To eliminate such an unpleasant symptom as bleeding gums, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory focus in the oral cavity, you need to know the reasons for its occurrence.
Only after identifying the original source of the problem, it is possible to select the appropriate treatment, consisting not only of medications, but also of traditional medicine methods applicable at home.
What to do if your gums are bleeding: what could be the cause of the symptom and how to stop it correctly
Bleeding gums is one of the most common symptoms indicating the onset of a pathological process in the oral cavity. Due to the absence of pain and other disturbing manifestations at first, many deliberately ignore the problem, believing that it will disappear by itself. Such a symptom may indeed be the result of a common soft tissue injury, but in other cases it becomes a direct signal indicating the development of a dental disease or a disorder in the functioning of internal organs and systems. Today we’ll figure out why gums may bleed when brushing your teeth and what to do about it.
General information
Bleeding gums is a fairly common phenomenon that almost every person experiences.
More often, bleeding gums appear while brushing teeth or chewing hard foods (carrots, apples, etc.). Bleeding in itself is not a disease. This is a symptom that indicates that inflammation has developed in the gum tissue, and bleeding is one of its manifestations. Healthy gum tissue usually does not bleed. It is dense, pale pink in color, the gingival papillae are pointed, elastic and dense, fit well to the teeth, fill the interdental space and tightly cover the necks of the teeth, there are no “points” visible to the eye.
Inflamed gum tissue bleeds even with slight pressure or touching it with a toothbrush and has a dark red color. In general, the severity of gum bleeding depends on the intensity of the inflammatory process. There are different types of bleeding - petechial-spotted, vasculitic, hematomatous, angiomatous and mixed. Gingival bleeding most often refers to a mixed type of bleeding with local bleeding.
Inflammatory diseases of periodontal tissues combine various pathological processes and, accordingly, diseases that can affect:
- Interdental papillae ( papillitis , gingival polyp ).
- Gum mucosa without compromising the integrity of the dentogingival junction ( gingivitis ).
- Structures surrounding the root of the tooth - gums, bone alveoli, ligaments of the tooth and others ( periodontitis ).
According to modern research, almost 80% of people have problems with inflammatory periodontal diseases. Thus, in adults, the incidence of periodontitis and gingivitis varies between 53-97.5%. At the same time, the incidence of periodontal diseases is higher among young people and reaches 80–95%. Currently, it is generally accepted that gingivitis and periodontitis are infectious and inflammatory diseases and their effective treatment involves, first of all, the normalization of the microflora of the oral cavity.
Possible causes of bleeding gums
Your gums may bleed when brushing your teeth or when biting into hard foods. In other situations, the symptom manifests itself unexpectedly, in the absence of external stimuli. In any case, the problem cannot be ignored. If you notice characteristic signs in yourself, be sure to contact your dentist. The most common cause of bleeding is insufficient oral hygiene, abundant accumulation of soft and hard plaque, including in the subgingival area.
In the course of their life, bacteria release various toxins that literally corrode hard and soft tissues, thereby provoking inflammatory processes. Over time, this leads to the formation of pathological periodontal pockets, in which deposits continue to accumulate. This is followed by carious processes, the first signs of gingivitis, and then periodontitis. In fact, there are quite a lot of potential causes that can lead to bleeding, so let's look at the main ones.
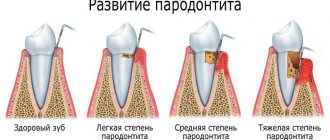
Gingivitis – inflammation of the upper mucosal epithelium
Inflammation of the mucosal surface, which manifests itself in the form of redness, swelling, pain and bleeding. If you ignore the problem, the symptoms will become more intense and may bother you even at night. Lack of timely treatment will lead to the spread of inflammation into the deeper layers of soft tissue and the development of periodontitis. The diagnosis is quite common among both adults and children. However, the disease is completely curable. The main thing is to seek qualified help in time.
