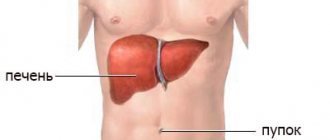
Most people know from school where appendicitis is located in a person. The appendix is located in the lower right side of the abdominal cavity, between the small and large intestines. The appendix collects a variety of small and solid parts of food that have not been digested. Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum is called appendicitis.
Causes and factors provoking appendicitis
Appendicitis does not select people; everyone is susceptible to it, regardless of gender and age . The exact reasons for its appearance have not yet been established - they are individual for each person, and it is impossible to single out a single cause for all patients. The main factors that can provoke this disease are:
- blockage of the appendix at the entrance to the rectum, which leads to inflammation of the walls of the appendix. It can be caused by various foreign bodies, poorly digested food, fossilized feces and the presence of adhesions;
- the presence of pathogenic bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci and E. coli), which, when the immunity of the appendix deteriorates, successfully penetrates the mucous membrane of the organ;
- the presence of fusobacteria in the appendix, which can lead to serious purulent-inflammatory processes in a very short time;
- intestinal diseases caused by infections and parasites (tuberculosis, typhoid fever).
- the body’s predisposition to frequent constipation (a polluted intestine is the best place to activate bacteria);
- unhealthy diet high in proteins and deficiencies in plant foods, overeating;
- abdominal trauma, heredity.
Functions of the appendix
Functions performed by the vermiform appendix:
- Secretory. The appendage secretes a secretion that affects intestinal motility and prevents coprostasis. 3–5 ml of biologically active substance is released per day.
- Contractile. The appendix contracts periodically, regardless of the rhythm of contractions of other parts of the intestine.
- Lymphocytic. Peak function is observed in adolescence. Every minute, a huge number of lymphocytes are released from the surface of the mucous membrane, which enter the venous blood. With old age, the walls of the appendix undergo sclerosis and the lymphatic tissue is destroyed. Until a person dies, the appendix remains a reserve of the immune system in an inactive state.
- Endocrine function. Performed during intrauterine development. From the moment of birth, endocrine function is taken over by the endocrine glands of the body.
- Production of immune system antibodies. The appendix is one of the links in the production of antibodies in the body's immune response.
- Participation in digestion. The shoot is involved in the digestion of fiber and starch.
- Maintaining the microbial background in the intestines. The appendix stores a supply of microorganisms that prevent food from rotting in the intestines.
Symptoms of appendicitis
The localization of severe pain during acute inflammation of the appendix will depend on where the appendicitis is located in a person.
Almost every person knows which side the appendix is on: in most patients it is located on the right side, between the navel and the ilium . There is an infrequent localization of the appendix in the lower pelvis or right hypochondrium . Well, very rare cases - the left-sided location of the organ in “mirror people” .
The attack begins with a dull pain (the main symptom) in the navel area, with frequent difficulty in determining its location. The wandering acute pain lasts up to 10-12 hours, and then the pain syndrome moves directly to the location of the appendix. Pain can also radiate to the hypochondrium, lower back, groin area and leg
Features of the surgical situation
Phlegmonous appendicitis is an acute pathological process in the area of the vermiform appendix - the appendix. The condition can occur in patients at any age, but more often manifest forms of acute abdomen are detected in children, adolescents, and pregnant women. The appendix is an adnexal process of the cecum and performs some useful functions for the body (preservation of beneficial bacterial microflora, participation in immune processes). Before you find out what phlegmonous appendicitis is, you should find out what stages of development the disease has. Appendicitis belongs to the field of study of abdominal surgery. Inflammation of the appendix is classified into several main stages of development:
- catarrhal (focal inflammation);
- phlegmonous;
- gangrenous;
- perforated.
