What kind of drug
Aspecard tablets are a derivative of acetylsalicylic acid. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and antithrombotic effects.
Available in packs of 100 tablets in a plastic bottle or 120 tablets in ten blisters. Packaged in a cardboard box, instructions for use included.
Refers to over-the-counter drugs.
What's included
Aspecard is produced in tablet form
which are white. They contain acetylsalicylic acid in the amount of 0.1 g. Auxiliary components - croscarmellose sodium, stearic acid, cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide.
The medicine is presented in pharmacies in a polymer container (100 pieces). There is also packaging in cardboard packages of ten blisters.
Each of them contains 12 tablets. Aspecard is produced by Ukrainian pharmaceutical company.
Pharmacological properties
Aspecard 100 tablets provide:
- antipyretic effect at elevated body temperature;
- anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect in rheumatic diseases;
- antithrombolytic effect in the treatment and prevention of blood clots.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
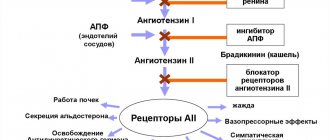
By irreversibly inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase, the union of prostaglandins is inhibited. Thanks to this process, the production of thromboxanes is reduced, the lumen of blood vessels expands and the gluing of platelets into clots is minimized. This increases the secretion of prostacyclins, which prevent platelets from attaching to the walls of blood vessels.
Excipients prolong the action of the main substance and reduce the local irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus.
Absorbed in the walls of the intestines and liver. The maximum concentration of the substance in the blood reaches 2.5-3 hours after administration.
It is excreted from the body by the kidneys and in small quantities through breast milk.
Combined effects of Aspecard
Acetylsalicylic acid has a number of effects that enhance or inhibit the effect of a number of drugs. In particular:
- ASA enhances the effect of any antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents;
- ASA enhances the antipyretic and analgesic effect of NSAIDs, enhances the antirheumatic effect of Meloxicam;
- when used together with cytostatics, it increases their gastrotoxicity;
- when taken with alcohol, the risk of developing complications of ulcers or bleeding increases;
- glucocorticoids increase the gastrotoxicity of Aspecard;
- ASA, when used together with diuretics, weakens the diuretic effect of Furosemide, Torsemide, and Spironolactone.
- "Aspecard" weakens the effect of uricosuric drugs: "Probenecid", "Etamide", "Sulfinpyrazone";
- Non-absorbable antacids significantly reduce the absorption of Aspecard.
Indications for use
According to the instructions, the indications for use of Aspecard are the following cases.
- To reduce the possible mortality of patients with suspected myocardial infarction, with a previous heart attack and in cases of stable and unstable angina.
- To suppress transient ischemic attacks and strokes in patients with TIA.
- In the treatment of myocardial infarction in people prone to developing cardiac and vascular pathologies due to diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity.
For prevention:
- thrombosis after surgical intervention on blood vessels - coronary artery and arteriovenous bypass grafting;
- deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism during prolonged immobility after surgery;
- recurrent stroke.
In higher doses it is used:
- to relieve elevated body temperature during colds and viral diseases;
- to relieve pain in rheumatic joints, toothache and headache, neuralgia, lumbago.
Instructions for use of the drug
The active substance of Aspecarda - ASA - belongs to the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with antithrombotic properties.
The effect of blood thinning is due to the effect on the adhesive (“stick” to the vascular wall) and aggregation (stick together) capabilities of platelets. Features of drug metabolism in the body:
- bioavailability (the amount of drug that is delivered to sensitive structures) - 40-50%;
- half-life from blood plasma – 20 minutes;
- the active substance begins to act a few minutes after absorption in the digestive tract;
- the maximum effect is determined in the portal system (vessels carrying blood from the intestinal wall to the liver).
“Aspecard” causes irreversible dysfunction of the platelet (for the entire life of the “blood plate”).
Indications
"Aspecard" is used to reduce the risk of cardiovascular "catastrophes" (stroke, myocardial infarction) for:
- acute coronary syndrome (ACS);
- rehabilitation of post-infarction patients;
- transient cerebral blood flow disorders (TIA) and stroke;
- angina pectoris: unstable, tension;
- diabetes mellitus type II;
- metabolic syndrome;
- obesity;
- hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- in elderly patients.
