Why is a cervical polyp dangerous and how to treat it?
Cervical polyp is an epithelial growth of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. The pathology may not cause a woman any inconvenience for a long time. In more severe cases, benign neoplasms can lead to infertility, accompanied by severe pain and heavy bleeding from the vagina. In 2-3% of patients, cervical polyps can transform into malignant tumors.
What is a polyp
Polyps according to their structure and formation are divided into:
- mucous membranes;
- glandular;
- fibrous;
- glandular-fibrous;
- adenomatous (atypical).
All types of polyps are classified mainly by their size; in some cases they can grow up to 2-3 centimeters, but often these are growths 2-3 mm in diameter.
They also vary in shape:
- compacted;
- round;
- in the form of a drop;
- like a rooster's comb.
The structure of growths on the uterine cervix can be either on a thin stalk or on a fairly wide base. As for the structural color, polyps of any type come in pale pink, bright red, and also burgundy with a bluish tint.
Reasons for appearance
Female representatives of the 40-50 year age category suffer from cervical polyps, but it is likely that nulliparous young women may also be at risk.
The fundamental factor in the growth of polyps is often:
- Hormonal disorder of the female body , in addition, infectious diseases of the genitourinary area should in no way be discounted.
- Mechanical violations of the integrity of the tissues of a given organ, inflammation, erosions that were not cured, untimely sutured tears during delivery - all this, one way or another, can ensure the formation and growth of polyps.
A gynecologist can establish and diagnose polyps of the uterine cervix through visual examination with mirrors, cervicoscopy, colposcopy, and histological examination of the mucous membrane.
Signs and symptoms
Single growths, as well as small polyps, do not show up in women’s everyday lives and their presence is often discovered only during a routine examination, or when visiting a doctor for other issues.
Exclusively in the case of an inflammatory phenomenon, infection after a violation of the integrity of the growth, the patient may exhibit such symptoms as:
- Nagging painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which become more pronounced before the onset of menstruation.
- Increased volume of vaginal leucorrhoea.
- If the integrity of this neoplasm is violated, bleeding may occur.
- In patients of reproductive age who are susceptible to this pathology, symptoms and manifestations may be accompanied by infertility or interruptions in the menstrual cycle. It is for this reason that doctors try to detect the dependence of these deviations on each other.
Can a polyp on the cervix develop into cancer? Yes, such a possibility exists, but in fairly isolated episodes, about 1.5%-2% of all cases of the disease.
A polyp must go through several stages before it degenerates into a malignant tumor:
- hyperplasia - the epithelium of the organ grows rapidly;
- metaplasia - one epithelial structure is transformed into another;
- dysplasia of the uterine cervix - a precancerous structure appears in the epithelium, with auxiliary factors, which very soon turns into oncological, malignant cells.
If a patient develops a growth during pregnancy, due to the reflex activity of the cervix, in particular in the initial stages, the risk of miscarriage (spontaneous termination of pregnancy) increases, and in addition, among other complications of the process of bearing a child, there is also isthmic-cervical inferiority, or low placement of the placenta .
Women must strictly visit the gynecological office for examination and additional tests if signs appear that characterize polyps of the uterine cervix and uterine body:
- Infertility, difficulty conceiving;
- Vaginal leucorrhoea, brown in color, between menses;
- Painful sensations and bleeding during and after sexual intercourse;
- Prolonged critical days, uterine bleeding;
- Discharges in small volumes.
How does pathology manifest itself?
A woman may not know about the occurrence of a small formation for a long time. Usually such a polyp is discovered by chance by a gynecologist during an examination. Symptoms occur only when the growth becomes infected, injured, or grows. You need to pay attention to the following signs:
- bleeding after sexual intercourse, which is associated with trauma to the growth;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- vaginal discharge with pus is a characteristic sign of a large formation;
- bleeding during the “dry period”, which indicates inflammation or torsion of the polyp leg;
- heavy menstruation with severe pain;
- low-grade fever due to infection.
Multiple polyps can also bleed after heavy physical activity or long walking. If you have such symptoms, you should definitely make an appointment with a gynecologist.
