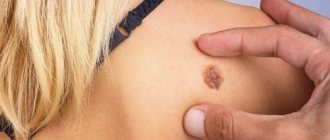
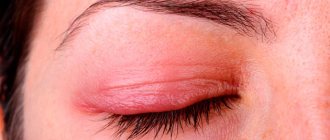
What is keratosis
The pathology consists in the compaction of epithelial cells, which provokes the development of a neoplasm with defined boundaries.
A keratoma may look like:
- plaque;
- spot;
- crust;
- node;
- growth
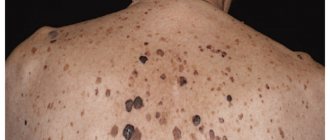
Keratosis of the skin, photos in adults are presented below, belongs to the category of age-related pathologies. But some types can be diagnosed in children. Keratosis usually affects people over 40 years of age. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of 55 and 65 years.
The disease develops in both men and women. In some cases it disappears without therapy. The neoplasm is classified as benign, but can develop into a malignant form. Flat cells are similar in morphology to malignant cells, so if pathology appears, it is advisable to immediately seek help from a specialist.
Establishing diagnosis
Actinic keratoses may look similar to other skin conditions such as psoriasis or skin cancer. A doctor usually discovers this condition during a physical examination, but the most accurate way to make a diagnosis is to perform a skin biopsy.
Stages and degrees of the disease
Keratosis of the skin develops gradually. Each type has its own clinical picture. In the cyanide form, as the tumor grows, the area of the skin affected by the pathology becomes dark and loose. At the second stage, cysts form in the tissues.
The skin becomes lumpy and begins to peel. When the keratoma is damaged, it begins to bleed and becomes painful. Sometimes an inflammatory process occurs.
In the initial stages of angiokeratoma, blue-black vascular nodules, the diameter of which is 2-5 mm, form on the patient’s skin. They are based on dermal cells. At the second stage, the nodules become rough and begin to peel off. At the last stage, the nodules begin to bleed and become inflamed. This form of disease also occurs in newborns.
The pathological process is localized in the area:
- scrotum;
- belly;
- hips;
- buttocks;
- armpits;
- oral cavity;
- vulva;
- stop;
- lips;
- cheeks;
- fingers.
Keratosis of the skin.
Photos of adults show what neoplasms may look like. The follicular form most often develops in women. It is characterized by the formation of flesh-colored keratinized plugs on the hair follicles. New growths are uneven. Their structure resembles flat, silvery scales. The size of the neoplasms is no more than 1.5 cm.
Most often localized in the area:
- faces;
- buttocks;
- neck;
- armpits.
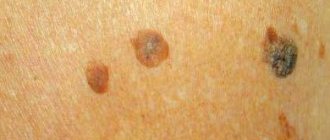
Keratosis of the skin (the photo in adults shows only external symptoms) begins in the cold season. In warm weather, the symptoms are erased. At a late stage of the disease, the nodules increase in size. The surface of the skin becomes rough. At the last stage, they may begin to bleed and hurt. The seborrheic appearance is characterized by slow development and chronic course.
A spot on the skin of a yellowish tint reaches a diameter of 3 cm. It has a dense morphology with scabs. At the second stage, the spot begins to increase in size and many layers form in it. The neoplasm becomes crusty. The thickness of the stain reaches 1.5 cm. On the last steel, the seal begins to turn black, crack and bleed.
The pathology is localized in the area:
- backs;
- breasts;
- faces;
- neck;
- scalp.
This type of pathology does not develop into an oncological form. In the actinic form, which often develops into a cancerous tumor, nerve rough spots appear in the first stage. At the last stage, they transform into keratinized scales of burgundy color.
Keratomas are located singly. They grow very slowly, reaching 2 centimeters. This form can disappear on its own, and appear under mechanical stress or injury.
In the initial stages of solar keratosis, a large number of small spots appear that begin to peel off. They rise above the epidermis. At the last stage of the disease, the spots transform into plaques covered with hard scales.
This form of pathology is localized in the area:
- faces;
- backs;
- soles;
- legs;
- hands
This form of the disease is considered precancerous. It is triggered by radiation. The initial stage of cutaneous horn is characterized by the appearance of gray or brown spots on the skin. At the second stage of keratosis of the skin, the spots begin to become covered with keratinized scales.
