Contrary to popular belief, urethritis is not only a male disease. It is equally widespread in both sexes, but in men it is diagnosed more often, along with prostatitis. This is explained by the fact that in women the symptoms are mild or completely absent. Unfortunately, this aggravates the disease, since strong signs are already observed in a fairly advanced, most often chronic stage. Urethritis is almost always associated with some kind of inflammatory and infectious disease of the genitourinary system. Of course, it is best to consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion or discomfort.
Symptoms and treatment of urethritis in women have their own specific features. With urethritis, the walls of the urethra (urethra) become inflamed. In women it is only 1 or 2 centimeters in length, but quite wide. You can look at a schematic photo on the Internet to better understand its appearance. The anatomical structure determines the ease of penetration of pathogens into the bladder and the absence of disturbances in the outflow of urine with significant swelling of the urethral mucosa. The disease occurs in close proximity to the rectal passage, which can cause the spread of infections and the occurrence of intestinal diseases.
Of course, urethritis is not a fatal disease, but it causes very unpleasant sensations that interfere with comfortable life. It is also dangerous for health complications. In women, two diseases often occur in parallel - cystitis and urethritis. Cystitis is the simplest complication of urethritis. Therefore, its treatment must be complete and timely - if the inflammatory process is started, an infection can develop, the complications of which are difficult to treat and are extremely dangerous.
Medicines for urethritis in women should have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. It is not recommended to choose a treatment on your own, because incorrect treatment will cause irreparable harm in the form of the development of resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to the drug. In addition, you cannot independently guess the causative agent of inflammation that caused urethritis. Doctors, knowing the peculiarities of the clinical course of the disease, rely on the results of urine tests. Only after them can you select effective pills for urethritis in women.
They have anti-inflammatory properties:
- antibiotics;
- sulfonamides;
- nitrofurans.
The doctor may prescribe the drug in the form of vaginal suppositories, tablets, solution for installing applications and ointments. The choice of medication depends on the type of disease and the severity of clinical manifestations.
What is Urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra. Its main manifestation is burning, stinging or pain when urinating, but at some stage of the disease the urethra begins to hurt constantly, day and night, day after day.
There is no need to confuse urethritis with cystitis - inflammation of the bladder. The manifestation of cystitis is frequent urination, or frequent false urge to urinate. Cystitis is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen or sharp pain in the urethra at the end of urination. With urethritis, the pain is strongest at the beginning of urination or the same throughout it. In addition, as already mentioned, the urethra can hurt constantly, without any connection with urination at all.
Cystitis and urethritis often occur simultaneously. At the same time, their manifestations can be equally pronounced, or the symptoms of one of the diseases can sharply predominate. In women, the symptoms of urethritis are less pronounced than in men and may go unnoticed altogether.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of urethritis is based on the patient’s complaints, the clinical picture of the disease and data from laboratory research methods:
- Analysis of urine sediment for the presence of leukocytes.
- Examination of a smear from the urethra to exclude gonococcal urethritis.
- Analysis of scrapings of the vagina and urethra for the presence of chlamydial infection, in some cases - examination of scrapings from the rectal area.
- Men are advised to undergo an ultrasound scan of the bladder, prostate and scrotum.
- Accelerated research methods are used - PCR and NASBA.
- When the disease progresses torpidly, the discharge is cultured on special media.
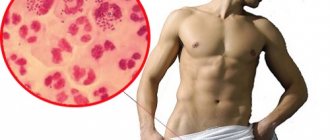
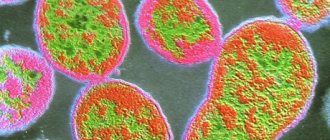
Rice. 10 and 11. The photo shows gonococci in smears (microscopy). Bacteria are usually located in bunches, reminiscent of a “swarm of bees.”
Who suffers from urethritis
Any woman can get urethritis. Moreover, it is a rare older woman who can say that she has never had similar symptoms in her life. Of course, the more predisposing factors, the greater the chance of developing urethritis, but there are so many of these predisposing factors, and they occur so often that literally any woman has a chance of getting sick.
