment for children under 3 years of age. In adult patients, the only method of getting rid of this defect is surgery.
The operation can be performed laparoscopically (using small punctures of the anterior abdominal wall and the introduction of special manipulation instruments), or in a standard way.
Patients undergo autoplasty (closure of the defect through which internal organs fall out using their own tissues) using the following method:
- Sapezhko;
- Mayo.
These are specific surgical techniques that have their own characteristics in the surgical technique, but have a common essence: the umbilical ring is first dissected and then sutured with application to the aponeurosis of the white line of the abdomen, followed by attachment to the fascia of the abdominal muscles.
Thus, a strong barrier is created from sewn own tissues, which the internal organs are no longer able to overcome.
Mesh for umbilical hernia
In some cases, when performing a surgical operation to eliminate an umbilical hernia, in order to close the hernial orifice, an endoprosthesis is inserted into the patient’s body - a polypropylene mesh, which acts as abdominal fascia and strengthens the anterior wall of the patient’s abdomen, preventing prolapse of the viscera.
These specialized meshes can be absorbable or non-absorbable. The doctor decides which one is necessary in each specific case.
Modern mesh endoprostheses are characterized by high strength, the absence of allergic reactions to the materials from which they are made and excellent patient tolerance.
Treatment of umbilical hernia in pregnant women
The most difficult treatment tactics are for patients in an “interesting situation.” If a hernia in a pregnant woman does not cause her significant discomfort and there are no signs of strangulation, surgical treatment should be delayed and, if possible, carried out after delivery.
To prevent the progression of the condition, the patient must wear a support bandage that prevents overstretching of the abdominal muscles and the growth of hernial protrusion, as well as use special compression garments.
Pregnant women with this pathology should be regularly observed and examined by a surgeon. If the slightest signs of complication of the pathology appear, the woman should be hospitalized in a hospital for possible surgical treatment.
Postoperative period
Immediately after surgery, patients are recommended to wear a support bandage for 1-1.5 months until the structure and function of the muscle tissue in the surgical area is restored.
Patients should monitor their diet; it should be enriched with fiber and fermented milk products that soften the stool. Fasting and eating dry food is unacceptable. You need to eat little and often, watch your stool and avoid constipation.
In the first few months, it is necessary to refrain from excessive physical activity and straining, since the body and abdominal muscles have not yet become stronger.
Treatment (treatment methods)
There are several types of treatment for umbilical hernias:
- Watchful waiting technique (under medical supervision). It is used only in the treatment of hernias in childhood. Before the age of 5 years, the hernia may disappear spontaneously. The decision whether to resort to a wait-and-see approach or more radical methods of treatment is made by the doctor based on the size of the hernia and the child’s concomitant diseases.
- Wearing a bandage . It does not solve the problem completely, but it minimizes the risks of developing pathology. It is prescribed if surgery cannot be performed urgently (for example, in late pregnancy).
- Surgery . Operations can be emergency or planned. Emergency surgical intervention is resorted to if the hernial sac is strangulated, the inflammatory process is pronounced, intestinal obstruction is diagnosed, and bleeding has developed. During emergency hernia repair, surgeons focus on abdominal operations. Rehabilitation after such operations is long. But when a hernia is strangulated, doctors fight for a person’s life, and therefore the use of abdominal surgery in this case is justified. During planned operations, surgeons resort to laparoscopic hernioplasty. Pain sensations are minimal. The recovery process is quite fast.
Surgical operations can be aimed at solving two problems - excision of hernias or suturing of the hernial orifice. Operations aimed at excision of hernias are called hernia excision. Suturing operations are better known as hernioplasty.
What kind of operation is prescribed for the patient - hernia repair (hernia repair) or hernioplasty - depends on the type of hernia. At the same time, the most effective and safe surgical techniques in the treatment of umbilical hernia are considered to be hernia repair without tension of tissues and plastic using allomaterial from mineral raw materials. With the help of operations, it is possible to reliably fix the hernial orifice, eliminate relapses, and reduce the time for rehabilitation.
In Minsk, surgical operations using modern hernia repair techniques, including the use of allomaterial, are actively practiced in the 5th Clinical Hospital.
Cost for Belarusians
Cost for foreigners
Disease prevention
To avoid the occurrence of this disease, you should follow simple rules:
- Strengthen your abdominal muscles: regular exercise, morning exercises, swimming pool exercises, active lifestyle;
- Avoid excess weight;
- Monitor bowel movements and avoid constipation;
- During the newborn period of the baby, parents should place the baby on the tummy more often, avoid situations in which the child screams for a long time and hysterically, and carry out massage and gymnastics that are appropriate for the age and development of the baby.
If symptoms of this disease appear, you should not try to eliminate it yourself, or trust the methods of traditional medicine, turn to herbalists or “grandmother whisperers”; the only correct decision would be to consult a surgeon in a timely manner.