Externally, in the photo of adults, they resemble a tubercle that rises greatly above the skin. Some neoplasms take the form of a flat, silvery plaque. At the last stage, keratomas begin to peel off and bleed.
The pathology is localized in the area:
- lips;
- nose;
- century;
- forehead;
- mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- ears;
- scalp.
This form can turn into an oncological form.
The essence of the pathological process
Solar or actinic keratosis is a skin condition. It develops in areas of the epidermis that are exposed to excessive sun exposure. This is, first of all, the face, ears, neck and lips. Most often, the pathological process is detected in people who spend a lot of time under the scorching sun.
It has a benign course, but can transform into squamous cell carcinoma. However, due to metabolic disorders, solar keratosis does not develop. The occurrence of neoplasms (keratomas) is not possible to predict. The affected areas of the skin may remain unchanged for a long time. In medical practice, there are also cases of self-healing, when keratomas disappear without therapeutic influence.
Symptoms of keratosis
Symptoms of the cyanide form include:
- the presence of multiple formations of brown or black color;
- the formation of round-shaped plaques with pronounced boundaries;
- the appearance of loose scales;
- the presence of small elevations above the level of the skin;
- formation of round or oval spots;
- formation of tumors on the back, chest and forearms;
- the appearance of plaques with a diameter of 1 mm to 2 cm.
Symptoms of angiokeratoma include:
- the presence of red or dark burgundy nodules with a diameter of 1-5 mm, rarely 1 cm;
- blurred boundaries of nodules;
- irregular shape of nodules;
- arrangement of spots in groups;
- elevation of tumors above the skin level;
- expansion of capillaries.
Follicular keratoma is characterized by:
- dry dermis;
- colored nodules gray or pink;
- clear boundaries of the nodule, the diameter of which is 1.5 cm;
- tuberosity of neoplasms.
The distinctive signs of seborrheic keratoma are:
- oval or round shape of neoplasms;
- slight elevation of tumors above the skin level;
- spot diameter up to 6 cm;
- yellow or dark brown spots;
- group arrangement of spots;
- itching;
- peeling.
The actinic form, whose texture resembles sandpaper, is distinguished by:
- absence of itching and peeling;
- rashes in the form of seborrheic warts;
- plaque diameter up to 4 cm;
- bleeding and painful growths.
The main signs of solar keratosis include:
- the presence of formations in the form of groups;
- plaque formation;
- slight elevation of plaques above the skin;
- the appearance of rough scales that are easily separated.
The cutaneous horn is characterized by:
- the appearance of gray or brown spots;
- compaction of neoplasms;
- keratinization of spots;
- peeling of tissue;
- bleeding.
Types of pathology
There are several types of solar keratosis. The differences between its forms are determined by the localization of the pathology. Let's consider only the most common of them.
- Hypertrophic keratosis. Atypical elements synthesize dark and light keratin.
- Pigmentary. The focus of the pathology is in the basal layer of the epidermis. The accumulation of melanin in large quantities contributes to the dark coloration of the neoplasm.
- Lichenoid. Lymphocytic infiltrates—pseudolymphomas—appear at the border of the basal layer of the skin. They are the ones who destroy the upper layers of the epidermis.
- Proliferative. This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of foci of hyperkeratosis, which implies a thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin.
- Atrophic. Localized exclusively in the upper layers of the dermis. “Gaps” and cracks form in the affected areas.
- Acantholytic. The pathology is accompanied by the growth of tumor-like formations that are located above existing cracks.
- Bowenoid. This is the initial stage of skin cancer, which is characterized by the same number of dying and emerging atypical elements.
The form of the disease is determined during a diagnostic examination. Studying the nature and localization of the pathology focus is necessary to prescribe effective treatment.
Causes of keratosis
The causes of senile keratoma include:
- genetic predisposition;
- malfunction of epithelial cells;
- the presence of chronic pathologies of internal organs;
- accumulation of toxins in the body;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- degeneration of the skin.
The causes of angiokeratoma are still unclear. Some forms have a genetic basis. Most patients are diagnosed with metabolic disorders.
Provocateurs include:
- mechanical damage;
- frostbite;
- burn;
- presence of calluses;
- injuries;
- insect bites.