The photo shows gingivitis
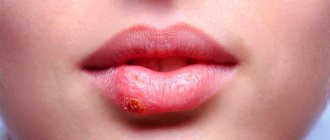
Stomatitis with painful ulcers
Damage to the mucous membrane, which is accompanied by increased salivation, the appearance of an unpleasant odor, the formation of a whitish or yellowish coating, as well as painful ulcers. The disease is often found among children, and one of the main factors of the bacterial form of the pathology is poor hygiene - abundant accumulation of plaque and tartar.
The development of stomatitis can also be triggered by a sharp drop in the body’s immune defense, problems with the stomach and intestines, or an allergic reaction. The mucous membrane turns red in one place or over the entire surface of the alveolar ridge, swelling and discomfort appear, turning into painful sensations.
Stomatitis is common in children
Periodontitis and periodontal disease
When the inflammatory process moves into the deeper layers of the mucosa and spreads to periodontal tissue, signs of periodontitis appear. The pathology is widespread and at the same time quite complex. It is considered impossible to completely cure the disease, but achieving stable remission is quite possible - for this you will have to undergo quite a long complex treatment. When the disease takes an acute form, the gums swell and begin to hurt very much, bleeding appears, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and swells.
With periodontitis, the gums become swollen, begin to hurt and bleed
The aggressive form of periodontitis against the background of long-term treatment can provoke the appearance of signs of periodontal disease. This diagnosis itself is quite rare and has nothing to do with the inflammatory process. Periodontal disease in its original understanding is a gradual atrophy of soft tissues and ligaments. In this case, the mucous membrane becomes pale, noticeably thinner and weakens. But today, periodontal disease as an independent disease has been excluded from the latest list of diseases, and now it is usually considered as a complication of periodontitis.
Mechanical injury
Sometimes bloody marks on a toothbrush only indicate damage to the mucous membrane. This often happens due to bad habits, such as chewing the end of a pencil or brushing your teeth too vigorously, as well as due to improperly installed fillings, crowns or dentures that rub and injure healthy tissue. A similar situation is typical during the period of getting used to braces.
During the process of getting used to braces, inflammation and swelling may occur.
Therefore, there is no need to sound the alarm ahead of time. First, you should carefully examine the oral cavity in the causative area, and it is better to immediately seek advice from a specialist. Even if the symptom is the result of a scratch, it is necessary to ensure proper healing of the wound. The doctor will prescribe antiseptic rinses to prevent infection and infection.
System-wide disorders and hormonal changes
Sometimes the symptom fades away against the background of system-wide disorders. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, you should also consider other possible symptoms that indicate problems with blood clotting or weakness of the vessel walls. In this matter, the only correct decision would be to rely on professional diagnostics from a specialist.
Among the factors that can trigger bleeding, experts identify the following phenomena and conditions:
- acute form of vitamin deficiency, for example, vitamin C deficiency,
- pregnancy period, against the background of hormonal changes in the body and weakening of the walls of blood vessels,
- constant exposure to nicotine smoke when smoking, which negatively affects the strength and elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, greatly thins them and makes them fragile,
- oncological pathologies and conditions arising during their aggressive treatment,
- hemophilia is a disease of the hematopoietic system in which the blood composition is characterized by a deficiency of certain coagulation proteins,
- diabetes,
- viral infections,
- autoimmune diseases,
- liver diseases.
This problem also occurs during pregnancy.
Bleeding is the result of a huge number of potential conditions, many of which are quite serious. If you notice such a symptom, it is better not to hesitate to consult a doctor.
Taking certain medications
The action of certain medications is aimed at thinning the blood, but sometimes this effect leads to bleeding. Usually the symptom disappears on its own, immediately after stopping the medication. But if the bleeding is pronounced and does not go away, it is better to consult a doctor.
Who should I contact?
Why gums bleed is discovered in dental clinics.
To make a diagnosis, you should contact the following specialists:
- Periodontist. He specializes in identifying the causes, as well as treatment and prevention of diseases of the tissues surrounding the tooth.
