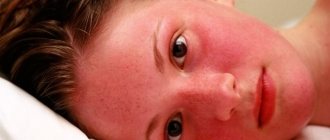
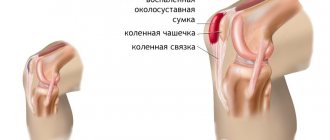
Hyperemia is a pronounced rapid flow of blood to the tissues, as a result of which a group of symptoms is formed: redness, a feeling of heat and itching at the local level.
Strictly speaking, this is not a disease. Such a diagnosis cannot be found in the ICD-10 classifier, which is considered the official list of pathologies.
We are talking about a symptom of various diseases: from damage to the endocrine system to disorders of the functioning of nervous tissues.
There are many accompanying symptoms that may indicate the cause. Taking into account the clinical picture allows you to quickly and accurately diagnose the essence of the primary pathology.
Treatment of the underlying disease makes it possible to simultaneously cope with hyperemia. Although doctors do not set such a goal, it is resolved itself during the course of therapy.
The symptom is not dangerous as such, but is extremely uncomfortable and poorly tolerated by patients.
Development mechanism
The named manifestation is complex in terms of the method of development. Because there can be many reasons. It would be more correct to talk about several ways:
- Mechanical dilation of the arteries as a result of drinking alcohol. The notorious action, which is assessed by the average person as useful. In fact, the hyperemia of the skin on the face is temporary; after 10-30 minutes it disappears, and vascular stenosis occurs. The opposite phenomenon.
- Compression of the arteries. As a result of the course of inflammatory and tumor processes. There are many options. In such a situation, normal blood circulation is disrupted.
- Allergic reaction, also inflammatory processes. In both cases, the excess amount of liquid connective tissue at the local level is due to the body’s desire to “drive” as many immune cells as possible with the blood in order to fight a real or imaginary threat.
- Disturbances in hormonal levels and through it the tone of blood vessels, which dilate too much and allow liquid connective tissue to pass through uncontrollably.
- Violations of innervation, and therefore regulation of the lumen of structures.
If we narrow the list of ways of developing hyperemia, we can talk about two mechanisms:
- Disorders of the arteries. As a result of one factor or another. Blood flows to the tissues in too large quantities. Which leads to the development of an unpleasant symptom.
- Insufficient speed and intensity of drainage of venous connective tissue.
The essence is approximately the same, but different types of vessels are involved.
Then everything proceeds according to an identical scenario. Excessive blood flow leads to a feeling of heat, itching, and an increase in local temperature.
Externally, the patient’s skin and mucous membranes change color to burgundy or crimson.
As was said, the condition itself is not dangerous; it is a sign of another pathological process.
It is necessary to identify the cause and carry out quality treatment. Because there are many diseases, some potentially fatal.
Hyperemia in children
Young children are even more prone to plethora, because their body reacts faster to adverse effects.
The delicate skin of a child is very sensitive, so the baby may develop heat rash at the slightest overheating. Hyperemia of the cheeks is observed during diathesis, sometimes this is the only sign of trouble. Redness with a small rash in a child may indicate rubella measles, however, measles itself is now, in general, not common, thanks to widespread vaccination.
The child’s body will react faster to high body temperature, which parents will already notice from the baby’s reddened face.
While crying, some children become very tense, and this causes a bright, pronounced redness to appear on the face, but this is physiological hyperemia, which quickly passes, as soon as the child calms down.
However, what may be a trifle for an adult can lead to serious problems for a child, therefore, if unexplained (non-physiological) hyperemia appears, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as high fever and rash, it is necessary to immediately call a doctor, because the range of diseases associated with plethora, in children is much wider.
Classification
Typification is carried out for a number of reasons. To be specific.
According to the criterion of the mechanism, the already mentioned two forms of violation can be distinguished:
- Arterial congestion is the result of excessive blood flow to tissues. As a rule, it becomes the result of vasodilation, deviations in the quality of tone regulation against the background of hormonal imbalance, pathologies or temporary disorders of the nervous system, and other issues. Occurs in approximately 60% of cases.
- Venous hyperemia is a consequence of insufficiently rapid outflow of liquid tissue from the skin and mucous membranes. It develops as a result of pathologies of the vessels themselves, less often against the background of other factors. Characterized by the same symptoms. It will be possible to differentiate the types only after an objective diagnosis.
- Separately, we can talk about induced forms of deviation from the norm. For example, vacant hyperemia is the result of a sharp drop in local barometric pressure.
A similar effect is observed, for example, after cupping therapy (the effect of vacuum). Such forms are almost always associated with the action of the person himself.
