The surface of our body, every organ and cavity is lined with epithelium - a layer of cells that protects the body's tissues from external influences. The epithelium of the skin, having served its term, dies, gathers into keratinized scales and disappears.
At the same time, the epithelium lining the mucous membrane of internal organs should not have this property. However, sometimes, for reasons that are still unexplained, it begins to form a stratum corneum. The neoplasm interferes with the functioning of the organ, causes inconvenience, and the most dangerous thing is that in 20% of cases a malignant tumor forms at the site of the abnormal growth.
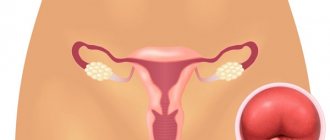
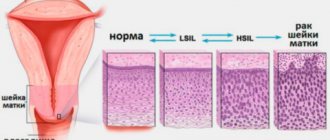
A keratinized layer of squamous epithelium located in an atypical location is called leukoplakia. The cervix is one of the most common locations of this pathology.
Causes of cervical leukoplakia
Among the many reasons that can trigger the development of a pathological process, three main groups can be distinguished:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. Diseases that tend to recur deplete squamous epithelial tissue and undermine the immune system. In 50% of cases, the occurrence of cervical leukoplakia is preceded by inflammatory processes in the uterus and appendages, human papillomavirus, and sexually transmitted infections.
- Hormonal dysfunction. Increased production of estrogen disrupts metabolic processes in the stratified epithelium of the female genital organs. Thus, in women with menstrual irregularities, cervical leukoplakia occurs 10% more often than in those whose menstrual rhythm is constant.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the cervix. This could be abortion, frequent childbirth, the consequences of surgery, the use of barrier contraceptives, or sexual intercourse performed with the use of physical force. Microtraumas occur even when sanitary tampons are used incorrectly. If microdamages are restored incorrectly, this forms pseudo-erosions. Against the background of which leukoplakia subsequently develops.
Systemic diseases also contribute to the occurrence of leukoplakia. For example, autoimmune or endocrine pathologies (in particular, diabetes).
Medicines
Photo: kak-bog.ru
In the presence of an infectious disease of bacterial etiology, antibiotics are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at destroying pathogenic microorganisms. As a rule, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are used, since they are effective against both gram-negative and gram-positive microflora. While taking antibacterial agents, various undesirable effects may appear, but the most common side effects are from the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea). As is known, taking antibacterial agents affects the quantitative composition of the normal microflora of the intestinal tract, which is why in some cases probiotics are additionally prescribed.
In case of herpes infection, acyclovir is prescribed. The dosage of the drug and the frequency of administration are determined by the attending physician, based on the severity of the process and the severity of clinical manifestations. While taking the drug, the following side effects may occur: periodic discomfort in the epigastric region, nausea, occasionally vomiting, increased stool frequency. It is also worth noting that while taking acyclovir, it is important to monitor creatinine and urea levels, since this drug is known to have a detrimental effect on kidney function. Accordingly, people suffering from chronic kidney disease are advised to refrain from using this drug or to more carefully monitor laboratory parameters to assess kidney function.
Antifungal drugs (fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole) have a fungicidal or fungistatic effect and are used for the treatment and prevention of mycoses. The most common undesirable effects that occur while taking antifungal drugs are: periodic discomfort or pain in the abdomen, heartburn, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, occasionally vomiting, flatulence, constipation, dry oral mucosa.
In the presence of an infectious-inflammatory disease of the reproductive system, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac) are prescribed. The mechanism of action is to inhibit the enzyme COX (cyclooxygenase), as a result of which the synthesis of prostaglandins is disrupted. Thanks to this mechanism of action, not only an anti-inflammatory effect is achieved, but also an antipyretic and analgesic effect. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used with caution by people with gastrointestinal diseases, since long-term use of these drugs, especially in large doses, leads to damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia
Leukoplakia does not hurt, but only causes some inconvenience. Symptoms and signs of cervical leukoplakia , as a rule, are not pronounced. Women do not associate the appearance of profuse and unpleasant-smelling leucorrhoea and spotting after sexual intercourse with possible leukoplakia. Moreover, most people are not even aware of the existence of such a disease. Most often, cervical leukoplakia by chance, during the next gynecological examination.
According to its structure, the disease can be:
- Simple cervical. With it, keratinization of the surface layer of the epithelium is clearly visible, but its cellular structures are not changed. This is a disease that at this stage does not have cancerous changes. Women who are wondering “ What is simple leukoplakia of the cervix?” “They mean specifically cervical leukoplakia.
- Proliferative. In this case, the structure and differentiation of all layers of the affected tissue are disrupted, and there are atypical cells. In fact, this is a precancerous condition of the cervix.
- Erosive. Forms cracks and areas of erosion.
- Warty. The formation rises above the epithelium, has a dense structure, individual areas are layered on top of one another.
Classification
According to morphological criteria, cervical leukoplakia is divided into two types: simple or proliferative.
- Simple cervical leukoplakia is a background change in the epithelial layer, representing parakeratosis or hyperkeratosis. This form of pathology is characterized by pronounced keratinization and thickening of the surface epithelial layer, but the parabasal and basal cell structures do not change.
