Home » Pneumonia »
- Hydrogen peroxide bath
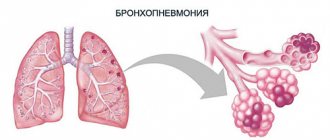
Pneumonia is a serious inflammatory disease of the lungs in which the alveoli (tiny air-filled sacs in the lungs) become filled with fluid or pus. As a result of inflammation, a person is unable to get enough oxygen into the bloodstream. If a diagnosis of pneumonia is made, it is necessary to urgently decide how to cure pneumonia. The disease can have a different course, depending on the age of the patient and the state of his immunity, concomitant diseases, as well as the factor that provoked the infection.
However, the typical and most common symptoms of pneumonia include:
- High temperature (above 38℃, chills, sweating).
- A feeling of weakness, similar to that of a cold or flu.
- Tingling and pain in the chest (intensified by strong inhalation and coughing).
- Increased heart rate.
- Cough with purulent sputum.
Pneumonia has at least thirty different causes. Although most cases of pneumonia are caused by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens, the disease can also be caused by non-infectious causes. These include: chemical damage to the lungs, inflammation caused by food accidentally entering the respiratory tract and allergic pneumonia. In this regard, pneumonia is classified into types depending on the cause of the disease.
How pneumonia develops with coronavirus
Coronavirus pneumonia occurs in several stages:
- Viremia. The course of the disease resembles a cold; this period lasts from 7 to 9 days .
- The turning point occurs from days 9 to 14 . The reason is damage to the epithelial cells of the respiratory organs, the addition of a bacterial infection. It is extremely important that the complication is identified at a critical stage - this increases the chances of a favorable outcome.
- If pneumonia is not detected early, it provokes respiratory distress syndrome. A person cannot breathe without the help of an artificial respiration device (ventilator).
- Stage of immunosuppression. Suppression of acquired and innate immunity occurs if the disease is not stopped at earlier stages.
With coronavirus pneumonia, the main pathogen of a viral nature is often accompanied by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a fungal infection.
Danger when self-medicating at home
The idea of self-medicating even for minor health problems can lead to complications. Taking medications without first consulting a doctor seems to save time and money. However, this can be much more expensive for your health. For example, the incorrect use of antibiotics has very dangerous consequences. Inaccurate dosage of medications is also dangerous for human health and life (especially for a child!).
Attention! Self-medication can cause irreparable damage to health, causing disability and even premature death.
Pneumonia due to coronavirus - symptoms of pneumonia
Pneumonia often develops after a period of relatively mild onset of illness during which:
- increase in body temperature within 37.5-38 degrees;
- sore and sore throat;
- bouts of dry cough;
- lack of sense of smell and taste;
- headaches, severe weakness.
This condition lasts from 2 to 8 days, after which the symptoms intensify:
- the temperature rises to 39-40 degrees, goes down with difficulty and does not last long;
- chest pain occurs when breathing or coughing;
- severe weakness and sweating are noted.
During a cough, there is no sputum or it comes out in small quantities and has a brownish tint. Due to shortness of breath, it is not possible to take a full breath. Respiratory rate is about 22 movements per minute. A person experiences a feeling of lack of air, characteristic of pneumonia due to coronavirus. This symptom manifests itself to its maximum during the period from 6 to 9 days from the moment of infection. That is why doctors advise patients to pay special attention to their own well-being during this time period, and if shortness of breath occurs, seek help.
Increasing respiratory failure can be recognized by the blueness of the nasolabial area. Breathing becomes forced - the intercostal muscles are involved in the respiratory act, the person tries to lean on his hands to make it easier to inhale.
Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain is manifested by:
- constant desire to sleep;
- confused consciousness;
- panic attacks, agitation.
With significant oxygen starvation of the brain, a fainting state develops.
Treatment of the disease - antibacterial therapy
For the treatment of pneumonia, macrolides and fluoroquinolone antibiotics are most often prescribed. To make treatment more effective, antibiotics must be taken according to a special regimen. At the first stage of treatment, the drug is administered parenterally (intramuscularly or intravenously), and then antibiotics are prescribed in tablet form.