Still, let’s list some of these factors here to make it clear what I’m talking about.
- Hypothermia - one-time severe or periodic not too strong, both can lead to the occurrence of urethritis.
- Sex life. The beginning of sexual activity under certain conditions becomes the beginning of suffering associated with urethritis. Violent sexual intercourse can cause symptoms of urethritis in any woman at any time. Women who suffer from urethritis for a long time usually note an exacerbation of urethritis after each sexual intercourse.
- Errors in diet. Hot, sour, salty, spicy, fried, pickled, bitter, alcoholic - all these substances enter the urine and, when released, irritate the urethra.
- Gynecological diseases. This is perhaps the most serious of all predisposing factors. Almost any disease in this area leads to disruption of the vaginal microflora and a decrease in local immunity. And any disease can thus lead to the development of urethritis.
- Urolithiasis disease. If crystals constantly form in the kidneys, they, released in the urine, can injure the walls of the urethra and cause symptoms of urethritis. Usually, sooner or later inflammation occurs, and severe urethritis develops.
- Medical procedures and interventions. A smear from the urethra in a woman can cause the development of urethritis. Catheterization of the bladder, cystoscopy - all this is familiar to women suffering from urethritis, and all this leads to an exacerbation of the disease, although it is carried out to treat it.
- Decreased immunity. In fact, all of the above is in one way or another connected with the immunity of the wall of the urethra, so there is little left to mention here. Pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding and the menstrual cycle are associated with changes in a woman’s hormonal levels, which cannot but affect the pelvic immune system and can lead to the appearance of urethritis without other visible causes. We will talk more about immunity problems with urethritis a little later.
- Toxic and radiation factors. This is already exotic and very rare. But I will tell you a case that my patient told me. In one respected and very expensive Moscow clinic (I do not give its name here, but if you ask me, I will not hesitate to name it) this lady was offered a course of physiotherapeutic procedures involving the insertion of an electrode directly into the bladder. The interesting thing is that the lady was treated exclusively for a gynecological disease, and why they needed to touch the bladder, I can’t imagine. After the first procedure, the lady developed such acute radiation cystitis and urethritis that all other problems were immediately relegated to the back burner. She had the prudence to refuse further procedures, and in this state she came to me. Fortunately, treating all diseases was not difficult.
Medications
Several drugs are used to treat urethritis in women. They have different directions of action: some suppress foreign bacteria, others strengthen the immune system, and others reduce the intensity of inflammation. Treatment of the disease depends on the type of pathogen and the presence of complications. For bacterial urethritis, antibacterial agents must be used. The most commonly prescribed groups of drugs are:
- Cephalosporins – Cifran OD, Cefoperazone, Cesoleks, Cephasin, Loraxim, Sefotak, Medaxone, Norakson.
- Macrolides - Azithromycin, Azax, Azimed, Azivok, Aziklar, Klabax, Clarithromycin.
- Fluoroquinolones – Clinafloxacin.
- Sulfonamides – Sulfazol, Urosulfan.
- Tetracyclines – Vibramycin, Doxycycline.
The choice of antibiotic is made taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms.
| Type of urethritis. | Group of antibacterial drugs. |
| Non-specific. | Cephalosporins, macrolides, sulfonamides, fluoroquinolones. |
| Gonococcal. | Macrolides, cephalosporins, rifampicin. |
| Trichomonas. | Metronidazole, ornidazole. |
| Candida. | Natamycin, nystatin. |
| Mycoplasma. | Tetracyclines. |
| Chlamydial. | Macrolides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones. |
Therapy is carried out with broad-spectrum antibiotics, the action of which is aimed at several groups of bacteria (gram-positive and gram-negative). After receiving test results, treatment adjustments are possible. One or two more drugs from another group may be added to the selected antibiotic. Antibacterial agents can be used in the form of capsules, tablets, powders, suppositories, gels, intramuscular and parenteral injections, and instillations into the urethra.