The follicular form can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- lack of vitamins A, C, D and group B;
- abuse of fatty, hot, spicy and salty foods;
- frequent consumption of coffee;
- use of hormonal-based drugs;
- stress and emotional stress;
- presence of syphilis;
- exposure to cold;
- HIV infection;
- tuberculosis of the skin;
- fungal infection of the feet;
- damage to the body by systemic lupus erythematosus;
- presence of scleroderma;
- allergy;
- hormone imbalance;
- prolonged exposure to x-rays;
- exposure to chemicals and poisons;
- wearing synthetic clothing;
- dysfunction of the digestive organs.
Experts have found that the pathology may have a genetic basis. The disease among adolescents and children is diagnosed in 50-80% of cases. Adult patients account for 40%.
The causes of seborrheic form include:
- heredity;
- malfunction of the immune system;
- skin aging;
- endocrine disorders;
- hormone imbalance.
Actinic form provocateurs include:
- living in a hot climate;
- presence of blond hair and freckles;
- presence of blue or green eyes;
- frequent sun burns;
- age above 45 years.
Keratosis of the skin (photos of adults indicate that this is a serious skin pathology) of the actinic variety, unlike the solar form, develops very slowly due to constant exposure to sunlight.
Causes of solar keratosis include:
- living in southern regions with a hot climate;
- exposure to stress;
- use of hormonal drugs;
- presence of blue eyes and blond hair;
- frequent sunburns.
The development of a cutaneous horn provokes:
- exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- endocrine system disorders;
- viral infection;
- presence of oncological tumors;
- skin trauma;
- genetic basis;
- obesity;
- lack of vitamins;
- malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disorders at the cellular level;
- alcohol and drug use;
- stress;
- burns;
- exposure to sunlight;
- poor hygiene.
Leser-Trélat syndrome
We can talk about this syndrome when a person suddenly develops many keratomas, especially on the torso. In 35% of cases, this condition is associated with acanthosis nigricans. About 50% of patients report severe itching in the area of the keratoma. [4]
Leser-Trélat syndrome may indicate the presence of malignant tumors of internal organs, some reports of late stages. Most often we are talking about adenocarcinomas of the stomach, colon, breast cancer, lymphomas or leukemia. The average life expectancy of patients with this syndrome is 11 months. [4]
This means that if multiple keratomas appeared gradually and have been present on the body for many years, most likely we are not talking about this syndrome.
Some researchers question the existence of the syndrome. This is due to the fact that these malignant tumors are more common in older patients, as well as seborrheic keratosis itself.
Diagnosis of keratosis
Keratosis of the skin (photos in adults indicate the stage of development of the disease) is diagnosed as a result of a medical visual examination. If the lesion has become large, bleeds and thickens, then there is a possibility that the neoplasm has degenerated into a malignant form.
To exclude a dangerous pathology, a biopsy is performed. The procedure involves taking skin samples. It is performed by a therapist using local anesthesia. The sample taken is sent for microscopic analysis.
Also, to diagnose keratosis, dermatologists carry out:
- dermatoscopy (the procedure is carried out using a dermascope apparatus that can detect morphological changes in the skin;
- Ultrasound of neoplasms.
The most common methods are biopsy and dermatoscopy. The cost of dermatoscopy in Moscow ranges from 500 to 3000 rubles. The cost of a biopsy is 1,480 rubles. The cost of dermatoscopy in Samara ranges from 250 to 2500 rubles. The price for a biopsy is 1,500 rubles.
Forecast
Actinic keratosis is a marker of severe changes and damage to the skin resulting from exposure to ultraviolet light. These changes put a person with actinic keratosis at high risk of developing skin cancer.
People who develop actinic keratosis sooner or later have a better chance of eliminating the risk of developing cancer. However, without treatment, actinic keratosis can develop into skin cancer.
After treatment for actinic keratosis, a person will likely need to schedule yearly visits with a dermatologist to check for recurrence and be screened for other signs of skin cancer.
Prevention of keratosis
In order to avoid complications, you should adhere to the following preventive rules:
- use creams with a moisturizing effect for the skin;
- include more foods containing vitamins in your diet;
- limit exposure to sunlight;
- wear special clothing and gloves when working with chemicals;
- do not sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium;
- strengthen the immune system;
- avoid skin injuries;
- maintain hygiene;
- When diagnosing dermatosis, undergo regular examination by a dermatologist.
Bibliography
- I. A. Lamotkin. Clinical dermato-oncology: atlas/M.: BINOM. Knowledge Laboratory, 2011.