- Proliferative leukoplakia - this pathological variety is characterized by impaired differentiation, proliferative changes in all tissue layers and the presence of atypical cellular structures. The proliferative form is classified as a precancerous condition; it is also called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical dysplasia.
Diagnostics
Leukoplakia of the cervix is clearly visible during a routine examination in a gynecological chair. Overgrown squamous epithelial cells appear as white, clearly visible spots.
The doctor’s task is to determine the type and size of the cervical lesion. And also evaluate the possibility of their degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
To do this, the patient will need to be given the following tests:
- General blood and urine analysis. This way the doctor will determine whether there are inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Blood chemistry. Elevated levels of sugar or protein indicate metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalance;
- Blood test for hormones. These data will indicate the nature of the ovulation cycle and the duration of menstruation;
- Blood test for tumor markers and hidden infections;
- Bacteriological analysis of a smear from the cervix. Necessary for assessing the state of microflora.
- Biopsy of affected tissues and their histological analysis. This will detect abnormal or cancerous cells, if any.
In addition, the gynecologist will conduct a colposcopic examination of the cervix, and an ultrasound doctor will examine the structure and shape of the pelvic organs and possible foci of the inflammatory process.
What it is?
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a condition in which its epithelium acquires a property uncharacteristic for this place - keratinization.
In a healthy woman, only skin cells are normally subject to this process - they are exfoliated and thus renewed. An abnormal property can appear not only in the cells of the squamous epithelium of the cervix, but also in the vagina, perineum, and oral cavity. The danger of leukoplakia is that its presence increases the likelihood of cancer developing in this area several times.
Leukoplakia is a precancerous disease. However, timely detection and treatment will avoid such disastrous consequences. Reviews from women who have suffered this illness confirm this. In each specific case, therapy is selected individually. For some, cauterization of cervical leukoplakia is suitable, while for others, laser or liquid nitrogen is better.
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia
In 99% of cases, leukoplakia is completely cured. If in the future the woman eliminates all risk factors, the disease will never return. But when attention to one’s own health is not enough, leukoplakia can relapse. According to statistics, in 15% of cases, it degenerates into a malignant tumor.
Simple leukoplakia is treated by a gynecologist, and his goal is to eliminate underlying diseases and eliminate the pathological proliferation of the cervical epithelium.
If the examination reveals atypical cells, treatment will be carried out by a gynecologist-oncologist. He needs to completely eliminate the foci of the disease.
For drug therapy use:
- antibiotics - in case of concomitant genital infections or inflammations;
- antiviral drugs if the disease is aggravated by the herpes or papilloma virus;
- immunomodulators from the interferon group and biological additives. They increase the body's defenses.
But using folk remedies, oils and homemade lotions is dangerous. They can strengthen keratosis, this will provoke the appearance of atypical cells.
In case leukoplakia needs to be removed surgically, the doctor will choose from the following methods:
- Cryodestruction. Treatment with liquid nitrogen. The procedure is painless and leaves no scars.
- Laser therapy. Expensive but very effective method. Treatment with a narrowly directed laser beam is painless, non-contact and protects against infection.
- Treatment with radio waves. A non-contact and painless method, the affected area is treated with radio waves of a certain frequency.
- Chemical treatment with acid solution. The procedure is painless, but is effective only for superficial leukoplakia.
After treatment for simple cervical leukoplakia, as well as more complex forms, is completed, the patient must undergo colposcopy every six months, take a smear for oncocytology and the infection that provoked the pathology. If the disease has not returned within two years, the woman is considered cured.
How does pregnancy proceed with leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia does not prevent pregnancy in any way. The presence of thickened cervical cells also cannot harm the development of the fetus. But the mother’s body is in serious danger during pregnancy - changes in hormonal levels can lead to the degeneration of leukoplakia into a malignant tumor.
Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, it is important to cure the disease.
If it was discovered during pregnancy, treatment will begin after birth. Leukoplakia does not interfere with the natural birth process. And only in rare cases of particularly intense growth of the stratum corneum will a cesarean section be performed.
I. BACKGROUND PROCESSES
- Hyperplastic processes associated with hormonal disorders:
- a) endocervicosis (simple, proliferating);
- b) polyp (simple, proliferating, epidermal);
- c) papillomas;
- d) leukoplakia (without atypia);
- d) endometriosis.
- Inflammation:
- a) true erosion;
- b) cervicitis.
- Post-traumatic processes:
- a) ruptures;
- b) ectropion;
- c) scar changes;
- d) cervicovaginal fistulas.
Prevention of leukoplakia
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a dangerous pathology. Her treatment is a long and complex process. Therefore, it is important to follow preventive measures and protect yourself from the occurrence of pathology:
- protect yourself from contracting sexually transmitted infections;
- avoid unprotected sexual contact;
- correct hormonal imbalances in a timely manner;
- undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist;
- avoid abortion;
- start treatment of inflammations and infections of the reproductive system in a timely manner.
Photo
With leukoplakia, white spots appear on the cervix, which are formed after structural changes in normal tissues. The affected area differs from the surrounding healthy area in color, increased dryness and lack of elasticity.
Below is what the disease looks like in the photo:
Similar tissue degeneration can occur in the vulva and clitoris area. There, a woman can easily notice pathological changes and consult a doctor in time. For early diagnosis of problems with the cervix, it is necessary to undergo annual examinations with a gynecologist and do colposcopy.