≡ Home → Ovaries → Ovarian cyst →
A corpus luteum cyst is an ovarian formation that forms after ovulation under the influence of luteinizing hormone. The pathology is detected mainly in women of reproductive age, including during pregnancy. The appearance of a cyst is accompanied by menstrual irregularities and pain. As the formation grows, the risk of its rupture and other dangerous complications increases.
Corpus luteum cyst does not require specific treatment, and in most cases observation is sufficient. In chronic cases of the disease, surgical intervention is indicated. It is important to know how the pathology manifests itself in order to notice the characteristic symptoms in time and avoid the development of complications.
About the yellow body
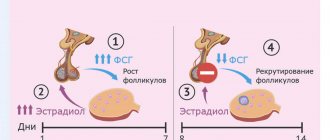
A woman's ovaries produce sacs called follicles. They are small, up to 2 cm, and filled with liquid. During the entire cycle, only one fully developed follicle is formed in the female body, where the egg is located. During ovulation, it ruptures so that the fertilized egg can be released and reach the uterus. In place of this vesicle, a corpus luteum appears, producing progesterone.
The hormone is needed to ensure the normal course of pregnancy. The gland lives no more than four months, then its function will be performed by the placenta. If conception does not happen, it leaves the body shortly before menstruation. All processes are controlled by the pituitary gland. It is responsible for the release of FSH and LH (follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone). Both hormones are involved in the process of gland and follicle formation.
In case of hormonal imbalances or other unfavorable conditions, the mature follicle does not rupture, but accumulates contents. This is how a follicular tumor appears. The same processes occur with the corpus luteum; it does not burst before menstruation, but accumulates fluid, which is why a cyst appears on the ovary.
It is considered normal (functional), and development cannot be prevented. But when the cyst grows sharply, danger arises. Most often, formations are diagnosed on the right ovary. The process is accompanied by hormonal imbalances and pain in the affected area. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately see a doctor.
Features of a corpus luteum cyst
The menstrual cycle of a healthy woman is a 2-phase period:
- Follicular phase;
- Luteal.
During the menstrual cycle, processes occur in the uterus and ovaries that create the conditions for fertilization and pregnancy.
During the onset of the follicular phase, every month, a gland develops in the ovary, which is called the corpus luteum. This gland produces progesterone, a hormone that ensures a normal, healthy pregnancy without complications.
The color of the gland is determined by the presence of a special pigment. The temporary gland can reach a maximum size of 2 cm. If fertilization does not occur, the gland involutes (returns to its previous form) and resolves, and hormone production stops. In case of pregnancy, the iron increases, progesterone is synthesized in large volumes.
Hormonal disruptions, dysfunction, structural changes in the reproductive organs lead to the fact that the temporary gland does not disappear. Blood circulation is disrupted, fluid accumulates, resulting in the formation of a cystic formation. The maximum size of the cyst can reach 8 cm.
In some cases, the tumor formation eliminates itself, its complete disappearance is observed within several months. The cyst in the expectant mother may disappear after the formation of the placenta (16th week of pregnancy).
Causes of luteal cyst
Often women do not know why a cystic corpus luteum forms. There is no clear reason for its occurrence. According to doctors, any change in hormonal levels or the process of supplying the ovaries with lymph and blood can serve as factors for the disease. In addition, the development of pathology is influenced by:
- Poor nutrition and strict diets.
- Problems with the thyroid gland.
- Constant physical stress.
- Stress.
- Heredity.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Abortion, ectopic pregnancy.
- Excessive use of emergency contraception.
- Inflammation, chronic diseases of the reproductive organs.
Most often, the problem appears during infertility treatment and stimulation of ovulation in preparation for IVF. If a woman takes hormonal medications, she needs to have regular ultrasounds and carefully monitor ovarian function.
Symptoms of a left or right ovarian cyst
During the development process, the neoplasm does not become active and does not interfere with the patient during the first three months. It often happens that after several menstrual cycles, the cyst is capable of voluntary removal from the body.
If a doctor has diagnosed a corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy, then in this situation the level of danger of exposure and the influence of education directly on the development of the baby and on the woman’s health in general is determined first.
If there is no danger, then such a neoplasm may disappear by the eighteenth week of pregnancy. It is extremely rare that a cyst begins to manifest itself as pain in the area of the uterine appendages, as well as causing discomfort and bloating, as well as a delay in the menstrual cycle.
If even the slightest signs of a cyst are detected, you must immediately consult a specialist doctor.
