Signs of a heart attack in women may have features that make diagnosis difficult. Myocardial infarction is an acute heart disease that is accompanied by the death of heart muscle cells due to the cessation of blood supply to it. Dead cells are replaced by connective tissue, which is why the functions of the heart muscle are not fully restored. It is important to know the signs of a heart attack in order to recognize it as quickly as possible and provide proper assistance - a person’s life may depend on it.
Signs of a heart attack in women in women over 50 years of age can be masked as an exacerbation of pancreatitis, an attack of arrhythmia, bronchospasm, neurological disorders, flu or a cold.
Difference in symptoms at 40-60 years old
The first signs of a heart attack in women, both young and old, are characterized by chest pain, shortness of breath, cyanosis and pallor. However, the symptomatic complex is not limited to this.
If a representative of the fairer sex is of fertile age and is currently undergoing a menstrual cycle, it is likely to be abruptly interrupted due to the release of stress hormones.
In women over 60 years of age and beyond, such signs are not observed; menopause occurs; climacteric moments generally make the symptoms scanty and do not allow timely attention to the patient’s condition.
All doubtful cases require hospitalization in a hospital.
conclusions
More than 15% of cases of heart attack at a young age develop as a result of hormonal disorders, changes in blood clotting, congenital pathology of the heart and blood vessels. In addition to atherosclerosis, the risk of a heart attack increases the risk of an unhealthy lifestyle, alcohol and smoking abuse, and excess weight. Often, a heart attack at the age of 35–45 years occurs with atypical symptoms, which complicates diagnosis and can lead to death if it is delayed to see a doctor. When the first alarming symptoms appear, you should call an ambulance. If a heart attack is confirmed, delivery to the hospital within 2–6 hours will allow stenting, minimizing the risk of consequences and preventing a dangerous outcome.
Symptoms of the previous condition
Signs that indicate a likely approach of a heart attack in the near future appear for approximately 2-3 months.
Asthenic moments
Manifested by weakness, drowsiness. Why is this happening? Myocardial infarction develops against the background of coronary insufficiency, when cardiac structures do not receive enough nutrients and oxygen.
The process moves gradually; there is usually no rapid progression. Due to a decrease in the contractility of the heart, a lack of blood circulation occurs in the brain. Hence increased fatigue.
Another point is the poor supply of nutrients and oxygen to muscle fibers. Metabolic processes are slowed down.
This is not enough to cause atrophy, but it is enough to make the patient lethargic. The same moments are observed during the rehabilitation period.
Sleep disorders
There are many forms. The classic ones look like this.
The patient lies down and prepares for the night's rest. After 10-15 minutes, awakening occurs, it is no longer possible to lie down, and an unpleasant, oppressive feeling of false cheerfulness develops.
After another half hour, fatigue sets in again. But again there is no point, it is impossible to fall asleep. And so on all night.
Another option is waking up frequently during rest.
Both conditions are extremely painful, leading to asthenia and constant fatigue. A complete “reboot” of the brain does not occur. In addition, a long-term regimen of this kind leads to an imbalance of melatonin in the body.
This is fraught with impaired reproductive function, decreased libido, increased vascular tone, and early aging. The body literally works for wear and tear.
Nocturia
Simply put, excessive urination at night. In a healthy person, daily diuresis predominates, the volume being up to 80-90% of the total amount of urine.
A change in balance indicates kidney damage or a compensatory mechanism. The body strives to remove excess fluid; it does not have enough time during the day.
To reduce the load and reduce the amount of circulating blood, the excretory system works more actively. This is a worrying sign.
Although coincidences are possible, diagnostic testing should be performed. At a minimum, ECG, ECHO, measurement of pressure and heart rate. Ultrasound of the kidneys.
Mental disorders, emotional lability
The disorders are associated with insufficient blood circulation in the brain. The production of serotonin, dopamine, and neurotransmitters decreases.
On a subjective level, this manifests itself as severe depressive states. The woman becomes irritable, angry, and whiny. Minor moments can drive you crazy. Relieving symptoms does not give full effect; identification of the root cause is required.