Criteria for choosing antibiotics for pneumonia
Antibiotics for the treatment of pneumonia in adults should be selected depending on the patient's age and severity of the condition.
Synthetic, semi-synthetic and natural antibiotics are used to treat this disease. Some of them have a selective effect (on one type of bacteria), and some have a wide spectrum of action.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed based on the course of the disease and the color of the sputum. To do this you need:
- Bacteriological analysis of sputum to determine the pathogen.
- Test for the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics.
- Antibacterial treatment regimen based on the test result.
For severe pneumonia, antibiotics are combined.
You should not prescribe antibiotics yourself, as this can lead to the development of bacterial resistance to certain groups of drugs. As a result, the treatment will be ineffective.
List of drugs and tablets for the treatment of pneumonia
If atypical pneumonia is diagnosed, then specialized antibiotics are used (Sumamed, Clarithromycin). But there is no need to give up broad-spectrum antibiotics.
A combination of two or three drugs, such as Ceftriaxone or Suprax plus Sumamed or Clarithromycin, is often used for pneumonia.
If the inflammatory process has spread to more than one segment, then a combination of drugs from the list is used, such as Ceftriaxone plus Amikacin or Suprax plus Augmentin.
How to take medications - dosages
Adults under sixty years of age with a mild form of pneumonia are prescribed the antibiotic Avelox at four hundred milligrams or Tavanik at five hundred milligrams per day for five days, along with Doxycycline (two tablets per day on the first day, the remaining days one tablet) for ten days. fourteen days.
If pneumonia is severe at any age, then you need to know how many days to inject Ceftriaxone. Treatment can be carried out with a combination of drugs such as Levofloxacin or Tavanic, which are administered intravenously, plus Ceftriaxone two grams twice a day or Fortum, Cefepime in the same dosage intramuscularly or intravenously.
In case of hospitalization in intensive care, combinations of Sumamed and Tavanik, Fortum and Tavanik, Targotsid and Meronem, Sumamed and Meronem are prescribed.
Contraindications
Antibiotics are contraindicated in cases where pneumonia is caused by a viral infection, as they will be ineffective or even dangerous. These drugs cannot destroy viruses and do not have any positive effect on the patient.
- Allergic reactions.
- Kidney and liver diseases. For chronic kidney and liver diseases, taking antibiotics can have a bad effect on their condition, since these organs are responsible for processing and removing antibiotics from the body.
- Childhood.
- Pregnancy. During this period, the woman’s body is very sensitive to medications. It is very dangerous to take antibiotics in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Recommendations for use
Currently, antibiotics are taken according to a special regimen, which is selected by the doctor.
If gram-positive cocci predominate, antibiotics are prescribed, which are administered intravenously and intramuscularly. These are penicillin or cephalosporin preparations of the first and second generation (Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, Cefoxin).
If gram-negative bacteria predominate, third generation cephalosporins (Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime) are prescribed.
In the case of atypical pneumonia, macrolides (Azithromycin, Midecamycin) and third-generation cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime) are used.
When intracellular organisms predominate, such as mycoplasmas and legionella, macrolides (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Roxithromycin) are also prescribed.
How does coronavirus pneumonia differ from normal pneumonia?
The inability to breathe air normally is the main difference between coronavirus pneumonia and other types of pneumonia.
Pneumonia of coronavirus origin is classified as atypical, community-acquired. This means that the cause of lung damage is a virus and a bacterial agent attached to it that is not one of the typical representatives of hospital microflora.
Against the background of a combined infectious process, the alveoli are affected (they lose elasticity), the vessels suffer (vasculitis and thrombosis develop). This course of the pathological process leads to massive (in most cases bilateral) damage to organs and tissues.
In addition to the version about viral-bacterial damage to the lungs, doctors have another one that explains the severe consequences of pneumonia.
It explains the fact that the lung tissue suffers in the almost complete absence of severe symptoms, and no changes are visible on CT images taken before the onset of severe symptoms. They appear after 1-2 days, when the person is already in serious condition.