Antibacterial agents
The following antibiotics are taken in tablet form:
- Azithromycin 250 mg – for inflammation of the urethra, 1-4 tablets are prescribed per day (depending on the indications).
- Amoxicillin 250 mg - take 1 tablet 4 times a day. Sometimes the dose is increased to 2 tablets at a time.
- Gatispan - used in a dose of 200-400 mg. The product is taken once a day. The duration of treatment with tablets is determined individually.
- Klion is a drug containing metronidazole. A 250 mg tablet is taken in the morning and evening, the course is 10 days.
- Nitroxoline 50 mg - take 4 tablets at an interval of 8 hours. Treatment lasts from 10 days to 2 weeks.
- Safocid is a combination drug containing fluconazole (150 mg), azithromycin (1 g) and secnidazole (1 g). Each medicine is contained in a separate tablet (there are four in total). Safocid is drunk once an hour before meals.
Azivok (250 mg) can be purchased in capsules. Daily dose – 4 capsules an hour before meals. A single dose is indicated for chlamydial urethritis. Minolexin (100 mg) is produced in the same form. The medicine is prescribed 2 capsules in the morning and in the evening. The course of antibiotic treatment lasts 1 week. Capsules are consumed after meals. They can be washed down with water or milk. Pipemidic acid (200 mg) – prescribed for 10 days at a dosage of 400 mg in the morning and 400 mg in the evening. It can be administered intravaginally.
The following suppositories are used for urethritis: Trichopolum, Batsimex, Metrovagin. The active ingredient in Bacimex and Metrovagin suppositories is metronidazole. Use 1 suppository intravaginally at night. They eliminate specific pathogens of urethritis, such as chlamydia.
Urethritis of infectious origin is treated with the following parenteral antibiotics:
- Aznam J is a powder for preparing a solution of 0.5 g in a bottle. It is administered intramuscularly, intravenously and as an infusion. For urethritis, a single administration of 2 bottles is prescribed.
- Amovycombe – bottles for intravenous administration of 1000 or 200 mg. Use 1 bottle 4 times a day. The dose is repeated daily for 2 weeks.
- Bactrim – contains sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. It can be administered intravenously and intramuscularly. Daily dose 1 or 2 bottles.
- Bacimex - one bottle contains 500 mg of active ingredient. It is administered every 6 hours at a dose of 15 mg/kg.
- Vicef – contains 1 g of ceftazidime in a bottle. Use 250-500 mg of the drug per administration. The interval between injections is 12 hours.
- Doxycycline - 200 mg vials for administration. Used intravenously 1 time per day. When the condition improves, they begin to take Doxycycline tablets.
Chronic cystitis and urethritis begin to be treated only after determining the pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs.
Creams and gels are used to eliminate germs. They are inserted into the urethra (lower part) 2-3 times a day. Treatment of symptoms is carried out by the following means:
- Miramistin.
- Nefluan.
- Rosex.
Miramistin ointment is used for urethritis that accompanies sexually transmitted infections. 2-5 ml of the product are squeezed out of the tube and slowly injected into the urethra. The course of treatment is one week. Nefluan gel can eliminate the causes and symptoms of the disease. It includes substances such as neomycin, fluocinolone and lidocaine. Neomycin is an antibacterial drug and acts on almost all pathogens of urethritis. Lidocaine has an analgesic effect. Fluocinolone is a glucocorticosteroid that reduces inflammation and enhances the effect of lidocaine. Rosex cream has a good bactericidal effect. It contains metronidazole and is applied externally 2 times a day. Creams, ointments and gels are effective only in conjunction with the main treatment.
Preparations for restoring microflora
A new treatment method is the administration of bacteriophages. The most common representative is Sextaphage. It contains phagolysates of Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Klebsiella, Escherichia, Pseudomonas and Proteus. It can be used topically and orally. The solution is used for irrigation, lotions, and tamponing. If there is drainage, Sextaphage is inserted into the cavity of the bladder or uterus.
