Oligohydramnios during pregnancy (oligohydramnios) is a complication of pregnancy associated with a reduced amount of amniotic fluid.
It is considered by doctors as a serious obstetric pathology, as it can cause the development of a number of congenital anomalies in the fetus:
- bone tissue deformations;
- curvature of the spine;
- clubfoot.
In addition, oligohydramnios can cause intrauterine growth retardation.
Amniotic fluid performs an important function in the process of fetal growth and development. They prevent excessive pressure from the walls of the uterus on the baby, and in addition, they are rich in nutritional components and microelements.
Oligohydramnios can be dangerous for the fetus, depriving it of necessary protection and part of the nutrition.
Oligohydramnios occurs in approximately 4% of pregnant women. Pathology can develop at any stage of gestation, but most often it is diagnosed in the third trimester (usually after 35-36 weeks) of pregnancy. This is due to a decrease in the functional activity of the placenta due to its aging.
In early pregnancy, oligohydramnios is extremely rare. With such a development of events, there is always a high risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
What does oligohydramnios mean during pregnancy?
- Amniotic fluid contains many substances necessary for the baby, such as salts, hormones, oxygen and vitamins. Also, amniotic fluid protects the fetus from many harmful external factors.
- But such a deviation occurs when there is little amniotic fluid and this seriously complicates the healthy bearing of a child
- At different stages, the amount of fluid is different, so, in the last trimester, it should be 0.8-1.5 liters. If the amount of water is less, then we are talking about low water
- There is a division of oligohydramnios into moderate and severe; to determine the severity of the deviation, the degree of fluid deficiency is important
Moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy
With moderate oligohydramnios, the volume of fluid is slightly less than it should be during a normal pregnancy, and is about 400-700 ml.
Treatment for such oligohydramnios consists of establishing a diet; you need to adhere to a special diet rich in vitamins and minerals, lead a healthy lifestyle, and regularly visit a doctor to monitor the dynamics of the disease and not miss the deterioration of the condition. As a rule, this is enough and moderate oligohydramnios does not harm the fetus.
Moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Severe oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Severe oligohydramnios means a strong deviation from the normal volume of amniotic fluid. In case of severe oligohydramnios, urgent and radical measures must be taken, because This condition is very dangerous for the life and health of the baby.
Treatment is usually carried out in a hospital under the constant supervision of doctors. If you have been diagnosed with this, it can affect your unborn child - due to oligohydramnios, there may be a delay in the development of the fetus, hypoxia, which in turn will lead to problems with the central nervous system, improper formation of the bone skeleton and tissues, and even abortion. pregnancy.
There are only 0.3-0.5% of women suffering from severe oligohydramnios.
Prevention
Prevention of oligohydramnios should begin at the planning stage and continue throughout the entire gestation period. It is expressed in the following activities:
- timely diagnosis and treatment of any gynecological and somatic pathology;
- early registration of a pregnant woman (up to 12 weeks);
- adherence to daily routine;
- correct alternation of work and rest;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- balanced diet with the obligatory inclusion of fresh vegetables and fruits in the menu;
- rejection of bad habits.
Signs of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
The pregnant woman herself usually does not feel that she has such a deviation as oligohydramnios. The only thing that can alert you is the appearance of a sharp pain in the abdomen when the baby pushes. This may indicate a lack of fluid in the amniotic sac.
During an examination, a doctor can identify the likelihood of oligohydramnios by the lag in the following indicators:
- increase in abdominal volume
- uterine fundus measurements
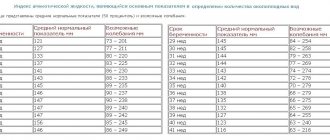
Table of norms for the height of the uterine fundus and abdominal volume during pregnancy
Based on these data, the doctor can make an assumption about a deviation from the norm and must refer the pregnant woman for an ultrasound examination, where an accurate diagnosis will be made.
