Rhinolalia is a distortion of the pronunciation of sounds and speech in general, caused by defects in the structure and, as a consequence, the functioning of the speech apparatus. As a result, the resonator function of the nasal cavity is disrupted: when sounds are formed, the air stream goes the wrong way, distorting pronunciation. With rhinolalia, the articulatory and acoustic components of speech are disrupted: vowels and consonants have a nasal sound, the voice becomes nasal and specific. Rhinolalia in children is accompanied not only by a serious distortion of the pronunciation of sounds, but also by impairments in written speech, a lag behind peers in the development of vocabulary and grammar, and psychological problems.
According to statistics, rhinolalia affects 1-2 people per 1000 population.
general description
In recent years, doctors around the world are increasingly faced with the problem of speech disorder in children.
This phenomenon has objective reasons (ecological deterioration, bad habits of parents, which leads to the development of anatomical defects in children, lack of contact with the child due to parents’ employment, and so on). There are several different diseases in which a child develops a speech disorder. One of them is rhinolalia. This concept in medicine refers to disorders of voice formation and sound pronunciation, which are caused by defects in the structure and functioning of the speech organs.
The speech of a child with rhinolalia is characterized by severe disturbances in the pronunciation of sounds, underdevelopment of the grammatical and lexical aspects of speech, and impaired writing.
To identify the disease and find out its causes, the patient needs a comprehensive examination by an ENT or maxillofacial surgeon. Elimination of rhinolalia is carried out using surgical and orthodontic treatment, physiotherapy. In addition, the patient needs the help of a speech therapist and psychologist.
Additional manifestations
- Specifics of phonemic hearing. Since rhinolalic children have not developed articulatory experience, they do not hear their speech defects. In the future, this leads to difficulties in mastering sound analysis and is an obstacle to mastering correct writing (substitutions, omissions, and the use of unnecessary sounds occur).
- Vocabulary and grammar are impaired. There is a meager vocabulary of words with a predominance of verbs and nouns. Phrases are constructed incorrectly.
- Insufficient mental development (increased irritability, anxiety, asthenic syndrome).
Classification of rhinolalia
The following main forms of the disease are distinguished:
- open rhinolalia - with this form of the disease, air passes simultaneously through the nasal and oral cavities;
- closed rhinolalia - due to the presence of an obstruction, air cannot pass through the nose, which leads to distortion of the pronunciation of sounds;
- mixed rhinolalia - and the patient experiences symptoms of two of the above forms at once, which is why the voice becomes nasal and has a nasal sound.
Based on the causes of occurrence, the following types of disease are distinguished:
1. Organic rhinolalia. Divided into two subspecies:
- open organic rhinolalia - caused by congenital (rarely acquired) defects in the development of the nose or oropharynx;
- closed form - caused by various deformities of the nose.
| Open and closed rhinolalia |
2. Functional rhinolalia. Also divided into two subspecies:
- functional closed rhinolalia - often a consequence of neurological diseases, air flows through the oral cavity;
- functional open rhinolalia - usually occurs after ENT diseases.
In addition, the following types of rhinolalia are distinguished by localization:
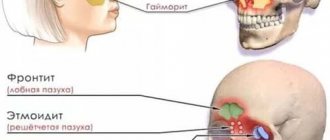
- posterior - is a complication of a deviated nasal septum, polyps or chronic rhinitis;
- anterior - develops as a result of the proliferation of adenoids.
Speech production workshop
The velopharyngeal mechanism consists of a complex group of structures that act in unison to control the flow of air through the nose and mouth by raising the velum and constricting the pharyngeal walls (lateral and posterior). Any disruption to this process can result in abnormal and difficult to understand speech.
The velopharyngeal seal is a “key player” in the unique function of sound pronunciation and resonance balance. It serves as a valve between the nasopharynx and oropharynx, creating pressure in the oral cavity to produce sounds and allow the voice to resonate normally.
