What functions does it perform?
The spleen is one of the most mysterious organs of the human body. It is located behind the stomach, in the left hypochondrium, and has the shape of an elongated hemisphere. For a long time it was believed that the spleen performs digestive functions, but modern scientists have proven its relationship to the immune system.
Functions of the spleen:
- formation of red blood cells and lymphocytes
- cleansing the blood of harmful microorganisms
- formation of immunity
- normalization of metabolic processes in the body
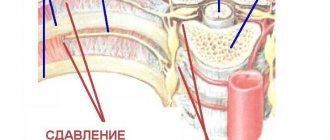
In an adult, the length of the spleen is about 8-14 cm and the width is 4-6 cm. Its weight does not exceed 400 g. The organ is covered with a capsule. The place where blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as nerve fibers, enter it is called the hilum. Fixation of the spleen is carried out due to intra-abdominal pressure, which is provided by special ligaments covering the organ on all sides (with the exception of the hilum of the spleen, as well as the place of contact with the tail of the pancreas).
Treatment with propolis
It is recommended to treat the spleen with propolis infusion. You can buy the product at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself. Before use, please note that it contains alcohol.
Preparation:
- Place propolis (60 g) in a dark glass container.
- Pour the bee product with alcohol, high-quality vodka, and homemade pervach (200 ml).
- Leave in a cool, dark place for a week.
Propolis infusion should not be taken in its pure form; before use, dilute with boiled cool water (30 drops of product per 60 ml of water). Reception is carried out according to the scheme. For a week and a half, take the composition daily every three hours. Take a short break (5 days), continue taking it, but use the product only three times a day.
Symptoms
Severe pain behind the stomach, in the area of the left hypochondrium, indicates a pathology of the spleen. Discomfort may extend to the shoulder blade area. Similar manifestations occur due to various cracks and wounds, ruptures of the spleen. If the problem is accompanied by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, the patient may experience an attack of shock. In this case, symptoms are observed:
- nausea and vomiting
- tremor
- paleness of the skin
- thirst
- lowering blood pressure
- anemia
- difficulty breathing
A protruding lump in the left side may indicate an enlarged spleen. At the same time, a person’s skin turns pale, especially on the face. When moving or straining, the pain in the left hypochondrium intensifies, and discomfort occurs in the navel. These manifestations are accompanied by excessive fatigue, decreased immunity, and damage to the lymph nodes.
Symptoms of an enlarged spleen:
- decrease in hemoglobin
- decreased immunity
- ulcers on the upper and lower extremities, as well as in the mouth
- increased heart rate
- frequent bleeding
- increase in temperature indicators
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach
If you experience such symptoms, you should seek medical help.
Sudden onset of pain
Sharp, sudden pain in the place where the spleen is located may be a consequence of physical activity or indicate the development of the disease.
To relieve pain, simple steps are required:
- Lie on a flat surface with your arms and legs extended at your sides.
- Calm down, relax. A sedative may be taken.
- Establish even breathing.
If the condition does not improve, an ambulance is required. Self-medicating and leaving signals that have occurred without a medical examination is dangerous. You cannot heat or cool the sore spot. This may cause deterioration in health.
↑
Causes
The peculiarity of the spleen is that it does not have pain receptors, so it cannot hurt. Discomfort occurs due to stretching of the splenic capsule against the background of various pathologies, open or closed injuries. Pain in the spleen is often a consequence of damage to other organs and systems. As a rule, the cause of this problem is injury, infectious diseases, tumors, abscesses, and tuberculosis.
Also, disturbances in the functioning of the spleen occur against the background of:
- congenital defects (absence of the spleen, its non-standard size or shape)
- twisting of the splenic pedicle (volvulus)
- irreversible degenerative processes in elderly people
- splenomegaly (pathological enlargement of the spleen due to infectious diseases, increased temperature or lymph nodes, jaundice, anemia, etc.)
It is impossible to identify the cause of pain in the spleen without qualified medical care. Timely consultation with a doctor increases the patient’s chances of recovery.
Infectious diseases
Infectious diseases of individual organs and systems caused by pathogenic biological agents (viruses, fungi, bacteria, etc.) cause dysfunction of the spleen.
As a rule, discomfort or pain in the spleen area occurs as a complication of the following diseases:
- sepsis
- typhoid fever
- measles
- meningitis
- scarlet fever
- anthrax
- sepsis
- syphilis
- malaria
- hepatitis
- mononucleosis
- lymphocytosis, etc.