Emotional and mental disorders are a nonspecific symptom of myocardial infarction. Differential diagnosis is necessary.
Arrhythmias
Various types of heart rate disorders. They are represented not only by the classic and well-known “general public” sinus tachycardia and the reverse phenomenon, but also by extrasystole, ventricular fibrillation (fibrillation, atrial flutter).
The development of such symptoms does not always precede a malnutrition of the cardiac structures. Perhaps the reason lies in the blockage of the bundle branches. An ECG test provides more information about the patient's condition.
Bleeding, disturbances in the rheological properties of blood
Basically, there is a release of liquid connective tissue from the gums. Such abnormalities also have no obvious connection with heart problems. But this is only at first glance.
In fact, a change in fluidity, an increase in vascular permeability affects the general situation. The symptom of pre-infarction in women occurs in 25% of cases.
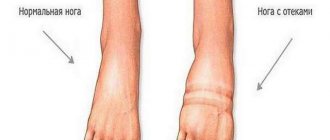
Edema of the extremities
Peripheral. Legs and ankles suffer. The symptom appears as a result of insufficient kidney function.
There is an excess load on the heart. The volume of circulating blood increases sharply, and disruption of the normal activity of cardiac structures develops. Heart rate rises, blood pressure too.
Urgent assistance required. At a minimum, mild diuretics are prescribed. Saving potassium and magnesium so as not to further worsen the situation.
Dyspnea
Characterized by the impossibility of normal gas exchange, even in a state of minor physical activity.
The manifestation is accompanied by dizziness, but not always. As the process progresses and approaches the critical point, the symptom develops in a state of rest. This is an alarming moment. Urgent diagnosis is required.
Causes and predisposing factors
In almost 90% of cases, the cause of myocardial infarction is atherosclerosis, which provokes clogging of the coronary arteries with fragments of atherosclerotic plaques. This process in the bloodstream causes a cessation of blood flow to the myocardium and cardiac muscle cells die due to oxygen starvation. As a result, an area of necrosis is formed, which after 1 - 2 weeks is overgrown with connective tissue, and the heart can no longer function normally.
In other cases, myocardial infarction is caused by the following conditions and diseases:
- thrombosis of coronary vessels;
- heart injuries;
- spasm of the coronary arteries;
- tumors.
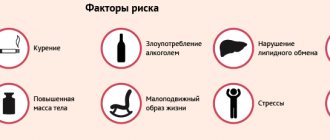
The following predisposing factors can contribute to the onset of a heart attack:
- atherosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- history of myocardial infarction;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- hypo- and adynamia;
- diabetes;
- increased levels of LDL (“bad” cholesterol);
- frequent stressful situations;
- disorders in the blood coagulation system;
- excessive physical or emotional stress;
- drinking alcohol in large doses and chronic alcoholism;
- postmenopausal age in women.
Immediate symptoms of a heart attack
The full clinical picture unfolds within a few hours or, in exceptional cases, a day. After, for example, a hypertensive crisis.
Read how to provide first aid for various types of HA.
Chest pain
There are two main options.
- First. The manifestations are unbearable, oppressive. Burning. It seems as if they sewed a heavy stone into the body. Nitroglycerin helps only partially; the effectiveness speaks specifically about its cardiac origin.
- Another possible type is moderate pain over a long period of time. More than 30 minutes.
The nature of the unpleasant sensations does not indicate anything. This is just an individual characteristic of a person. It is possible for an extensive form to occur without any pain at all.
Dyspnea
In this case, it appears in a state of complete rest. The patient cannot take in air. Hence the emergence of a panic attack: severe anxiety, fear of death.
A person at such a moment is inadequate and can be dangerous to himself. An urgent call to the emergency team is required. The reason is an acute violation of the trophism of the heart and brain. Simultaneously.
Suffocation
Evolution of a previous symptom. Develops as a result of insufficient blood circulation in the pulmonary circle. By accelerating the activity of the lungs, the body tries to compensate for its own condition.
The pressure in the arteries increases, the process only gets worse. Therefore, a general violation of respiratory function begins.
