- Causes of urticaria
- Classification of urticaria
- Common symptoms of urticaria
- Diagnosis of urticaria
- Why is urticaria dangerous?
- Treatment of urticaria
- Prevention of urticaria
- Urticaria in children
- Urticaria during pregnancy
Urticaria is the name of a group of diseases characterized by the appearance of sharply itchy, inflamed rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. According to the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, almost 25% of the country's population experiences symptoms of urticaria at least once in their life.
Causes of urticaria
There are two categories of factors that cause urticaria:
- external - physical, mechanical, chemical;
- internal - dysfunctions of the nervous system, pathologies of internal organs.
A variety of circumstances can trigger an attack of urticaria:
- Food,
- medications,
- plant pollen,
- UV,
- a bite of an insect,
- sudden cooling or overheating,
- diseases of the liver, kidneys and other organs,
- infections,
- heredity,
- toxicosis of pregnant women,
- stress, etc.
Sometimes identifying the cause of hives can be difficult or even impossible.
Classification of urticaria
There is no generally accepted classification of urticaria yet - an attempt to classify the phenomenon leads to the proposal of cumbersome, complex schemes that are difficult to use in practical healthcare. Therefore, in clinical practice it is customary to distinguish urticaria according to its course:
- spicy,
- subacute,
- chronic,
- chronic recurrent.
Acute urticaria. The disease begins suddenly - severe itching of individual parts of the body or its entire surface. It is characterized by a monomorphic rash - multiple blisters of the same type. Acute urticaria may be accompanied by a headache and a rise in body temperature to 390. The blister turns pale as the swelling increases, and detachment of the epidermis is possible in the center. Elements can be placed separately or merged into three-dimensional figures with bizarre outlines. The duration of acute urticaria ranges from several hours to several days.
Subacute urticaria is the next acute stage. It can last up to 5–6 weeks.
Chronic urticaria is subacute urticaria, the total duration of which exceeds 5 weeks.
Chronic recurrent urticaria - can last for several decades with periods of partial or complete remission (weakening). It is often accompanied by Quincke's edema. Severe itching forces patients to scratch their skin until it bleeds. In 70% of cases, the causes of chronic urticaria remain unclear.
Classification according to the pathogenetic principle is also used:
- Immune (allergic) - disorders of the immune system:
- food;
— instinctual — arising as a result of an insect bite or contact with their metabolic products;
- due to transfusion reactions - a reaction to the introduction of immunoglobulins or platelets, leukocytes, erythrocytes;
- medicinal.
May be combined with pathologies of the digestive system.
- Non-immune (pseudo-allergic) - the immune system is not involved. It may be a consequence of previous severe intoxications, infection with parasites, or hypersensitivity to drugs.
- Physical - due to various physical effects on the skin:
- cold,
- cholinergic,
- vibration,
- solar,
- mechanical irritation - pressure, friction,
- aquagenic, etc.
- Hereditary.
The difficulty of classifying urticaria is due to the variety of causes of its occurrence.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face treatment with ointments, diet, folk remedies
2 comments
- Zirka author 07/29/2015 12:38
My daughter had hives when she was about 2 years old, only once. I think her appearance was provoked by drinking a glass of milk. She had allergic reactions to food before (fortunately, she outgrew them by the age of three), so we introduced complementary foods later, and I gave milk with great caution. Who knows what was in that milk - maybe they went too far with antibiotics. How scared I was! The whole body was covered with blisters, severe itching! Fortunately, Google is here to help, as they say: informed means armed. Fenistil drops saved me. This never happened again.Answer
- Oksana author 06/20/2018 11:12
The doctor recommended taking Erius for hives. But when I saw the price at the pharmacy, I realized that I couldn’t afford it. It’s good that a sympathetic pharmacist recommended me a more affordable domestically produced analogue - Ezlor. I liked the effect, it helps immediately, did not cause any side effects.Answer
Common symptoms of urticaria
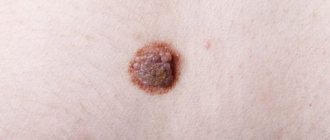
Numerous rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes within a few minutes - bright red, sometimes with white spots, dense blisters with clearly defined boundaries, like a nettle burn. They can be small - a few millimeters or form a continuous layer on the skin and mucous membranes (see photo).