- Orthodontist. Determines the presence of dental anomalies and provides assistance in getting rid of them.
- Dental hygienist. His job is to carry out professional oral hygiene, mainly removing soft and hard plaque. The hygienist will provide training in the rules of dental care and give practical advice on choosing the necessary products in a specific clinical case.
- Orthopedist. Deals with oral prosthetics.
Only a dentist can cope with periodontal diseases
In the absence of specialized specialists, a dentist or dentist can provide professional assistance.
Your child’s gums are bleeding – what could be the cause?
In childhood, a fairly common diagnosis is gingivitis, the main manifestations of which are bleeding and pain. Usually the cause is insufficient oral hygiene, irregular teeth brushing, the presence of abundant plaque and dental deposits due to the abuse of sweets and carbonated drinks. All this leads not only to the development of caries, but also to inflammation of the mucous membrane. Another prerequisite is the period of eruption of baby or permanent teeth.
Poor oral hygiene leads to caries and inflammation of the mucous membrane
Another common cause of problems with teeth and gums in a child can be a traumatic incorrect bite; orthodontic treatment with the installation of a brace system will help correct the situation. Against the background of a cold and weakened immunity, stomatitis often develops - damage to the oral mucosa, which is accompanied by inflammation, the formation of plaque and ulcers, pain and bleeding. All these problems are completely solvable, but it is important to recognize disturbing symptoms in time and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Diagnostic features
In order to choose the right treatment tactics and provide an integrated approach to solving the problem, it is important to first conduct a competent and comprehensive diagnosis. X-ray examination is only one of the mandatory diagnostic measures, but far from the only one. The best option would be to undergo a computed tomography (CT) scan, which provides the most detailed and informative image in 3D format. With its help, the doctor will be able to assess the real current state of affairs, the condition of not only the soft tissues, but also the jaw bone.
3D diagnostics makes it possible to study the problem in more detail
In diagnosing diseases of the oral mucosa, be it gingivitis or periodontitis, a differentiated approach is also necessary. A comprehensive examination will help you understand what exactly became the “trigger” - poor hygiene or pathological disruptions in the body. Thus, to obtain answers to all of the above questions, the following activities are carried out in dentistry today:
- visual and instrumental examination allows us to assess the depth of periodontal pockets and the volume of deposits in both the supra- and subgingival areas,
- collecting information about the patient’s current condition, that is, communicating about complaints and accompanying symptoms,
- CT for a more accurate assessment of the condition of the periodontium and the degree of destruction of the jaw bone in the presence of atrophic processes,
- seeding of deposits from periodontal pockets for aerobic microflora and sensitivity to certain medications,
- blood tests for sugar, hormone levels and vitamins if necessary.
If it is not so difficult to determine the signs of gingivitis, because it is an inflammation of the upper layer of the mucous membrane with its redness, swelling and pain, then with periodontitis the pathological process spreads deeper into the periodontium and periodontium. Over time, inflammation reaches the ligamentous apparatus and leads to tooth mobility. In this case, the process is accompanied by the formation of voluminous periodontal pockets in which bacteria and food debris, plaque and dental deposits accumulate, which further aggravates the clinical picture.
Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis
Thus, periodontitis usually manifests itself with the following symptoms: aching pain while eating, bleeding, redness or darkening of the mucous membrane, especially in the area of the gingival papillae, bad breath due to abundant deposits in periodontal pockets and their suppuration, recession (lowering) of the level mucous membrane simultaneously with gradual atrophy, that is, destruction of bone tissue. Mobility as a consequence of disruption of the ligamentous apparatus occurs in the later stages of the disease. At the same time, the acute phase is also accompanied by a general deterioration in health, fever, and weakness. The appearance of at least some of these symptoms should alert you and become a good reason to seek professional diagnosis.