Doctors believe that the alveoli suffer from hemosiderosis, in which (under the influence of a virus) the pigment hemosiderin (it consists of iron oxide) is split off from hemoglobin. The pigment accumulates inside macrophages located in the alveoli and stroma of the lungs. The accumulation of pigment interferes with the normal supply of oxygen to tissues. Which hypothesis among those that explain the severity of pneumonia during coronavirus is correct - doctors have not yet come to a consensus. But they believe that both are equally fair.
Concept of pneumonia
Pneumonia or pneumonia is a process of infectious etiology that leads to the accumulation of mucus in the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs. Normally, inhaled air penetrates the walls of the alveoli and enters the blood. During inflammation, the pulmonary vesicles fill with fluid, which prevents the penetration of air and, as a result, disrupts the body's oxygen supply. Most often, pneumonia occurs as a complication after ARVI.
Diagnosis of coronavirus
If Covid pneumonia is suspected, diagnosis is carried out in several stages. A sick person is sent for a test to identify the pathogen on the respiratory mucosa or a blood test to determine antibodies to the virus.
An X-ray, ultrasound or computed tomography scan of the lungs is performed. In the latter case, it is more possible to detect pneumonia at an early stage.
According to the results of tomography, it is possible to visualize foci of tissue changes in the lungs - from one to several (often four).
Attention! During auscultation, even if there are changes, the doctor cannot always hear wheezing.
Radiologists note that in the images one can notice a characteristic sign of covid pneumonia - a decrease in the airiness of the lungs. Externally, this anomaly resembles frosted glass.
During auscultation of the chest, the doctor pays attention to the respiratory rate ( usually 22 movements ). If the number of respiratory movements is more than 30 , doctors interpret this as a sign of a serious condition.
An additional way to monitor the condition of a sick person is pulse oximetry. A device on the finger of the hand measures the number of heart beats and blood oxygen saturation (saturation). If the device shows saturation less than 95% , the patient requires hospitalization.
When diagnosing pneumonia, the results of laboratory diagnostics are also taken into account. A complete blood count reveals a low level of leukocytes. Biochemical examination shows an increase in C-reactive protein.
Against the background of coronavirus, blood pressure may decrease and problems with urine excretion may arise.
Dear reader, we have collected all the most important and up-to-date information about COVID-19 on 1 page - the main thing about coronavirus. Also, current statistics are available for: Russia, Moscow, Moscow region and cities, St. Petersburg and all regions of the Russian Federation and countries of the world.
Requirements for antibacterial drugs
When prescribing treatment, the following requirements for the antibiotic must be taken into account:
- high activity against the causative agent of the disease;
- good tolerability and high safety;
- ability to penetrate well into bronchopulmonary tissue.
Additional requirements for drugs used in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia include high bioavailability when taken orally and ease of use in an outpatient setting.
How to treat pneumonia due to coronavirus
There is no specific treatment that can stop coronavirus pneumonia. The main efforts of doctors in the fight against the disease are aimed at maintaining body functions and eliminating secondary infections. Antiviral and antibacterial drugs are used to treat patients. Cough, headache, and antipyretic medications help alleviate the condition of pneumonia.
Treatment in hospital
In the hospital, doctors assess the patient’s condition based on symptoms and the results of the examination conducted in the hospital. It includes:
- clinical blood test with counting of formed elements;
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical analysis, study of blood glucose levels;
- radiography (CT or ultrasound of the lungs);
- cardiogram (particular attention is paid to the QT interval).
Medicines are prescribed on an individual basis. The guideline for doctors is the form of the disease, the presence or absence of complications and concomitant pathologies.
Moderate severity
Patients from the risk group are hospitalized: over 65 years of age with pathologies of the heart, liver, respiratory system, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, arterial hypertension.
Treatment is mainly symptomatic:
Antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol) at temperatures above ( 38.5 ), for patients with chronic pathologies of the heart, kidneys, central nervous system - 38 degrees . Paracetamol dosage is no more than 1 g per day, no more than 3 times a day. Ibuprofen dosage should not exceed 2400 mg per day. Blood thinners (low molecular weight heparins) in the absence of contraindications.