Probiotics have a good effect. For urethritis and cystitis, the following suppositories are used:
- Bifinorm.
- Lactozhinal.
- Vaginorm S.
Bifinorm is used in the treatment of urethritis. One bottle contains 10 million CFU of bifidobacteria. The drug is also available in suppositories. They can displace pathogenic microflora, activate metabolism and increase non-specific immunity. One suppository is administered in the morning and one before bedtime for 10 days. The bottles are used to prepare a solution that is used to moisten tampons. To dilute Bifinorm, you need to take 20 ml of boiled water (cold) and 5 doses of the drug. The tampon is inserted intravaginally and left for 2-3 hours. Duration of therapy is 10 days.
Drugs to strengthen the immune system
To increase immune strength, medications with vitamins and minerals are prescribed. It is more convenient to take them in ready-made complexes. For adults, you can use drugs such as Vitrum and Undevit. Vitrum includes 13 vitamins and 17 minerals. The drug is taken once a day after meals. Duration of treatment is 1-2 months. Undevit contains B vitamins, vitamin A, E, C and P. The recommended daily dose is 1 tablet. The drug is taken for a month.
The combination drug Genferon is often prescribed. It is produced in suppositories containing 1 million IU of human recombinant interferon-alpha, 10 mg of taurine and 55 mg of benzocaine. Vaginal suppositories are administered in the morning and evening for 10 days. For chronic urethritis, Genferon is used 3 times a week for 3 months. To maintain immunity, the effective drug Lavomax is used. It contains 125 mg tilorone hydrochloride. In the first two days, take 125 mg daily, then 1 tablet every other day. In total, you need to take 10 tablets per course. Taking immunomodulators also strengthens local and systemic immunity and ensures the fight against bacteria and viruses.
If cases of urethritis or other microbial diseases recur several times a year, the treatment regimen is supplemented with immunostimulants and immunomodulators.
Local impact
Instillations can help treat the cause of the disease. This is the infusion of liquid medications into the urethra or bladder. It refers to the local treatment of female urethritis, since the injected substances are not absorbed into the blood. A thin catheter is used during the procedure. For instillation into the urethra, the following antiseptic solutions are used: collargol, silver, methylene blue, trichomonacid 1%, antibiotic solutions.
For cystitis and urethritis, rinsing with antiseptics is carried out 1-2 times a day. Thanks to this method, it is possible to eliminate discharge of various types, avoid adhesions and stenoses, and restore the mucous membrane of a hollow organ.
Sitz baths are also used for local treatment. Medicines are dissolved in water, the temperature of which does not exceed 37-38⁰C. You can take baths until the liquid cools down. The skin is blotted with a clean towel or napkin. Rubbing the skin is not recommended. Sitz baths reduce muscle spasms, have an antiseptic effect, and reduce discharge from the urinary tract.
Other medicines
Taking a large number of medications can affect the functioning of the liver. To protect it from toxins, hepatoprotectors and antioxidants are used. Karsil Forte is available in capsules and contains milk thistle fruit extract. The standard dose is 1 capsule 3 times a day. It is washed down with plenty of water. Therapy lasts from 1 to 3 months. Phospholipids have a good restorative and protective effect. Livenciale can be purchased in 5 ml ampoules containing 250 mg of phospholipids. It is administered intravenously in a stream of autologous blood or drip in a dextrose solution. The duration of treatment and the drug are prescribed by the doctor.
To treat urethritis in women, drugs such as No-Shpa are used. It reduces pain and relieves spasms. At one time you can take 1-2 tablets of 40 mg. In case of severe spasm, 4 tablets are allowed. The drug is used as needed. For severe itching and redness, use antihistamines. These include Tavegil, Suprastin.
Treatment during pregnancy has its own characteristics. Antibacterial agents are rarely prescribed. Local preparations and herbal remedies are often used.
“When a diagnosis of urethritis is made, the sexual partner must be examined. If necessary, he is also prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy.
