Neurocirculatory dystonia is an independent diagnosis, a pathological process of mixed origin (involving the central nervous system, hormonal background and endocrine system, also the heart) with a highly variable clinical picture.
The disease is accompanied by severe paroxysmal discomfort, sometimes for no apparent reason, but it only seems so.
Typical signs of NCD are weakness of the whole body, low adaptive capabilities of the body.
By carrying out specialized measures, changing lifestyle and prescribing medications within reason, it is possible to eliminate the pathological process completely. Although it is difficult to achieve a cure, since the patient still has a tendency to repeat the negative scenario and worsen it.
NDC has its own ICD-10 code - F45.3. Somatoform dysfunction or vegetative-vascular dystonia. There are several names.
Formalization is used to clarify the nature of the process and its complete description.
Why does this happen?
The autonomic nervous system permeates the entire human body and is responsible for the innervation of internal organs and systems of lymph and blood circulation, digestion, respiration, excretion, hormonal regulation, as well as tissues of the brain and spinal cord. In addition, the autonomic nervous system maintains the constancy of the internal environment and ensures the body’s adaptation to external conditions.
The operation of all systems is ensured by the equilibrium behavior of its two departments: sympathetic and parasympathetic. When the function of one department predominates over another, changes appear in the functioning of individual systems and organs. With this phenomenon, the adaptive abilities of the body naturally decrease.
Interestingly, damage to certain organs and disruption of the endocrine system can themselves lead to an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system. Neurocirculatory dystonia is the result of an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system , therefore the form of NCD depends on the predominance of a particular part of the ANS (sympathetic or parasympathetic).
Complications
NCD is not an independent disease, but it can cause the development of dangerous conditions. In severe dystonia and lack of adequate therapy, it can cause:
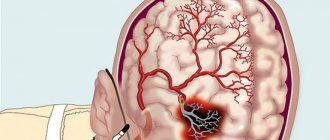
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- cholelithiasis and urolithiasis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension that does not respond to classical treatment regimens.
Malfunctions of the ANS also affect the immune system. Resistance to infections with this pathology is significantly reduced.
The impetus to the disease
The question of why someone gets sick and someone doesn’t is inherent in NCD just like other diseases. In the etiology of neurocirculatory dystonia, the main factors can be identified:
- The family nature of the disease, where heredity plays a significant role, however, it should be borne in mind that it is not the disease that is transmitted, but the characteristics of the organism, which is similar to the parent. In the case of neurocirculatory dystonia, the mother has a greater chance of transmitting a predisposition to the pathology;
- Social environment, which includes living conditions and relationships in the team, affecting the psycho-emotional state;
- Temperament and personality traits;
- History of traumatic brain injury and neuroinfections;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Infectious and allergic diseases;
- Excessive mental and physical stress;
- Change of climatic living conditions.
The combination of several or all factors together leads to the body's reaction to stimuli. This reaction causes the formation of pathological conditions that are manifested by disorders:
- Metabolic processes;
- Innervation of internal organs;
- Works of the gastrointestinal tract;
- In the blood coagulation system;
- Activities of the endocrine system.
The course of the mother's pregnancy, hypoxia and birth trauma also have a negative impact on the state of the autonomic system and can cause neurocirculatory dystonia in children.
Inconsistency in the operation of systems ultimately leads to a vascular response - their spasm. Thus, the manifestation of neurocirculatory dystonia begins.
Preventive actions
You can avoid the development of hypertensive type dystonia or exacerbation of the disease by following the following recommendations from specialists:
- Avoid overwork;
- Get proper rest, devoting at least 8 hours of sleep throughout the day;
- Avoid stressful situations;
- Give the body regular, moderate physical activity;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle by giving up bad habits;
- Promptly treat diseases of a cardiac, neurological, hormonal, or vascular nature.
NCD of the hypertensive type in adults is a fairly widespread disease that significantly reduces a person’s ability to work and quality of life. With proper, timely treatment, complete recovery and restoration of normal functioning of the body is possible. However, experts note that in order to achieve a stable, positive result, treatment of pathology must necessarily be accompanied by correction of the patient’s lifestyle!