Maintenance therapy:
- Favipiravir: on the first day, a loading dose of 1600 mg twice a day, then 600 mg twice a day. Duration of treatment is from 5 to 14 days. Favipiravir has a teratogenic effect, so the drug is not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, as well as people with contraindications;
- Hydroxychloroquine on the first day, 400 mg at intervals of 12 hours, then 200 mg 2 times a day (5 days). Hydroxychloroquine therapy is accompanied by daily monitoring of the cardiogram (QT interval) and potassium levels in the blood. When the patient is discharged home, Hydroxychloroquine is discontinued.
Severe course
Diagnosed when more than 1 of the following symptoms are present:
- respiratory rate more than 30 times per minute in adults and more than 40 times per minute in children;
- blood oxygen saturation is less 94%;
- the presence of infiltrates in the lungs over 50% of the organ area.
Maintenance treatment is carried out in the ward or in the intensive care unit: low molecular weight heparins; antimicrobial drugs (broad spectrum) or antifungal; oxygen.
Maintenance therapy:
- Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Hydrocortisone) in tablet or injection form (intravenously) for 7-10 days or until discharge from the hospital. While the patient is taking corticosteroid hormones, strict monitoring of the concentration of glucose in the blood is carried out.
- Remdesevir - on the first day, a loading dose of 200 mg (once a day, intravenously), from days 2 to 5, 100 mg of the drug is administered. Remdesevir is prescribed to patients who do not require connection to a ventilator or membrane oxygenation. During the period of use of Remdesevir, glomerular filtration rate is monitored daily.
- Favipiravir - on the first day, a loading dose of 1600 mg twice. Next - 600 mg twice a day for 5-14 days.
- Tocilizumab is prescribed from the 7th day of illness for clinical symptoms or from the 14th day based on the results of X-ray diagnostics, if the therapy does not give the expected effect, the patient’s condition worsens, developing: acute respiratory failure due to interstitial pneumonia; respiratory failure increases, the patient needs to be connected to a ventilator; there are signs of damage to other organs; A blood test shows elevated levels of C-reactive protein, D-dimer, and ferritin.
Critical course of the disease
Determined by the presence of symptoms such as:
- respiratory dysfunction;
- sepsis;
- change in consciousness;
- multiple organ failure.
Basic treatment:
- Ventilation of the lungs mechanically or mechanically.
- Therapy: prevention of thrombosis with low molecular weight heparins;
- Prevention, treatment of acute respiratory dysfunction, pulmonary fibrosis;
- Track secondary infections.
Maintenance therapy:
Intravenous or oral administration of corticosteroids, use of antiviral drugs (Remdesevir or Favipiravir), Tocilizumab.
Treatment at home
Treatment at home requires maximum compliance with quarantine standards. A sick person should be separated from household members and use individual utensils. The room must be wet cleaned with disinfectants at least 2 times a day and ventilated.
For mild pneumonia, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Doctors recommend taking antipyretics at temperatures above 38 degrees . The patient must record temperature readings, as well as breathing and pulse rates in a special diary.
Be sure to drink plenty of fluids (table water, berry fruit drinks, sugar-free broth). You need to calculate the amount of fluid consumed based on the fact that 30 ml of drink should be consumed per 1 kg of weight.
To avoid congestion in the lungs, you need to change your body position and do breathing exercises.
Important! The patient should carefully monitor his health, and if it worsens, immediately contact his family doctor.
If, after 5 days from the onset of the disease, hyperthermia, severe weakness, and shortness of breath during physical activity persist, the doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy. The antibiotic Azithromycin is the most effective for covid pneumonia. On the first day of administration, its dose is 500 mg, then 250 mg should be taken for another 4 days.
Additionally, it is recommended to take Paracetamol (Ibuprofen) at a dosage of 200 mg if the temperature is above 38 degrees .
Treatment of pneumonia in a hospital
More severe lung disease requires hospital treatment. The reason for hospitalization may be poor blood tests, a clear decrease in blood pressure, impaired consciousness, as well as the age of the sick person, which exceeds 65 years. Among other things, those people who have bilateral pneumonia, purulent discharge, high respiratory rate or, conversely, difficulty breathing, are also hospitalized. Severe dehydration, fever with a feeling of nausea, as well as people without relatives or loved ones, require hospital treatment.