So, what symptoms may indicate the appearance and development of a cyst:
- feeling of heaviness on the right or left;
- discomfort in the abdominal cavity, right or left;
- delay of critical days;
- leg torsion;
- acute stomach;
- vomit;
- gas and stool retention;
- intoxication.
When diagnosing a cyst, doctors often use the technique of palpation of the abdomen, which allows them to feel the tumor. During the procedure, the specialist feels the tumor in the right or left ovary by touch.
As mentioned earlier, the neoplasm usually reaches small volumes and when pressing on the cyst, the woman does not feel any pain.
Classification
Formations can occur behind the uterus and on the side. Depending on the location, there is a cyst of the right ovary (common) and the left ovary. There are three forms of pathology:
- Without symptoms - the tumor is not removed, it must be monitored,
- Symptomatic – painful, occurs once and requires treatment,
- Recurrent – appears once, must be treated.
The formation on the right ovary is more common, since it is there that the egg usually matures. This is due to the location and presence of a large number of vessels.
Preventive measures
The negative impact of ovarian cysts on a woman’s quality of life is undeniable. Even if at this stage the disease is asymptomatic, this does not mean that it will not lead to complications. To reduce the risk of developing ovarian cysts, women are advised to monitor their diet and lifestyle - avoid bad habits, exercise regularly, and do not overwork.
An important condition for preventing the disease is maintaining the health of the pelvic organs - systematic gynecological examinations and timely treatment of identified diseases. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The medications, especially those based on hormones, that helped your friends may not be suitable for you personally. Any medications used must be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
Symptoms
The pathology is not easy to recognize, since in the early stages it does not bother the patient. The first signs appear when the formation reaches a certain size or concomitant diseases develop.
The main symptoms of a corpus luteum cyst:
- Aching pain in the area where the tumor is located.
- Discomfort during sex.
- Cyst retention, uncontrolled discharge.
- When the endocrine gland is large, it puts pressure on the bladder, which causes frequent urge to go to the toilet.
It happens that the tumor does not resolve and ruptures.
The condition is characterized by severe symptoms:
- Bleeding,
- Severe cramping pain
- Pale skin, possible loss of consciousness,
- Body temperature without other manifestations of ARVI,
- Dizziness, vomiting not associated with eating,
- Rapid heartbeat, arrhythmia.
Symptoms of rupture should alert the patient; their occurrence requires mandatory hospitalization.
Why does a cyst form?
Doctors agree that a corpus luteum cyst appears as a result of a hormonal imbalance in the female body, which leads to ovulation failure.
Among the main reasons are the following:
- hormonal imbalance;
- genetic predisposition;
- abuse of hormonal drugs;
- gynecological pathologies;
- installation of an intrauterine device with progesterone;
- history of diabetes mellitus;
- endocrine diseases;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- irregular sex life;
- frequent abortions;
- failure to maintain intimate hygiene.
Overweight and underweight women are at risk. In addition, heavy physical activity and constant stress can serve as a trigger for the development of pathology.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the doctor examines the patient, analyzes complaints, and performs palpation. If the size of the cyst is small, manual examination is not enough; small tumors are detected by ultrasound. Often they can cause an ectopic pregnancy, so additional manipulations are prescribed during diagnosis:
- Blood test for hormones - allows you to identify hormonal dysfunction.
- Dopplerography is a study of blood vessels to determine their rupture.
- Laparoscopy - a part of the tissue and contents of the tumor is taken to confirm the benign course.
- Ultrasound – using ultrasound, the size of the formation and its presence are determined.
Ultrasound is performed transabdominally or transvaginally. In the first case, the patient needs to empty the bladder, in the second, such measures are not relevant, since urine transmits ultrasound rays well. You may also need a blood test for sexually transmitted pathologies, tumor markers, and coagulation.
How to detect pathology
The following methods help to make a correct diagnosis:
- Gynecological examination. On palpation, the cyst is identified on the side or behind the uterus and is felt as a round, mobile and painless formation. The appearance of pain indicates the development of complications (torsion of the legs, hemorrhage under the capsule, suppuration);
- Laboratory methods. The level of specific tumor markers is assessed: CA-125, CA-74 and CA-19. Detection of these indicators in the blood indicates possible malignancy;
- Ultrasonography. On ultrasound, the cyst is visible as a round hypoechoic formation with clear contours. The study is carried out in the first phase of the cycle in order to distinguish the cyst from the corpus luteum. Normally, there should be no corpus luteum before ovulation;
- Color Dopplerography makes it possible to distinguish benign from malignant formations, as well as from true ovarian tumors;
- MRI helps to clarify the diagnosis and identify concomitant pathologies;
- Laparoscopy is performed in situations where it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with other pathology of the appendages.