Types of NDC
Neurocirculatory dystonia occurs differently in everyone. The essence of these phenomena lies in the predominance of a certain part of the autonomic nervous system and in the formation of the type of NCD. One person’s heart hurts or “pops out”, another feels dizzy as soon as the ambient temperature changes a degree or two. And, if God forbid, there is excitement, stress or a sudden change in weather - the reaction is generally uncontrollable. The symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia are vivid and varied, but the sensations are always unpleasant.
You can feel anything. Dizziness, lightheadedness, accompanied by nausea or an unpleasant “lump” in the stomach. The feeling is such that sometimes you want to lose consciousness in order to get relief later. Often, fainting is a salvation for some people, because after it comes a pleasant languor and relaxation...
Treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia is long-term, due to the undulating course of the process, and is aimed at preventing relapse. In addition, the complex of medications directly depends on the type of NCD and changes in the cardiovascular system.
Types of neurocirculatory dystonia are divided depending on blood pressure indicators:
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type - blood pressure tends to increase, regardless of age and circumstances;
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type - lethargy, weakness, decreased blood pressure and pulse;
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of a mixed type, it’s difficult to keep track of how and when everything will turn out. The worst thing is that the patient does not know in advance and waits with trembling for either an increase or decrease in pressure.
Hypertensive type of NCD
Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type is characterized by an imbalance of the autonomic nervous system, expressed by the predominance of the tone of the sympathetic system over the parasympathetic department (sympathicotonia) and is expressed by:
- Increased blood pressure;
- Headaches that depend on physical activity and intensify with it;
- Dizziness;
- Dependence on weather conditions (headaches, rise in blood pressure);
- Rapid heartbeat, sometimes intermittently;
- Mitral valve prolapse on ultrasound examination of the heart;
- Violation of thermoregulation - high body temperature in children with infectious diseases;
- Changes in the gastrointestinal tract in the form of weak peristalsis, and hence a tendency to constipation;
- Insufficiency of the function of the lacrimal glands (“dry tears”);
- Changes in mood (sadness and melancholy);
- Fatigue quickly.
Hypotonic type of NCD
When the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system predominates (vagotonia), neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type develops, the main symptoms of which are:
- Reduced blood pressure;
- Rare pulse (bradycardia), which can quickly increase in speed (tachycardia);
- Pain in the heart (cardialgia);
- Dizziness;
- Frequent fainting conditions, especially characteristic in the presence of neurocirculatory dystonia in children (mainly girls) during puberty;
- Headaches associated with weather conditions, physical and mental stress;
- Increased fatigue and low performance;
- Biliary dyskinesia, which is associated with uneven and chaotic contraction of the gallbladder;
- Digestive disorders (tendency to diarrhea and flatulence);
- Violation of thermoregulation: decreased body temperature and prolonged low-grade fever due to infections in children;
- Complaints of “shortness of breath” and “sighs”;
- Tendency to allergic reactions;
- Pale skin (marbling), cyanosis of the extremities;
- Cold sweat.
Mixed type of NDC - when there is no agreement between departments
Uncoordinated work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic departments leads to dysfunction of systems and organs. If the pressure “jumps”, if the complexion suddenly turns red or pale in a matter of minutes, if the body reacts unpredictably even to minor events, then a mixed type of neurocirculatory dysfunction can be suspected.
Signs of mixed-type neurocirculatory dystonia include symptoms characteristic of both hypotonic and hypertonic types. Which part of the autonomic nervous system will prevail at what moment, such signs will be inherent in the patient’s condition.
Video: how does NCD manifest itself?
Causes
There are a lot of development factors. If we consider the most common reasons:
- Past infectious diseases.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. Use of drugs, caffeine.
- Changes in weather and time zones.
- Improper and unbalanced nutrition.
- Insufficient or excessive physical activity.
- Burdened heredity, genetic factor.
- Peak hormonal states. Puberty, pregnancy, menstrual cycle, menopause (occurs in men and women, but manifests itself differently).