Indications for the use of Aspekard for preventive purposes:
- postoperative thromboembolism (with vascular interventions: transluminal angioplasty, endarterectomy, coronary artery and arterioveous bypass surgery);
- venous thrombosis and TELA (pulmonary embolism) in patients with forced long-term immobilization (immobilization after trauma, abdominal surgery, paralysis);
- prevention of repeated occlusions (narrowing of the lumen) of cerebral vessels.
Mechanism of action and composition
1 tablet of Aspekarda contains 100 mg of ASA. There is no strip on the surface of the drug, so it cannot be divided in half or chewed.
ASA, by acetylation, blocks the activity of cyclooxygenases (COX) in platelets. The pharmacological effects of the interaction are presented in the table.
| Effects | Clinical significance |
| Decreased synthesis of prostaglandin endoperoxides (PGH2, PGD2) | Blockade of the inflammatory cascade |
| Inhibition of thromboxane A2 and arachidonic acid production | Prevention of increased blood clot formation |
| Reduces the formation of prostacyclins | Expands the lumen of blood vessels, improves the rheological properties of blood |
| Stimulation of transcription in genetic material | Synthesis of anti-inflammatory mediators |
| Decreased ability to oxygenate lipoprotein complexes | Prevention of atherosclerosis |
| Increases ferritin synthesis | Increasing the oxygen capacity of the blood, improving iron metabolism |
| Induction of production and release of adenosine, P-selectin, endothelial growth factor | Anti-inflammatory effect |
The disaggregation effect of Aspecard is based on the inhibition of COX-1 of platelet membranes and the thromboxane activation mechanism.
Additional cardioprotective effects are due to the ability of ASA to stimulate the formation of proresolution mediators - substances that:
- eliminate signs of aseptic inflammation;
- promote tissue regeneration (restoration);
- influence the exchange of NO synthetase in the vascular endothelium with the subsequent release of nitric oxide, a molecule that expands the lumen of the arteries.
Acetylation of COX-2 changes the structure of the molecule, converting it into lipoxygenase. After enzymatic transformation, “aspirin-induced” lipoxin is formed, which has anti-inflammatory properties and enhances reverse cholesterol transport.
Increasing the dose of Aspecard does not affect the antiplatelet properties, but increases the risk of adverse reactions.
Directions for use and doses
The concentration of the active substance in Aspekard is designed for a single dose.
Recommendations for use:
- take the tablet 30 minutes to an hour before meals;
- drink plenty of fluids (to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects);
- use the drug in the evening.
The latter is explained by the circadian rhythms of platelet aggregation (peak activity occurs at 22 hours).
The standard dose for the prevention of cardiovascular accidents is 100-200 mg/day for 1 month with further revision of the dosage of the drug and the presence of indications for continued ASA therapy. Alternative regimen: 300 mg of Aspecard once every 48 hours.
Recommendations of the American Heart Association for ACS and unstable angina:
- start therapy with ASA at a dose of 150-325 mg as early as possible;
- transition to maintenance treatment at 75-150 mg/day.
Such a system reduces cardiovascular mortality by 23% from repeated myocardial infarction and by 50-70% from fatal arrhythmias in the acute phase.
To prevent recurrent strokes, it is recommended to start treatment with Aspecard 24-48 hours after the onset of symptoms. If the patient is planning to undergo thrombolytic therapy, the use of ASA should be delayed for 24 hours.
Contraindications and symptoms of overdose
The use of Aspecard is contraindicated for:
- hypersensitivity to ASA and other salicylates;
- aspirin-induced bronchial asthma;
- patients with a history of asthma attacks after using other NSAIDs;
- acute ulcers of the digestive tract (including Crohn's disease, colitis);
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- end-stage renal failure;
- severe liver dysfunction;
- high degree of circulatory failure;
- when taken together with Methotrexate at a dosage of more than 15 mg/week (the combination increases hematological toxicity);
It is not recommended to take Aspecard in the first and third trimesters of pregnancy. Up to 12 weeks, the use of high doses of ASA (more than 100 mg/day) increases the likelihood of arbitrary abortion and the birth of a child with developmental anomalies:
- gastroschisis - incomplete rotation of the intestine in the embryonic period with non-fusion of the anterior abdominal wall;
- “cleft palate” – a cleft in the hard palate;
- spina bifida;
- heart defects;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- hypospadias in boys.
