The walls of the veins are damaged during open and closed injuries, which can be accompanied by severe bleeding. Loss of blood leads to ischemia or insufficient nutrition of various parts of the body where hemorrhage occurs. To save the life of the victim, you will need to provide first aid for venous bleeding.
Loss of blood leads to ischemia or malnutrition of various parts of the body.
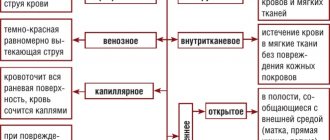
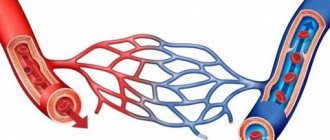
When a vein ruptures, blood comes out in a copious stream or oozes. Such a lesion is sometimes accompanied by edema and hematoma. The activity of the arteries is not impaired, and the skin does not change its color. If there is no fracture or dislocation, the limb moves freely.
Differences in venous bleeding
Venous blood is the blood that flows back from the organs to return carbon 2-monoxide. It contains no useful elements and produces a low concentration of O2. But, enriched with end products of metabolism, it contains a large amount of sugar. It is characterized by the highest temperature regime, so you can often hear “warm”. It is taken away for laboratory diagnostics. Nurses administer all medications through veins.
Human venous blood, in contrast to arterial blood, is darker in color. The pressure in the vascular bed is lower, bleeding that occurs when the veins are injured is insignificant. Blood does not flow quickly. Bleeding can usually be controlled with a pressure bandage. To prevent the reverse movement of venous blood there are special valves. They prevent backward flow. pH is low.
Note! There are more veins in the human body than arteries. They are located closer to the skin; in people with fair skin types, they can be seen visually.
Medical care for bleeding should be in the knowledge base of any person. Anyone may encounter a situation where bleeding occurs in relatives or a random person on the street. During the time the ambulance is traveling, a person can lose a large amount of blood, which will negatively affect his health. And with bleeding from deep vessels, death cannot be ruled out. Venous bleeding can be of different locations and medical care is different. There is bleeding:
- Vessels of the head and neck.
- Superficial vessels of the arms and legs.
- Deep vessels of the arms and legs.
Causes of bleeding:
- Injuries and cuts.
- Bleeding from dilated vessels as a result of varicose veins.
- Pathologies of the circulatory system.
- High pressure.
In order to provide quality help, you need to be able to distinguish the type of bleeding. Signs of venous injury are as follows:
- Flow of dark maroon blood from the wound without pulsation or in a weakly pulsating stream.
- Pale skin, weakness, and with a great loss - fainting.
- Drop in blood pressure.
- Tachycardia (fast pulse).
When the vessels of the extremities are injured, slight blood loss is observed. Often she stops on her own, and quite quickly. But you should not hope for this and not provide first aid, because this can also result in minor injury to the deep veins.
With high blood pressure, alcohol intoxication and blood diseases, the rate of thrombus formation slows down, and blood loss may be greater. It is worth paying attention that the deep veins are located on the inside of the arms and legs, therefore, if the injury is localized in this place, you must immediately assume their damage and provide the necessary medical care. Blood can enter from a vessel anywhere in the body, and medical care varies.
What could it be from?
Causes of internal bleeding:
- Blunt mechanical injuries of the abdominal cavity, in which rupture of the liver or spleen tissue occurred. Less commonly, such injuries lead to damage to the pancreas and intestines.
- Rib fractures when sharp bone fragments rupture blood vessels and the pulmonary pleura.
- Traumatic brain injuries are the most dangerous. The limited cavities in the skull lead to the fact that even a small volume of blood contributes to compression of the brain structures, and this can be fatal.
- Intra-articular type of fracture, extensive bruises of the articular tissue.
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system - rupture of blood vessels causes cancer, peptic ulcer of the duodenum and stomach, erosive gastritis, esophageal varicose veins.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
Rarely, bleeding can occur caused by a single intake of a large amount of food (if a person has cracks in the walls of the stomach).
In women, rupture of blood vessels in the organs of the genitourinary system can be caused by ectopic pregnancy, surgical termination of pregnancy, or ovarian rupture. During pregnancy, such a pathological phenomenon can provoke placenta previa and placenta abruption.
Urgent actions
You can stop serious loss of blood from the veins on your own. First aid for venous bleeding will help avoid negative consequences. Algorithm of actions step by step:
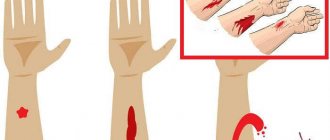
- Elevate the injured limb: this will make it possible to reduce, and possibly completely stop, blood loss.
- You can stop it by using “folds”. To do this, the victim’s limb must be bent at the elbow or knee, and then tightly fixed, bandaged to the body.
- To stop blood loss, the use of a pressure bandage is indicated. For this purpose, the medical staff uses an individual dressing package. In a situation where there is no material at the scene of the incident, any clean cloth can be used.
Advice! While the search for the necessary material for bandaging is underway, you must ask an assistant or the injured person to press the area below the bleeding with a finger.
The use of a pressure bandage to stop bleeding from a vein is the main point that requires description in detail:
- The wound site is treated with an antiseptic, and the edges with iodine.
- The dressing material is wrapped several times around the injured area below the wound.
- To cool the injured area, use a cold compress: ice, snow, freezing from the refrigerator.
Cooling “helps” the pressure bandage in stopping blood from flowing from the vein. It is necessary to apply several fingers to the vessels that go below the wound. The pulse should be clearly audible there. If there is no pulsation, this means the bandage is very tight and needs to be replaced or loosened.