An ultrasound machine makes it possible to measure the amount of amniotic fluid and determine whether it is enough or not.
If according to an ultrasound you have moderate oligohydramnios, do not rush to be upset, it is better to redo the ultrasound examination in another place, perhaps the doctor is mistaken or the device is not accurate enough, and the results will be different.
Oligohydramnios is not a disease, but a symptom
Oligohydramnios is not classified as an independent disease. This is a symptom accompanying another pathology of the fetus or pregnancy. It cannot be considered one of the main diagnostic criteria, since modern research methods make it possible to identify problems in fetal growth with great accuracy.
Oligohydramnios is diagnosed infrequently: mostly established cases (3-4 per 1000 births) are classified as functional. Among them, only 0.2-0.3% are pathological.
Causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
All the reasons why oligohydramnios occurs have not been fully studied, but experts identify the following:
- Leakage of amniotic fluid or, scientifically, amnionic hydrorhea. Leakage of water occurs long before PDR due to rupture of the membranes. Doctors believe that this happens due to infection of the membrane or its premature aging, which leads to its thinning and the appearance of a gap. This deviation is treated with bed rest, while the fluid has time to be restored and its loss does not harm the child
- Disturbances in the development of the fetal membrane. There are quite a few such disorders and the reasons for their occurrence, too, the most common include genetic disorders and the harmful effects of the environment
- Infection of the amniotic sac. There are a number of viruses from which the placenta cannot protect the baby and the fetal bladder becomes infected, its proper functioning is disrupted, which leads to oligohydramnios.
- Postmaturity of the fetus. The placenta and fetal membrane no longer work at full capacity, the baby does not receive the nutrients he needs and the condition of his body worsens, blood circulation in the membranes also becomes difficult, which in turn leads to a decrease in the production of amniotic fluid
- Underdevelopment of amniotic sac tissue or poor secretory function
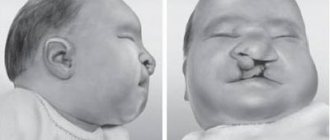
- Pathologies in fetal development. Here doctors identify genetic abnormalities in the development of the face and kidneys
- Bacterial infections in rare cases can penetrate not only into a woman’s birth canal, but also into the amniotic fluid
- During multiple pregnancies, there are cases when the blood in the placenta is not distributed correctly and therefore one child does not receive enough of the necessary substances, while the other receives too much of them
Oligohydramnios in multiple pregnancies
Bottom line
Amniotic fluid plays a key role in the development of the child, as it protects it and provides nutrition. Oligohydramnios during pregnancy is a dangerous condition for the health of the baby and mother. Amniotic fluid contributes to the rapid dilatation of the cervix during childbirth, without which independent delivery is impossible. Amniotic fluid protects the embryo from compression by the walls of the uterus, which can cause severe skeletal deformation and even dislocation of limbs. Therefore, monitoring an acceptable level of amniotic fluid is an important task for the obstetrician and the expectant mother.
To prevent the development of pathology, you need to follow the recommendations of the gynecologist, follow a daily routine, eat nutritiously, and eliminate stress and bad habits. A pregnant woman should know that worries and worries negatively affect her own health, as well as the well-being of the baby. Preventive measures, reading useful literature, a healthy lifestyle are the path to successful childbirth and the postpartum period.
What hormonal medications did you take to stimulate ovulation?
- Gonal 34%, 4676 votes
4676 votes 34%4676 votes - 34% of all votes
- Clostilbegit 25%, 3412 votes
3412 votes 25%
3412 votes - 25% of all votes
- Menopur 17%, 2297 votes
2297 votes 17%
2297 votes - 17% of all votes
- Puregon 14%, 1947 votes
1947 votes 14%
1947 votes - 14% of all votes
- Decayed 8%, 1077 votes
1077 votes 8%
1077 votes - 8% of all votes
- Menogon 3%, 406 votes
406 votes 3%
406 votes - 3% of all votes
Total votes: 13815
Voted: 10191
January 17, 2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
What are the dangers of oligohydramnios during pregnancy?