In the third trimester, Acetylsalicylic acid provokes premature closure of the ductus arteriosus with the development of cardiopulmonary failure, kidney damage in the fetus, weakness of labor, postpartum hemorrhage, and the formation of cephalohematoma in the newborn. Low-dose ASA should be discontinued 4 weeks before delivery.
Long-term use of high doses of ASA is accompanied by the risk of chronic salicylate intoxication. Symptoms of drug overdose:
- vertigo (dizziness);
- noise, ringing, buzzing in the ears;
- dyspepsia (indigestion);
- migraine;
- increased sweating;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- acid-base imbalance (shift to the acidic side);
- hyperventilation, pulmonary edema;
- increased bleeding;
- renal dysfunction.
Therapy for “salicylicism” includes gastric lavage, sorbents, forced diuresis and correction of the acid-base state.
Treatment of hemorrhagic complications from the gastrointestinal tract is carried out in a surgical hospital.
special instructions
"Aspekard" is prescribed with caution to patients with:
- allergies to painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antirheumatic drugs;
- history of ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- with simultaneous treatment with direct anticoagulants (Heparin, Fraxiparin);
- circulatory disorders: renal vascular pathologies, congestive heart failure, massive surgical interventions, blood loss;
- lack of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzymes (high probability of hemolysis);
- liver failure.
The combined use of ASA with Ibuprofen enhances the antithrombotic effect.
In patients with gout, Aspecard causes an exacerbation of the process due to a delay in the excretion of uric acid.
The use of ASA during fever in children with acute respiratory viral infections provokes the development of Ray's syndrome (severe liver damage).
Long-term use of drugs containing ASA increases the risk of gastropathy. Therefore, parallel use of H2-blockers or PPIs (Ranitidine, Omeprazole) is recommended. Recent studies have shown that the combined use of ASA and nitrates equally reduces the risk of damage to the gastric mucosa, as do H2 blockers.
ASA is protected from the ulcerogenic effect by an enteric coating, which prevents the acid from affecting the stomach. In such forms, the onset of drug release is delayed by 2 hours, which is not suitable for providing assistance in emergency situations.
Contraindications
The use of Aspecard is prohibited in case of hypersensitivity to one or more components of the composition. The presence of the following pathologies is also a contraindication:
- acute liver or kidney failure, as well as impairment of their functions;
- hemolytic anemia;
- dysfunction of the coronary circulation;
- ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- thrombocytopenia;
- bronchial asthma, including those caused by salicylates;
- period of childbearing and breastfeeding;
- age up to 16 years.
Taking Aspecard tablets during anticoagulant therapy is also contraindicated.
Application of medicine
For Aspekard, the instructions for use from the manufacturer are a non-basic guide for the patient to therapy. It does not contain information about the use of the drug for various clinical manifestations, ranging from preventive measures for thrombosis and ending with acute changes in the blood flow of the heart and brain. These types of omissions are a dishonest attitude towards the production of medicines and accompanying information, and the recommended doses differ from each other.
The drug "Aspekard", like other secondary ASA, has an adverse effect on the stomach and intestines. Therefore, the peculiarities of use are that the tablets should be taken after meals, washed down with plenty of water. It would be better if it was a dairy product. This especially applies to patients who suffer from diseases of the stomach and intestines. The quantitative dose of the active substance in the tablets is selected so that only if taken correctly, it can reduce the adverse effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Patients with bronchial asthma should take Aspecard tablets with extreme caution, in particular if the medication is taken simultaneously with Coumarin or Heparin. For patients who are prone to allergic diseases, taking the drug can lead to the development of bronchial asthma
For patients who are prone to allergic diseases, taking the drug can lead to the development of bronchial asthma.