Try to make the difficult path to correct speech, giving yourself the ability to communicate, to be understood, and therefore accepted into the world around you.
Causes of rhinolalia
The etiology of the disease may be different. The congenital form of rhinolalia develops due to the appearance of facial clefts in the initial period of embryonic development.
The causes of the development of such severe pathologies can be nervous shocks, endocrine diseases, bad habits, and some diseases suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy.
The acquired form may be the result of mechanical damage to the nasal cavity, deformation of the soft palate, injuries to the vagus or nasopharyngeal nerve.
The cause of the open form of the disease may be the removal of the adenoids or the development of paresis of the soft palate after diphtheria. The congenital open form of the disease has such characteristic symptoms that it can be diagnosed immediately after the birth of the baby.
When feeding a baby, milk leaks out of the nose. Due to the disease, the air does not warm up enough, which leads to frequent rhinitis, otitis media, and pneumonia.
The organic closed form of the disease usually develops as a result of damage to the nasal cavity or nasopharynx.
Symptoms of rhinolalia
Clinical manifestations depend on the form of the disease. Open rhinolalia is manifested by breathing problems. As a result, liquid food begins to flow through the nose, which makes feeding the baby very difficult.
The result of the open form of the disease can be a developmental delay in the child. Such a baby pronounces his first word late, has a nasal voice, and finds it difficult to pronounce sounds correctly. The child pronounces most sounds deafly. This is due to the fact that the greatest load during conversation falls on the root of the tongue, and not on its tip.
A symptom of the closed form of the disease is the constant flow of mucus down the back wall of the throat, which greatly worries the child. The baby often suffers from colds, he develops a chronic runny nose, and his pronunciation is impaired.
Many experts believe that such speech defects affect the child’s psyche and make him more withdrawn compared to his peers. Such a child prefers to spend more time at home, he speaks little and is reluctant to make contact with strangers.
A platform for optimism
The experience of specialists and statistics confirm the favorable development (mental and school performance) of children with congenital clefts, subject to early corrective comprehensive intervention. They attend school, clubs, and speech rehabilitation is soon completely completed with reaching a normal level of pronunciation.
There are many people who, after surgery for cleft palate, successfully graduated from college (with honors), entered graduate school, and some became scientists. Family life also turned out well.
It is only his ideas that make a person happy or unhappy, not the outside world!
Diagnosis of rhinolalia
A comprehensive examination for rhinolalia. A large number of different specialists can participate in its implementation (ENT, psychologist, dental surgeon, phoniatrist, speech therapist and a number of others).
During a speech therapy examination, the doctor pays special attention to the structural features and degree of mobility of the patient’s speech apparatus and identifies voice disorders.
To diagnose the open form of the disease, a special test is performed, the essence of which is that the patient pronounces the sounds “i” and “a” by sequentially opening and closing the nose. When the nasal passages are pinched, sounds become muffled, and the wings of the nose vibrate strongly under the specialist’s fingers.
In addition, the doctor checks the patient’s pronunciation of all sounds, evaluates vocabulary, level of grammar and vocabulary. If the child is already in school, then the level of writing and reading is assessed.
Of the instrumental methods, rhinoscopy, electromyography, radiography of the nasopharynx, and pharyngoscopy are most often used.
Based on the data obtained as a result of a comprehensive examination of the patient, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes corrective therapy.
You should not ignore the problems that arise in a child with rhinolalia. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease progresses, which can cause the development of a number of complications.
Prevention measures
To prevent this disease, it is very important to try to prevent or get rid of anatomical defects and functional disorders of the speech apparatus in a timely manner. Prevention of rhinolalia includes the following methods:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle while bearing a child;
- avoid infectious diseases in the mother;
- prevention by doctors of birth injuries;
- timely detection of disorders in infants;
- prevention of head and jaw injuries in infancy;
- regular visits to a speech therapist at an early age;
- preventing hypothermia in the child's body.