The symptom worsens when lying down, especially after physical activity. Recovery is required in a short time. Death from failure due to an ongoing heart attack is possible.
Arrhythmias
According to the type of tachycardia at an early stage. After a few hours, contractility decreases. The rapid heartbeat may persist, but the pulse will be palpable extremely weakly.
A deviation can only be registered based on the results of objective research. Another clinical variant is alternation with bradycardia.
Both types have unfavorable outcomes, with the likelihood of death increasing exponentially. Corrective measures are required.
The problem is that glycosides are contraindicated, and antiarrhythmic drugs can only make things worse. The doctor is required to be highly qualified.
Headache
The result of disruption of normal blood flow in cerebral structures. Recovery is urgent, ischemic stroke is likely to develop. Acute necrosis of accumulations of nerve tissue.
Peripheral edema
For the same reasons. Impaired blood pumping. The kidneys also receive insufficient nutrients. Hence the drop in filtration rate.
Pale skin
The patient becomes like a wax figure. The shade of the dermis is marble.
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle
Blue discoloration of the area around the mouth.
Excessive sweating
Hyperhidrosis is of a reflex nature. Due to insufficient nutrition of the hypothalamus, the brain structure sends chaotic signals, the result is a false desire of the body to cool down. There is no effect from this.
Risk group
Character traits inherent in women such as caring for the family, worries about the fate of children, dedication and self-sacrifice contribute to their being at risk. Such women practically forget about themselves, do not care about their own health, ignore or simply forget about visiting a doctor for preventive purposes. Without paying due attention to the warning signs of the disease, they may end up in a situation where irreversible processes occur.
Women who live a lifestyle that is far from healthy are also at risk of having a heart attack. Those who engage in heavy (harmful) physical labor or suffer from chronic diseases are also not insured.
It is very important for women over 50 to see a cardiologist regularly.
Statistics show that the rate of cardiovascular disease is so high that women aged 30 or 40 may also be at risk. Therefore, preventive methods should be applied starting at an earlier age.
Manifestations of atypical forms of MI
Classic symptoms of a heart attack in women include chest pain, breathing problems, and other issues. Is this always an axiom? No. It is possible that some signs may be strengthened and others weakened.
Abdominal type
Described rather sparsely. There is not enough empirical material, so it is impossible to say exactly the reasons.
The clinical picture of this type of infarction is characterized by manifestations that are pathognomonic for an acute abdomen.
This condition develops with peritonitis, inflammation of the appendix, intestinal obstruction and other conditions.
Symptoms:
- Unbearable pressing, cutting pain in the abdominal cavity. They can be easily removed with Nitroglycerin, which should prompt doctors to the origin of the unpleasant sensation. There are no specific tests, such as Shchetkin-Blumberg, Lenander and others. Against the background of abdominal factors, this practically does not occur.
- Vomit. Repeatedly. Unlike other types of condition, such as poisoning, it does not mitigate the course of the main pathological process. It is reflexive in nature, so there is no relief.
- Heartburn and other dyspeptic symptoms. Like flatulence and increased gas formation.
Often such patients are referred to gastroenterology. Precious time is wasted, which is why urgent on-site diagnostics are indicated. This imposes certain requirements on the qualifications of middle and senior personnel.
Asthmatic form
Accompanied by respiratory symptoms. The patient is unable to draw air into the chest normally. In the lying position, asphyxia develops, this is a threatening condition.
Physical activity is impossible in principle, even minimal. Characterized by the absence of pain as such. The heart does not make itself felt, which only complicates the diagnosis.
Additionally, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and pronounced pallor of the skin are noted.
Arrhythmic type
What is the difference between this form of pathological process and a violation of the normal heart rate? Intensity of the sign. An arrhythmic heart attack is accompanied by a significant drop in heart rate to critical levels.
The patient quickly loses consciousness, and standard methods cannot bring her out of fainting. Urgent hospitalization is required. A minimum of diagnostic measures and emergency assistance to restore myocardial contractility.
The prospects are vague, as are forecasts in general.