During long-term treatment with the drug, constant monitoring of the blood clotting rate, number of red blood cells, platelets, etc. should be carried out.
Directions for use and dosage
The dosage of the drug depends on the disease and severity.
In the presence of risk factors for the prevention of myocardial infarction, the daily dose is 75-150 mg.
In other cases, according to indications (repeated heart attack, NS, thromboembolic complications, stroke), 150-300 mg is used daily.
To reduce the risk in patients with TIA, 100 to 300 mg/day.
For the prevention of thrombosis after surgery, the daily dose is 100-200 mg.
The duration of the course is individual depending on the results of clinical examinations prescribed by the attending physician.
Description of the drug
The broad-spectrum antiplatelet agent Aspecard is a non-narcotic analgesic that not only prevents the formation of blood clots, but also has an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect.
This is because the drug contains acetylsalicylic acid, more popularly known as aspirin. Due to the fact that tablets with acetylsalicylic acid perfectly thin the blood in the blood vessels, they are successfully used in the treatment of hypertension or coronary heart disease, which can result in a heart attack or stroke without timely treatment.
Aspecard has been successfully used by doctors in the fight against blood clots for many years due to the fact that it prevents platelets from sticking together. Moreover, the effect of taking even one tablet lasts for 5-7 days.
Composition and forms
To prevent platelets, aspecard tablets are used, which have doses of 50, 75 and 100 mg of acetylsalicylic acid.
The dosage of the drug is calculated individually depending on the initial disease, its severity and the characteristics of the patient’s body. If for some reason it is impossible to consult a doctor, you must strictly follow the instructions for use included with the tablets.
For ease of administration, the drug is available in different packaging, that is, in blisters of 12, 24 pcs or in polymer containers of 100 pcs. Moreover, each release form has a certain dosage of the active substance necessary for treatment and obtaining a quick therapeutic effect.
Aspecard indications for use
Antiplatelet tablets are most often used for unstable angina and myocardial infarction.
In addition, it is indicated as a prophylactic drug for the following factors:
- prevention of recurrent heart attack;
- prevention of thrombosis;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- late stage hypertension;
- postoperative period, where the vessels were affected;
- atrial fibrillation;
- valvular heart defects;
- vascular diseases of the lower extremities.
Instructions for use of aspecard
Before starting to use Aspecard tablets, the instructions for use should be studied as much as possible in order to avoid side effects and negative effects on the body.
Tablets are prescribed with extreme caution to persons who have peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, since acetylsalicylic acid tends to corrode the internal walls in an unchewed form. As a rule, Aspecard is prescribed once a day after meals at the same time.
In case of a high risk of myocardial infarction, the doctor increases the dose to 2-3 tablets per day, while the duration of treatment in this mode should not exceed more than 3 months and no more than 300 mg per day of the active substance
As a rule, Aspecard is prescribed once a day after meals at the same time. In case of a high risk of myocardial infarction, the doctor increases the dose to 2-3 tablets per day, while the duration of treatment in this mode should not exceed more than 3 months and no more than 300 mg per day of the active substance.
When taking Aspicard75 tablets, the instructions for use should be studied by the patient for contraindications, according to which the drug is taken 1 tablet per day for 2-3 months.
Contraindications and side effects
Despite the fact that the drug is well tolerated by a large category of patients, aspecard contraindications include the following:
- peptic ulcer and erosive disease of the stomach and duodenum;
- decreased tendency to blood clot;
- severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- severe heart failure;
- tendency to frequent bleeding.
In addition to the listed factors, taking the medication is contraindicated during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, and during breastfeeding, as well as in children under 14 years of age.
Analogs
If treatment with acetylsalicylic acid is prescribed, this drug can be replaced with similar analogues.
Moreover, if you take Aspecard tablets and Aspecard analogues, their price ranges from 5 rubles to 150 rubles, depending on the dosage, additional substances and the country of manufacture.
There are the following analogues of Aspecard, which have similar descriptions and purposes:
- acetylsalicylic acid;
- Akard;
- Anopyrine;
- Aspirin Cardio;
- Acekor Cardio;
- Thrombogard;
- Ekorin;
- Lospirin;
- Cardisave;
- Chime;
- Ticlopidine;
- Integrilin.