Another way of classification is localization. As a rule, the disorder affects the mucous membranes and skin.
To elaborate on this point, the following locations are distinguished:
- Skin hyperemia is a generalized type of disorder that includes all others. Accompanied by redness of the area, itching, a feeling of heat: characteristic manifestations.
- Damage to the limbs. Arms and legs suffer equally often.
- Redness of the mucous membranes. Nose, mouth, pharynx, genitals. The essence depends on the specific diagnosis and the severity of the pathological process.
- Hyperemia of the face or torso. Both a focal variant is possible (for example, only the face turns red), and a diffuse one: the skin tone changes throughout the body.
- Possible damage to the eyes (usually the conjunctiva). Internal organs (stomach and others, the phenomenon is detected during instrumental diagnostics).
Depending on the origin of the symptom, two more types of the disorder are called:
- Physiological. Has a natural nature. For example, after intensive rubbing of an area of the skin, thermal effects, changes in blood pressure due to physical activity.
This is a temporary manifestation that goes away on its own as soon as the provoking factor ceases to act.
- Pathological variety. The result of the course of a particular disease. There are many of them.
Separately, they talk about the collateral form. In which hyperemia covers the tissues surrounding the immediate site of the lesion.
The other option is local. Point areas. In this case, pronounced asymmetry and irregular coloring are possible, which clearly indicates the pathological origin of the phenomenon. Except for some individual cases.
We can also talk about local and general, generalized forms, acute and chronic types.
Attention:
All classifications are used to clarify the nature of the process and its more accurate documentary description.
Other types of plethora
In the literature you can find other types of hyperemia, although each of them will be mainly active in nature, local or general, pathological or physiological, acute or chronic:
- Medicinal – the use of certain medications causes hyperemia, sometimes quite pronounced, for example, nicotinic acid preparations;
- Toxic (the entry of toxic substances into the body sometimes causes hyperemia);
- Reactive is a temporary phenomenon, a reaction to a stimulus (physiological);
- Reflex – a reaction to a stimulus that came from the outside, and, unlike reactive, has a slightly different mechanism of occurrence;
- Functional or working occurs when the function of individual organs or the entire organism is enhanced;
- Artificial is used for medicinal purposes, for example, for venous stagnation;
- Post-ischemic occurs when blood flow is restored at the site of ischemia;
- Hypostatic accompanies heart failure.
And even here the classification of hyperemia does not end, since there are several more types associated with irritation of the vasodilator nerves or damage to the vasoconstrictor center.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of hyperemia itself is represented by a group of components:
- Pain syndrome of minor intensity. Feels like a tingling or burning sensation. Does not accompany all cases of violation.
- Local redness. The business card, which forms the basis of the deviation.
- Change in temperature of the area, its growth. The sign can be detected by simply touching the area.
- Itching. It is also relatively rare, only with the development of an allergic reaction or infectious, purulent or erysipelas of tissue.
- Swelling. Increasing the volume of the involved area.
However, hyperemia, as has been said, is not a disease, but just a symptom, albeit a complex one.
The condition must be assessed based on the accompanying moments. Which may shed light on the origin of the disorder.
Most often, redness affects four areas: the skin, mucous membrane of the throat, genitals, and conjunctiva.
For eye damage (conjunctival hyperemia)
The following manifestations are noted:
- Feeling of strong pain when blinking and focusing your gaze. The symptom intensifies with insufficient production of specific tear secretion.
- Dryness. It was as if sand had been poured in.
- Discharge of a large amount of liquid pus, which, as it dries, causes the eyelids to stick together.
- Decreased vision. Inability to focus your eyes.
These are signs of acute inflammation of the conjunctiva. The process may be infectious or allergic.
Skin damage
Regardless of localization. As a rule, the signs are varied; usually additionally noted is severe itching, burning of the dermis, the formation of papules, and rashes.
These are nonspecific signs inherent in a number of pathological processes.
Oropharyngeal dysfunction
- Nasal congestion. Inability to breathe normally. A person is forced to gasp for air, which affects the state of the respiratory tract, causing additional discomfort in the throat. Soreness and cough.
- Pain in the soft palate. Sensation of a foreign body, distension. These are signs of an inflammatory process.
- Severe pain of a pressing, raw or burning nature.
- Swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa. It can be dangerous because it often provokes disruption of normal breathing. And even asphyxia with critical tissue growth in volume.
Against the background of acute allergic reactions, the clinic unfolds rapidly and often ends with deadly signs. Against the background of infections, there is more time to respond.