How to eliminate bleeding - treatment features
Before moving on to treating a symptom, you need to find out the cause of its occurrence. Adequate therapy is impossible without making an accurate diagnosis and identifying the original source of the problem. In any case, first you will have to undergo a professional cleaning procedure to remove plaque and solid deposits. Then anti-inflammatory therapy must be carried out. Let's take a closer look at the therapeutic and preventive measures that are universal and mandatory in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Comprehensive oral hygiene
An effective method for removing soft and hard plaque is professional cleaning using ultrasound, for example, the Vector device. If there are no dental problems, it is enough to undergo this procedure once every six months for prevention. But proper comprehensive hygiene should not be limited to just removing plaque and tartar - in fact, there should be a multi-step approach to cleansing the enamel and normalizing the condition of the mucous membrane.
Only complex treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s clinical picture, will help achieve a noticeable improvement in the condition of the gums, elimination of areas of inflammation and bleeding, and a pronounced whitening effect due to the removal of plaque and pigmented areas. Listed below are 5 main areas that are used in combination to cleanse enamel and improve gum health:
- removing deposits using a scaler - through a special tip, the device delivers ultrasonic waves and microvibrations, which together contribute to the destruction of tartar. At the same time, a small amount of cooling water is supplied to prevent overheating of the enamel, as well as to wash out crushed particles. To carry out this procedure, a laser can also be used, the action of which is based on light waves rather than vibration. The laser provides a targeted effect on problem areas, promotes the breakdown of deposits without harmful effects on the enamel and mucous membranes. Its use is considered more gentle without sacrificing quality and efficiency,
- air-abrasive cleaning with Air-Flow - carried out after removing solid deposits. It can be used as an independent technology, but with an integrated approach it always becomes an addition to ultrasonic or laser treatment. A jet of water mixed with tiny abrasive particles, the size of which does not exceed 14 microns (micrometers), is supplied through the tip under high pressure. The method helps to clean interdental spaces and other hard-to-reach places,
The photo shows the method of brushing teeth with the Air Flow system. - enamel polishing – the top layer of teeth has a porous structure. Composite materials also lose their density over time. Bacteria and coloring pigments accumulate in micropores. To level the enamel surface, polishing is carried out using special abrasive pastes. The individually selected product is applied using a brush with a rotating head,
- strengthening dental tissues - involves fluoridation by applying fluoride varnish in the form of a gel to the enamel. The product relieves sensitivity, strengthens the outer layer of teeth, forming a special protective film that prevents bacterial attack. To avoid damaging this film, experts advise refraining from eating or drinking for an hour after the procedure.
Fluoridation will help strengthen tooth enamel - restoration of gums: due to the removal of supra- and subgingival deposits, natural normalization of the mucous membrane occurs, since the main factor contributing to the development of inflammation disappears. As additional measures, the mucous membrane is treated with a special antimicrobial solution and covered with a soothing hydrogel that stimulates the regenerative functions of epithelial cells and tissues. A resorbable membrane is also fixed - collagen plastic, impregnated with extracts of medicinal plants. It effectively relieves inflammation, promotes compaction of soft tissues, and restores their strength and elasticity. The membrane dissolves on its own within an hour, so there is no need to remove it.
“For problems with gums, professional cleaning should be based on an integrated approach and nothing else. Removing plaque and tartar alone is not enough - comprehensive treatment is necessary, including the affected areas of the mucosa. We use both special membranes with natural ingredients and modern effective drugs that promote the regeneration and restoration of soft tissues. At the same time, not only complexity, but also systematicity is important. You should undergo comprehensive hygiene at least once every six months,” explains Victoria Nikolaevna Kashaeva, dental hygienist and expert in artistic restoration of teeth at one of the leading dental centers in Moscow.
It should be noted that against the background of inflamed periodontal disease, the accumulation of bacterial plaque occurs much faster and more intensely. At the junction of the tooth and the mucous membrane, periodontal pockets are formed, in which bacteria and food debris also accumulate. Removing deposits from there is much more difficult, and sometimes it is necessary to resort to more radical measures - closed or open curettage of the gums. In the first case, the doctor removes deposits from under the gums using special hook instruments - a simple method, but not very effective for pockets more than 5 mm deep.
