Autoimmune thyroid diseases occur predominantly in children and women. Against the background of such an illness, the immune system incorrectly reacts to the cells of its own body and begins to actively fight it. This condition can be dangerous during pregnancy. What to do if AT to TPO is very elevated? What does this mean, what are the dangers and what treatment measures need to be taken? When can pathology be suspected and who is usually most susceptible to it? The answers to all these questions will be given below.
What does the At-TPO analysis show?
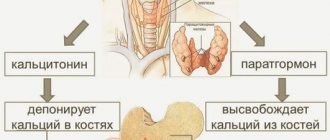
Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) is an enzyme that functions in the tissues of the thyroid gland.
It ensures the formation of an active form of iodine, accelerates the production of hormones that are responsible for many important processes in the human body: general growth and development, proper metabolism, transmission of nerve impulses, thermoregulation and others. Antibodies to this enzyme (Ab-TPO) are produced when immunity is impaired.
Ab-TPO is highly elevated in women with autoimmune thyroid diseases, that is, when the immune system exhibits pathological aggression towards its own body.
Antibodies block the activity of this enzyme, which ultimately leads to a decrease in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, affecting all systems of the body. Their detection in the blood is the most sensitive and accurate way to detect autoimmune abnormalities.
Basedow's disease
This disease is an autoimmune disease called diffuse toxic goiter. Basedow's disease manifests itself with pronounced symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism:
- Weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Hypertension;
- Hypersecretion of sweat glands;
- Arrhythmia;
- Tachycardia;
- Psycho-emotional disorders accompanied by irritability, apathy;
- Tremor of the upper limbs and body;
- Low-grade fever.
Treatment
- Drug therapy includes the prescription of thyreostatic drugs.
- The action of thyreostatics is aimed at blocking the function of the thyroid gland, as a result of which the condition of the entire body is normalized and maintained.
- Radioiodine therapy is also used for diffuse toxic goiter, which successfully helps in treating the disease and is safe.
However, pregnancy is a contraindication for radioiodine therapy.
When is a test ordered?
Anti-TPO testing is prescribed in the following cases:
- diagnosis of thyroid disorders;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and the course of the disease;
- when an enlarged thyroid gland is detected against the background of normal or reduced levels of the thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH4 in the blood;
- before prescribing Amiodarone for patients with arrhythmia, as well as for those people who take interferons, since treatment with these drugs increases the risk of developing thyroid diseases;
- differential diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, as well as non-autoimmune pathologies;
- with TSH<2.5 mU/l in pregnant women, as this indicates a risk of postpartum Hashimoto's thyroiditis;
- in the presence of autoimmune diseases of other organs;
- after radiation exposure to control complications;
- with an increase in the periocular tissues (if Graves' disease is suspected) or with swelling of the patient's legs (possible development of myxedema - a violation of the flow of thyroid hormones into the blood).
Ab-TPO is strongly elevated in women also in some types of malignant tumors. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, it may be necessary to perform a puncture biopsy - taking biomaterial from the thyroid gland using a thin needle.
conclusions
If a person has been tested for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, and the required norm is exceeded, under no circumstances should you immediately panic. Small deviations in values are quite possible even among healthy people. If you still have some minor deviations, you can bring your tests back to normal without using additional medications. To do this, you will simply need to reconsider your diet and give up all sorts of bad habits, after first getting rid of excess weight. Most doctors advise completely avoiding regularly wearing necklaces and chains around the neck, as some metals can negatively affect the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Norms for women
The normal limits of Ab-TPO depend on the method of testing blood serum.
Most often, 2 methods are used:
- Enzyme immunoassay on strip polystyrene plates. The norm of antibodies in the blood in this case is 10-30 (in some laboratories the upper limit is 35) IU/ml.
- Chemiluminescent immunoassay on microparticles. Reference values are <6 U/ml.
The medical form must indicate two indicators - the one obtained as a result of the test and the normal one for this laboratory method. The study is usually carried out in conjunction with the determination of the thyroid-stimulating hormones TSH and T4.
Normal value and deviations
TPO Ab is short for “thyroid peroxidase antibodies.” These antibodies mistakenly perceive thyroid enzymes as foreign and begin to fight them. Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme (also called “thyroid peroxidase”) that affects the production of hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid peroxidase is stimulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is produced by the pituitary gland. Thus, the antibody attack on thyroid peroxidase leads to a decrease in the production of T4 and T4. It is these 4 indicators (TSH, AT TPO, T3, T4) that are the main ones for such a blood test.
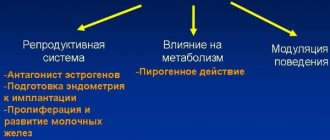
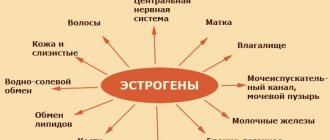
The influence of T3 and T4 (thyroid hormones) is great. They do not have “targets”, but work with all cells of the body. If the production of these hormones is disrupted, the general metabolism in the body is disrupted, which leads to pathologies: hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is manifested by the appearance of goiter, excess weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and constipation.
Hyperthyroidism can manifest itself as increased sweating, increased heart rate, sleep disturbances, weakness and trembling of the hands, and weight loss.
During research, a certain logical chain of research is formed, where several analyzes are combined:
- A decrease in T3 and T4 levels indicates an underactive thyroid gland.