Cerebrovascular form
Symptoms arise mainly from the central nervous system.
- Headache. Unbearable, localized in the back of the head, crown, and temporal region. Pressing, baling in nature. Follows the beat of the heart. The patient takes a forced position, lying on his side or back.
- Vertigo. As a result of circulatory problems in the brain. There is no ability to normally navigate in space.
- Nausea. Vomiting is less common.
- Darkening in the eyes
- Dyspnea.
- Tinnitus, strong ringing.
- Impaired consciousness such as a decrease in the speed of mnestic and cognitive functions. Memory and thinking weaken. Head in a fog.
- Loss of consciousness. Repeatedly for several hours.
Additional signs include paresis, paralysis, and a feeling of goosebumps running throughout the body. Especially in the event of a stroke. A parallel course of acute necrosis of cerebral structures is also possible; this is a typical complication.
Question: what to do
Because a person who has had a heart attack does not suddenly return to normal life. Sometimes he becomes completely incapable of the previous loads. Therefore, relatives must surround him with care for some time.
It is useful to learn how to give massage to elderly people who have suffered a myocardial infarction.
Caring for yourself
If the family is large, everyone can take turns caring for the patient. Then the consequences of myocardial infarction in the elderly will not be too noticeable for the financial burden of working loved ones.
Hire an assistant
After a myocardial infarction in older people, a nurse or home assistant is hired. During the first period of rehabilitation, it is necessary that someone be with the patient and help around the house, look after his well-being, help him eat, remind him to take his pills on time, measure his blood pressure, and do everything that is necessary.
Invite a social worker
For single men over 60 and women over 55, the state assigns social workers. They do part of the work for free in caring for an elderly person who is mobile but lives without children or relatives:
- purchase and delivery of groceries and medicines (one-time service rate is 4 kg);
- preparing food, helping with meals;
- Payment of utility services;
- cleaning the apartment, washing clothes (in an automatic machine or laundry);
- assistance in obtaining a voucher to a sanatorium;
- psychological support;
- measuring pressure, temperature, dressing, first aid.
Choose a boarding house for the elderly
If children live in another country and are able to pay for professional care and care after a myocardial infarction in the elderly, they have the opportunity to choose a good boarding house.
First aid technique
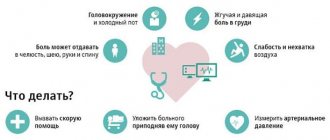
You can't help radically on your own. You need to call the emergency team. While the doctors are on their way, a number of actions need to be taken.
The algorithm is as follows:
- Open a window or window. When a heart attack develops, both the systemic and pulmonary circulation suffers. This means that the efficiency of gas exchange decreases significantly. Excess CO2 in liquid tissue makes adequate nutrition impossible. An increased supply of oxygen is required. In the absence of a special cylinder, adequate ventilation must be ensured.
- Measure blood pressure, heart rate. Signs of a heart attack in women over 50 years of age are blurred. It is necessary to find out what caused the feeling.
- Give 1 tablet of Nitroglycerin. It must at least partially relieve severe pain, which is extremely painful for the patient. If there is no beneficial effect, you can give another one after 10-15 minutes. It is not recommended to drink anything else.
- Make the victim sit down. It is impossible to lay it down, since there is a high probability of asphyxia and death from suffocation. In a semi-sitting position with a cushion placed under the back, the condition quickly returns to normal. The arms and legs should be below the level of the heart so that the peripheral blood flow does not decrease on the one hand, on the other, in order to avoid deterioration of hemodynamics.
- Turn your head to the side. In case of loss of consciousness. This will prevent aspiration of stomach contents when vomiting. After an episode, it is recommended to clear the mouth of food debris using a gauze roll placed on the fingers.
In case of cardiac arrest, perform direct massage. Place open palms one above the other and place them on the chest. Press rhythmically, at a speed of 100-120 movements per minute until normal cardiac activity is restored.
Attention:
If you have no experience with artificial respiration, you should not do it. It won't work out correctly anyway, and time will be wasted.