Types of polyps
Similar to endometrial polyposis, cervical polyps are divided into:
Adenomatous – such neoplasms are called atypical, they have a different homogeneous structure and are capable of increasing to 40 mm or more. Such growths are characterized by a significant risk of transformation into oncology and cervical cancer, which is why, following their surgical removal, women are almost always prescribed chemotherapy;- Glandular-fibrous - the structure of these growths reveals a glandular structure and a connective tissue base. As usual, such neoplasms do not exceed 25 mm in diameter;
- Fibrous - formed from connective tissue. Such polyps usually occur in women who have crossed the age of 40 and quite often develop into a malignant tumor;
- Mucous - similar polyps develop from the glandular structures of the cell. It happens that such growths are observed in women of childbearing age, and rarely grow larger than 15 mm. This type of polyposis almost never occurs again and very rarely can develop into cancer.
When to see a doctor
If signs of polyposis appear, it is recommended to immediately consult a specialist for a full diagnostic examination. Treatment of such pathologies is carried out by a gynecologist.
Even in cases where diagnostics reveals only a single neoplasm, the disease should not be ignored in order to exclude complications.
Diagnostics
Polyposis on the cervix is often determined during a routine examination in the gynecologist's office. If any signs of doubt appear, every woman should consult a gynecologist and undergo a series of examinations.
The most basic of which is a visual examination using gynecological speculum.
To confirm the diagnosis of cervical polyposis, a woman undergoes ultrasound diagnostics. Metrographic, hysteroscopic examination, etc. are used as auxiliary techniques.
Survey
In order to diagnose cervical polyposis, vaginal visual examination, cervicoscopy, and colposcopy are used.
Visual inspection of the vaginal walls and cervical canal
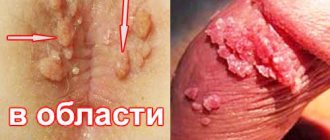
During a routine gynecological examination, the doctor can see in the mirrors an enlargement of the cervix, its thickening, and also mushroom-shaped growths, usually of a rich pink color, similar to a bunch, or round in shape.
In the case when the formation has been subject to keratinization and has multilayered epithelium on top, it is characterized by a whitish color; if the neoplasm acquires a purple or dark cherry color, this means that its blood supply is impaired.
Mostly, formations that appear inside the vaginal walls have a dense elastic or soft structure.
Cervicoscopy
Cervicoscopy allows for a detailed examination of the lumen of the uterine cervix, using a video camera, the gynecologist can examine even minor polyps, establish their structure, possible cell necrosis, the inflammatory process, or the occurrence of ulcers on the surface, and also other deviations of the cervical canal.
Ultrasound
If polyps of the uterine cervix are visible, external descriptions of their branches may also indicate the likely presence of endometriotic growths, namely polyps in the body of the uterus.
Regarding either exclusion or confirmation, a gynecological ultrasound is performed; it makes it possible to assess the structure and thickness of the inner layer of the uterus, the condition of the body and appendages of the uterus, tubes and ovaries.
Analyzes
For an accurate diagnosis, histological examination of scrapings taken from the cervical canal is also used.
In order to exclude or confirm an oncological etiology at the time of hysteroscopy, the doctor performs a knife sampling of cervical tissue, with partial curettage of the uterine wall for examination under a microscope.
In some situations, this biopsy makes it possible to remove the growth, even if it is small in size.
Removal of endometrial fibrous polyp
The optimal method for removing fibrous polyps of the uterine body is hysteroresectoscopy or surgical hysteroscopy
Therapeutic hysteroscopy is performed using a hysteroresectoscope - an operating hysteroscope. It consists of two parts: an optical system and a working one, equipped with a tube with an instrumental channel. Through this canal, surgical forceps, scissors, loop electrodes, and other instruments are inserted into the uterine cavity.
Mandatory conditions for polypectomy:
- All intrauterine manipulations to remove a polyp are carried out under visual control of hysteroscopy.
- After excision and removal of the polyp tissue, selective destruction (excision, ablation) of the basal endometrium adjacent to the polyp stalk is carried out down to the muscular layer of the uterus.