Symptoms of rhinolalia are clearly visible to parents and others. The faster the diagnosis is made to identify the nature of pathologies of the speech apparatus and treatment, the faster the child will begin to speak normally. This will allow him not to lag behind in development and not acquire the traits of a gloomy loner.
Treatment of rhinolalia
Comprehensive correction of rhinolalia includes:
- surgical correction of defects (if indicated);
- orthodontic treatment and preventive measures aimed at preventing repeated deformations of the patient’s speech apparatus;
- regular sanitation of lesions to prevent hearing loss;
- exercise therapy;
- help from a psychotherapist.
| Surgical correction of defects in rhinolalia |
Both closed and open rhinolalia in children should be treated as early as possible in order to complete therapeutic measures before the onset of puberty.
The main directions of speech therapy correction of rhinolalia are:
- normalization of breathing (both physiological and speech);
- control over the overall development of the child’s speech skills;
- restoration of physiologically correct closure of the pharynx and palate;
- preventing the development of pathologies such as dyslexia and dysgraphia;
- formation of correct articulation in the patient;
- production of sounds for rhinolalia;
- elimination of nasal voice;
- consolidation of acquired skills.
Corrective work requires a lot of patience and endurance, both from the doctor and from the patient, as well as from his parents, who must take an active part in the therapy process and work with the child additionally according to the recommendations of the speech therapist.
The doctor must constantly correct the child’s speech, monitor whether he is breathing and articulating correctly.
The effectiveness of rhinolalia correction depends on many internal and external factors. The result of treatment is considered positive if the child gets rid of the nasal tone in his voice and normalizes his speech, clearly pronouncing all sounds.
When preparing a child with rhinolalia for school, it is necessary to take into account psychological aspects, preparing him for what he can expect in class. During school, it is necessary to correctly distribute the child’s workload so that he does not get overtired and has time not only to do his homework calmly, but also to work with a speech correction specialist.
Correction methods
Treatment of rhinolalia includes a whole range of measures aimed at maximizing the elimination of speech defects.
If a child is diagnosed with congenital rhinolalia, then correction of the disorder begins with the elimination of defects of anatomical origin. From birth, such children begin to be fed using a tube, which is selected taking into account the characteristics of the cleft.
A special prosthesis, an obturator, is also made to close the nonunion. This prosthesis facilitates the processes of eating, breathing and speaking.
Late use of an obturator is less effective, since the child begins to develop incorrect tongue position with age. The obturator changes as the child grows and is used until the moment of surgical intervention, which, unfortunately, cannot be done without.
Maxillofacial disorders are subject to surgical intervention. Nasality with open rhinolalia is treated both before and after surgery.
As a rule, cleft lip surgery is performed at 2–3 months of a child’s life. Operations on the palate are carried out after two years, if the child has lost all his teeth. In weakened children, surgery is postponed to a later date or carried out in several stages.
Surgeries allow you to restore the integrity of the speech apparatus and the proper functioning of the palate.
Forecast of rhinolalia
If treatment is started on time and completed, the prognosis is favorable. When selecting a correction program, it is necessary to take into account the child’s age, level of development and intelligence. Class materials should be understandable and interesting to the child. This is the only way to make progress in treatment.
In addition, the effectiveness of therapy depends on the following factors:
- how timely treatment was started;
- does the child have any concomitant pathologies?
- how successfully the surgical intervention was performed;
- how developed the child is intellectually, and what is his character and a number of others.
The willingness of parents to get involved in the process and spend a large amount of time on independent activities with their child is crucial. The functional form of the disease has the most favorable prognosis.
| Speech therapy session for rhinolalia |
Forecast
The prognosis for different types of disease differs. Functional rhinolalia, as a rule, has a favorable prognosis and is eliminated with the help of phonopedic exercises and speech therapy classes.
The effectiveness of overcoming organic rhinolalia is largely determined by the results of surgical treatment, the timing of the start and completeness of speech therapy work.
Fulfillment of prescriptions and regular training usually lead to good results.