Consequences
Heart attack is a disease that has an unfavorable prognosis. About 40% of patients are re-hospitalized within a year. The mortality rate in the first year is 10-12%. Many patients develop complications after a heart attack:
- ventricular arrhythmia;
- blockade of the sinus, atrioventricular node - disruption of the generation and conduction of the cardiac impulse;
- cardiogenic shock;
- post-infarction angina;
- mitral valve regurgitation;
- rupture of the papillary muscle;
- Dressler syndrome
- rupture of the ventricular wall or interventricular septum;
- chronic pericarditis;
- chronic heart failure;
- arrhythmias;
- atrial fibrillation;
- left ventricular dysfunction (poor prognostic factor);
- heart failure.
A person’s life changes after a myocardial infarction. To prevent relapses, he will have to reconsider his lifestyle: start eating right, moving more, quit smoking, stop abusing alcohol, and normalize his weight.
What you definitely shouldn't do
- Meals are excluded. If you lose consciousness, profuse vomiting will occur, which will affect the likelihood of mechanical asphyxia.
- Take medications. Many are strictly contraindicated in emergency conditions.
- Wash with cold water. To avoid reflex narrowing of the coronary arteries and aggravation of the situation.
Upon the arrival of doctors, the patient is urgently hospitalized.
Precursor symptoms and the actual signs of a heart attack are heterogeneous. But if you look closely, they can be recognized quite easily.
Verification (confirmation of suspicion) is carried out during diagnosis. Treatment in 90% of cases can prevent the development of pathology and save the woman’s health, and most likely also her life.
Rehabilitation after a heart attack
Recovery of patients after a heart attack should always be comprehensive and aimed at minimizing the risks of recurrent attacks and eliminating the consequences. The rehabilitation course begins during hospital treatment and is compiled individually for each person. It may include the following activities:
- Constant use of medications. The patient may be prescribed the following medications: Aspirin and other antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants, beta blockers, angiotensin inhibitors, lipid-lowering drugs, diuretics, etc.
- Making adjustments to motor activity. The motor mode after an attack expands only on the doctor’s recommendations and does not tolerate forcing events. The amount of physical activity is determined for each patient separately.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Nutrition correction. Your diet should include foods high in vitamins and minerals that are good for your heart. The consumption of caffeine, animal fats, fried foods and salt is mandatory.
- Minimizing overwork and stressful situations.
- Fighting obesity.
- Mandatory follow-up with a cardiologist including echocardiography, ECG, blood tests and exercise tests.
- Sanatorium-resort treatment: sleeping in the fresh air, mineral and gas baths, massage, physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
Diagnostic methods
Based on the clinical picture, it is very difficult to distinguish unstable angina from extensive myocardial infarction or microinfarction. Their symptoms may largely coincide. Even taking an ECG cannot give a clear answer to the question: whether there are areas of necrosis of the heart muscle or not.
To confirm the diagnosis and differentiate it from myocardial infarction, additional instrumental studies are necessary:
- Determination of the level of biomarkers of infarction. If the level of troponin, troponin 1 does not exceed 0.1 ng/ml, there is no increase in the activity of CPK, MB-CPK, LDH, AST or does not exceed 50% of the norm, it is considered that there is no myocardial infarction.
- ECG in 12 leads. Gives the doctor information about the conductivity of the heart muscle.
- Holter monitoring is a continuous recording of an electrocardiogram for 24 hours. Allows you to judge the presence/absence of a heart attack by changes in the dynamics of the cardiogram.
- Ultrasound of the heart. Helps identify areas of the heart with reduced contractility. In case of angina pectoris, as the patient's condition stabilizes, contractility is restored or becomes more pronounced, and in case of a heart attack the changes are irreversible.
- Angiography of the coronary vessels. Allows you to determine the number and size of cholesterol plaques, the degree of vasoconstriction. To perform angiography, the patient is injected with medical dye intravenously. It fills the vessels of the heart, making their outlines clearer on X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Biochemistry and a general blood test are necessary to identify markers of possible complications. For example, low potassium levels indicate a risk of developing ventricular arrhythmia.