- Kennedy C, Bajdik CD, Willemze R, De Gruijl FR, Bouwes Bavinck JN. The influence of painful sunburns and lifetime sun exposure on the risk of actinic keratoses, seborrheic warts, melanocytic nevi, atypical nevi, and skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol, 2003.
- Yeatman JM, Kilkenny M, Marks R. The prevalence of seborrhoeic keratoses in an Australian population: does exposure to sunlight play a part in their frequency? Br J Dermatol, 1997
- Hafner C, Vogt T. Seborrheic keratosis J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2008 Aug; 6(8):664-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2008.06788.x.
- Vun Y., De'Ambrosis B., Spelman L., Muir JB, Yong-Gee S., Wagner G., Lun K. Seborrhoeic keratosis and malignancy: collision tumor or malignant transformation? Australas J Dermatol. May 2006; 47 (2): 106–8.
- Rajabi P., Adibi N., Nematollahi P., Heidarpour M., Eftekhari M., Siadat A.H. Bowenoid transformation in seborrheic keratosis: A retrospective analysis of 429 patients. J Res Med Sci. Mar 2012; 17 (3): 217–21.
- Thomas I., Kihiczak NI, Rothenberg J., Ahmed S., Schwartz RA Melanoma within the seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Surg. 2004 Apr; 30 (4 Pt 1): 559–61.
- Birnie AJ, Varma S. A dermatoscopically diagnosed collision tumor: malignant melanoma arising within a seborrhoeic keratosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. July 2008; 33(4):512-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1365–2230.2008.02715.x. Epub 2008, May 6.
- Zabel RJ, Vinson RP, McCollough ML. Malignant melanoma arising in a seborrheic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000, May; 42(5 Pt 1): 831–3.
- Terada T., Kamo M, Baba Y., Sugiura M. Microinvasive squamous cell carcinoma arising within seborrheic keratosis. Cutis. 2012, Oct; 90 (4): 176–8.
- Mitsuhashi Y, Kawaguchi M, Hozumi Y, Kondo S. Topical vitamin D3 is effective in treating senile warts possibly by inducing apoptosis. J Dermatol 2005; 32:420–423.
- Herron MD, Bowen AR, Krueger GG. Seborrheic keratoses: a study comparing thestandard cryosurgery with topical calcipotriene, topical tazarotene, and topical im-iquimod. Int J Dermatol 2004; 43: 300–302.
- Herron MD, Bowen AR, Krueger GG. Seborrheic keratoses: a study comparing the standard cryosurgery with topical calcipotriene, topical tazarotene, and topical imiquimod. Int J Dermatol. 2004 Apr; 43(4): 300-2.
- Lebedeva UV, Davidov AB Clinical assessment of prevalence of seborrheic keratosis face skin and a neck among oncological patients. Dentistry 2009.
Other articles:
- Removing warts at home: a review of drugs
- Skin cancer: symptoms, stages, photos
- Removal of moles on various areas of the skin
- Vitamin D, tanning and melanoma
Useful article? Repost on your social network!
Treatment methods for keratosis
Keratosis is eliminated through drug treatment. Folk remedies are used as additional therapy and only after consultation with a specialist. Physiotherapeutic procedures are used to relieve pathology. In case of complicated course of the disease, they resort to the surgical method.
Medications
| Antibiotics | Zinnat, Doxycycline, Azithromycin |
| Ointments | Efudex, Fluorouracil, Imicvod, Fluoroplex, Solcoderm |
| Vitamin complexes | Milgamma, Bnevron BF, Vitamin A Bartel Drugs, Retinol |
The drug Zinnat is used for the inflammatory process. Prescribed 500 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. The cost of the drug 500 mg is 420 rubles. There are 10 tablets in a package.
Imicvod ointment is used 3 times a week. Treatment should continue until symptoms disappear completely. The maximum course of treatment is 4 months. The price of the drug 5% is 5087 rubles. The tube contains 250 mg of the substance.
Vitamin A capsules Bartel Drugs take 1 tablet per day 15 minutes after meals. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The cost of the drug is 150 rubles. There are 50 capsules in a package.
Traditional methods
To relieve the symptoms of keratosis, you can use folk remedies:
- Agave leaves, after three days of freezing, are applied to the affected area overnight. After removing the compress, the keratome is treated with salicylic alcohol. The course of treatment lasts 3 weeks.