Treatment can last from 5 days to several months, depending on the type of urethritis, the severity of the process and the state of the immune system. Urethritis is common, especially at the age of 20-35 years. It is not dangerous, but significantly reduces the quality of life. Acute urethritis is treated at home. A follow-up examination with a doctor is carried out every 3 days. On the same days, blood and urine are donated. If purulent complications occur, hospitalization is carried out in a urological hospital.
How does urethritis develop?
I was able to divide the course of female urethritis into three stages. It is characteristic that any of these stages can last for a very long time and does not necessarily go into the next one. Or, on the contrary, it may be very short-lived.
Stage 1. It all starts with periodic exacerbations of urethritis. They occur infrequently and can be expressed in different ways, from minor manifestations to very severe ones. The point is that exacerbations pass quickly and nothing bothers the woman in the intervals between exacerbations. Most often, exacerbations are not so frequent as to force a woman to see a doctor, but even if she visits a regular urologist or gynecologist, everything will end with the prescription of mild antibiotics and will be postponed until the next exacerbation. As a rule, any antibiotics at this stage quickly relieve the exacerbation.
Stage 2. Exacerbations are happening more and more often, antibiotics are helping worse and worse. To relieve an exacerbation, only the most powerful and expensive drugs help. In the interval between exacerbations there are no (or almost no) symptoms, but a calm life has already been replaced by anxious anticipation. The woman begins to visit doctors. It all starts with a visit to a urologist and gynecologist at a district clinic, then through friends or to commercial medical centers. Various diseases are found and treated, a large number of different medications are taken, and nothing changes. You begin to limit yourself in many things - food, clothing, sex life. Life takes on clear stages - from exacerbation to exacerbation.
Stage 3 is the hardest. Remission of the disease actually does not occur; the woman feels either bad or very bad. The urethra constantly “aches” or “feels”, it hurts when urinating, and during exacerbations it constantly hurts. Antibiotics at this stage either bring significant and short-term relief, or have no effect, or even provoke an exacerbation. A woman begins to be afraid of the cold, tasty food, and sex life. My patients told me that during these periods they lost good jobs, their husbands left them, and they attempted suicide. To be honest, I still feel a little uncomfortable when I listen to these stories, and the only thing that consoles me is that now I can cure these women, I can give them back a normal life.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine can be a good addition to the main treatment. They can also be used during remission to prevent urethritis. Traditional medicine methods are safe, can be used for a long time, and can be used to treat adults and children.
To relieve inflammation in the urinary tract, the following plants are used: green chickweed, burdock, bay leaf, parsley, bearberry, lingonberry, cranberry, black currant, linden, thuja, chamomile, cornflower, corn, mint.
Before using any infusion or decoction, it must be cooled and large particles removed (pass through cheesecloth or a strainer). Herbal preparations can be taken orally, prepare baths, douche, and moisten tampons. The course of treatment ranges from 10 days to several months.
To prepare an infusion of green chickweed, take 1 teaspoon of the herb and pour 200 ml of boiling water. The solution must infuse for 12 hours. Then take it 1 glass 2 times a day. It is recommended to prepare a fresh solution every day. An infusion of blue cornflower is prepared in the same way. Use 2 tablespoons of the drug 2 times a day before meals. You can make fruit drink, juice from cranberries, mix them with honey, or eat whole berries. Drink 1 glass of fruit drink 3 times a day.
To make an infusion of blackcurrant, you need to put 3 teaspoons of its leaves in an enamel container and add 500 ml of boiled water. Drink the resulting solution as tea, 3-4 times a day. Parsley leaves are often used to treat urethritis. You need to take 1 teaspoon of herb and pour 500 ml of cold water. The solution is made in the evening, and can be taken in the morning. To reduce the symptoms of the disease, take 3 tablespoons of parsley infusion every 2 hours.
Linden is brewed as tea and drunk 4-5 glasses a day. It contains natural estrogens, so only women can drink it in such quantities. A decoction of burdock roots is prepared in a water bath. Take 10 grams of dry matter and add a glass of hot boiled water to it. Stir constantly over low heat. You can drink 100 ml of the decoction orally before each meal. The duration of treatment is 14 days. Burdock decoction can be used externally for compresses, irrigation, rinsing, and washing.