- After direct removal of the polyp and selective ablation of the endometrium, a control hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine mucosa is required.
Polyp removal is usually carried out using mechanical and electrosurgical techniques.
Single polyps are excised with scissors or bipolar electrodes and removed from the uterine cavity with forceps.
The technique for removing large mural fibrous polyps is similar to hysteroresectoscopic myomectomy. This surgical procedure is quite complex, so it is performed exclusively in a hospital, preferably in a large operating room.
Typically, the entire procedure for removing a fibrous polyp lasts no more than 15-30 minutes. The operation is performed under general short-term intravenous anesthesia. Polypectomy is well tolerated by patients and proceeds without complications.
Features of the postoperative period
After hysteroscopic removal of a fibrous polyp, the patient can be discharged from the clinic by the evening of the day of surgery or the next morning. There are no special appointments.
Sometimes, according to indications, the attending surgeon may prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory or painkillers to the patient. But more often than not, this is not necessary.
Within 2-4 weeks after removal of the polyp, mild bloody or bloody discharge from the uterus is observed. In the first days after surgery, small pieces of mucous tissue may come out of the genitals. The patient does not need to be afraid of such phenomena. This is the norm.
A repeat examination is scheduled 2 weeks after surgery. Sexual activity is permitted after a scheduled visit to the gynecologist, i.e. 2 weeks after polyp removal.
Return to contents
Polyp during pregnancy
If this neoplasm is discovered during pregnancy, then you should not panic.
If conception has already occurred, then polyps cannot affect a successful pregnancy and childbirth. As a rule, such growths are removed without difficulty after the birth of the child.
In some situations, bleeding may occur due to trauma during sexual intercourse, or due to a gynecological examination.
A distinctive feature of polypous formations in women in an interesting position is that their polyps begin to develop more rapidly and acquire a pronounced color.
Prevention
Fibrous-glandular polyp of the endometrium appears in women of different ages, but it is much easier to prevent the disease than to treat it. It is necessary to adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle, eat more vegetables and fruits, and also avoid drinking alcohol.
In addition, it is recommended to pay attention to physical activity, which will help prevent obesity. Patients who take hormonal medications must regularly visit a doctor, he will monitor the level of sex hormones. It is also prohibited to independently extend the course and increase the dosage of drugs.
During menopause, a woman is recommended to alleviate her condition by taking herbal medicines that normalize hormonal levels. The best method of preventing the disease is considered to be regular examination by a doctor, which allows you to detect signs of a disorder at the initial stage.
If the patient has a hereditary predisposition to endometrial diseases, artificial termination of pregnancy should be avoided. Such manipulation is allowed only if there are strict indications.
Why is a polyp on the cervix dangerous?
The appearance of polyps is for the most part a consequence of more complex pathologies. These neoplasms often play the role of background, and naturally, without any manifestations.
This is where their threat to the health of the female body lies. Without eliminating cervical canal polyps in a timely manner, any woman runs the risk of ending up in a cohort of cancer patients.
In addition, a number of difficulties arise with polyps:
- Blood loss, which leads to anemia and iron deficiency;
- Compression of the polyp by the uterine cervix requires surgical intervention;
- Infertility.
- Interruptions in the production of hormones and for this reason an imbalance;
- Miscarriages during pregnancy, in any trimester;
- The ability to transform a growth into an oncological neoplasm of the reproductive organ.
Drug therapy after surgery
It is important! Medicines can be taken only with a doctor’s prescription in order to avoid endocrine disorders, hormonal dysfunctions, and the formation of new tumors.
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed immediately after surgery to prevent the risk of infection. Broad-spectrum antibiotics (fluoroquinoline antibacterials) are usually prescribed.
If, after the histology results arrive, it is confirmed that the polyp is glandular-fibrous, it is recommended to start hormone replacement therapy.
The pelvic organs - the uterus, ovaries, appendages, and cervical canal - are hormone-dependent organs, so after surgery, hormonal imbalance is possible.
The balance is normalized by synthetic hormones - progesterone and estrogens:
- Duphaston;
- Utrozhestan;
- Jess, Janine, Yarina and other oral contraceptives.