- Grated raw potatoes are applied to the affected area. The top of the potatoes is covered with a clean cloth and cellophane. After 40 minutes, the bandage is removed and the potatoes are washed off with water.
- Take 2 tbsp. l. dry leaves of celandine. They are filled with 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture is infused for several hours. Lotions are made on its basis. You can wipe the skin with the infusion.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. onion peels. Pour 1 tbsp of vinegar into it. Leave the mixture in a dark place for a week, then strain. It is recommended to make lotions. They are left on the affected area for 30 minutes. It is important to avoid contact with healthy areas to avoid burns.
Other methods
Since conservative treatment is not effective in all cases, they resort to drastic measures - removal of growths. They are especially used when there is a possibility that the tumor will degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
The following types of treatment are used:
- Cryodestruction . It involves freezing the growths using liquid nitrogen. The method is used when the skin lesion is extensive. When frozen, plaques undergo necrosis. A possible complication of the operation may be increased skin pigmentation.
- Removal via radio waves . This manipulation involves excision of the tumor with a radio knife under the influence of radio waves.
- Electrocoagulation. Represents cauterization using high-frequency electric current. Performance involves anesthesia. There is a risk of scarring and age spots.
- Laser destruction . A targeted effect on the keratoma with a carbon dioxide laser is used. This is the most effective method of treating keratosis, which is characterized by painlessness, speed and absence of side effects.
- Photodynamic therapy involves the application of methyl aminolevulinate followed by exposure to a light wave of a given length. This process causes tissue necrosis. In this case, healthy tissues are not damaged. After the procedure, you should not be in the sun for 48 hours.
- Curettage is used to treat solar keratosis . This is an operative method in which individual areas of the lesion are scraped out using a curette. Curettage is not used to treat the actinic form, as it can cause scarring.
- Dermabrasion . Removing tumors using an abrasive brush.
- Plasmolifting involves the use of plasma injection, which stimulates local immunity and promotes skin regeneration.
- Biorevitalization involves injections of hyaluronic acid, which improve the morphology of the skin, promote rejuvenation, and increase the level of regeneration.
- Chemical peeling . It is used for minor lesions. For chemical treatment of warts, lactic or glycolic-salicylic acid is used.
Reviews
ANASTASIA, 51 YEARS OLD:
“I immediately went to the doctor when, after returning from a vacation at the seaside, I discovered flaky “freckles” on my legs that were quickly growing in size.
The doctor diagnosed keratosis, prescribed ointment and increased intake of vitamin products. Six months later, the spots disappeared, but I visited the dermatologist again. He said that I sought medical help in time, but I shouldn’t overexpose myself to the sun.”
IGOR, 48 YEARS OLD:
“At work I wore a not very comfortable uniform - its collar was rubbing my neck.
Then the wife saw a compacted brown spot in the place of rubbing. I didn’t go to the doctor, I made my own lotions from aloe leaves and rubbed oil on the affected area. The result was zero.
However, the stains “ran away” 2 months after changing work clothes, when the shirt did not rub the neck. My advice to those who like tight clothes is not to wear such outfits.”
ELIZAVETTA, 66 YEARS OLD:
“About 2 months ago, a slight thickening of a yolk tone appeared on the forehead under the hair.
It increased dramatically, which forced me to go to the doctor. After the examination, he removed the keratoma; I went home after the operation 15 minutes later with a plaster on my forehead. It took a little time for the wound to heal, now the seam is gradually smoothing out.
There is no need to delay a visit to a medical facility if keratosis has formed on the face or body. This way there is a chance to level out the problem.”
Possible complications
The main complications of keratosis include:
- development of microbial eczema;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- degeneration of growths into a cancerous tumor;
- tooth loss.
Keratosis of the skin is fraught with serious complications, and the photo of adults shows that this pathology is a serious skin disease that requires treatment by a dermatologist and excludes self-medication.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have cracks in the corners of your mouth or lips, you should visit a dentist. Most experts consider keratoses to be a sign of cancer. To protect yourself, it is better to consult a dermatologist if suspicious spots appear. A harbinger of malignant transformation is severe itching and bleeding spots. An unfavorable sign is increased inflammation, ulceration or thickening of the plaque. In this case, keratosis will be treated by an oncodermatologist.