- Overwork.
- Psycho-emotional tension and constant stress.
- Pathologies of the central nervous system. Including previous injuries, tumors, vascular problems.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, especially at the level of the cervical spine (a special case is vertebrobasilar insufficiency).
- Endocrine abnormalities. Diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, adrenal tumors and others.
Identifying the specific cause of NCD is vital. Without this, there is no quality treatment.
At the same time, it is not always possible to get to the etiology, at least not quickly. Episodes of neurocirculatory dystonia also occur in healthy people, as a response to overload.
Crises of neurocirculatory dystonia
Neurocirculatory dystonia, which arose in childhood, can become “enriched” with symptoms over time and in young people give more vivid vegetative manifestations in the form of crises. Attacks during neurocirculatory dystonia also depend on its type, although they often do not have a clear picture of the identity, but are of a mixed nature. High activity of the parasympathetic division of the ANS can cause a vagoinsular crisis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Sweating and nausea;
- Sudden weakness and darkening of the eyes;
- Reduced blood pressure and body temperature;
- Slowing heart rate.
After a vagoinsular crisis, the patient still feels tired and weak for several days, and is periodically dizzy.
When the sympathetic department takes “primacy,” another type of neurocirculatory dysfunction develops. Neurocirculatory dystonia with sympathoadrenal crises makes itself felt by the sudden appearance of causeless fear, to which is quickly added:
- Intense headache;
- Heartache;
- Increased blood pressure and body temperature;
- The appearance of chills;
- Skin redness or pallor.
Video: how to deal with exacerbations of NCD?
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist. It is also necessary to involve doctors dealing with heart problems and hormonal status (cardiologist and endocrinologist).
Approximate list of events:
- Oral survey. We need to collect all the complaints and create a single picture, a list. This will allow you to formulate hypotheses and then rule them out in specific ways.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, family history, previous infections. Individual characteristics are also taken into account: gender, age, body weight, height and others.
- Routine neurological examination. Testing basic reflexes. Electroencephalography. To assess brain activity and cerebral structures.
- ECG. To exclude heart pathologies or detect the degree of functional disorders.
- ECHO-KG. It is intended to consider the structure of the myocardium and large vessels. As part of the diagnosis of possible defects.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate per minute. Also 24-hour Holter monitoring. To exclude persistent hypertension or, conversely, a drop in numbers.
- Functional stress ECG tests are mandatory. Hyperventilation (fast breathing), orthostatic test (change of body position), assessment of the effect of beta blockers. Bicycle ergometry is also indicated.
These methods make it possible to diagnose NCD and identify its etiology (origin). The methods are informative enough to draw conclusions.
Autonomic dysfunction and pregnancy
Although pregnancy is a physiological condition, it is then that neurocirculatory dystonia can manifest itself, occurring latently (hidden), because during pregnancy the body is rebuilt and prepares for the birth of a new life. Hormonal levels, the regulator of all pregnancy processes, undergo significant changes. The internal organs are “packed” differently, making room for the ever-expanding uterus. And all this is under the control of the autonomic nervous system, which could not always cope without such a load, but here...
Women suffering from NCD may find out they are pregnant even before the test, because the first sign may be fainting. Neurocirculatory dysfunction during pregnancy has a more pronounced clinical picture, so pregnancy is more difficult.
Reaction to everything that is “wrong”, tears for every reason, heart pain and hysterics, decreased blood pressure, and it’s better not to get into transport... Pregnant women are often visited by a feeling of lack of air and stuffiness, and those with neurocirculatory dysfunction even know the “smell of fresh blows."
But everything may not be so bad and you shouldn’t be upset. There have been many cases of disappearance of manifestations of NCD after childbirth. What is the reason for this - either “restoring order” in a woman’s body, or a responsible occupation associated with caring for a baby - is unknown. But patients themselves often note that if they are distracted by important matters, the vegetative-vascular complex recedes.