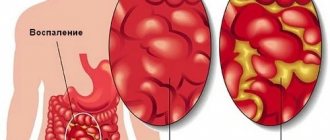
Image of inflamed appendicitis
Thus, phlegmonous appendicitis refers to the second stage of development of appendicitis. The clinical condition has a rapid course, which is characterized by an increase in pain and intoxication. The inflammatory focus literally melts the walls of the adnexal process, but for some time the appendix retains its integrity and does not allow the purulent exudate to spread beyond the cavity. Phlegmonous appendicitis develops already 12 hours after the onset of the catarrhal stage, and according to its symptoms it is considered a condition of “acute abdomen”. Almost 85% of all clinical cases of acute abdomen account for the occurrence of acute appendicitis, and the phlegmonous form of the condition occurs only in 40% of cases. Phlegmonous appendicitis, photos of which are presented in many medical sources, is a serious condition that requires immediate treatment.
Clinical stages of appendicitis
Due to the individual anatomical features of the location of the appendix, there are several clinical forms of this inflammation:
- Acute appendicitis: catarrhal (damage to the mucous layer of the appendix)
- phlegmonous (damage to the submucosal layer, accumulation of pus)
- gangrenous (necrosis of the walls of the appendix)
- perforative (destruction of the walls of the appendix, leakage of pus into the abdominal cavity)
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis);
Diagnostic measures
Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum is considered an acute condition, so diagnosis is carried out in a targeted and quick manner. So what is acute phlegmonous appendicitis and how to identify it? Diagnosis of acute appendicitis of the phlegmonous form consists of the following measures:
- patient complaints;
- study of clinical history;
- palpation of the iliac space;
- ultrasound examination;
- x-ray of the peritoneum;
- blood test (general, biochemical detailed).
The main task of differential diagnosis is to exclude other acute conditions associated with the abdominal organs:
- attack of cholecystitis (when the process is deviated upward);
- disease of the female genital organs and urinary system;
- renal colic (especially when the appendix deviates backwards).
Even if the patient’s clinical history suggests the likelihood of developing conditions with similar symptoms, self-medication in this case is considered unacceptable. To confirm an accurate diagnosis, you must consult a doctor. Acute phlegmonous appendicitis, a photo of which is presented in practical manuals on surgery, does not tolerate any alternative treatment methods other than surgery. Treatment of acute phlegmonous appendicitis is carried out only by surgery. In cases where appendicitis is still in the catarrhal stage of development, surgeons recommend urgent removal of the appendix. The surgical procedure to remove the appendix is called an appendectomy.
Surgery to remove appendicitis
The operation requires general anesthesia. There are three main methods of performing an appendectomy:
- abdominal incision of the peritoneum (open access);
- laparoscopic appendectomy (for localized inflammation without spreading beyond the appendix);
- transluminar removal (removal of the appendage through the stomach using special instruments).
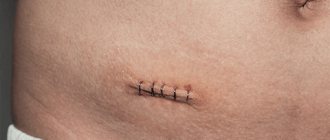
After the operation, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy. Sutures during abdominal surgery are removed on the 7th day. The operation to remove the appendix for uncomplicated appendicitis is considered to be relatively safe and simple. The recovery period involves following certain doctor's instructions for complete recovery of the body.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing inflammation of the appendix, palpation and visual inspection are used. In this case, painful sensations appear when pressing the lower abdomen on the right, the abdomen becomes tense, an increase in right-sided pain and when the patient turns over on the left side. But this does not always make it possible to accurately diagnose the disease.
Additionally, the patient is sent for a detailed blood and urine test (detection of elevated levels of leukocytes and ESR). If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, ultrasound, computed tomography and MRI methods are used. Diagnostic laparoscopy may also be performed - examination through an opening in the abdominal wall of the abdomen using a probe equipped with a camera.
There are additional studies that help carry out correct diagnosis in women:
- examination of the vagina with retention of the cervix (the diagnosis of appendicitis is confirmed if there is no increase in pain);
- pressing on the area below the navel while lying down (if the appendix is inflamed, the pain increases when standing up).