Treatment
Drug therapy for cervical canal polyps as the main method of treatment is used very rarely, for example, in a situation where a woman categorically refuses surgery.
Drug treatment
The whole point is that it is impossible to cure cervical tumors with drugs, but it is only possible to suppress the process of their enlargement, as well as a decrease in the manifestations of this pathology.
And yet, drug therapy can often help in getting rid of concomitant diseases that caused the occurrence of cervical polyps.
For cervical polyps, the following drug treatment may be prescribed:
- hormone treatment;
- antibacterial therapy;
- anti-inflammatory treatment;
- vitamin treatment.
Polyp removal
Surgical treatment is mandatory.
There are several methods for removing polyps, the purpose of one of them depends on the patient’s health condition, the type of abnormality that became the basis for the formation, the patient’s age, and histology results.
In addition, it is taken into account whether the woman is pregnant at the time of planning the operation and whether she wants to have children in the future
In any case, the treatment is not as scary as the words with which it is characterized.
Polypectomy
- The method involves unscrewing the growths of the uterine cervix. Large polyps, up to 3 cm in circumference, are simply unscrewed, and the base is cauterized with electric current.
- If the base of the growth is located at the borders of the external pharynx, it is removed and the surface of the wound is sutured with a catgut suture. After this, it is necessary to scrape out the entire mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
- If the pathological neoplasm is located higher, it is removed in a targeted manner and the process is controlled under a hysteroscope.
Due to the fact that polyps often form against the background of an actively growing inner layer of the uterus, it may be necessary to scrape the mucus of the cervical canal for subsequent examination. If there is definitely a disturbance in the functioning of the entire reproductive system, then suitable hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a gynecological examination of the cavity of the reproductive organ using a hysteroscope (fiber optic device).
Often, at the time of hysteroscopy, hysteroresectoscopy is performed - elimination of a polyp in the uterus (removal of a growth on the inner layer of the uterus) with cutting out the polyp bed.
The surgical material is examined for histology. Hysteroresectoscopy is the newest method for surgical removal of growths on the cervix.
Diathermocoagulation
Diathermoexcision is a method of electric knife. The effect is absolutely painless, so the woman at the time of the procedure is under the influence of a local anesthetic.
The disadvantage of this method is traces on the canal, scars and cicatrices, which can lead to tissue tears during delivery. Complete tissue healing is likely after 2-3 months.
Cryodestruction
Polyps of small sizes are treated with cold - this is a method of cryodestruction.
One of the most effective methods for eliminating growths in current medical practice. The procedure is usually performed on days 8-10 of the menstrual cycle.
A polyp on the cervical canal is treated with liquid nitrogen brought to a very low temperature.
Following this procedure, the mucous membrane of the organ is restored within 2-3 months. The healing time depends on the size of the base of the polyp being removed.
Radio waves
Excision using radio waves. When removing formations with radio waves, the integrity of the tissues of the uterine cervix is not so much disrupted, which certainly affects healing. Recovery time ranges from 6-8 weeks.
Laser
Laser coagulation or the use of a laser to eliminate tumors. There are no bruises, scars or other marks during the operation. It is best to carry out this procedure at the very beginning of the cycle, on days 5-7.
After polyp removal
If the polypous tissue is not completely removed during surgery, then the pathology may return.
This is possible in the case when a polyp grows again from the base of the growth, in some cases there may be the appearance of thermal burns, compression of the structure of the uterine cervix, which are caused by cauterization of the location.
During the 14-21 days after the elimination of cervical formation, sometimes mucous or bleeding may occur, or a painful feeling in the lower abdomen.
However, this goes away very quickly and does not require treatment; you can take painkillers such as No-shpa or Ibuprofen.
In addition, for 14 days it is not recommended to:
- Carry out douching;
- Sex;
- Use of aspirin, acetylsalicylic acids;
- Visiting a sauna, bathhouse, taking a bath;
- Use of tampons, only sanitary pads can be used;
- Cancellation of sports activities, heavy physical activity, exercise.
Answers to possible questions
Before surgery, many women have a whole list of questions. We will try to answer the most popular ones.