Symptoms
The symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia are very diverse and form the basis for the classification of pathology. However, it is possible to identify a number of common features that are characteristic of most types of NDC:
- frequent mood changes;
- constant fatigue and drowsiness;
- lack of strength, weakness;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- increased sweating;
- weather sensitivity;
- anxiety;
- feeling of lack of air, etc.
An exacerbation of the disease can be triggered by any stressful situation: an excess of positive or negative emotions, lack of sleep, or even a simple change in time zones.
Disease or syndrome?
When discussing vegetative-vascular disorders and what to call them, scientists still haven’t decided. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is considered a more correct name, since it expresses the pathogenesis of the disease. The most recent trend in defining this condition was the syndrome of vegetative dystonia, which did not become an independent unit in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
The ICD 10 code for neurocirculatory dystonia is F45.3 , where the letter F indicates a psychogenic origin, which, in general, is the case. According to the same classification, NCD is recognized not as a disease, but as a symptom complex arising as a result of inadequate behavior of the autonomic nervous system (uncoordinated and unbalanced interaction of two parts of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic). It is unlikely that people who are well acquainted with this complex of symptoms will “get better” from this, but today this is the case.
Vegetative-vascular dysfunction raises many questions when the time comes to repay one’s debt to the Motherland. How are neurocirculatory dystonia and military service compatible? As varied are the manifestations, so should be the approach.
Classification
Now there are two classifications of NCD, etiological and according to the severity of symptoms.
The etiological classification was developed by S. A. Abbakumova and V. I. Makolkin, they identified the following main factors:
- Essential – manifests itself due to hereditary predisposition.
- Psychogenic, occurs against a background of constant stress.
- Infectious-toxic.
- Due to constant physical stress.
- Features of a person's profession.
There are also three forms of the disease according to severity: mild, moderate and severe.
Preparing for military duty: NDC and the army
Of course, some are so eager to join the ranks of defenders of the Fatherland that they forget about the disease. Or are they hiding? Others, on the contrary, having had an NDC entry on their card since childhood, are trying to rid themselves of military duties. In this regard, the commission’s approach should be objective and versatile. On the one hand, seeing a conscript for the first time, who does not show any complaints and is “eager to fight”, who is only identified by low or high (below 100/60 or above 160/100) blood pressure and obvious vegetative disorders on the “face”, in breathing and heart rhythms, you can satisfy his desire. However, a qualified commission must find out this for the first time, periodically or permanently. The situation is the same with those who present a lot of complaints, and only meager entries in the child’s card indicate illness. Of course, there is also an average: the clinic also has complaints indicating the presence of autonomic disorders. In all cases, the commission’s task is to find out:
- Are the complaints persistent?
- Is blood pressure persistently high or low?
- Do you have cardialgia and heart rhythm disturbances?
- To what extent do NCD symptoms affect a conscript’s performance?
To study the health status of a young person, related specialists (neurologist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist) are required to be involved.
In addition, when deciding on suitability for military service in the case of neurocirculatory dystonia, differential diagnosis is carried out with other diseases to clarify the diagnosis and exclude diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, heart and lungs, which may be similar to NCD in symptoms.
Who does “Farewell of the Slav” sound like?
For an objective approach to resolving the issue, the conscript is sent to a hospital for examination, after which he may be declared temporarily unfit under Article 48. In this case, the young man is subject to treatment for neurocirculatory dystonia, but if it turns out to be ineffective, and the symptoms indicate persistent disorders of autonomic innervation, then the conscript is not subject to military service and receives a military ID with a mark of unfitness under Art. 47 "a".
The commission acts similarly with those young men who clearly have persistent vegetative-vascular disorders with an increase or decrease in pressure, there are clear signs of heart rhythm disturbances, and pain in the heart is constant.
Well, the one who had the only record of a disease of the autonomic nervous system, but did not confirm it, must go with honor to serve the Motherland and Fatherland. Ancient, but still unchanged and unique, the march of Vasily Ivanovich Agapkin with its solemnity will make his own mother and his beloved girl cry... Nothing terrible - a little time will pass and yesterday’s healthy, mature and self-confident conscript will return home, completely forgetting about the illness.