Herbal infusions and decoctions have anti-inflammatory, diuretic and antimicrobial effects. They cannot cure urethritis without antibacterial agents, but they speed up the treatment process and normalization of the microflora.
Causes and development of the disease
Let's now talk about the most interesting thing - why everything happens this way.
So, I would venture to say that all cases of urethritis in women are associated with a gynecological disease - a violation of the vaginal microflora, or vaginal dysbiosis. Dysbacteriosis is that instead of the normal microflora, some bacteria appear in the vagina in large quantities, which normally either should not be there at all, or should, but in very small quantities. This bacterium can also become a sexually transmitted infection - chlamydia, ureaplasma, trichomonas, etc., but most often it is either a mixed flora or an opportunistic pathogen.
I constantly hear the question - where does it (flora) come from there? I answer. The term "opportunistic" means that the bacterium becomes pathogenic, that is, causes inflammation, only under certain conditions. In fact, this only happens when there are a lot of bacteria, that is, when there are conditions for their reproduction. And in small quantities, all these pathogens are found in our body in a variety of places - on the skin, in the intestines, in the lungs, etc.
Numerous factors can lead to disruption of the vaginal microflora - hypothermia, gynecological diseases, antibiotic treatment, stress, unhealthy diet, etc. In my life, I have seen only a few women whose vaginal microflora was not disturbed, and I have never seen normal vaginal microflora in women suffering from urethritis or cystitis.
So, we have a pathogen in the vagina. It constantly enters the urethra and causes chronic inflammation. As long as the immunity of the urethral wall copes with the situation, no symptoms of the disease arise.
During sexual intercourse, a more intense discharge of microflora into the urethra occurs; in addition, sexual intercourse itself is a considerable load for the urethra. Therefore, exacerbations of urethritis are almost always associated with sexual activity. But not only with her.
Pathogenesis
The incubation period for non-gonoccocal diseases varies in length - from 1 to 5 weeks or more. There are cases of transient carriage, when pathogens remain in the lacunae and glands of the urethra for a long time without causing inflammation.
With venereal urethritis, infection, as a rule, occurs simultaneously with several pathogens.
Pathogens such as fungi and pyogenic bacteria cause inflammation due to a violation of the integrity of the urethral mucosa or its injury.
Morphological changes in the disease depend on the severity of the process:
- In acute and subacute urethritis, inflammation is diffuse in nature, the exudative component predominates and the integrity of some areas is impaired. There is leukocyte infiltration in the subepithelial layer and vasodilation.
- In the chronic course, proliferative processes prevail. Inflammatory areas are delimited, thickened and replaced by scar tissue, which leads to a narrowing of the urethra - strictures. The cylindrical epithelium undergoes metaplasia, papillomatous growths appear (in men, most often in the prostate zone).
- With traumatic urethritis, areas of damage and necrosis appear.
Rice. 6 and 7. The photo shows a normal view of the urethra in men: on the left - the anterior section, on the right - the posterior section (sperm tubercle - 1, lobules of the prostate gland - 2).
The role of immunity in the development of urethritis
As soon as the described situation develops, everything begins to be in the pathogen-immune balance. The immune system maintains the number of pathogens at a certain level, preventing them from developing further. This can go on for years and decades, and very often this is what happens. Moreover, a sharp sudden increase in the immune system may occur, and then the woman will think that the disease has gone away on its own. This happens extremely rarely.
But overall it is like a time bomb where no one knows when it will explode. Sooner or later, a failure occurs in the immune system, the number of pathogens increases sharply, and the disease enters a new stage. In addition, the woman begins to periodically take antibiotics, and antibiotics tend to reduce immunity. While the flora is sensitive to them, these processes seem to compensate for each other - when taking an antibiotic, immunity decreases, but the number of bacteria in the vagina also decreases. But when the microflora loses sensitivity to antibiotics, taking them either does not bring relief or even provokes an exacerbation.