The photo below shows an ultrasound image. Visible corpus luteum cyst:
Below, for comparison, is a normal corpus luteum in the second phase of the cycle:
The following photo shows a hemorrhagic cyst - a cavity filled with blood:
The clinical picture of a corpus luteum cyst is similar to signs of pregnancy in the early stages. There is a delay in menstruation - long-term, up to a month. Against the background of increased production of progesterone, breast engorgement occurs, and dubious signs of pregnancy may appear (nausea, changes in taste preferences, etc.). The cyst also disguises itself as an ectopic pregnancy, manifesting itself as pain in the lower abdomen on one side.
The following methods help to distinguish ovarian pathology from pregnancy:
- Blood test for hCG. The specific hormone increases only during pregnancy;
- Ultrasound. At 3-4 weeks the fertilized egg is visible, at 5-6 weeks the embryo is clearly visualized. Ultrasound allows you to distinguish an intrauterine pregnancy from an ectopic one.
On a note
Measuring basal temperature with an ovarian cyst is not indicative. Increased production of progesterone leads to an increase in rectal temperature and gives false hope of pregnancy.
The photo below shows a corpus luteum cyst. Pregnancy not detected:
Complications and consequences
Usually the formations do not pose a danger and disappear on their own after a while. If the course of the disease becomes more complicated, the following occurs:
- Torsion of the cyst stalk can be complete or partial. As a result, due to pressure on nerve fibers and blood vessels, the nutrition of the ovaries is disrupted. The patient complains of severe pain that radiates to the groin. There is also a feeling of anxiety, dizziness, nausea, and blood pressure decreases. When torsion occurs, the basal temperature rises, and the pain does not go away, even if you lie down or sit comfortably,
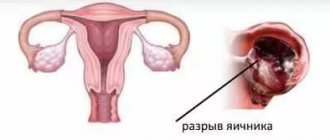
- Cyst rupture - when the formation bursts, there is piercing pain in the ovaries, cold sweat, lightheadedness and dizziness. In such cases, hospitalization is mandatory,
- Cycle disruptions - hormonal imbalance provokes a delay of 1-2 weeks. After this time, menstruation comes, but it is painful and with clots. This type of menstruation is often called uterine bleeding.
- Internal bleeding - when the gland bursts, a hematoma occurs, which increases and bursts the organ. As a result, the ovary ruptures, and blood enters the peritoneum and pelvic area. The patient is in a state of shock, severe weakness is observed, blood pressure decreases and the pulse quickens.
The occurrence of such complications occurs due to the rapid growth of the tumor, sudden body movement, and intense sexual intercourse.
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopic intervention is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. Through one of them, in the navel area, a laparoscope - an instrument with a miniature video camera. It broadcasts an enlarged image onto the screen. For better visualization during surgery, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
Special laparoscopic instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the cyst is removed with the help of them.
Depending on the specific situation, the scope of the operation varies:
- Often it is possible to remove only the cyst, preserving the ovary.
- In some cases, it is necessary to remove the entire ovary - to perform an oophorectomy (oophorectomy) - while the second ovary can be saved. This has to be done if a malignant tumor is suspected, or if the cyst is in an “inconvenient” location, when it is difficult to remove it separately.
- In rare cases, both ovaries may have to be removed. This operation is performed only in extreme cases, especially in women of reproductive age, since menopause occurs after removal of both sex glands. The levels of female sex hormones decrease, and this can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, hot flashes, etc.
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor questions before surgery. Ask what is the likelihood that during the operation you will have to remove both ovaries, what negative consequences this threatens, and how to cope with them.
How is the treatment carried out?
It is not necessary to treat a small cyst if it is not accompanied by various symptoms. This also applies to multiple formations (thecallutein cysts). Such tumors are observed for several cycles in a row, and ultrasound is performed regularly. After 3 months they usually disappear.
If the gland does not regress, conservative treatment is prescribed, which consists of:
- To restore hormonal balance, a woman needs to take combined oral contraceptives.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs that eliminate inflammation and associated pathologies in the ovaries.
- Carrying out physiotherapy, including magnetic therapy, laser therapy, phonophoresis and electrophoresis.
- Corrections of diet and lifestyle - the patient should eat a balanced diet, give up bad habits and exercise regularly.