The photo shows the closed curettage procedure
Open curettage involves cutting the mucosa, cleaning and treating the root area, polishing the root and then suturing after all manipulations. Accordingly, rehabilitation in this case will be more complex and lengthy, but the procedure is effective and guarantees a long-term result.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
Typically, the course of anti-inflammatory therapy lasts from 8 to 10 days. Carrying out therapeutic measures at home involves regular rinsing with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs, the use of special gels and ointments in the form of applications or by external use. After diagnosing and identifying the cause of the problem, the dentist will definitely explain in detail how to treat the inflamed tissues and what exactly to rinse them with. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs can provide a certain effect in this regard, but they can only be used after consultation with a doctor.
Gargling with medicinal herbs will help in treatment
“At one time I tried to rinse with oak bark, but, to be honest, I didn’t notice much effect. Moreover, I often forgot to do this, so the bleeding either went away or reappeared. Then the doctor advised me to buy Cholisal, and it really helped. As soon as I notice the first signs of inflammation, I immediately start rinsing..."
Elena_Mir., from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
The standard scheme comes down to treating the soft tissues of the oral cavity twice a day - morning and evening. It is also important to remember to rinse your mouth every time after eating. For minor inflammation in the initial stage, it is usually sufficient to use chlorhexidine at a concentration of 0.05%. If the symptoms are more acute, antiseptic solutions may be prescribed at a concentration of 0.2-0.25%. Doctors also often prescribe the use of “Cholisal” or “Parodontocide” gels.
Preparations for regeneration of bone and soft tissue cells
In advanced cases, when inflammation has already led to the development of periodontitis, there is a noticeable thinning of the mucous membrane and resorption of the jaw bone; special preparations are used to restore tissue. Thus, as part of open curettage, artificial bone material is often transplanted to replenish atrophied areas with the simultaneous use of bioactive materials that stimulate the growth of one’s own cells - BoneCeramic and Bio-Oss with a collagen membrane from Straumann or Creos from Nobel. Additionally, APRF membranes are used - they are created on the basis of the patient’s own blood, that is, platelet mass obtained from it.
The photo shows a protective membrane
To stimulate the regeneration and growth of mucosal cells, the drug Emdogain from Straumann is used. It has a cooling effect, helps normalize metabolic processes in mucosal cells, and ensures their saturation with nutrients. The product is applied to the cleaned root surface, where it forms an extracellular matrix, which, in turn, helps to launch natural regeneration processes. This is not a one-time procedure - it is performed on a regular basis throughout the course of treatment.
Toothpaste for sensitive gums
Self-hygiene necessarily involves the use of a special toothpaste, the components of which do not irritate the mucous membrane and do not provoke even greater swelling and bleeding. Before purchasing a product for sensitive gums, you must undergo professional cleaning at the dentist, and also consult with a specialist.
An additional remedy for the treatment of bleeding gums is a properly selected toothpaste.
Some of these pastes contain a high concentration of medicinal plant extracts: mint, echinacea, sage, chamomile, mineral salts and zinc citrate. All these components help eliminate signs of inflammation, relieve swelling and bleeding.
The right toothbrush
Many people make a common mistake when they notice that bleeding appears while brushing their teeth - they decide to stop hygiene procedures for a while in the hope that this will make the symptom go away on its own. You shouldn’t do this - on the contrary, you need to strengthen your hygiene and oral care. If after a few days the bleeding has not gone away and continues to worsen, then you should urgently consult a doctor.
During periods of exacerbation and treatment, it is better to give preference to a soft toothbrush.
If the disease is in the acute phase, you need to abandon the hard brush and prefer one with soft bristles. It is also not recommended to use it constantly - only for a while while therapy is ongoing. It cannot provide sufficiently thorough cleaning of the surface of the teeth and interdental spaces, but while the tissues are inflamed, it is better to use just such a brush.