- Upon visual assessment of the pharynx, it is hyperemic (reddened), mucus flows down the back wall, the tissue structure is loose and granular. Heterogeneous.
These manifestations are typical for pharyngitis or tonsillitis. Other pathologies. Diagnostics under the supervision of an ENT doctor and therapist, if necessary, puts an end to the issue.
Damage to the genital organs
Most typical for women.
The following points are revealed:
- Unbearable itching.
- Swelling of the genitals.
- Pronounced redness. The mucous membrane is hyperemic, this can be detected with the naked eye, in other cases with a visual assessment everything becomes obvious.
- Pathological discharge of a transparent, cheesy or purulent nature with a strong unpleasant odor. They are especially common in venereal diseases.
- Also an increase in temperature and symptoms of general intoxication.
The signs are typical for colpitis and other disorders.
In all cases, a private clinic is found. Hyperemia of the skin is nonspecific and provides the least information.
A “universal” pathology is considered to be an allergic reaction in a specific form (urticaria, Quincke’s edema).
Because against the background of an abnormal immune response, hyperemia of various localizations with a complete specific clinical picture may develop: pharyngitis, colpitis, eye damage: it doesn’t matter.
Nutrition and hygiene for redness
During treatment for skin hyperemia, doctors recommend that patients adhere to the principles of proper nutrition:
- Avoid foods and drinks high in sugar, salt, and spices.
- Minimize coffee consumption.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks and fast food.
- Make sure that foods you eat are not hot.
- Include as many vegetables, fruits, fresh berries and lean meats in your diet as possible.
- Steam or bake food in the oven.
- Refuse flour products in favor of cereals.
In addition to normalizing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, in order to normalize the appearance of the skin, the patient should follow the rules of personal hygiene.
Features of the procedures for existing areas of affected skin are:
- The need to wash only with warm water, while avoiding friction during the process.
- Do not use cosmetics with a high content of fragrances and fragrances.
- Regularly wipe the skin with soothing and protective creams, lotions, and ointments. When applying the product to the redness, avoid applying pressure or vigorously rubbing the injured area.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or outdoors during gusty cold winds.
Skin hyperemia is not a disease in itself, but its consequences may require drug treatment. Redness of various types is a reaction of the body to an internal failure, which must be identified immediately after detecting the symptoms of the phenomenon in question.
This is the only way to not only eliminate the disease at its initial stage, but also minimize the risk of maintaining skin defects for life.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Possible reasons
There are many development factors. The research could become a source for a large number of specialized works and monographs.
In short, the most common factors are:
- Infectious diseases. It doesn't matter what localization. The increased blood flow is designed to deliver more immune cells to fight the disorder.
- Allergic reaction. The mechanism is generally identical to the previous disorder, with the difference that the answer is false. There is no one for the defense forces to fight.
- Injuries. Bruises.
- Autoimmune diagnoses. The essence is inflammation, but not septic. Because there is no infection. The body attacks itself and its own cells as a result of a malfunction.
- An increase or jump in blood pressure.
- Heat stroke, overheating. Hot weather.
If we talk about natural reasons:
- Manual influence. Friction, massage. For example, to keep warm.
- Sexual arousal.
- Exercise stress.
- Stressful situation.
- Alcohol consumption. At the first moment. The face turns red, then possible hyperemia of the skin throughout the body.
- A sharp tilt of the body, a change in position in space. Observed as a result of rapid correction of hemodynamics and blood flow.
- Smoking, especially with little experience of consuming tobacco products. Not everyone.
The assessment of causes is carried out in the system. To better understand the nature of hyperemia and the origin of the disorder.
Hyperemia of mucous membranes
What to do if your eyes are red? There's probably a reason for this. Perhaps this is a long stay at the monitor and the eyes “ask” for rest, or perhaps there is a disease. And this should be found out. Eyes may become red as a result of:
- Fatigue;
- Injuries;
- Hemorrhages (a ruptured vessel, which happens with high blood pressure or excessive stress);
- Inflammation (conjunctivitis, keratitis, iridocyclitis).
If everything is more or less clear with trauma and hemorrhage, then infectious and inflammatory eye disease requires special attention. If your eyes turn red, begin to water, and your eyelids stick together after sleep, then a trip to the ophthalmologist is inevitable. The eyes require serious treatment.
Hyperemia of the pharynx is a symptom of a wide range of diseases . A red throat is observed not only with sore throat (from catarrhal, when moderate hyperemia is noted, to phlegmonous, when it is pronounced). Soreness and hyperemia accompany the prodromal stage of influenza, adenovirus infection and pharyngitis. In addition, examination of the pharynx helps in diagnosing quite serious infections:
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- Corey;
- Tularemia;
- Listeriosis;
- Foot and mouth disease;
- Meningitis.