These diseases can provoke the occurrence of an arterial thrombus, which, in turn, causes a severe pathology - splenic infarction. Another consequence of infectious diseases is spleen abscess. Enlargement of the organ occurs due to damage by toxins, poisons, and pathogens.
Closed and open injuries
According to the generally accepted classification, splenic injuries can be open or closed. The first type is wounds (gunshot or stab wounds), with damage to nearby organs and systems. According to statistics, open wounds of the spleen are much less common than closed ones. As a result of such injuries, the functionality and integrity of the stomach, liver, lungs, gall bladder, etc. are impaired. Closed (or subcutaneous) injuries to the spleen occur as a result of injuries, bruises, single or multiple ruptures. With such injuries, the integrity of the capsule and parenchyma is destroyed (separately or together). The most severe complications of closed-type spleen injuries are rupture of the capsule, hemorrhage into the peritoneal cavity, and complete separation of the organ.
Infectious diseases
Swelling of the spleen is one of the common signs of infectious diseases. The organ increases in size within 350-550 g, its structure and color change. If the patient has an infectious disease, the spleen becomes very fragile. Minimal trauma or bruise can cause rupture of this organ. A person feels mild discomfort or acute pain in the left hypochondrium due to enlargement and stretching of the spleen capsule.
Splenic infarction
Vascular spasms, blood clots or embolism can provoke a serious disease - splenic infarction. The pathology is characterized by the death of organ tissue (necrosis). In advanced cases, the following clinical picture can be observed:
- discomfort, heaviness, pain in the left hypochondrium
- temperature increase
- stool disorders
- general intoxication
To make a diagnosis, studies using ultrasound, MRI, and CT are required. In the final stages of the disease, death of large areas or all of the splenic tissue can be observed. The pathology is common between men and women, whose average age is about 65 years.
Typically, splenic infarction occurs from spasm or blockage of the splenic artery. Such conditions lead to:
- hematological pathologies
- deterioration of blood properties
- heart or vascular diseases
- benign or malignant formations
- open and closed injuries
- infections and parasites
A splenic infarction develops due to a disruption of the blood supply to the tissues of the organ and blockage of the arteries. This affects the immune system, endocrine and metabolic processes in the body.
Abscess
A splenic abscess is an abscess (suppuration) of a certain area of the organ. This is a cavity filled with pus, which is often a consequence of another disease: an infectious process, hematoma, or splenic infarction. The formation can be large, single, or collected from multiple small ulcers, capable of connecting with each other as the disease progresses.
Symptoms of splenic abscess:
- pain in the left hypochondrium area
- pain may radiate to the left side of the body and intensify with breathing, tension, or increased load
- weakness
- dizziness
- temperature increase
- digestive disorders: nausea, vomiting
The cause of an abscess can be trauma, infection, parasites, or splenic infarction. As a rule, the patient is indicated for urgent surgical treatment in combination with drug therapy. Patients suffering from immune system disorders: HIV infection, lymphocytic leukemia, anemia, leukemia are predisposed to abscesses. A spleen abscess can cause the development of complications: fistulas, intestinal bleeding, purulent contents entering the abdominal cavity, sepsis.
Tuberculosis
In most cases, splenic tuberculosis is a complication of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients. As an independent disease, this pathology is much less common. The causative agents of the disease are pathogenic bacteria that spread throughout the body through the blood or lymph. Tuberculosis of the spleen is characterized by the appearance of small single or multiple nodules on the tissues of the organ. A provoking factor in the development of the disease can be reduced immunity, polluted air, or the presence of a patient diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis. As a rule, the disease progresses slowly, without pronounced symptoms. Over time, the pathology becomes chronic.
Symptoms of chronic tuberculosis of the spleen:
- temperature rise to 37-37.5 degrees
- pain in left side
- loss of appetite
- weakness, low performance
- pain in the left side of the body
- enlarged spleen
- changes in blood composition, decrease in blood clotting
- anemia
- liver tuberculosis
Splenic tuberculosis in acute form is manifested by a sharp increase in temperature, a decrease in platelets and leukocytes in the blood. The person becomes weak and sick.
Oncology
Malignant tumors of the spleen are rare. As a rule, this problem is a consequence of other oncological processes in the body.