Urethritis in women and sexually transmitted infections
Bacterial sexually transmitted infections, namely gonococcus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma and trichomonas, can cause urethritis when located on the wall of the urethra. They can also cause disruption of the vaginal microflora, against which various opportunistic microflora easily develop, which in turn causes urethritis. It turns out that sexually transmitted infections can cause inflammation of the urethra in two ways.
Treatment of urethritis due to sexually transmitted infections is no different from the treatment of ordinary urethritis. The only difference is the selection of drugs for antibacterial therapy.
Urethritis and urolithiasis
With urolithiasis, crystals, so-called salts or sand, constantly form in the urine. Excreted in the urine, they injure and irritate the wall of the urethra, causing symptoms of urethritis. If at this time all the above processes occur in the vagina, then an infectious inflammation will develop on the wall of the urethra. If not, then the symptoms of urethritis will periodically bother the woman, but usually not too much. But, as practice shows, sooner or later bacterial inflammation develops, and the course of the disease noticeably worsens.
Treatment of urethritis against the background of urolithiasis, among other things, aims to reduce the formation of salts to a minimum. This is greatly facilitated by increased drinking regimen and forced diuresis.
Complications of urethritis
We won’t have to talk about the complications of urethritis for a long time; there are very few of them. The most serious complication is the transition of inflammation of the urethra to the stage when it constantly hurts and no treatment can change it.
With urethritis, the inflammatory process can spread to the bladder, and then cystitis will develop. This happens very often; these two diseases constantly accompany each other. Further, the inflammatory process can spread to the kidneys with the development of pyelonephritis.
Long-term neglected chronic urethritis can lead to deformation of the urethra and the development of its stricture - narrowing. This is manifested in the fact that when urinating, urine is not released in a vigorous, cheerful stream, but with difficulty, as if overcoming an obstacle. Sclerosis of the bladder neck manifests itself in the same way, which sometimes develops with cystitis. But all this happens relatively rarely.
Other complications of urethritis are so exotic that they will not be discussed here.
Other therapies
Additional methods of treating urethral inflammation include:
- Physiotherapy. She suggests doing daily lotions or sitz baths for the genitals. You need to prepare a decoction of medicinal plants (chamomile, St. John's wort) and add it to the bath. Make lotions with the same solution, applying to the external genitalia. In the case when the urethra or bladder is inflamed, physiotherapeutic procedures are of great benefit and benefit in therapy.
- Lifestyle changes. You need to give up bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol) at least for the duration of treatment. Alcohol and nicotine provoke an exacerbation of inflammation and prevent healing: they make medications ineffective and inhibit organ recovery.
Treatment of urethritis in women
In the treatment of urethritis, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs that are active against the pathogen, and immunostimulating drugs, including multivitamins, are traditionally prescribed. Physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended, especially for urethritis complicated by cystitis. It is important to follow these dietary rules: drink plenty of fluids, avoid alcohol, spicy and spicy foods. For acute gonorrheal urethritis, a gonorrhea treatment regimen is applicable; local treatment involves the introduction of antiseptic solutions into the urethra.
If the patient's treatment was timely, the treatment outcome is favorable. Prevention of urethritis consists of maintaining personal hygiene, culture of sexual activity, timely detection and treatment of diseases that can cause the development of inflammation of the urethra.
What factors contribute to the disease?
In addition to the impact of a specific pathogen, the following factors influence the occurrence of inflammation in the urethra:
- hypothermia of the body;
- injury to the genital organs, disruption of innervation during surgery on the uterus and vagina;
- decreased immunity after suffering stress or serious illness;
- undermining the body’s protective function through poor nutrition and restrictive diets;
- consequences of alcoholism;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiencies;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases (tonsillitis, tuberculosis, sinusitis, caries, cholecystitis, adnexitis);
- diseases of the urinary system;
- pregnancy and menopause;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene.
How should treatment be carried out?
When treating chronic urethritis in women, three main tasks are solved.