After hospitalization, doctors carry out all the necessary diagnostics, on the basis of which appropriate treatment is prescribed. Diagnostics may include:
- Visual examination by a doctor.
- X-ray.
- Ultrasound.
- CT.
- Sputum and blood tests.
- PCR.
Hospital therapy is, in principle, no different from home treatment; antibiotics, expectorants, painkillers, cough suppressants, etc. are also used here. However, in addition to medications, breathing exercises and physiotherapy can be used.
The length of stay in the hospital directly depends on the progress of treatment, namely on the individual characteristics of the body. The patient is considered healthy in cases where the body temperature is within normal limits, and there are no signs of disease on X-ray images. On average, pneumonia is cured within 3 weeks.
Degrees of lung damage due to coronavirus pneumonia
Specialists, based on the patient’s complaints and radiological diagnostics, identify the degree of damage to the lung tissue. The patient’s well-being and his prognosis for recovery depend on them.
I degree : no more than 5% of the lung tissue is affected by the pathological process. The course of the disease is mild, the prognosis is favorable.
II degree : damage from 5 to 25% . Blood oxygen saturation is more than 95%. You need to see a doctor and start treatment. In elderly people, the pathological process is likely to transition to a severe form.
| Age, years | Mortality, %, with 20-40% damage |
| <15 | 0.03 |
| 18 — 30 | 0.96 |
| 30 — 50 | 4.15 |
| 50 — 70 | 9.95 |
| 70 — 100 | 19.15 |
III degree : damage from 25 to 49% . The chances of recovery are high if you seek medical help and treatment in a timely manner. With such a lesion, hyperthermia is often observed and saturation decreases. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
| Age, years | Mortality, %, with 50% damage |
| <25 | 1.15 |
| 25 — 40 | 2.35 |
| 40 — 60 | 7.75 |
| 60 — 80 | 14.25 |
| >80 | 21.1 |
IV degree : damage from 50 to 70% . The pathological process is spread over a large area of lung tissue, so the doctors’ prognosis is conditionally favorable. Against the background of such a massive lesion, pulmonary fibrosis develops and the organ loses its elasticity. After coronavirus comes disability.
| Age, years | Mortality, %, with 60% damage |
| <25 | 1.4 |
| 25 — 40 | 2.9 |
| 40 — 60 | 8.75 |
| 60 — 80 | 16.15 |
| >80 | 25.1 |
V degree: more than 75% of lung damage. Doctors give a conditionally unfavorable prognosis. But the outcome of the disease is influenced by where the patient is located. At home, it is extremely difficult to recover from such massive damage to the respiratory organ; in a hospital, the chances of recovery are high. The disease provokes pneumosclerosis, an acute lack of oxygen in the blood.
Severe patients are sent to the intensive care unit. The most severe cases are put into a medical coma and connected to a ventilator.
| Age, years | Mortality, %, with 70% damage |
| <25 | 1.7 |
| 25 — 40 | 3.5 |
| 40 — 60 | 10.65 |
| 60 — 80 | 17.5 |
| >80 | 27.1 |
How is the percentage of lung damage determined?
To calculate the percentage of damage to the respiratory organ due to coronavirus, radiologists use tomography data and a special formula. Conventionally, the lungs are divided into several lobes - 2 (left) and 3 (right). The image shows darkened areas - “frosted glass”.
Based on the size of the darkening, the lobes of the lungs are assigned points:
- 1 - corresponds to a lesion of less than 5%;
- 2 — 5–25%;
- 3 — 25–49%;
- 4 — 50–75%;
- 5 – more than 75%.
The specialist sums up the scores for each lobe and multiplies the resulting number by 4, obtaining the percentage of damage.
Purpose principles
Antibiotics for pneumonia are selected by the doctor based on a number of general principles, compliance with which is extremely important for the successful outcome of therapy.
- When treating pneumonia, a combination of several antimicrobial drugs is used – usually 2-3 items.
- Before taking any antibiotic, the doctor must make sure that the patient is not allergic to drugs from this group. In addition, the patient’s age, characteristics of his body, concomitant diseases and contraindications should be taken into account.