- Oligohydramnios during pregnancy can cause quite a few complications. If there is not enough water, the walls of the uterus begin to strongly compress the amniotic sac, which puts unnecessary pressure on the baby
- In this case, the baby will be bent in a position that is uncomfortable and unnatural for him. This development of events leads to curvature of the child’s spine and clubfoot, and the skin can grow together with the fetal membrane
- In addition, Simonartian ligaments may form, which wrap around the fetus and limit its movements, which can even lead to injury.
- If these ligaments become entangled in the umbilical cord, the child will not receive enough nutrients, fetal hypoxia and impaired blood flow may occur, which will lead to developmental delays and possibly even fetal death.
- Amniotic fluid, moreover, protects the baby from the external environment, which can harm him, and its lack will lead to unreliable protection or its absence
- If there is a lack of water, the cervix may open slowly during childbirth, and labor becomes weak. The contractions are painful, but not strong enough. Bleeding may occur after childbirth
If severe oligohydramnios was discovered late and has irreversible developmental disorders of the fetus, doctors insist on early termination of pregnancy.
Moderate oligohydramnios can be said to never have a negative effect on the child, if, of course, the diet and lifestyle of the pregnant woman is adjusted.
Consequences of oligohydramnios
In most cases, with timely diagnosis and active treatment of oligohydroamnion, doctors are able to maintain pregnancy until 37-38 weeks and thereby allow the woman to give birth to a healthy, full-term baby.
If oligohydramnios occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, as well as when it is combined with other obstetric pathologies, the prognosis is unfavorable. In this situation, there is a high risk of a number of dangerous complications:
- intrauterine fetal death;
- hypoxia and fetal malnutrition;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- formation of malformations of the musculoskeletal system in the fetus (clubfoot, torticollis).
How to treat oligohydramnios during pregnancy?
A woman should understand that even with a diagnosis of “moderate oligohydramnios,” she should not self-medicate or ignore it altogether.
The doctor will prescribe additional examinations: general blood and urine tests, tests for infections, fetal CTG (cardiotocography), ultrasound, water smear if there is a suspicion that they are leaking.
Ultrasound for oligohydramnios during pregnancy
These examinations will help to assess the child’s condition and the severity of the deviation. Based on their results, the gynecologist will prescribe the necessary treatment. You should also try to determine the cause of oligohydramnios, this will help you choose the right treatment.
- If the cause of oligohydramnios is obesity and metabolic dysfunction in the body, then you need a proper diet, vitamins and medications that improve blood supply to the placenta. If oligohydramnios is moderate, treatment can be done at home, but if it is severe, then hospitalization is necessary.
- If the cause of oligohydramnios is a viral infection, then antiviral drugs are prescribed and restorative therapy is carried out. The doctor will definitely prescribe a vitamin complex and medications that improve blood microcirculation
- If the reason lies in impaired development of the amniotic sac, doctors try to maintain the pregnancy and prevent infection of the fetus. In this case, treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital and the woman is prescribed additional examinations to assess the condition of her body and the condition of the fetus.
- In case of post-term pregnancy, doctors puncture the amniotic sac and induce labor with stimulating drugs.
- It is also important to reduce physical activity, reduce physical activity and adherence to bed rest.
- In case of oligohydramnios, doctors direct the woman to do ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound more often in order to monitor the dynamics of the deviation and changes for the better or worse in the mother’s body and the condition of the child
- If the pregnancy is already long and the baby is full-term, the doctor may recommend premature birth, which will be caused by special stimulating drugs
Do not forget to tell your doctor if you have already had this diagnosis in previous pregnancies, and it is better to conduct a couple of additional ultrasound examinations to exclude this abnormality or detect it as early as possible.