And yet: what to do with it?
We can talk about neurocirculatory dystonia for a long time and a lot, fortunately there are numerous names for this pathology, and this allows for diversity. But those who have such “happiness” are looking for ways to escape from this symptom complex, which pretty much poisons life and manifests itself in the most unforeseen situations. In general, a significant part of humanity is occupied with the question of how to treat neurocirculatory dystonia, which has a dozen other names. After all, changing the name will not affect the patient’s well-being in any way.
Oddly enough, vegetative-vascular dysfunction does not like physical inactivity. And despite the fact that the manifestations of the disease are especially noticeable after physical activity, physical exercise not only does not harm the patient, but is also indicated. True, we should be talking about targeted, therapeutic physical education, dosed and deliberate.
Mandatory adherence to the work and rest regime is also an integral part of the treatment process. Of course, working night shifts, lack of sleep, and spending a long time near the monitor are unlikely to help you feel light in your head and body. But fresh air, quiet evening walks, a warm bath with soothing herbs, on the contrary, will ensure good healthy sleep and improve your mood.
Patients should pay special attention to their psycho-emotional state. Avoid stressful situations, engage in auto-training, take soothing tea and do everything possible to create a calm, friendly environment at home and in the team for yourself and those around you.
No matter how trivial it may sound, diet also plays a significant role here. Neurocirculatory dystonia does not like spices, spicy foods, or alcohol. Anything that excites the nervous system can aggravate the process, so it is better to avoid excesses and not overexert yourself. But foods rich in potassium (eggplants, potatoes, bananas, prunes and apricots) will “like” the “capricious” nervous system.
Prevention
Prevention of NCD is important not only for healthy people who are at risk, but also for those who are already closely confronted with this pathology. Changing your lifestyle, adjusting your diet and physical activity help strengthen the body and significantly reduce the risk of unpleasant symptoms. Doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- eliminate overtime, ensure daily proper rest;
- create the most peaceful atmosphere at home and at work;
- go to bed on time (duration of sleep at night is 8 hours or more);
- do not ignore walks in the fresh air;
- choose a suitable sport that will allow you to practice for your pleasure (swimming, walking, cycling, yoga, Pilates, etc.);
- adjust nutrition: the daily diet must meet the standards for caloric content, the ratio of dietary fat, the content of vitamins and microelements;
- minimize the consumption of food stimulants: tea, coffee, fatty foods, smoked foods, alcoholic drinks;
- drink at least 2 liters of clean water daily (other drinks do not count).
Compliance with these rules is useful for the prevention of not only neurocirculatory dystonia, but also many other diseases. The body always responds gratefully to care for it and begins to cope much better with inevitable stress and physical activity.
Treatment prescribed by a doctor
It is highly advisable to carry out drug treatment for neurocirculatory disorders with general health measures and physiotherapy. Therapeutic massage, electrophoresis with sedatives on the collar area, electrosleep and a circular shower will help strengthen the nervous system and give the positive emotions that patients with neurocirculatory dystonia so need.
What a wonderful procedure - acupuncture. Using it, you can stop taking medications for a long time and feel great only thanks to the annual repetition of acupuncture. Thin gold or platinum needles placed in the neuromuscular bundles will lead to long-term and stable remission, and the disease will recede...
Vitamin therapy and an antioxidant complex (Doctor Theiss, Gerovital, etc.) will be an excellent addition to general strengthening measures.
Medicines for the treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia are taken on the recommendation of a doctor and prescribed by him.
No advice from friends or the Internet is inappropriate here, since drug treatment is prescribed taking into account blood pressure, the presence of cardialgia and the state of the heart rhythm. It is clear that what will help a patient with high blood pressure can have a detrimental effect on the condition of a person with low blood pressure, so it is unlikely that egilok (a beta-blocker) will be indicated for the hypotensive type.