Malignant formations in the spleen area:
- sarcoma
- lymphosarcoma
- reticulosarcoma
- fibrosarcoma
- angiosarcoma
At the initial stages of the disease, an enlargement of the spleen and its bulging may be observed. The patient's general condition remains unchanged, as do the blood composition indicators.
Discomfort on the left in the hypochondrium area, extending to the scapula area, can occur in the later stages of cancer. Such a symptom indicates the neglect of the disease, and possible death within several years.
Women may develop cysts in the spleen. The reasons for their appearance are one or a combination of several unfavorable factors:
- frequent changes in hormonal levels;
- bad ecology;
- poor nutrition;
- other diseases;
- injuries;
- bad heredity, etc.
Symptoms of cysts in the spleen include stool disturbances and pain in the left hypochondrium. A woman may feel heaviness in the stomach and nausea immediately after eating. Manifestations of allergies may occur; upon palpation, the doctor diagnoses an enlarged spleen.
The best painkillers
Drugs called analgesics are designed to reduce the severity of pain.
The most effective painkillers contain the following active ingredients:
- Ibuprofen.
- Nimesulide.
- Ketorolac.
- Analgin.
- Paracetamol.
All analgesics are non-narcotic or narcotic in nature. The latter are used only as prescribed by a doctor.
The rating of the best painkillers is:
- Ketanov. The active ingredient is ketorolac. A powerful remedy. The result of its impact appears quickly, within forty minutes. To achieve a more effective analgesic effect, Ketanov is taken on an empty stomach. The duration of pain relief is up to six hours. Often a one-time dose is enough for minor ailments. The maximum daily dose is four times, the course is five days. Allowed for admission from the age of sixteen.
- Nurofen. A non-narcotic pain reliever based on the analgesic ibuprofen. It begins to act forty-five minutes after administration and provides pain relief for up to eight hours. The drug is convenient because it has a wide range of release forms: syrup, effervescent tablets, rectal suppositories, gel. It has antipyretic properties and acts quickly. The speed of action is comparable only with paracetamol, not much inferior to it. Nurofen is approved for treatment even in pediatrics and has few side effects.
- Nise. Has a powerful analgesic effect. But it has a short period of pain relief. The action begins half an hour after administration, and its concentration is maximum within three hours. The composition contains the active substance nimesulide. The medicine reduces the temperature. It is produced in the form of tablets, including soluble tablets, suspensions for use by children aged two years and older, and ointments.
- Novigan. Combination agent. The composition includes the analgesic ibuprofen in combination with the antispasmodic pitofenone. Thanks to this, it has a long-term pharmacological effect. Reduces the severity of an attack within twenty minutes after taking it. Available only in tablets, limited to the age of use - from 16 years.
- Pentalgin. Mixed medication. It contains drotaverine, paracetamol, caffeine, naproxen, pheniramine. This makes the medicine universal in its action. The patient receives analgesic, antipyretic, antispasmodic, and relaxing effects. Relief occurs within a period of ten to forty minutes. Contraindicated for children.
- Mig 400. Made from ibuprofen. The release form is tablets with a division exactly in the middle. The whole tablet is prescribed for a single dose for unbearable pain. For moderate painful manifestations, half is enough.
- Dexalgin. Strong painkiller. Suitable for postoperative, post-traumatic pain, cancer metastases. Analgesia is observed after half an hour and lasts up to six hours. Available in ampoules and tablets.
- Spasmalgon. One of the components of the medication is analgin (metamizole sodium).
- Analgin. Relieves spasms, reduces inflammation. It is easily absorbed, which ensures rapid pain relief - within the first twenty minutes. Side effects are minor and rare. It acts for a short time, which makes it suitable for mild pain. Can be used from the age of eight.
- Paracetamol. The antipyretic effect of the drug is much stronger than that of the anesthetic. Safe to use even in the field of obstetrics and pediatrics. Available in different forms. These are suppositories, syrup, capsules, solution for parenteral administration, powder for preparing a solution. Valid for up to six hours. Not approved for long-term use. Combination with salicylates increases the risk of urinary tract cancer.
In addition to non-narcotic drugs, there are also narcotic drugs. They are prescribed for use only by a doctor under conditions of severe unbearable pain. These drugs include Promedol, Tramadol.
↑
What to do
Spleen diseases are rarely diagnosed at an early stage. A person begins to suspect a problem after the organ increases significantly in size, causing severe discomfort or severe pain. If you have alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor without waiting for the condition to worsen.