- Before determining the causative agent of the pathological process, the patient is prescribed first-line antibiotics, usually from new generation drugs or the penicillin group. They must be taken regularly so that the required concentration of the active substance is constantly maintained in the blood.
- After diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a drug that has a therapeutic effect on a specific type of bacteria - most often broad-spectrum antibiotics. If a person has been diagnosed with atypical pneumonia caused by chlamydia, mycoplasma or legionella, you need to take special medications - for example, summed or clarithromycin, in addition using broad-spectrum drugs.
- Antimicrobial therapy must be complemented by symptomatic treatment - antipyretic, expectorant, and restorative drugs.
The effectiveness of antibiotic therapy depends on the correct selection of the treatment regimen and compliance with the conditions for taking medications. Antimicrobial drugs enter the site of inflammation through the bloodstream, after which they have different effects on pathogenic microorganisms - some (bactericidal) destroy their structure, others, called bacteriostatic, prevent the proliferation of bacteria.
It should be noted that the causative agents of pneumonia are constantly mutating , developing resistance to certain groups of drugs, so conventional antimicrobial drugs may be ineffective for various forms of pneumonia. Hospital-acquired pneumonia, a disease that develops within the walls of a medical institution, is especially difficult to treat.
REFERENCE! The most effective drugs for adults and children are the new generation of broad-spectrum drugs, as they are able to fight several types of pathogenic microorganisms.
What antibiotics are prescribed for pneumonia and coronavirus
Doctors make the choice of an antibacterial drug for the treatment of coronavirus pneumonia individually. The list of antimicrobial agents includes representatives of several groups:
- macrolides (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin);
- penicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin);
- antipneumococcal fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin);
- 3rd generation cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime).
The starting drug is selected empirically; in parallel, a blood sample is sent for bacteriological analysis of sensitivity to antibiotics. If the condition does not improve with the selected antibiotic, the drug is changed.
Have you lost your sense of smell and taste while infected with COVID-19?
Yes
81.25%
No
18.74%
Voted: 36151
Choice of etiotropic therapy
Etiotropic therapy includes the use of antibacterial drugs, taking into account the severity of the disease and identification of the pathogen.
The choice of drug is made by the doctor, taking into account many factors.
The choice of antibiotic is determined by the following factors:
- age;
- features of the clinical picture;
- concomitant diseases;
- epidemiological situation;
- X-ray data;
- cardiac, hepatic or renal failure affecting the concentration of the antimicrobial agent in the blood;
- contraindications to the use of the drug or a history of indications of side effects (allergic reactions) during previous antibiotic therapy;
- the use of other drugs that may affect the pharmacokinetic processes of the antibiotic.
How to protect your lungs during pneumonia - advice from doctors
Coronavirus pneumonia, according to pulmonologists, is not a complication, but a manifestation of an infectious process. A sharp deterioration in the condition on days 7-9 is a sign that the virus has undermined the immune defense and a bacterial infection has become active in the lungs.
To protect your lungs from damage, doctors recommend:
- get vaccinated against pneumococcus - vaccination provides immunity from bacteria dangerous to the lungs for a period of 5 to 10 years;
- monitor the air humidity - in the room it should be at least 40–45%. Humidified air prevents the formation of mucus plugs in the bronchi and infection in the lungs;
- from the first day of the onset of coronavirus symptoms, drink a lot of fluid to relieve intoxication, maintain low viscosity and easier removal of sputum from the bronchi and mucus from the nose.
In mild to moderate cases of the disease, it is necessary to avoid congestion in the lungs - move, perform simple exercises.
The main bacterial pathogens of pneumonia
| Pathogen | Age | |||
| newborn | 1-3 months | 4 months-4 years | from five years | |
| Pneumococcus | + | +++ | ++++ | +++ |
| hemophilus influenzae | + | + | + | +- |
| Streptococcus pyogenes (a type of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus) | — | + | + | + |
| staphylococcus | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Streptococcus agalactia | +++ | + | — | — |
| Escherichia coli | ++ | + | — | — |
| mycoplasma | — | + | + | ++++ |
| chlamydia pneumonia | — | + | + | ++ |
| legionella | + | + | + | + |
| chlamydia trachomatis | + | ++ | — | — |
| pertussis stick | +- | ++ | + | + |
++++very common pathogen, +++common, ++ relatively uncommon, + rare.