In addition to severe itching and burning, depending on the extent of the lesion, a person may experience:
- headache,
- nausea,
- drowsiness,
- weakness.
Possible increase in temperature - nettle fever. Blisters and symptoms may disappear without a trace after a few hours, or the condition may be stable or wave-like over several days or even months. Usually, after disappearing, there are no traces left on the skin. In some cases, urticaria blisters can become hemorrhagic in nature - after disappearing, pigment spots remain.
Complications
This pathology, like any disease, can cause complications that manifest themselves in physical and mental conditions.
The consequences that urticaria can often lead to:
- Depression. Disturbances in the emotional background are a fairly common complication; it is observed in 15 % of adult patients suffering from a chronic form of the disease. The cause of depression is light sleep, since the patient is prevented from getting enough sleep by constant nighttime itching. Moreover, blisters are a skin defect, which also negatively affects the patient’s self-esteem.
- Bacterial infection. It is a common consequence of the disease, developing on the affected areas of the skin. As a rule, this complication develops only in acute forms of the disease, when pronounced large blisters appear on the patient’s body. If a bacterial process is attached, the patient develops painful ulcers and boils on the skin.
- Quincke's edema. It is the most severe consequence of this pathology, affecting the larynx, which interferes with the normal respiratory process. If left untreated, swelling can be fatal.
In children, urticaria is dangerous because parents mistake the manifestations of other serious illnesses for symptoms of urticaria. In particular, such common childhood diseases as rubella, measles, and scarlet fever are manifested by a rash that has similar features to urticaria. In order to prevent the condition of a small patient from worsening, adults need to promptly consult a doctor if any rash occurs.
Symptoms of allergic urticaria
In the case of urticaria, the main symptom that distinguishes it from other types of allergic reactions is the appearance of blisters on the skin (see photo).
In appearance, the blister resembles a protruding area of skin, like a mark from an insect bite or a burn left by nettles. The affected area is accompanied by itching. There may be redness. Most often, the rash is symmetrical.
The number of blisters is also individual, it varies from a few spots to hundreds. In severe cases, there are so many spots that they merge and cover the entire skin. Symptoms such as vomiting and nausea occur extremely rarely. They indicate irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, which is very dangerous.
Danger of disease
Quincke's edema poses a great danger not only to the patient's health, but also to his life. Since the course of the disease and the rapidity of symptoms does not leave much time to take action, you should immediately call an ambulance. Otherwise, suffocation may occur.
Urticaria can have either mild manifestations that can be quickly relieved, or very severe ones that require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms that require immediate medical attention:
- loss of consciousness;
- vomit;
- lack of air;
- swelling of the face;
- swelling of the neck;
- severe nausea.
Important! If the body reacts strongly (in the form of such manifestations), it is necessary for the sick person to administer suprastin or another antihistamine intramuscularly as soon as possible.
Even in the absence of obvious manifestations that are life-threatening, complications are possible. For example, when scratching itchy skin, a fungal or bacterial infection may occur.
Diagnosis of urticaria
Making a diagnosis in most cases is not difficult at all. But to determine the form of urticaria and find out its causes, anamnesis and an in-depth examination are taken.
Anamnesis
In addition to the duration of this episode, the presence of possible stimuli for its exacerbation is determined. During the interview with the patient, the doctor finds out:
- the cyclical appearance of elements and the duration of their “life”;
- presence of itching;
- description of possible stimulants of the phenomenon - stress, taking drugs, illness, etc.;
- a history of allergic diseases;
- the presence of traces after the disappearance of blisters - pigmented, flaky spots, vascular patterns;
- effectiveness of antihistamines;
- family history of urticaria.