After this, you will need to undergo an examination and pass all tests prescribed by a specialist. If you have severe acute pain in the spleen, you need to call an ambulance. After this, the patient needs to take a lying position. In this case, it is recommended to monitor the patient’s breathing - it should be deep and calm. It is forbidden to apply hot or warm compresses to the sore spot, as such actions can harm the patient’s condition.
Septic spleen
This is a disease that is characterized by severe stagnation of blood in the organ. Leads to the fact that the tissues soften to the state of porridge.
The spleen gives a signal about the disease of other organs.
If it hurts and the spleen radiates to the liver, then this may be a sign of incipient cirrhosis.
Also, some diseases of the circulatory system affect the functioning of the spleen:
- leukemia;
- hypoplastic anemia;
- Gaucher's disease.
Symptoms:
- mucous membranes bleed;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
Pain in the organ can be a symptom of diseases such as:
- typhoid fever;
- malaria;
- hepatitis A;
- sepsis;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- gallstones.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have pain in the spleen, you should consult your family doctor or general practitioner. In the future, the patient will need the help of highly specialized doctors - a gastroenterologist or surgeon. Treatment of spleen diseases is carried out under the supervision of a specialist. In advanced cases, surgical removal of the organ is recommended. This procedure will not affect the patient’s performance in the future. Drug therapy for pain in the spleen is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, relieving pain, and stabilizing the functions of the organ.
As prescribed by a doctor, the following can be used:
- allergy remedies
- anti-inflammatory and/or painkillers
- antibiotics
- vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system
- antitumor or antituberculosis drugs, etc.
Treatment of spleen diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Traditional medicine can be used as supportive medications (after consultation with a specialist).
Where and how exactly does this organ hurt?
In order to understand that it is the spleen that hurts, you need to analyze your condition in detail. The following signs will help suggest damage to this particular organ:
- pain of moderate intensity;
- bothers the left side under the rib in the depths;
- pain of moderate intensity, bursting, dull or aching in nature;
- discomfort is not associated with eating or physical activity.
It is important not only to understand where the spleen hurts, but also to establish the cause of this condition. A one-time episode is not a cause for concern. A constant feeling of discomfort is a reason to contact your doctor.
Diagnostics
The very first and most important methods for diagnosing spleen diseases are a visual examination of the patient, palpation of the sore spot, and taking an anamnesis. Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the following may be prescribed:
- X-ray - allows you to see an increase in the size of the spleen, gall bladder, stomach, adrenal gland, kidney. Before the procedure, oxygen is injected into the patient’s abdominal cavity to improve the information content of the study.
- Examination of an organ sample obtained by puncture. The method is used extremely rarely due to its complexity.
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
The difficulty of diagnosing diseases of the spleen arises due to the close location of this organ to the gallbladder.
Forecast
Decisive for the prognosis for all diseases of the spleen is early diagnosis and correct therapy. The vast majority of spleen diseases can be treated without surgery. More than 90% of diseases in children can be treated without surgery.
If only part of the spleen is removed, the remaining tissue can completely “take over” the function of the removed one. In 4% of cases, patients develop sepsis. Life-threatening effects usually occur within the first 24 to 72 hours. About 80% of patients with a ruptured spleen recover within 7-10 weeks.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle will help to avoid problems with the spleen: a balanced diet, regular exercise. The body must receive a sufficient amount of nutrients, especially copper, in the form of vitamin complexes.
Other recommendations:
- avoid bruises and wounds in the abdominal area
- drink enough water to cleanse the body, in particular the spleen
- give up alcohol, especially low-quality alcohol
- Conduct regular preventive examinations and laboratory blood tests
- wear loose clothing that does not cause discomfort while moving
The diet of patients suffering from spleen diseases must contain a sufficient amount of nuts, beef liver, and fish. It is recommended to eat carrots and beets as vegetables. Timely treatment of any diseases, including infectious ones, will avoid the development of complications in the form of disruption of the spleen. It is also necessary to examine injuries and bruises of the torso, in particular those resulting from fights and falls.
Risk group
There is a certain group of people susceptible to the problem of pathological diseases of the organ. For example, there are congenital pathologies. In addition, do not forget about risk factors, including alcohol abuse, the development of liver cirrhosis, the use of illegal drugs, viral hepatitis leading to cirrhosis, dangerous sports - boxing and others.
How do people live without a spleen? More details