Some blood diseases (acute leukemia, agranulocytosis) cannot do without hyperemia of the pharynx.
Diagnostics
It takes place under the supervision of a specialized specialist. Which one exactly depends on the likely provocateur. The examination begins with a consultation with a therapist. He gives the necessary recommendations.
An approximate list of future events:
- Oral interview with a person. To understand what complaints there are besides redness.
- Anamnesis collection. To determine the possible cause of a pathological deviation. Bad habits, lifestyle, the presence of current diseases, and already diagnosed diagnoses are examined. Everything matters.
- Assessment of the skin, examination of the mucous membranes. Palpation if necessary.
- Damage to the dermal layer involves taking a sample or scraping for bacteriological examination. Detailed imaging may require the use of a special magnifying device. A specialist of the same name deals with skin problems. Dermatologist.
- Throat swab for laboratory testing. Sowing. Identification of specific infectious pathogens. Used in the practice of ENT doctors. Other techniques are prescribed as needed. As a rule, everything is obvious and understandable. It remains to clarify some points.
- Complete gynecological examination.
As part of advanced diagnostics, angiography and ultrasound examination are performed to determine the speed and quality of blood flow.
Why should you see a doctor?
If hyperemia is the result of a serious illness that is accompanied by headache, difficulty breathing, chest pain, dizziness, muscle cramps, and sometimes even loss of consciousness, it is vitally important to consult a doctor immediately.
First you need to call an ambulance team. Where competent specialists will take emergency measures and take care of preserving human life. In the future, you need to visit a dermatologist who will conduct a diagnosis, identify the cause of hyperemia and take measures to eliminate it.
Treatment
The method of treatment depends on the specific diagnosis. There is no need to eliminate hyperemia itself, and there are no effective methods. Unless you apply cold to the affected area to provoke vasoconstriction, reduce blood flow and discomfort.
Other situations are varied.
ENT pathologies of infectious origin require the use of a group of drugs:
- Antibiotics. Strictly those to which the flora is sensitive. Accordingly, without bacteriological culture there is no point in prescribing them.
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin. Nimesulide, Ketorol.
- Antiseptic rinse solutions. Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. Regular Furacilin is also suitable. It is better not to use soda and salt. They dry out the mucous membranes.
- Antipyretics if necessary. Based on ibuprofen (Nurofen, etc.), Paracetamol is also suitable.
Gynecological diseases require the use of identical medications. Paradoxically, the basis of the violation is the same.
The same is true for other infectious conditions. Only the methods and forms of local preparations differ: solutions, ointments, drops.
Allergic reactions require the use of antihistamines. There are three generations of them in total.
The first is the most powerful, short-acting. Causes a lot of side effects (Suprastin, Pipolfen, Diphenhydramine, others). Third - with a mild effect, they work several times longer (Citrine and analogues). The second are intermediate, but can seriously affect the heart.
In severe cases, glucocorticoids are prescribed. Dexamethasone, Prednisolone to eliminate inflammation.
Autoimmune processes require the administration of cytostatics. These medications are extremely difficult to tolerate. Their main area of application is cancer processes. To reduce the rate of division of “fast cells”.
These include specific immune structures. Additionally, the same glucocorticoids are prescribed.
There are plenty of options. But the task is to eliminate the root cause. Not the symptom itself.
How to treat hyperemia?
Hyperemia itself cannot be cured if the disease of which it is a symptom is not treated.
Allergies are treated with antihistamines (anti-allergic) drugs, infections - with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of emotional lability, measures are taken to strengthen the nervous system and reduce its excitability. In a word, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause of plethora.
Prevention
To prevent the sudden formation of red eyes, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- spend less time on electronic gadgets, read in moderation;
- spend more time in open space, where the eyes do not need to get used to nearby objects;
- take vitamins, harden yourself to support the immune system;
- Visit an ophthalmologist annually to prevent the development of many serious diseases.
Preventative measures will not completely eliminate the risk of redness, but they will significantly slow it down.
Complications
If the causes of redness are not eliminated in time and treatment is not started, the following adverse reactions may occur:
- the spread of a bacterial or viral infection into the lacrimal sac, conjunctiva, cornea and inside the eyeballs;
- spread of a bacterial or viral infection into the nasopharynx, which can cause sinusitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis;
- gradual decrease in visual acuity;
- inflammatory condition of the eyelids, cornea, eyelids, conjunctiva.
The formation of complications can be easily prevented with timely therapy.