Diagnostic methods
Ultrasound is considered the most informative method for diagnosing oligohydramnios. However, there are other ways to determine pathology.
Ultrasound
During the period of bearing a child, the expectant mother undergoes 3 screening ultrasound examinations, with the help of which the condition of the umbilical cord, placenta and amniotic fluid is determined. As a rule, if pathology is present, it is diagnosed on one of these three ultrasounds, since severe symptoms are rarely observed. To diagnose oligohydramnios, the doctor only needs to determine the volume of amniotic fluid and also calculate the AFI.
General tests
Among the general tests, the expectant mother is prescribed a blood test for testosterone, as well as intrauterine infection. In addition, they do a blood test for urogenital infections and take a smear from the vagina.
CTG
To assess the functioning of the baby’s cardiovascular system, cardiotocography is performed, thanks to which it is possible to record the heartbeats of the embryo. For this, an ultrasonic sensor is used, which is absolutely safe for both women and children. CTG is also used to evaluate uterine contractions. Based on the data obtained, abnormalities such as fetal hypoxia are diagnosed.
On one's own
It is almost impossible to independently determine the presence of oligohydramnios at home, since the pathology is not accompanied by characteristic symptoms. If an expectant mother experiences nausea and dizziness, she should visit her gynecologist, as these manifestations may simply be signs of toxicosis.
Index of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
During an ultrasound examination, a diagnosis of “oligohydramnios” is made based on the amniotic fluid index (AFI), which is calculated by an ultrasound machine. The device measures the amount of water in several places and calculates the IAF.
Table of AFI at different stages of pregnancy
In the third trimester:
- if the index is within 5-8 cm, then the amount of water is normal
- if the index is 2-5 cm, then this is “moderate oligohydramnios”
- if the index is below 2 cm, a diagnosis of “severe oligohydramnios” is made
However, it is worth noting that AFI varies depending on the stage of pregnancy:
- at 16 weeks the norm is considered to be from 73 to 201 mm
- at 20 weeks from 86 to 230 mm
- at 25 weeks from 89 to 240 mm
- at 30 weeks from 82 to 258 mm
- at 35 weeks from 70 to 279 mm
- at 40 weeks from 63 to 240 mm
The amount of amniotic fluid changes as the fetus grows, swallows fluid, and urinates. But you shouldn’t worry about the baby’s condition, because... amniotic fluid is renewed every 3 hours, and every 3 days it completely changes.
Where does amniotic fluid come from?
Amniotic fluid is produced by the placenta. But we all know that there is no placenta at the beginning of pregnancy. It matures only at the end of the first trimester. Where does amniotic fluid come from in the first months of pregnancy?
This is one of the unsolved medical mysteries. Doctors do not yet know exactly what causes the amount of amniotic fluid to increase before the placenta appears.
The main theory is that water accumulates due to extravasation of maternal blood plasma through the chorion and amnion. It is also assumed that this may be the plasma of the fetus itself - it seeps directly through the skin before its keratinization (hardening) occurs.
In the second trimester, the placenta begins to function. Yet the main source of amniotic fluid remains the fetus. During this period, the amount of amniotic fluid depends on how quickly urine, alveolar fluid accumulates, and their excretion (absorption), ingestion by the fetus and outflow through the amniotic membrane.
Every day, the fetal lungs produce an average of 350 ml of fluid. She is deprived of protein.
Its osmolarity is the same as that of blood plasma. The fetus also produces urine quite intensively. Its amount ranges from 0.4 to 1.2 liters per day. From 20 to 40 weeks, the amount of urine produced increases 10 times.
Starting from the 18th week, swallowing of amniotic fluid by the fetus can be observed. This is the main mechanism of amniotic fluid resorption. At week 20, the unborn baby swallows 200 ml per day, at week 40 - 500 ml. The rest of the liquid is absorbed into the maternal blood due to its greater “salinity” - more sodium chloride.