- Using additional treatment - acupuncture, taking homeopathy medications, vitamins, etc.
In the absence of positive dynamics, surgical treatment of the ovarian corpus luteum cyst is prescribed. Such treatment is necessary for rupture of a gland or organ, as well as torsion of a leg. The operation is performed using laparoscopy, which is done in two ways:
- Ovarian resection – the tumor and affected tissue are removed. The functions of the organ are not fully restored, so the number of follicles decreases,
- Removal of the tumor - healthy ovarian tissue is not affected. After the operation, the organ works as before.
Treatment is selected exclusively by a doctor to avoid complications. Patients should monitor their health and avoid abdominal injuries or thermal procedures. A woman is also recommended to be treated with folk remedies as an additional therapy. It includes medicinal baths based on medicinal plants, douching, compresses, etc.
Effective folk methods:
- Chaga tincture - for preparation, take chaga and ordinary clean water at a ratio of 1:5, heat the liquid to 50 degrees, leave to infuse for 2 days, filter. The infusion is drunk every day on an empty stomach, 30 mg. Course – up to 3 months.
- Decoction of pine nut shells - take 100 g of raw material, add 0.5 water and boil for an hour. Drink 1/3 cup of the decoction three times a day before meals.
- Compress – used before bed and applied to the lower abdomen. For a compress, take a 10% solution of table salt.
- Decoction of walnut partitions - take 4 tbsp of raw material, add 3 glasses of water, boil for 40 minutes. The decoction is infused until it cools, then 125 mg is drunk several times a day.
Burdock juice has proven itself well. It is taken for 30 days in a row, 2-3 times a day. You can use traditional medicine only after consulting a doctor. Prescriptions are intended for additional therapy, which is used in conjunction with the main treatment.
How to recognize the disease
If you read reviews from women who have suffered from this disease, you can identify several key symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities. There is a long delay in menstruation - up to 2-3 weeks or a month. After a delay, menstruation comes heavy, prolonged, and painful. Often, menstruation with a luteal cyst turns into uterine bleeding;
- Prolonged menstruation. Your period comes almost on time, but it becomes heavier than usual, and the discharge lasts several days longer;
- Feeling of heaviness, discomfort, fullness in the lower abdomen on the affected side (right or left, depending on the location of the formation);
- Pain in the lower abdomen in the projection of the right or left ovary with irradiation to the groin and buttock region, to the lower limb.
The main manifestations of an ovarian cyst.
In rare cases, there may be spotting outside of menstruation, but this symptom is not very typical for a corpus luteum cyst. Cycle failure is associated with the effect of formation on the endometrium. There is an uneven growth and equally sudden rejection of the mucous layer of the uterus. This causes the appearance of acyclic bleeding.
A corpus luteum cyst up to 3 cm in size usually remains asymptomatic. This formation does not hurt, does not bother, and is usually detected by chance during an ultrasound. If the outcome is favorable, a woman may never even know that at some point in her life a cavity filled with fluid has formed in her ovaries. Luteal cysts are prone to spontaneous regression, which is why they are called functional (temporary). Spontaneous resorption of the formation occurs within 2-3 months (rarely up to 6 months).
If the cyst does not regress, it continues to grow. An increase in size of the formation leads to the appearance of the following symptoms:
- Compression of the bladder and disruption of its function. Urination becomes more frequent, urine comes out in small portions;
- Compression of the intestines and the development of constipation. The appearance of ribbon-like feces speaks in favor of a tumor-like formation of the small pelvis.
The ratio of the sizes of normal ovarian formations and cysts.
A luteal cyst rarely grows more than 10 cm, so such complications almost never arise against its background. This pathology is dangerous due to other conditions:
Capsule rupture
One of the most common complications that occurs against the background of significant physical activity. Sports activities, sharp turns and jumps can cause damage to the capsule. Known cases of hemorrhages in the ovary after rough sex.
If the luteal cyst bursts, the following symptoms occur:
- Sudden severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- Radiation of pain to the leg, buttocks, groin area;
- Tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall;
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting;
- Retention of stool and urination;
- Bloody discharge from the genital tract.
Torsion of the pedicle of the formation
This complication also occurs after exercise and is accompanied by typical symptoms of an acute abdomen. There is sharp pain in the projection of the affected ovary, nausea, and vomiting. Possible loss of consciousness. Torsion of the cyst stalk is accompanied by its subsequent necrosis, so an increase in body temperature is possible.
It is important to know
With complete torsion, symptoms appear suddenly, with partial torsion they gradually increase over several hours.