The main causes of the disease
In modern medical practice, umbilical hernia in women is quite often diagnosed. Its symptoms may vary. But before considering them, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the main reasons for the formation of a hernial sac:
- genetic inheritance;
- weakening of connective tissue elements;
- being overweight, varying degrees of obesity;
- undeveloped abdominal muscles, lack of abdominal muscles;
- excessive physical activity;
- difficult pregnancy, childbirth with complications, multiple births;
- poor nutrition;
- chronic constipation;
- the presence of postoperative scars;
- serious disturbances in the digestive tract.
In fact, there are many more risk factors. For example, a hernia is more often diagnosed in people exposed to bad habits, in particular smoking and alcoholism. A hernia can also be triggered by frequent, severe coughing, which creates additional tension in the abdominal wall.
Basic diagnostic methods
First, the doctor must conduct a general examination. An umbilical hernia in women can be detected by palpation of the abdomen. In the future, additional examinations are prescribed in order to determine the stage of development of the disease, check which organs are affected, whether there is infringement and necrosis. In particular, ultrasound and fluoroscopic examinations, as well as gastroscopy, are very informative. In addition, during the diagnostic process, the cause of the disease must be discovered, since without its elimination, the risk of relapse is very high.
Treatment of hernia in women without surgery
If for some reason the patient is contraindicated for surgical intervention, then treatment of the hernia may involve other methods of therapy. It is immediately worth noting that such methods, where there is no surgery, are possible for small hernias, especially in the initial stage of its development.
Non-surgical treatment methods:
- daily use of a special bandage;
- massage of the umbilical area (rubbing, stroking);
- some types of therapeutic massage, you can learn more about this from a gastroenterologist;
- minimize physical activity;
- The weight that can be lifted should not exceed 3 kg.
Traditional methods in the fight against hernia
You need to mix a glass of boiled warm water with a spoonful of 6% vinegar. You should soak a piece of cloth in the solution and apply it to the sore spot. Afterwards you need to carry out another procedure with an infusion of oak bark. The raw materials are brewed in boiling water and allowed to brew for a couple of hours. You can prepare a more complex composition: acorns, leaves, oak bark are crushed and mixed with tart wine. The composition is poured into a dark glass container and kept in a cool place for a month. Lotions are made from this drug every day after being treated with a vinegar solution.
When is surgery needed?
Surgical intervention is necessary in later stages of the disease, as well as in cases where conservative treatment has not produced the necessary results. After careful preparation for the procedure, the umbilical hernia in women is “closed.” The operation is quite simple (in the absence of incarceration and necrosis), and is performed under general anesthesia. There are several main methods for carrying out the procedure:
- With tension herneoplasty, the area around the navel is strengthened using the patient's own connective tissue. This technique is effective for small hernias.
- At later stages of the disease, tension-free herneoplasty is performed, which involves strengthening the umbilical ring with the help of synthetic implants.
- In some cases, minimally invasive laparoscopy can be performed. During the operation, two small punctures are made in the abdominal wall, through which the hernia is closed with a special stack. This technique ensures low trauma and a short rehabilitation period. On the other hand, laparoscopy requires special equipment and appropriate surgical skills, so it is not performed in every hospital.
- A strangulated umbilical hernia in women is an emergency condition that requires urgent surgical intervention. During the procedure, the patient makes an incision on the abdominal wall, after which the pinching ring is cut.
After surgery, it is extremely important for a woman to follow the doctor’s recommendations, wear a special bandage, limit physical activity and follow a diet.
Is it possible to cure the disease without surgery?
There are cases when a hernia can be successfully treated without surgery. The treatment regimen is chosen by the doctor depending on the symptoms of the disease. If the form of the disease is mild, then treatment may involve unconventional methods.
The umbilical zone defect can be corrected in the following ways:
- compresses based on gauze and filling in the form of mumiyo, yellow and red clay, oak bark, honey, camphor oil, nettle leaves, etc.;
- using herbal infusions that will help correct the position of the navel, relieve pain and tension in the muscles. The decoctions are brewed in boiled water, allowed to brew, then filtered and drunk. They are made from cinquefoil, meadowsweet, weeping grass, twisted cornflower and other herbs;
- massages - this method stimulates muscle tissue, you can do it manually in a circular motion or use special jars;
- special exercises - they are aimed at strengthening the muscles in the abdominal area. Lying down, you need to arch your chest and lift your torso off the floor;
- medicinal patches - their effect in terms of treatment is quite weak, but they can be used even by pregnant women and children;
- by applying copper to the navel - there is a theory that if you apply a copper coin to the navel, the hernia will go away. Effectiveness has not been proven.
If the hernia gives even minor complications , you feel severe pain, and the place turns red, then the methods listed will not help. Contact your doctor immediately so that he can prescribe treatment on time, otherwise you will not survive without complications.
Add a comment