Nutrition for oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Proper nutrition during oligohydramnios
You need to eat properly and balanced during oligohydramnios:
- try to eat several times a day (more than 5 meals), but in small portions
- products must contain many vitamins and minerals and be nutritious
- choose natural, minimally processed foods
- exclude fast food products from the menu (burgers, hot dogs, etc.)
- reduce the amount of sugar and salt you consume
- eliminate fatty foods from your diet
- try to use less spices and spices
- avoid products containing preservatives, flavors and dyes
- meat, fish and seafood must be well-heated; you should not eat them raw or half-cooked
- refrain from eating blue cheese, unboiled milk and raw eggs
- do not drink strong tea, try to avoid coffee and completely eliminate alcohol
- Instead of sweets and sugar, eat more fruits
Be sure to monitor your weight gain, because... its rapid increase can also lead to oligohydramnios or worsening of an existing deviation.
Functions of amniotic fluid
The presence of fluid in a small volume is determined already from the 3rd week of pregnancy. There is a constant exchange between the fetus and its environment: until the fourteenth week of gestation - through the skin, subsequently, due to its compaction, liquid with nutrients is swallowed by the fetus, and part of the water is excreted in the form of urine. This is how the fetus “feeds” and is cleansed of metabolic products.
In addition to this, there are a number of other important functions:
- maintaining a constant comfortable temperature (+37°C);
- noise insulation;
- shock absorption (protecting the child from injury due to sudden movements of the mother);
- protection against infections due to the bactericidal substances it contains;
- “help” in the birth of a child.
Tendency to oligohydramnios during pregnancy: how to determine?
A woman may be prone to oligohydramnios during pregnancy in the following cases:
- expectant mother smokes
- multiple pregnancy
- the woman has metabolic disorders in the body
- there are abnormalities in the development of the amniotic sac
- gestosis - toxicosis in late stages
- dehydration due to vomiting or diarrhea
- there is a bacterial or viral infection
- woman suffers from diabetes
- presence of chronic diseases in the expectant mother
- post-term pregnancy
- there are fetal kidney defects
- I had oligohydramnios in previous pregnancies
Controlling weight gain during oligohydramnios
If you fall into a risk category, the doctor will prescribe additional examinations and tests for you in order to promptly identify deviations from the normal volume of amniotic fluid and begin treatment as early as possible.
Complications
Why is oligohydramnios dangerous during pregnancy? In the first trimester, oligohydramnios is often a sign of genetic pathologies of the fetus and ends in termination of pregnancy.
Oligohydramnios is always the cause of delayed fetal development in the womb. Thus, the risk of perinatal death increases.
In 26% of cases, premature labor begins. In other cases, on the contrary, oligohydramnios leads to pronounced weakness of labor. The risk of bleeding after childbirth increases.
Because of this pathology, the child suffers greatly:
- low body weight;
- underdevelopment of the lungs;
- abnormal skeletal development (narrow chest, curved spine, skull deformation, clubfoot, dislocated hips, etc.);
- atresia of the digestive tract;
- oxygen starvation;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- decreased activity;
- disturbance of brain activity;
- excessive dryness and increased wrinkling of the skin;
- children get sick more often;
- characterized by increased excitability.
How to treat oligohydramnios during pregnancy: tips and reviews
Let's summarize and determine the main measures to prevent oligohydramnios:
- Proper fractional nutrition, products should be as healthy as possible
- Dieting if you have problems with excess weight
- Additional intake of complex vitamins
- Eliminate physical activity and replace it with walking in the fresh air
- Timely visit to the gynecologist, taking tests, passing the necessary examinations
- If there are endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, for example, or obesity), you need to undergo appropriate treatment
When I was pregnant, I couldn’t get enough of the fact that I had a small belly, as it later turned out on an ultrasound - oligohydramnios. But it was probably moderate, because... The doctor did not prescribe any medications and only said that I would not be allowed to nurse, but my son did not wait long, he was born a little premature - the birth was easy, there were no problems with the child’s health. Masha, 24 years old.