Sometimes urticaria is only a single episode in a person’s life.
Physical examination
It allows you to draw up a plan for subsequent laboratory and instrumental studies. Typically, a physical examination includes:
- measuring body temperature;
- measurement of blood pressure, heart rate;
- palpation of the abdominal cavity - determination of the size of the spleen and liver;
- auscultation of the heart, lungs;
- determination of the size of lymph nodes.
Additional laboratory and instrumental studies and tests allow us to determine the nature of urticaria, find out its causes and exclude diseases with a similar diagnosis:
- urticarial and hypereosinophilic vasculitis;
- pruritus;
- erythema multiforme and fixed, erythema nodosum;
- parasitic infestation;
- anaphylactic reactions;
- prodromal period of bullous pemphigoid or non-bullous pemphigoid;
- contact urticaria.
In addition, urticarial papules and itchy spots that appear in women in the third semester of pregnancy disappear after childbirth.
Laboratory and instrumental studies
Laboratory tests are not used for isolated episodes of acute urticaria.
Recommended laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- blood tests - clinical, biochemical;
- general urine analysis;
- colonoscopy;
- bicycle ergometry;
- radiograph of PPN and OGK;
- Ultrasound - according to indications;
- ECG and EGDS;
- parasitological examination;
- bacteriological cultures from the pharyngeal mucosa for flora;
- bacteriological studies of feces and duodenal contents;
- X-ray examinations of the paranasal sinuses and thoracic organs.
Diagnosis of physical types of urticaria is carried out using provocative tests - hot baths, water compresses, mechanical irritation of the skin, bicycle ergometry, etc. Tests with autologous serum are also used to identify the causes of urticaria.
Based on the results of research, a dermatologist may recommend consultations with other specialists:
- allergist,
- rheumatologist,
- oncologist,
- endocrinologist,
- parasitologist,
- gynecologist, etc.
Specialists together determine treatment regimens and methods.
Diet for allergies and urticaria
The doctor must select products to compile a list that is suitable for treatment. From this list should be excluded those that are identified as allergens that caused the disease.
Little by little you can eat butter, lamb, bananas, carrots, onions, and garlic. If the disease occurs periodically, the popular diet No. 5 is recommended, which limits the consumption of fat, salt and liquid.
Popular dishes allowed for this disease
Puree potato soup.
To prepare it you need to take: 3 peeled potatoes, 2 leeks, 2 large spoons of olive oil, a little salt, water. Pour the oil into a saucepan, then add the finely chopped white part of the onion. It should be simmered over low heat until transparent. Then add potatoes cut into squares and continue simmering for another 5 minutes. Then you need to add 500 ml to the pan. boiling water, add salt and cook for 15 minutes. When the potatoes can be easily pierced with a fork, the contents of the pan should be crushed using a blender. Immediately before eating, you can sprinkle the soup with herbs.
Macaroni with apple or cheese sauce.
Durum wheat pasta should be cooked in the same way as usual. For the cheese sauce, heat a large spoonful of butter and twice as much cream in a suitable container. To them you should add two large spoons of mild grated cheese and mix everything until smooth. To prepare apple sauce, remove the skin and seeds from two apples, cut them into pieces and add water. Then they need to be put on fire, and when they soften, grind them into a paste. There you need to add sugar and a little cinnamon to taste, put it back on the fire and cook a little, stirring constantly.
Patients must adhere to the diet for at least four weeks. Only after the symptoms have completely disappeared is it possible to gradually, in small portions, add food to the menu from products that were previously strictly prohibited. The only exceptions are those that can cause a relapse of the disease. It is also recommended to keep special records in which all the foods eaten and the skin’s reaction to them will be recorded.
Remember!
The main thing in following a diet is not only the consumption of foods from the list and the exclusion of provocateurs from the diet, but also proper preparation. Food should be cooked primarily by steaming and baking.