If a pressure bandage, applied correctly, becomes saturated with blood, it is prohibited to replace it! Before the ambulance arrives, do not perform an autopsy, but apply several more layers of dressing material to the wound.
Diagnostics
A medical examination, which is carried out in a hospital setting, will help determine the cause and source of pathological processes. Taking into account the initial examination and preliminary diagnosis established by the surgeon, the patient is prescribed the following diagnostic measures.
Scroll:
| Name | Description |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | The patient is prescribed gastric intubation, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, and colonoscopy. |
| Intra-abdominal | Consultation with a surgeon or traumatologist is necessary. The patient is referred for abdominal puncture and laparoscopy. |
| Gynecological bleeding | The examination is carried out by a gynecologist. Additionally, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. |
| Pulmonary | The main diagnostic method is chest x-ray and pleural puncture. |
| Intra-articular | The examination is carried out by a surgeon or traumatologist. The patient must undergo an x-ray examination and puncture of the joint. |
Diagnostics will allow you to determine the location of internal bleeding and its main cause. Based on the results obtained, the specialist selects the most effective therapy for the patient.
Ways to stop venous bleeding
First aid for venous bleeding involves stopping it. Depending on the location of the injury, first aid to stop bleeding differs. The most effective ways to stop the flow of blood from a vein are:
- Applying a rigid bandage.
- Lifting the limb upward.
- Pinching the area of the injured vessel with your fingers.
Medical care to stop blood loss from a vein includes disinfection of the wound site. A good remedy is hydrogen peroxide. A sterile bandage is applied over the wound. If it is absent, you can take any pure matter. Then apply a tight cotton ball. And they bandage it tightly over it, despite the fact that venous bleeding is not active.
Sometimes a pressure bandage is powerless. This indicates deep vein injury. Then the method of pulling with a tourniquet is used. If deep veins are damaged, it is important to immediately go to the emergency room or call an ambulance. After all, a person can very quickly lose a critical amount of blood. A major loss will provoke a state of shock and kidney problems. If bleeding from deep veins is suspected, the following steps should be taken:
- Place a cushion under the injured leg or arm.
- Apply a tourniquet.
- Cool the injury site.
- Take the injured person to the first aid station.
Knowledge about providing assistance will never be superfluous; no one is immune from accidents.
Further treatment
Combined methods are mainly used.
First of all, it is necessary to eradicate the source of the disorder. This problem is solved by surgical intervention methods.
The vessel and tissues are sutured, and the damaged area is eliminated (if necessary, doctors perform a resection and remove part of the altered structures). Mandatory measures are also taken regarding the consequences of the pathological process.
In parallel, transfusion is necessary to restore lost blood volume and the introduction of saline solutions to correct the balance of electrolytes. The patient's condition is constantly monitored in a hospital setting.
Rules for applying a tourniquet
Application of a tourniquet for blood loss from a vein is used very rarely: it is necessary only when large vessels are injured, most often arteries.
Attention! By unprofessionally applying a tourniquet or holding it on the human body, the rescuer provokes a danger that can cause tissue death.
This complication can only be removed with the help of surgery, amputation of the limb. However, if the victim has profuse blood loss, and according to the rules, a pressure bandage and other methods of eliminating blood loss have not yielded results, the bleeding can only be stopped if a tourniquet is applied. The actions are:
- Find a material that you will use as a tourniquet: scarf, handkerchief, rubber tube, rope.
- Step back from the wound site approximately 50 mm downwards.
- “Tighten” the tourniquet until the blood stops flowing.
Degrees
Hemorrhage most often results from various injuries with a violation of the anatomical integrity or diseases occurring in the body of a sick person. These could be various pathological malfunctions of the cardiovascular system, cancer and much more.
According to severity they are divided into:
- lungs : with this type of bleeding, only 10-15% of all blood is lost;
- medium : from 15% to 20% of the volume of available blood is lost;
- severe : blood loss is 20-30%.
We are talking about massive blood loss if 30% to 50% of the blood is lost. A loss of 50-60 percent of all circulating blood is considered fatal; a loss of more than 60% is considered absolutely fatal.
Forecasts
After the injured person is brought to the clinic, the doctor will assess his condition and determine the location of the injury. If necessary, he will perform an operation in which the ends of the veins are sutured. Depending on the complexity of the surgery, the location of the veins, the severity of blood loss and the condition of the injured person, the operation is performed under general or local anesthesia. Next, the doctor applies a sterile bandage to the wound. If the injury is not too serious, the patient is allowed to go home.
Depending on the speed of regeneration, the wound is restored within 7–28 days. At this time it is necessary:
- limit physical activity;
- refrain from drinking alcohol.
If bleeding starts again, you should seek medical help from a doctor.
Knowing how to provide first aid to a victim can sometimes save a person’s life. The main thing is to follow the rules and go to the hospital after bleeding stops.
Consequences
Damage to the integrity of the walls of blood vessels with a large volume of blood leaking into the cavity without timely assistance provokes dangerous consequences. The functioning of organs located in the abdominal cavity is disrupted. Soft tissues deprived of blood circulation do not receive nutrients and oxygen; necrotic processes can develop in them, which can cause organ loss.
Internal hemorrhages may require resection of an internal organ, such as the stomach or uterine cavity in women. After such operations there is a long and difficult recovery period with a high risk of developing various complications.
Bleeding in the skull often leads to fatal consequences. If the risks of death can be eliminated, there is a possibility that important brain centers will be affected. This will further negatively affect the mental, mental or physical state of a person.
A decrease in blood pressure can lead to cardiac arrest. Bleeding often contributes to death if the victim is not provided with medical assistance in time.