Lung recovery after pneumonia from COVID
Experts point out that it is possible to talk about pulmonary fibrosis after covid pneumonia a year later. This is exactly the amount of time a person who has been ill has to restore their lungs.
You need to start restoring the organ from the first days of illness, doing breathing exercises at least 3-4 times a day.
They continue it after recovery. The intensity of the load during exercise depends on your physical condition. Classes should not be conducted through overcoming. Shortness of breath, dizziness, weakness or nausea are a signal to take a break and change the load.
Doctors recommend a set of exercises that includes several components. Independent active movements are aimed at developing and strengthening the muscles of the diaphragm, chest, and shoulder girdle.
Tapping is necessary to enhance the removal of mucus. They begin to do it when the patient is bedridden. After a light massage of the chest and back, patting and tapping movements are carried out in the direction from bottom to top. While tapping, the person should lie so that the body is slightly lower than the legs.
Breathing simulators also help restore the lungs after coronavirus pneumonia. You can use the Fokin simulator or try inflating balloons. The effect in both cases is noticeable after 2-3 weeks of regular exercise - lung capacity increases and ventilation improves.
A nutritious diet after covid pneumonia is one of the main rules of recovery. The menu should include light but satisfying dishes, rich in vitamins, fats of plant and animal origin.
We must not forget about the benefits of walking in the fresh air. Daily exercise after pneumonia should last at least 40 minutes.
Antibiotic treatment of pneumonia in adults according to the type of pathogen
The most dangerous forms of lung damage are considered to be infections caused by streptococci and legionella (Legionella disease).
The mortality rate from these types of pneumonia is 48 percent of all registered deaths.
Antibiotics for pneumonia should be prescribed from the first day of diagnosis.
After receiving the results of bacteriological culture, the treatment regimen is adjusted taking into account the identified pathogen.
What drugs are prescribed to patients for various harmful agents?
| Type of pathogen (representative of pathogenic flora) | Antibiotics used for treatment |
| Haemophilus influenzae | "Amoxicillin", "Amoxiclav", "Aminopenicillin". |
| Legionella | Erythromycin, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, rifampicin. |
| Streptococcus | Benzylpenicillin, third generation cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone), aminopenicillin, macrolides |
| Klebsiella and Escherichia coli | Third generation cephalosporins |
| Staphylococcus | Oxacillin, aminopenicillin, first and second generation cephalosporins |
| Mycoplasma, chlamydia | Tetracycline, macrolides, fluoroquinolones |
The duration of treatment is 10-14 days - during this period, a sufficient amount of components with biological activity accumulates in the blood, and pathogenic flora is destroyed.
If there is no therapeutic effect, the drug is replaced on the 3-4th day of treatment (if necessary, the dose or dosage regimen is adjusted).
Reviews from survivors of coronavirus pneumonia
My son brought the infection into the house.
I got sick 3 days after his sick leave was closed. At first I just had a sore throat and a dry nose. Then it suddenly became difficult to breathe. I called my doctor, she prescribed Amoxiclav for me, I took it for a week. It got better after 4 days of taking antibiotics. Natalya, 48 years old
Pneumonia came as a complete surprise to me.
I took an x-ray of my lungs to get a job and was told to go to a pulmonologist with the results. Then I had to donate more blood - the indicators confirmed the hidden process. I was treated at home, the temperature rose low, up to 37.8 for a couple of days. I didn't take antibiotics. Anatoly, 63 years old
I started to have a cold, it seemed to be easier, but on the 4th day I felt pain in my chest.
I know that this could be a symptom of Covid, so I immediately went to a private clinic for a test and tomography. The doctor confirmed it and prescribed treatment without antibiotics. Svetlana, 25 years old
I am asthmatic and diabetic, so I immediately went to the doctor when I got sick.
It all started with a slight cough and dry throat. Covid was confirmed by analysis, and a tomogram showed that the process had already invaded the lungs. I was treated in a hospital, they gave me IVs, they gave me hormones and antibiotics. I am healthy now, thanks to my doctors! Stepan 67 years old
Share your opinion or experience - write comments. Did you like the article? – Share it with your friends on social networks.