Does it hurt to remove
Most polyp removal methods are virtually painless. If the patient is highly sensitive, doctors use local anesthesia. The most painful method is diathermocoagulation. Otherwise, a woman may experience only minor pain during and after the procedure.
Is it possible to have an intimate life?
After surgery, the patient should follow the following precautions:
- do not have sex for four weeks;
- do not lift weights, do not give your body serious sports loads;
- don't douche.
All this must be observed for 1-2 months until the tissue heals. Otherwise, you can get an infection and cause complications.
Polyp on the cervix during pregnancy
Polyps do not affect the course of an already existing pregnancy; a woman can carry and give birth to a child without problems. During pregnancy, there is no need to touch the polyps, but after the birth of the child, treatment can begin. If the formations were discovered in the early stages of pregnancy (up to three months), they can be removed.
If polyps are present during pregnancy planning, they often cause difficulty conceiving and a woman cannot become pregnant for a long time. Why is this happening:
- The cause of polyps is hormonal. A reduced level of progesterone, the hormone responsible for pregnancy, prevents conception. The course of ovulation and the menstrual cycle is also disrupted and fertilization of the egg becomes more difficult.
- Large polyps located in the cervix can block the passage to the uterus and make it difficult for sperm to pass through and attach to its walls.
If you are planning a pregnancy and you have polyps, you need to cure them, and only then you can get pregnant.
Is it possible to get pregnant after surgery to remove
After removal of the formations, a woman must undergo gynecological control for about a month. The doctor looks at how the epithelium is healing, to see if there are any complications. The first examination is carried out 5-7 days after surgery. As soon as the wounds heal, you can plan a pregnancy. The sooner the better, since sometimes the disease can return if the cause of its occurrence has not been eliminated. Typically, pregnancy occurs within six months after removal of the formations. If growths reappear in the cervix after pregnancy, then there is nothing to worry about. They do not affect the development of the fetus and the upcoming birth.
Folk remedies
Yarrow
If a woman has been diagnosed with polyps on the cervix, she simply must stock up on a plant such as yarrow. This herb normalizes the functionality of the uterus and dissolves almost all formations.
It can be used in several ways:
- It is recommended to use yarrow internally. For these purposes, you need to take 1 teaspoon of dry yarrow and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Cover and leave for 5-10 minutes. You need to drink the infusion warm, from 1 to 4 glasses per day, depending on the condition and size of the growth on the cervix. Duration of treatment is 2-3 months.
- Traditional medicine recipes also include yarrow baths. For these purposes, 100 grams of dry grass (in the summer it is possible to collect at least a whole armful of yarrow) pour 3 liters of water at room temperature. Infuse all this all day, then bring to a boil, strain and pour into a bathtub filled with water. The water level should cover half of the body below the waist. The procedure time is 15 minutes at a temperature of no more than 40 ° C. Take this bath every 2 days until the growth in the area of the uterine canal becomes smaller.
Nettle
Nettle therapy works great for growths on the neck.
This herb can be consumed in the form of different methods:
- Tea for internal use: pour 1 teaspoon of dry herb or nettle flowers with 1 glass of boiling water. Cover and leave for about 4 -5 minutes. Drink 1-2 glasses of tea per day until symptoms are completely eliminated and the functions of the reproductive organ are normalized.
- In addition, douching can also provide great benefit - pour 1 tablespoon of dry nettle into a liter of water, heat to a boil, cool to room temperature, strain and douche 3-5 times a day.
- From this tincture you can prepare tampons for formation on the cervix. Twist a piece of cotton wool into a tampon, soak it in nettle infusion and insert it into the vaginal cavity overnight. The course of treatment is until symptoms are completely eliminated.
Other recipes
There are other folk ways to get rid of polyps:
- Horsetail lotions. For polyposis on the cervical neck, compressed lotions made from horsetail can provide great results. They are prepared as follows: 5-6 tablespoons of dry horsetail herb should be placed on a sieve and placed over a container of boiling water - so that the steam reaches and wraps the plant. After a few minutes, when the grass becomes wet and hot, you need to move it onto gauze and apply it to the area below the abdomen. Additionally, wrap yourself in a warm blanket. As soon as the compress composition has cooled, it must be heated again. The same herb can be used four times a day, periodically heating it. This method should be performed daily until the polyp on the cervical canal is completely eliminated. For the vast majority of patients, this effect provided the opportunity to avoid surgical intervention.