1. Restoring the properties of the wall of the urethra. This must be done in any case, but this task takes on particular importance in severe cases of the disease, when inflammation is no longer directly related to infection.
2. Restoration of normal vaginal microflora. As long as there is a constant infection of the wall of the urethra with microorganisms from the vagina, urethritis will return again and again. There is only one way to interrupt this - to populate the vagina with the microorganisms that should live there. This is not at all easy to do; this part of the course of treatment cannot be standard and can only be selected individually.
3. Restoration of the immune system. When the vaginal microflora is disturbed, with prolonged inflammation of the urethra, and very often during attempts at treatment, the body’s immunity in general and the immunity of the bladder wall in particular suffers. If it is not restored, the treatment will not have a lasting effect. It is very important to constantly remember that general and local immunity are restored in different ways, in completely different ways. Limiting yourself to prescribing a weak immunomodulator is the same as doing nothing.
Prevention of urethritis
Prevention of urethritis is to minimize all factors that can lead to disruption of the microflora in the vagina and to a decrease in immunity. Let's list the main ones.
- Severe hypothermia.
- Hormonal changes: pregnancy, childbirth, abortion, menstrual irregularities, withdrawal of oral contraceptives, menopause, etc.
- Severe stress.
- Irregular sex life.
- Neglect of hygiene rules.
- Sexual infections.
- Treatment with antibiotics.
- Problems with bowel movements, both constipation and diarrhea. Especially if these problems are chronic.
- Irregular and unhealthy diet, lack of essential nutrients and vitamins.
- Sleep problems, regular lack of sleep.
Here it is appropriate to remember the rules of sexual hygiene, since failure to comply with these rules also contributes to the appearance of urethritis.
- You cannot move from anal intercourse to vaginal intercourse, from anal sex to caresses in the vaginal area.
- Try to visit the toilet before and after each sexual intercourse.
- Try to have a regular sex life without episodes of prolonged abstinence and, on the contrary, excessive activity.
- Never forget about contraception and STD prevention. It is best to combine a condom with antiseptics or spermicides. Don't forget that STDs can be transmitted through both oral and anal sex!
- Even if there is no reason, you should visit a gynecologist and get checked for STDs every six months.
Predisposing factors are so common in the life of any modern person that it is completely impossible to exclude them. Therefore, all that remains to be done is to be regularly observed by a doctor, and if the slightest deviation is detected, carry out preventive treatment. I can say with confidence that prevention is much easier and more enjoyable than treatment.
Forms of the disease
According to the clinical course, there are two forms of urethritis:
- An acute form with a clearly and clearly defined clinical picture at the initial stage of the disease. At this stage, the first symptoms appear, which should be a signal to immediately consult a doctor (urologist). Inflammation of the canal membrane, detected within 20 days from the onset of formation, can be quickly and successfully treated.
- The chronic form of urethritis is a consequence of the acute form, at the stage of which the symptoms are ignored, the disease is not identified and drug treatment is not prescribed. After 20 days, the disease passes into a latent chronic stage, becomes stable, has a less pronounced manifestation, the chronic form is difficult to treat, manifests itself with hypothermia, weakened immunity, poor diet, gynecological disease, urolithiasis and after violent sexual intercourse. The chronic form provokes inflammatory processes in other organs (cystitis, pyelonephritis) and can cause deformation of the urethra. The form lasts for months and years.
According to etiology there are:
- Infectious (pathogens fungi, viruses and pathogenic microorganisms) are divided into two types: specific (pathogens Gardnerella, Chlamydia, Trichomonas, gonococci, mycoplasma);
- nonspecific (causative agents: pneumococci, staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli).
Based on the type of pathogen, they are divided into:
- Gonorrheal (causative agent gonococcus).
- Non-gonorrheal (candidiasis) (causative agents of candida, trichomonas, bacteria, viruses and fungi).
According to the mechanism of development of foci:
- Primary (processes start in the channel).
- Secondary (processes begin due to infection from another organ that has undergone inflammation).