If your doctor prescribes Aspecard, you can buy the tablets in any pharmacy in the country at a fairly affordable price when compared with analogues.
In childhood, during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Aspecard tablets are contraindicated during pregnancy, since acetylsalicylic acid quickly penetrates the amniotic fluid and can affect the intrauterine development of the child.
Breastfeeding is discontinued while taking the drug.
Due to the possible development of Reye's syndrome, Aspecard is not used in children and adolescents under 16 years of age, except for special indications.
Overdose of the drug Aspecard, symptoms and treatment
Mild intoxication may cause nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region, tinnitus, dizziness, headache, decreased visual acuity and hearing (especially in children and elderly patients). With a significant overdose, incoherent thinking, confusion, drowsiness, collapse, tremor, shortness of breath, an attack of suffocation, severe dehydration of the body (decrease in the buffer capacity of tissue fluid), hyperthermia, coma, alkaline reaction of urine, impaired core function (first respiratory alkalosis, then metabolic alkalosis) are noted. acidosis), carbohydrate metabolism disorders (decreased blood glucose levels). The lethal dose of acetylsalicylic acid for adults is more than 10 g, for children - 3 g. Depending on the state of the core and electrolyte balance, infusion solutions of sodium bicarbonate, sodium citrate or sodium lactate are administered.
Side effects
Instructions for use of Aspecard tablets warn of possible adverse reactions in the form of:
- stomach pain, nausea, heartburn, vomiting;
- dizziness, decreased hearing and vision, tinnitus;
- bronchospasm, rhinitis, sinusitis;
- swelling of the larynx, urticaria.
With long-term therapy with the drug, renal failure and increased symptoms of heart failure, hypercalcemia and edema may occur.
When used in childhood - the occurrence of Reye's syndrome.
Side effects
- from the hematopoietic system: increased frequency of bleeding gums, nosebleeds, hematomas (bruises), bleeding from the genitourinary tract or postoperative bleeding; possible - severe cases of gastrointestinal bleeding, cerebral hemorrhage (more often with arterial hypertension, concomitant therapy with anticoagulant drugs), including life-threatening ones; acute or chronic iron deficiency or posthemorrhagic anemia as a result of hidden bleeding (accompanied by symptoms such as pale skin, asthenia, hypoperfusion);
- from the digestive system: most often – abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, vomiting; rarely - ulcers of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum; very rarely - perforation of ulcers of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, gastrointestinal bleeding, increased activity of liver transaminases, transient impairment of liver function;
- from the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions - mild to moderate severity of reactions from the skin, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract and/or cardiovascular system (including skin rash, itching, urticaria, rhinitis, swelling of the nasal mucosa, Quincke's edema, cardiorespiratory distress syndrome); bronchospasm (asthmatic syndrome), anaphylactic shock and other severe reactions;
- from the central nervous system: possible - dizziness, hearing loss, headache, tinnitus.
special instructions
Due to increased coagulopathy and the risk of possible bleeding, the drug should be stopped a week before planned surgical interventions.
During treatment with Aspecard, to avoid undesirable consequences from the gastrointestinal tract, you should not drink drinks containing alcohol.
For elderly patients, the drug is prescribed in lower doses and at intervals between doses.
There was no observed effect of Aspecard on the ability to drive a car. But taking into account possible negative reactions, such as decreased hearing and vision, dizziness, safety measures must be observed.
Do not use a product that has expired.
Characteristics of reviews from specialists and patients
Patient reviews describing the drug Aspecard are in many cases biased. They positively evaluate the price of the medicine, since it is almost the lowest among its analogues. However, reviews regarding practical use are less indicative due to the inability of patients to assess the degree of reduction in the risk of vascular thrombosis. In terms of side effects noted by patients, the drug is characterized as quite safe.
The opinions of experts are clear: firstly, the drug effectively reduces the risk of thrombosis, and secondly, patient adherence to antiplatelet therapy is higher due to the low price of the drug Aspecard. Analogues in the class of antiplatelet agents are much higher. The domestic enteric drug “Acecardol” is 50% more expensive, while the cost of imported drugs is 7-10 times higher. But, based on the fewer side effects of enteric-soluble drugs, as well as on economic conclusions, it is advisable to give priority to Acecardol. The cost of monthly treatment will be about 20 rubles.