In fact, doctors exaggerate everything; there is nothing wrong with oligohydramnios. Well, this is understandable, they are playing it safe. But my friend was persuaded to give birth prematurely, she did not agree and carried the child to term. The son was born healthy and on time. It grows and gets stronger. Diana, 32 years old
In both pregnancies I was diagnosed with “moderate oligohydramnios”, and both times at 30-32 weeks. During the first pregnancy, they did not prescribe treatment; they said that at this stage, moderate is not scary, but in the second, they gave injections. The doctors were different. Both girls are healthy, and this is the most important thing! Christina, 27 years old
Why is it dangerous?
Oligohydramnios has a bad effect on pregnancy and threatens the child with serious consequences. If you have this disease, you need to minimize the danger so that it does not cause abortion.
Drink the right amount of water
It is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's instructions. If there is a tendency towards oligohydramnios, prevention should be carried out:
- observe drinking regime;
- eat right, eliminate harmful foods;
- sleep more and walk in the fresh air;
- undergo regular scheduled examinations with a doctor (free of charge or in a commercial clinic).
Ignoring recommendations is fraught with deterioration in the health of the mother and her fetus. Be sure to listen to your doctor's advice to avoid consequences.
Function of amniotic fluid
The presence of amniotic fluid is a prerequisite for bearing a child. This is the embryo’s habitat, which protects it from noise and damage. The umbilical cord is protected from compression by amniotic fluid. But it is important that it is free (to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the baby).
Amniotic fluid supports the metabolism of the unborn child. Thanks to this fluid, the baby's lungs develop. This liquid also acts as a barrier against germs and infections, preventing the fetus from becoming infected.
Review Reviews
Medical reviews of oligohydramnios during pregnancy indicate that 95% of all detected pathologies of this type disappear within a month after correcting nutrition, lifestyle, vitamin therapy and taking vascular-strengthening drugs.
By studying reviews from pregnant women, the predictions described above can be confirmed. The diagnosis is suspected in half of pregnant women, but it is confirmed only in 4-5% of women after repeated studies. Sometimes advice on forums can have negative consequences, so before exploring the Internet, you should ask all your questions to the gynecologist who is supervising the pregnant woman.
Is treatment required?
Medical measures aimed at eliminating varying degrees of oligohydramnios begin after the first detection of a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid. In order not to miss time and prevent negative consequences for the unborn baby and mother. The specialist decides how to treat oligohydramnios individually, depending on the causes and severity of the pathology.
What should a woman do?
When a reduced volume of amniotic fluid is initially detected, the expectant mother is prescribed vitamins and a drug to improve microcirculation “Curantil” for a month. The doctor supervising the pregnancy will tell you what a pregnant woman should do if she has oligohydramnios, how to eat, and what lifestyle to lead.
What is the treatment and in what cases?
Treatment of oligohydramnios in a hospital is carried out when a decrease in amniotic fluid is established during three dynamic ultrasound examinations. If there is pathology of the placenta, which can be seen on the initial examination, as well as noticeable malformations, the woman should be hospitalized.
In a pregnancy pathology hospital, treatment is prescribed depending on the cause:
- vitamin preparations (ascorbic acid and group B);
- diet with a high content of protein, mineral and plant components;
- bed rest if there is a threat of miscarriage or leakage of water;
- means for improving blood supply to the placenta (Actovegin, Curantil);
- symptomatic treatment of the underlying disease of the pregnant woman, which has caused a condition with a reduced amount of amniotic fluid (hypertension, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, heart disease, thyroid disease and vascular pathology);
- antibiotics for infectious pathologies;
- termination of pregnancy in case of fetal pathologies incompatible with life;
- opening the membranes to induce labor in post-term pregnancy;
- Caesarean section with severe oligohydramnios and signs of increasing fetal hypoxia.