Signs of appendicitis in men can be diagnosed by spontaneous pulling up of the right testicle (Larocque's symptom) and detection of severe discomfort in this area when the scrotum is pulled back (Horne's symptom).
Difficulties in identifying appendicitis in children under five years of age are due to the fact that the symptoms of this disease in them are not as pronounced as in adults. Often, inflammation of the appendix can masquerade as an upset stomach. The child often cannot explain exactly where and how his stomach hurts. The main guidelines for determining the disease in this case should be diarrhea, high fever and coated tongue.
A characteristic feature of appendicitis in older people is the absence of pain, which is the reason for inaction on the part of patients and their late seeking medical help. Therefore, in this group of patients all kinds of complications of this pathology are very common.
Treatment of appendicitis
Due to the high likelihood of complications, treatment (removal) of appendicitis is performed exclusively surgically .
It is carried out immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, using incisions (laparotomy) or punctures (using endoscopic instruments).
For some types of appendicitis, laparoscopy is possible. If there are complications, all layers of the abdominal wall are opened.
Prevention
There are many simple and accessible methods to prevent appendicitis. Since appendicitis is a component of the digestive system, the main prevention of this disease is the establishment of a proper diet.
must be present in every person’s diet .
Thanks to its fibers, it serves as a cleanser for the intestinal walls, and therefore ensures that the appendix remains uncontaminated.
Your food should contain all kinds of fruits and fresh vegetables, mushrooms, legumes and greens. Also, do not neglect fermented milk products, which, thanks to their beneficial bacteria, will quickly help strengthen the immune system. But seeds and berries with seeds are undesirable components of your diet.
In addition, it is necessary to minimize the presence of constipation - one of the main causes of intoxication in the body. To do this, twenty minutes before eating, you should drink a glass of warm water. To this you need to add an active lifestyle, which will contribute to the proper functioning of internal organs.
To prevent appendicitis, it would not be amiss to change your drinking regime. It is worth drinking more pure water, herbal decoctions and infusions. Water perfectly rejuvenates the body and is an excellent way to cleanse the intestines.
Forecast
In general, the prognosis for the treatment of appendicitis is favorable. If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, complications after surgery are unlikely.
When treating the pathology at a later stage, inflammation of the appendix can spread to other internal organs or cause peritonitis. In this case, the body is exposed to mortal danger, and the nature of the prognosis depends on the condition of the body and the skills of the surgeons. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a timely examination and receive qualified medical care.
Rehabilitation period
Despite the simplicity and familiarity of the surgical procedure, the postoperative period must be treated with full responsibility. The doctor explains in detail to patients what recommendations are important to follow for a speedy recovery. The main doctor's instructions include the following:
- It's better to get out of bed after a few hours. Here it is important to understand the general condition of the patient, the presence of a complicated medical history, and the nature of the preoperative condition. Typically, patients go to the toilet on their own within 8 hours after surgery;
- breathing exercises, exercise therapy. Allows you to activate lung function, fill blood vessels with oxygen, activate muscle activity and rapid restoration of internal organs;
- special diet. Dietary food should contain a lot of fiber, vitamins, and microelements. Food should not contain aggressive ingredients (salt, pepper, spices and seasonings, fats). Nutrition should be entirely aimed at restoring the body’s previous resources, ensuring normal intestinal motility, and adequate stool passage;
- wearing a bandage. The postoperative wound needs fixation. For this, an ordinary wide bandage made of a sheet or thick tape will be sufficient. For convenience, you can purchase a special post-operative bandage at the pharmacy chain;
- dressings. Dressings should be done daily. During the procedure, the wound fragment is treated with antiseptic solutions, and the degree of healing of the postoperative scar is assessed.
If the sutures were placed subcutaneously with absorbable threads, there is no need to remove them. External sutures are removed on the 7th day if healing is favorable. For another 3 months after discharge from the surgical department, it is important to avoid strong physical activity.