Overdose
With long-term use or single use of a large dose, the occurrence of clinical general toxic and gastrointestinal intoxication syndromes is possible. Treatment is symptomatic, taking absorbents and laxatives, drinking plenty of fluids.
In case of moderate intoxication, hospitalization is necessary.
Elderly patients over 65 years of age are at greatest risk. It is recommended to monitor the concentration of the active substance in the blood. Clinical analysis is carried out in laboratory conditions.
In more severe cases of poisoning - convulsions, acute pulmonary and renal failure, shock. It is necessary to immediately call an ambulance for further hospitalization.
Overdose and its signs
A mild degree of poisoning, which is caused by taking the drug not as prescribed by a specialist, is manifested by the following symptoms:
- dizzy;
- pain in the area of the pit of the stomach, around the navel;
- Possible lower back pain (often in people with kidney problems).
If you exceed the dose or use the medication for a long time, bleeding occurs in the stomach and intestines. Serious changes in the functioning of the kidneys and liver also occur. The larynx swells, azotemia, papillary necrosis, and aseptic meningitis develop.
In case of mild poisoning, the first thing to do is to induce vomiting using plenty of cold drink, taking activated carbon, enterosorbent, and also take the person to the hospital.
The instructions do not specify toxic doses of the medication. They differ depending on the age and height of the patient. The occurrence of a significant overdose in an adult is observed when consuming 7–9 grams of tablets, and in children – 2–2.5 grams. Overdose is manifested by such disorders as:
- confused thinking;
- noise in ears;
- slurred speech.
Frequent vomiting occurs, during which the patient loses fluid. His breathing quickens, acute urinary retention occurs, and his temperature increases.
With such symptoms, it will not be possible to help the victim on your own. It is necessary to take him to the hospital for infusion treatment with lactate, sodium bicarbonate.
In case of overdose, the following is also noted:
- salicylic syndrome;
- spasms;
- numbness;
- to whom;
- sharp degradation;
- swelling of the lungs;
- state of shock;
- renal failure.
Drug interactions
The drug Aspecard enhances the effect of oral antidiabetic agents, anticoagulants, and thrombolytics.
Reduces the effect of therapy with Sulfinpyrazone, Phenylbutazone, Spironolactone.
Combined use with antacids reduces the concentration of the active substance in the blood.
Taking Aspecard tablets with alcohol is incompatible, as the risk of gastric bleeding increases.
Analogues and substitutes
The original Aspecard is temporarily unavailable on the Russian market. The drug is produced at the request of Stirolbiopharm Baltikum LLC at factories located in different countries.
There are imported analogues of medications on the market—medicines with identical composition and indications for use:
- Akard (Poland);
- "Anopyrin" (Slovakia);
- "Aspirin Cardio" (Germany, Switzerland);
- "Godasal" (Germany);
- "Reocard" (USA);
- "Trombopol" (Poland);
- "Ekorin" (India).
The cheapest substitute for Aspecard is Acetylsalicylic acid. To prevent cardiovascular complications, enteric forms of tablet coating have been developed. The main goal is to minimize the adverse effects of ASA on the inner lining of the stomach. “Acetylsalicylic acid” is a product without the necessary protective “capsule”.
If there is no effect or intolerance, you can purchase substitutes for Aspecard at the pharmacy (medicines with a different composition but similar effects):
- "Cardiomagnyl" (Austria). Magnesium hydroxide in the composition provides additional protection for the gastric mucosa.
- "Clopidogrel", "Agrel", "Clodia", "Lopirel", "Plavix". The active substance blocks platelet ADP receptors, providing an effect similar to Aspecard.
- "Dipyridamole", "Curantil". The drugs block platelet phosphodiesterase.
There are combinations of ASA with indirect anticoagulants: Clopidogrel (Aspigrel, Coplavix) or Dipyridamole (Agrenox). These drugs are expensive and are indicated for use in the acute period of TIA or after an ischemic stroke.