Taking vitamins and microelements
If your gums start to bleed, this does not guarantee a serious dental problem. Perhaps the body is simply lacking something; there is a deficiency of some important vitamins and microelements. A lack of certain substances can lead to fragility of blood vessels and capillaries, which, together with poor oral hygiene, often leads to bleeding. This is especially true for vitamin C - if there is a deficiency, it is recommended to take it as part of a multivitamin complex. In this case, it is very important to strictly monitor the recommended dosage, since exceeding the norm can provoke the opposite effect.
Vitamins will help strengthen the immune system
Additional therapeutic measures
All of the above measures are universal and mandatory in the treatment of periodontal diseases. But if they are enough to eliminate the signs of gingivitis, then more radical measures are sometimes required to treat periodontitis and periodontal disease.
“Adequate treatment of periodontitis requires time and an integrated approach. This is a rather complex disease that is optimally treated in courses. Moreover, for each stage of pathology, our clinic has developed a separate treatment regimen - a complex, which includes all the necessary therapeutic and preventive procedures with an average perspective of a year. It is important to take into account not only the stage of periodontitis, but also the individual characteristics of the clinical picture of each individual patient. This is the only way to achieve the desired effect and stable remission,” comments Marina Igorevna Tarabanovskaya, dental therapist and periodontist at the Smile-at-Once clinic.
Along with the comprehensive prof. hygiene, closed or open curettage is carried out, sometimes with the implantation of osteo-replacement chips and correction of the gingival contour, as well as a course of plasmolifting (precise injection of autoplasma) and laser therapy is carried out to restore soft tissue cells. In advanced cases, antibiotics are prescribed, splinting of mobile teeth and removal of already destroyed ones, implantation and prosthetics are prescribed to restore the integrity of the row, but only after a full course of rehabilitation.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of bleeding gums you should:
- Brush your teeth regularly.
- After cleansing, rinse your mouth with chamomile infusion and clean water.
- Eat hard fruits (apples, carrots).
- Visit the dentist twice a year.
If bleeding gums are detected, it is recommended to contact a qualified specialist who will determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen. At home, inflammation can be eliminated with the help of medicinal decoctions and special toothpastes.
Why is bleeding gums dangerous?
Plasmolifting in the fight against bleeding gums
Today in periodontics, a relatively new method of gum treatment is actively used - plasma lifting. The essence of the procedure is the targeted injection of the patient’s blood plasma into problem areas, which, in turn, contains a high concentration of platelets. The technology is called Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF) - platelet-rich fibrin. Essentially, it is a protein that is always formed at the site of injured areas and promotes faster tissue healing. And platelets are blood cells that, when living tissue is damaged, form a kind of blood clot along the edges of the wound, thereby preventing further bleeding. Thus, the technique is based on stimulating the natural regenerative functions of living cells and tissues.
The photo shows the plasma lifting procedure
The procedure is indicated for gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease, as a maintenance therapy for pathologies of periodontal tissues, in the presence of voluminous periodontal pockets, and also as a preventive measure to prevent relapses of inflammatory processes. The technology looks like this:
- taking blood tests to identify possible contraindications - taken a couple of days before the procedure,
- on the appointed day, venous blood is taken from the patient,
- The tube is placed in a centrifuge, which literally separates the blood into its individual components. Plasma separation usually occurs within 15-30 minutes,
- The patient is given autoplasma precisely through injections.
The course of such injections usually includes from 2 to 5 procedures1. One session as part of the comprehensive treatment of periodontal diseases will cost the patient approximately 1,500 rubles. Before starting the course, it is important to undergo professional cleaning of plaque and stone, and possibly undergo curettage or flap surgery in the presence of deep periodontal pockets. By the way, PRF technology is actively used, including in implantology. So, for example, during the implantation of implants and the replanting of osteoreplacement material, PRF membranes are often sewn into soft tissues, which contribute to faster recovery.