Treatment of urticaria
There is simply no radical remedy against urticaria. The chronic form is forever. But treatment will help reduce the frequency and duration of attacks, reduce the risk of death due to complications such as Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
The treatment method is selected by the doctor individually, depending on the causes of urticaria, its course, the patient’s condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases. Modern medicine offers medications with various effects:
- antihistamines,
- immunomodulators,
- antidepressants.
Self-administration of medications can provoke anaphylactic shock or angioedema and cause death. Treatment at home is possible only if the treatment plan is agreed upon with a doctor.
You can relieve itching and reduce inflammation by wetting the blisters with weak solutions of salt, soda, herbal and alcohol infusions, 2% salicylic alcohol, and lemon juice. But only after consulting a doctor!
Emergency care for urticaria
It happens that strong manifestations of this disease can provoke a serious condition in the patient . You should call an ambulance immediately. In such cases, doctors often have to take the necessary measures directly at the scene of the call in order to prevent irreversible consequences.
If urticaria suddenly appears in a severe form, emergency care should consist of clear actions:
- Immediate exclusion of resumption of interaction with the stimulus, if it is established
- If urticaria develops as a result of an insect bite, apply a tourniquet. It should be tightened slightly above the bite site
- Mezaton or Adrenaline is administered intramuscularly or intravenously, Noradrenaline is also suitable
- When the blood pressure returns to normal, antihistamines are administered.
- Symptomatic treatment is carried out
Important!
If everything is done correctly, the signs of the disease will immediately begin to recede: the patient turns pale, the itching and rash disappear. When this does not happen, the patient is hospitalized.
Causes
In adults and children, urticaria can be caused by various reasons.
- Taking medications: antibiotics (penicillin), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin), hormonal contraceptives. Sometimes the reaction appears after a few days
- Food consumption: honey, fish, seafood, eggs, nuts, some fruits. In this case, urticaria usually occurs in children
- Contact with certain substances: latex, household chemicals
- Insect bites: wasps, bees, mosquitoes. Hives at the site of the bite sometimes persist for a day
Certain diseases can trigger the development of urticaria:
- infectious diseases (hepatitis, herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus)
- parasitic diseases
- pharyngitis, tonsillitis
- fungal diseases
- pathogenic microflora in the intestines
- the presence of Helicobacter pylori in gastritis and ulcers often accompanies chronic urticaria
- systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases
- cryoglobulinemia
- serum sickness
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- thyroid disease
Physical causes: sunlight, vibration, pressure, water, heat, cold, physical activity.
Top
Kinds
In addition to urticaria in acute and chronic form, there are other types of the disease. The most common type of this pathology is photodermatitis, which is also called sun allergy or solar urticaria. Cold urticaria is also common.
Main types of urticaria:
- solar;
- cold;
- food;
- aquagenic;
- cholinergic;
- dermographic;
- urticaria due to stress.
Cold urticaria
This variety is manifested by the appearance of blisters on the skin, which appear almost immediately after exposure to low temperatures. This pathology is detected in patients of different ages and genders, but most often it affects females aged 30-40 years.
Factors that provoke the appearance of a characteristic rash can be natural phenomena (cold air, snow, rain). Also, similar symptoms can be caused by eating cold food, drinks, cold showers, drafts and other reasons that lead to a drop in body temperature.
Aquagenic urticaria
This is a type of disease in which characteristic symptoms appear after the patient comes into contact with water. This form is quite rare and usually occurs in adult patients.
Experts call this type of illness a water allergy. The main feature of this form of the disease is its tendency to progress. As the disease progresses, symptoms occur more frequently and become more pronounced.
Causes
The cause of this type of urticaria is moisture on the mucous membranes or skin of a person. However, it is worth noting that it is not water that causes an allergic reaction, but the presence of various chemical compounds in it. Rashes may appear immediately after contact with water, snow, or rain.