How to take antibiotics correctly?
As mentioned above, antibiotics are potent medications, and therefore require compliance with certain conditions of administration.
- Follow the instructions and recommendations of the doctor. Some antibiotics are more effective if taken with food, while others need to be taken before or after meals.
- Maintain equal intervals between doses. It is necessary to take medications at the same time of day at regular intervals.
- Follow the recommended dosage. The dosage when taking antibiotics must be observed very strictly, since exceeding it can lead to serious side effects, and decreasing it can lead to the formation of drug-resistant strains of microorganisms.
- Do not interrupt the course of treatment. In order for therapy to produce the desired effect, a certain concentration of the active substance in the patient’s blood is required. That is why you should take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your doctor. You cannot interrupt the course even after relief occurs.
- Take the tablets only with clean water. It is recommended to drink any antibiotics with exclusively clean, still water. Tea, coffee, milk or fermented milk products cannot be used for these purposes.
- Take probiotics. Since antibiotics destroy not only pathogenic, but also beneficial bacteria. To avoid problems with the gastrointestinal tract, when taking such drugs you need to drink probiotics (Linex, Narine, etc.), which restore the natural intestinal microflora.
The drug Linex
All of the above rules not only contribute to a quick recovery, but also minimize the side effects of taking antibiotics and their toxic effects on the body.
Carbapenems
Tienam is a modern highly effective antibiotic for severe pneumonia
These are reserve antibiotics; they are used when other antibacterial agents are ineffective, usually for hospital-acquired pneumonia. Carbapenems are often used for pneumonia in patients with immunodeficiencies (HIV infection) or other serious diseases. These include:
- meropenem (Genem, Merexid, Meronem, Meronoxol, Meropenem, Meropidel, Nerinam, Penemera, Propinem, Cyronem);
- ertapenem (Invanz);
- doripenem (Doriprex);
- imipenem in combination with beta-lactamase inhibitors, which expands the spectrum of action of the drug (Aquapenem, Grimipenem, Imipenem + Cilastatin, Tienam, Tiepenem, Cilapenem, Cilaspen).
They are injected intravenously or into a muscle. Side effects include:
- muscle tremors, convulsions, headache, sensory disturbances, mental disorders;
- decrease or increase in urine volume, renal failure;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the tongue, throat, stomach;
- inhibition of hematopoiesis, bleeding;
- severe allergic reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- hearing loss, ringing in the ears, impaired taste perception;
- shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest, palpitations;
- pain at the injection site, thickening of the vein;
- sweating, back pain;
- candidiasis.
Carbapenems are prescribed when other antibiotics for pneumonia cannot help the patient. Therefore, they are contraindicated only in children under 3 months of age, patients with severe renal failure without hemodialysis, as well as in cases of individual intolerance. In other cases, the use of these drugs is possible under the control of kidney function.
Macrolides. Aminoglycosides
Macrolides are used to neutralize cocci, legionella, and chlamydia. They are well absorbed into the body, but food intake somewhat slows down this process. Allergic reactions are very rare. Representatives of this category are drugs such as Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin. Their main area of application is infectious processes in the respiratory tract. However, liver dysfunction is a contraindication to taking such medications.
Aminoglycosides are antibiotics for pneumonia that actively act on aerobic gram-negative microorganisms. They are also used in cases where the disease is caused by more than one type of bacteria, and therefore it is necessary to combine antibacterial drugs to achieve the desired result. Representatives of the group are drugs such as Gentamicin and Amikacin. The dosage is calculated depending on the patient’s body weight, age, and severity of the disease. When taking such drugs, control of glomerular filtration in the kidneys is necessary.
Complications
In some cases, coronavirus is not only pneumonia, but also life-threatening conditions that complicate it (see cytokine storm for covid):
- Acute respiratory failure
- Respiratory distress syndrome
- Septic shock
- Multiple organ failure
Long-term consequences of Covid include pulmonary fibrosis (replacement of lung connective tissue) with chronic respiratory failure.