List of sources
- Grudyanov A.I., Fomenko E.V. Etiology and pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal diseases. - M.: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2010. - 96 p.: ill.
- Nikiforenkov L.A., Ulashchik V.S. Conservative treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases // Dental Journal. 2010. - No. 1. - P.6-11.
- Grigoryan A.S., Grudyanov A.I., Rabukhina N.A. Periodontal diseases. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment: [guide for doctors] // Medical Information Agency, 2004. pp. 63–90.
- Karakov K.G., Zoloev R.V., Kasimova G.V., Sarkisov A.A. Periodontal diseases. methods of treatment, medicines // Stavropol, 2013. (2nd edition, updated). P. 187.
- Yudina N.A. Antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of periodontal diseases //Modern dentistry. – 2008. – No. 3. – P.11-14.
What to do if your gums bleed during pregnancy
The symptom often takes women by surprise at different stages of pregnancy. This is a common phenomenon that occurs against the background of high concentrations of estrogens, progesterone and prostaglandins in the blood, and can also be associated with severe toxicosis. Changes that occur in the hormonal background are only a predisposing factor, and the main reason is still the same - plaque and heavy deposits.
Regarding how and with what to treat gums during pregnancy, it should be noted that local therapy is practically no different from that prescribed to all other patients. Typically treatment includes the following:
- removal of dental plaque using ultrasound or hand instruments,
- anti-inflammatory therapy with rinses and medicinal applications,
- proper nutrition - try to avoid snacks, excessive consumption of sweets and carbonated drinks,
- proper self-hygiene - using a special paste for sensitive gums and a soft brush, rinsing the mouth after each meal, using an irrigator.
Treatment during pregnancy directly depends on the duration of pregnancy.
Treatment tactics largely depend on the duration of pregnancy. So, in the first trimester, that is, until the 55th day from the moment of fertilization, it is not recommended to carry out any serious therapeutic interventions. During this period, toxicosis and weakness usually manifest themselves especially acutely, so only emergency measures are omitted when the patient’s condition cannot wait.
Starting from the 55th day until the 6th month of pregnancy, that is, the second trimester is considered the most suitable for the treatment of any dental problems. In the last trimester, preventive measures can also be carried out, but not all. Thus, using ultrasound to cleanse dental plaque is contraindicated, as are more radical measures. Closer to childbirth, the sensitivity of the uterus increases significantly, which, under certain circumstances, can lead to premature birth.
Preventive measures - how to prevent the problem
All prevention of dental diseases is based on proper hygiene and maintaining oral health. In this regard, dental experts provide the following recommendations:
- You need to brush your teeth at least twice a day, with a properly selected brush and toothpaste,
- floss should be used after meals (only not during exacerbation of bleeding), and also rinse the mouth after each meal,
- for better cleaning of hard-to-reach places, you should purchase an irrigator and use it as part of your daily hygiene procedures,
- for prevention, you can use antimicrobial solutions for rinsing the mouth, gels and ointments to strengthen soft tissues, but only in consultation with your doctor,
- It is recommended to introduce into the diet foods high in vitamins and beneficial microelements, including fluoride and calcium. It wouldn’t hurt to take vitamin supplements from time to time.
A good oral care product is an irrigator.
If the first signs of a problem have already appeared, it is better to remove from the diet foods that are too salty or spicy, which have an irritating effect. It is worth limiting the consumption of smoked meats, monitoring the temperature of food and drinks, and avoiding sudden changes. It is also better to avoid foods high in sugars and carbohydrates - they contribute to faster plaque formation and bacterial growth.
To be able to recognize the problem in time and prevent its consequences, it is enough to take a responsible attitude towards the health of your teeth and oral cavity. It is important not to forget to visit the dentist regularly - at least twice a month, and also not to ignore the symptoms that signal the onset of a pathological process.