First aid for rupture or torsion of a corpus luteum cyst is the same:
- Provide the woman with peace;
- Place cold on the lower abdomen (a bottle or heating pad with cold water, ice wrapped in a cloth);
- Call an ambulance.
Further treatment is carried out in a gynecological hospital. If complications develop, surgical intervention is indicated.
Schematic representation of torsion of an ovarian cyst.
Cyst suppuration
The source of infection is an inflammatory process in the uterus or genital tract of a woman. Suppuration of the formation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Increased body temperature;
- The appearance or intensification of pain in the lower abdomen;
- Severe weakness and other signs of intoxication.
Inflammation of an ovarian cyst is a dangerous condition. Without treatment, it threatens the development of peritonitis and sepsis.
Prognosis and prevention
Usually, if there are tumors in the ovaries, pregnancy is possible. If regression or planned tumor removal has occurred, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. To prevent complications, it is necessary to regularly visit the gynecologist's office and have an ultrasound scan.
It is better to prevent pathology than to treat it later. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- You should not take hormonal medications or oral contraceptives on your own.
- It is necessary to treat inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system in a timely manner,
- It is advisable to lead an active lifestyle, give up bad habits, get adequate rest and nutrition,
- Avoid abortions, being in places with high harmful conditions, and regularly lifting heavy objects.
Simple recommendations will help prevent many women's problems.
Despite the fact that a cyst in most cases is not dangerous, you need to constantly visit a doctor and follow his advice. Any unfavorable circumstances can aggravate the course of the pathology and cause a number of complications.
Prognosis for ovarian cyst
Many people are interested in the future forecast, and for good reason.
A cyst is one of the neoplasms that can develop from benign to malignant. Therefore, to avoid problems, you need to be examined in a timely manner, take measures, and be treated according to doctor’s prescriptions.
Often, a cyst begins to form during pregnancy. What is the prognosis and is there any reason for concern? With a developing pregnancy, there is no threat to pregnancy.
However, this does not mean that you can forget about the diagnosis and move on with your life with peace of mind. It is necessary to visit a doctor regularly to examine and evaluate the condition of the tumor.
It also often happens that the cyst begins to grow sharply and this frightens many. In this case, many decide to undergo surgical interventions. You need to take care of your health and not delay it, because the cyst can behave differently.
As you know, it can burst, or a torsion can form, which is also unsafe for the female body. If all is well, then after three months the cyst may resolve on its own. In this case, no medical intervention will be required.
How much does the operation cost?
Women diagnosed with an ovarian cyst can undergo treatment in both public and private medical institutions. The cost of services in private clinics is higher, but the patient receives high-quality treatment that meets international standards and comfortable conditions of stay.
Before starting treatment, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital explain to the patient how much it costs to treat an ovarian cyst and what components make up the cost of the service, which is calculated according to the current price list.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital help every patient who comes to them. Women who have signs of an ovarian cyst or have been diagnosed with the disease can consult a highly qualified gynecologist. Making an appointment in advance allows you to save time and optimally plan your working day. Contact specialists by calling the Yusupov Hospital to make an appointment.
Education process
There are three phases of the menstrual cycle - follicular, ovulatory and luteal. In the first phase, the follicles mature; their rupture marks the course of ovulation.
Immediately after the release of the egg, a corpus luteum is formed at the site of the burst follicle - it is necessary for the production of the hormone progesterone, which stimulates the attachment of the fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus, and subsequently maintains the course of pregnancy. In the absence of conception, the iron undergoes regression, leaving the body along with menstrual blood.
If the production of progesterone or other hormones is disrupted, the corpus luteum does not regress. It continues to function, but in a less intensive mode. At this time, a serous fluid with admixtures of blood accumulates inside the gland, increasing the size of the temporary organ. Gradually, the tissue of the gonad completely turns into a cyst, the average size of which is 3-7 cm.
The production of hormones continues due to the functioning of the luteal cells on the membrane of the formation - this is what often causes a delay in menstruation and subsequent cycle failure.
Reasons for appearance
A cyst on the ovary appears unexpectedly, often causing hormonal dysfunction. Scientists have not precisely established the root causes of the disease, but there are risk factors that some women fall into.
Reasons for development:
- imbalance of hormones in the body;
- interventions in the uterine cavity (abortions, miscarriages, frozen pregnancies);
- regular stressful situations;
- chronic diseases and inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- heredity;
- menopause
Uncontrolled growth of the cyst can cause infertility and is subject to emergency surgical removal.