There are cases where the cause of this type of illness was the patient’s own sweat. The causative agent of the disease can be any form of water or any type of liquid, which reduces the patient’s quality of life.
Food urticaria
This type of disease is the body’s response to any product. This pathology most often occurs in babies during the period of introducing complementary foods. Adult children also suffer from food urticaria. In adult patients, this type of disease is extremely rare and, as a rule, occurs in a chronic form, caused by diseases of the digestive tract.
Symptoms
In children, this form of the disease manifests itself in the form of small, bright red blisters with characteristic itching. Food-borne urticaria develops much more often than other forms of the disease and is accompanied by the appearance of Quincke's edema. The patient's cheeks, lips and larynx swell.
A common manifestation of this type of disease is disruption of the digestive tract, which occurs in adults and children. Patients complain of discomfort in the abdomen (in rare cases, pain), nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur.
Dermographic urticaria
Dermographism (dermographic urticaria) is a type of pathology in which blisters appear on the skin, similar to scars, resulting from mechanical stress.
This disorder is characterized by rapid onset and resolution of symptoms. Often, patients with dermographism experience self-healing without subsequent relapses.
Symptoms
The main symptom of this type of disease is linear blisters that appear after mechanical impact on the skin. As a rule, various elements of the wardrobe (belt buckle, shirt collar) act as an irritant. Depending on the time of onset of symptoms, delayed and immediate dermographism are distinguished.
With delayed dermographism, symptoms occur only after prolonged skin irritation , and with immediate dermographism, blisters appear immediately after exposure.
Urticaria due to stress
Often people develop nervous rashes on their skin that are characteristic of urticaria. Most often this phenomenon is accompanied by itching. This pathology in medicine is called neurogenic or psychogenic urticaria.
Symptoms
The psychogenic form of the disease is characterized by large blisters. They merge with each other and cover fairly large areas of the body. Some elements of the rash have a round/oval shape, but when they are combined, these formations acquire polygonal, even outlines.
The color of the bubbles ranges from white to pink, and sometimes they can be two-tone (pink on the edges and white in the center). A mandatory symptom of neurogenic urticaria is intense itching.
Cholinergic urticaria
This type of urticaria occurs when the skin is exposed to high temperatures, stress and increased sweating. Most often, this type of urticaria occurs when a person spends a long time in a sauna or gets nervous.
The development of this form of pathology is based on the body’s sensitivity to acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter of the nervous system, which is involved in neuromuscular transmission.
A sudden entry of a large amount of acetylcholine into the patient’s blood contributes to the appearance of blisters and itchy spots on the skin, which is the main manifestation of this type of disease. This type of disease is also called pruritic dermatosis.
Prevention of urticaria
It is impossible to predict the appearance of the acute form, but you can try to avoid relapses of the chronic one. Prevention of urticaria means:
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases that are or may cause urticaria;
- regular examination and treatment of inflammatory and other diseases;
- Healthy lifestyle - giving up smoking, drinking alcohol, drugs, observing sanitary rules and personal hygiene rules;
- avoiding hypothermia, overheating, UV irradiation, stress, tight clothing;
- careful handling of household chemicals and cosmetics;
- taking medications only under the supervision of a doctor.
Before planning a trip to the sea or to the mountains, you should also consult with your doctor.
Doctors do not have a consensus on the need for a diet for chronic urticaria, primarily due to the variety of causes of the disease. Diet is usually recommended during an exacerbation. In the future, the diet is determined individually. For example, in case of allergic forms of urticaria, the doctor may recommend completely abandoning the allergen product or, conversely, taking it in food, but only in microscopic quantities - so that the body “remembers” that this product is not dangerous.
A patient diagnosed with chronic urticaria is recommended to have with him:
- medical kit with first aid supplies;
- an extract from the clinic or a note indicating possible reasons that could trigger an attack of the disease.
These measures help, if not completely get rid of the rash, then at least control the itching, allowing the person to remain socially active, work and live relatively comfortably.