Drugs that regulate heart rate are serious and require special care, so “amateur” in such cases is useless. Often, patients with autonomic disorders are prescribed drugs from the group of tranquilizers - adaptol, afobazole, grandaxin. The herbal preparation Gelarium, which has antidepressant properties, has a remarkable effect. To relieve spasms, bellataminal is often prescribed, which also gives a sedative effect.
Hawthorn, valerian, motherwort – alcoholic infusions of these plants are very familiar to patients with neurocirculatory dystonia; they are constantly stored in the home medicine cabinet and serve as an “ambulance”.
Video: expert opinion about NDC
How can traditional medicine help?
The variety of recipes for treating neurocirculatory dystonia with folk remedies is even more striking than the variety of clinical manifestations. The contrasting souls, breathing exercises of Tibetan monks and the Austrian healer Rudolf Breuss are undoubtedly wonderful, but for some reason people prefer the Russian “creation”. A popular drink made from the church “Cahors” and a mixture of garlic, lemon, beet, carrot and radish juices, flavored with natural honey, is passed down “from mouth to mouth and from generation to generation.”
However, to treat NCD with folk remedies, one should not forget about pressure, so traditional healers also recommend different treatments. For example, for high blood pressure, people use infusions of mint and white birch leaves, calendula flowers and dill seeds. Alcohol infusions of magnolia and mistletoe are good for reducing blood pressure.
Strong tea and coffee are not recommended for the hypertensive type of NCD, but in the morning you can drink amazing tea prepared at home:
- Dry blueberries, chokeberries, currants and barberries are taken in equal parts, ground, mixed and consumed, poured with boiling water.
With normal blood pressure levels and a downward trend, prepare infusions of elecampane and immortelle, drink freshly squeezed juices of carrots and rose hips. They say it helps a lot.
Of course, valerian root (you can take it internally, you can take baths), hawthorn, hot milk with honey at night - everyone knows. Such folk remedies are, perhaps, in every home, even where neurocirculatory disorders are not found.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Doctors at the Energy of Health clinic do not downplay the significance of the symptoms of NCD. We guarantee each patient a thorough examination, including all the necessary samples and tests, as well as selection of the most gentle, but at the same time effective treatment. At your service:
- drawing up a medication correction regimen in accordance with the characteristics of the course of the disease (not only the complex of symptoms, form and stage of the disease are taken into account, but also the emotional background, chronic diseases, hormonal status, characteristics of the patient’s work, etc.);
- restorative procedures: physiotherapy, massage;
- selection of physical exercises to perform in the gym with an instructor and at home;
- acupuncture;
- help from a psychotherapist and psychiatrist;
- selection of a resort for treatment in a sanatorium, collection of necessary documents;
- detailed recommendations for correcting lifestyle, nutrition, and physical activity.
We will help keep the disease under control and will always come to the rescue in case of exacerbation.
How is the diagnosis made?
Autonomic dystonia syndrome is not based solely on patient complaints. Before the doctor makes a diagnosis, the patient must undergo tests and undergo instrumental examinations, therefore the main stages “on the path” to NDC will be:
- General blood and urine tests, which do not deviate from the norm for this disease;
- Blood pressure profile for 10-14 days to establish the type of NCD;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and heart to exclude independent diseases of these organs;
- Rheoencephalography;
- ECG, FCG, echoCG;
- Consultations with an endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist, ophthalmologist.
In addition, to determine the cause, there is often a need for a detailed study of the function of the kidneys, adrenal glands, hypothalamus and thyroid gland.
Forecast
The disease does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, so a favorable course of the disease is predicted.
If a person is constantly exposed to factors that constantly provoke the appearance of symptoms, they go away on their own.
In old age, NCD can cause a decrease in a person’s performance, and the speed of response to treatment of emerging symptoms also decreases.
The name of the disease speaks for itself: neuro (nervous) and circulatory (blood circulation). Therefore, you should not ignore the symptoms of this disorder, because the situation may gradually worsen. And the person gets worse and worse.
NCD of the hypotonic type, hypertensive and mixed are diseases associated with disruption of the ANS. Therefore, all therapeutic and preventive measures are carried out according to the same principle, but the individual characteristics of the patients are taken into account.