Tampons
To eliminate cervical growths, different tampons are often used:
- You need to mix honey and aloe juice in equal proportions , saturate a cotton swab with the mixture and insert it inside the vagina overnight.
- Finely chop the garlic cloves, mix it with olive oil , saturate the tampon with the composition and insert it as deep as possible into the vaginal cavity. Duration - until the polyp on the cervical canal disappears completely. You should not be afraid of a burning sensation or a garlic smell - garlic does not irritate the vaginal mucous membranes, and the uterine secretion very quickly gets rid of the smell after using a garlic tampon.
- Mix propolis with water at room temperature until smooth. Apply the composition to a cotton pad and insert into the vaginal cavity.
- Onion tampons will help eliminate growths on the cervix. Grate the onion, mix with honey, moisten a cotton swab with the mixture and insert it inside the vagina overnight. Perform the procedure every evening for 10 days. When there are particularly large formations on the cervix, several courses of therapy are required.
Forecast
The main property of cervical polyposis is the ability to recur. Return of polyps occurs in almost more than 50% of episodes of the total occurrence of the disease in intervals of 1.5-6 months, following the treatment measures.
In addition, recurring uterine polyps in 1.5% of cases are characterized by dangerous malignant transformation. For this reason, after completing treatment for cervical polyps, patients need constant medical supervision.
Why do they appear?
The reasons for the appearance of cervical polyps have not yet been precisely discovered. The most common factors provoking education:
- chronic infections;
- hormonal imbalance;
- mechanical injuries of the uterine cervix.
Inflammatory processes
A polyp in the cervical canal can provoke a number of inflammatory and chronic pathologies.
- The inflammatory process in the lining of the uterus is endometritis.
- An inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the cervix caused by an STI – cervicitis.
- Infection with the human papillomavirus – HPV.
These pathologies affect the structure of the epithelium, the functioning of the glands, and the regenerative processes in tissues. Therefore, the likelihood of polyp formation is high.
Related article: cervicitis of the cervix - what is it?
Hormonal disorders
If the ovaries do not work properly, then a hormonal imbalance occurs in the female body, the amount of estrogen increases sharply, and progesterone decreases. Excess estrogen leads to thickening of the mucous membrane in the cervix, which can cause polyps to appear. Reduced progesterone provokes the formation of cystic neoplasms
Injuries
During mechanical abortions, curettage for diagnostic examination, and cleansing, the tissue structure of the uterine cervix is disrupted. If injuries are complicated by infectious pathologies, then the progress of damage recovery slows down significantly. Polyps grow on injured areas of the epithelium.
Preventive measures
The most acceptable measures to prevent polyposis are those measures that can ensure the elimination of the root causes of growths:
- Avoid stress and depression;
- Carry out a systematic examination in the clinic , at least once a year;
- Quitting smoking and alcohol abuse;
- When polyposis is caused by diabetes , blood glucose levels need to be monitored;
- Cure in a timely manner infectious diseases of the genitourinary and reproductive organs, such as erosions or pseudo-erosions;
- The use of protective equipment such as condoms, etc.
Polypous cervical growths can cause carcinoma on the cervix, so this deviation should never be left to chance. It is better to start treatment without waiting for undesirable consequences.
Treatment after removal of a fibrous polyp
Patients who have only endometrial fibrous polyps do not need additional treatment, including hormonal treatment, after their removal.
Dispensary observation by a gynecologist with ultrasound control is recommended once every 6 months.
There is no special prevention for fibrous polyps. It is enough to lead a healthy, physically active lifestyle, avoid sexually transmitted infections and regularly visit a gynecologist.
Treatment of disease relapse
For patients over 42 years of age with recurrent fibrous polyps in combination with adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, spotting from the uterus, and bleeding, hysterectomy is recommended.
Return to contents