Folk recipes
In complex cases, urticaria cannot be cured using folk remedies alone. Such recipes can only be used in addition to other therapy.
Mint tea
Ingredients:
- mint (20 g);
- boiling water (1/4 l.).
Preparation:
- Pour boiling water over the leaves.
- Leave for 60 minutes.
- Drain.
- Drink 3 tbsp. l. three times a day.
Treatment with potatoes
To relieve itching and weaken red rashes, compresses made from ordinary potatoes are used.
Preparation and use:
- Grate the potatoes.
- Place it on the affected areas.
- Place film on top.
- Leave for half an hour.
Yarrow
Ingredients:
- chopped herb (1 tbsp);
- boiling water (1 tbsp.).
Preparation and use:
- Pour boiling water over the herb.
- Leave for a quarter of an hour.
- Strain.
- Drink 70 ml four times a day.
Alcohol tinctures
For urticaria, it is recommended to use pharmaceutical alcohol settings, diluted in water. Enough 30 drops in ½ tbsp. water at night.
The following are suitable for tinctures, which are mixed in equal parts:
- motherwort;
- valerian;
- hawthorn.
Determining the allergen that caused hives, eliminating it and following all medical recommendations will help you cope with the disease.
Treatment
First, you need to avoid contact with an irritating factor (taking medications, exposure to physical factors, etc.). Secondly, start drug treatment: taking antihistamines should start with a minimum dosage. New generation antihistamines. If they do not help, then use hormonal medications (prednisolone). In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe immunosuppressants. Ointments containing hormones and non-hormonal ones are also used. Read about how dangerous hormonal ointments are.
Hospitalization and treatment under the supervision of a physician may be necessary. The regimen eliminates contact with allergens, stress, and physical activity. It is necessary to detoxify the body and follow a hypoallergenic diet. Treatment in hospital may take 5-10 days.
You should not ignore hives, even if it occurs once. If the rashes recur, then you need to consult a doctor who can prescribe proper treatment. Do not forget that this disease can have many causes. Read more about modern methods of treating urticaria in adults here. Hives are a possible symptom of a more serious condition. Take care of your health!
Top
Did you like the article? Follow new articles on social networks: Odnoklassniki, VKontakte, Facebook, Twitter and Google Plus
Urticaria in children
Symptoms, diagnosis, classification, prevention and treatment of childhood urticaria are similar to “adult” types. The only difference is that during the examination, parents must answer the doctor’s questions regarding the suspected cause of the disease. Therefore, if bright red blisters appear on the baby’s skin, adults need to try to remember:
- what the child has eaten in the past hours;
- what the baby was doing - playing with pets, digging in garden beds, a long walk, etc.;
- the presence of chronic forms of diseases in close relatives from both parents.
What matters is the appearance of a new type of household chemical or a new perfume for mom, playing with stray animals or launching boats in a cold puddle.
The pediatrician may recommend consultations with an otolaryngologist, allergist, etc.
To prevent urticaria from becoming chronic, strict parental control is required.
Urticaria during pregnancy
In addition to the reasons described above, toxicosis can provoke the appearance of red itchy blisters in pregnant women. Hives do not have a direct negative effect on the baby; it only causes inconvenience to the woman herself. But the sensations of itching and discomfort do not improve the mood of the expectant mother and her condition as a whole, which cannot but affect the condition of the child.
Most medications for the treatment of urticaria are contraindicated in pregnant women, so treatment usually comes down to various measures to reduce itching and taking mild sedatives.
Urticaria caused by toxicosis disappears completely after childbirth.
Briefly about the main thing
The term “urticaria” hides a wide group of diseases of different nature, but with similar symptoms. The course of urticaria, as a rule, passes without complications, although they cannot be completely excluded. In this material you will learn about the symptoms, complications of the disease and, of course, you will be able to look in detail at the photo, what urticaria is and what causes it.