- If TSH is normal or elevated, this means that there is a problem with the thyroid gland. Moreover, if the AT to TPO is too high, then the problem is there; if not, then there is another problem (for example, mechanical injury, etc.).
- If TSH is low and TPO AT is normal, then there is a problem with the pituitary gland.
The norm in women, as assessed by AT to TPO, does not differ significantly from men. A special case is pregnancy. During pregnancy, hyperthyroidism can masquerade as symptoms of pregnancy. But problems with the thyroid gland have a negative impact not only on the expectant mother’s body, but also on the child’s body. Therefore, you should be careful about the blood test for TPO AT. The fact is that during pregnancy a situation is possible when T3 and T4 are normal, but TSH and AT TPO are increased. Due to hormonal changes in the body of a pregnant woman, the pituitary gland produces an increased amount of TSH, the excess of which is neutralized by TPO AT. But this situation cannot last forever. Sooner or later, perhaps after the end of pregnancy, but most likely sooner, this balance will cease, as antibodies to thyroid peroxidase will disable more and more thyroid cells. An exacerbation can occur at any time, and in a very strong phase.
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase pose a particular danger to the fetus, since they easily cross the placental barrier and enter the child’s body from the mother’s blood. This creates a danger of disrupting the functioning of the baby’s body in the womb.
How to prepare for research
To obtain reliable results, several conditions must be met:
- It is preferable to take the test in the morning, after a period of overnight fasting (8-14 hours). If only Ab-TPO is tested, the last meal is allowed 4 hours before.
- The day before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude physical and emotional stress; it is not recommended to visit the bathhouse or sauna.
- If you have bad habits: stop drinking alcohol at least 24 hours before and quit smoking at least 3 hours before the medical test.
Preparing for a blood test
In preparation for donating blood, it is necessary to perform a number of activities:
- You should not take any medications on the day of blood donation;
- do not chew chewing gum;
- blood is donated on an empty stomach before 11.00 am;
- no smoking.
A blood test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach.
If there have been surgical interventions recently or there have been infectious diseases, the test result may be inaccurate.
When preparing for the test, it is important to stabilize the emotional background and avoid stressful situations. Immediately on the day of the analysis, you can drink clean still water.
How the biomaterial is collected
Blood to determine the level of antibodies is taken from a vein.
This procedure proceeds as follows:
- The patient's position is sitting. If he finds it difficult to tolerate such manipulations, then blood sampling can be done while lying down.
- The subject's hand is placed on the table, the nurse prepares consumables - sterilization wipes, test tubes, a disposable needle.
- A tourniquet is applied 10 cm above the puncture site. It is held for no more than 1 minute.
- The patient is asked to clench his fist in order to better see the vein and to ensure blood flow.
- The puncture site is disinfected with napkins (or cotton swabs) soaked in medical alcohol.
- The nurse inserts a needle into the vein at an angle of approximately 20° to the surface of the skin.
- As soon as the blood begins to flow into the test tube, the tourniquet on the arm is loosened. This action is performed to prevent the destruction of blood cells and distortion of test results. The patient is also asked to unclench his fist.
- Blood is drawn into a test tube.
- The needle is removed from the vein, and a napkin is applied to the puncture site, which must be pressed tightly until the bleeding stops completely.
What does this hormone mean?
Everyone knows why a person needs immunity. It protects the body from harmful viruses and bacteria that can harm health. Defenders are various antibodies, which consist of proteins that can detect the “villain”.
But this mechanism does not always work smoothly and correctly; a failure, already described above, may occur - antibodies will begin to fight with healthy cells of the body.
The abbreviation AT to TPO stands for Antibodies to Thyroid Peroxidase.
Thyroid peroxidase is an organic substance consisting mainly of protein produced by the thyroid gland, which is involved in the hormonal synthesis of organic compounds.
For various reasons, the immune system may consider this enzyme an enemy and try to get rid of it. Because of this, AT to TPO increases, as a result of which the synthesis of many important hormones is disrupted.
Decoding analysis responses
At-TPO and its values can only be correctly interpreted by a doctor, since the results of the analysis are not the only correct ones for making a diagnosis.
If this parameter is greatly increased in women, then this serves as a marker of the possible development of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Final confirmation of the diagnosis is made after additional laboratory and instrumental studies.
Anti-TPO antibodies are detected in 95% of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis and in 85% of patients with Graves' disease.
However, their presence in the blood does not always indicate the development of pathologies. Thus, according to medical statistics, 15-20% of healthy people are carriers of this group of antibodies. If there are no other signs of pathological changes in the thyroid gland, then treatment is not required.
The following factors may also affect the test result:
- recent surgical operations performed on the thyroid gland;
- radiotherapy;
- taking medications (iodine-containing drugs and thyroid hormones).
Additional medical and public assistance
The importance of the thyroid gland should never be underestimated. And if malfunctions occur in its working functions, you need to immediately contact a doctor. As a rule, this refers to situations where there is a significantly increased titer of antibodies to an enzyme such as peroxidase. Treatment of this type of disorder is carried out through the use of medications. The doctor usually prescribes hormone replacement therapy on an individual basis.
As part of the development of autoimmune thyroiditis, the occurrence of hypothyroidism cannot usually be excluded. It is necessary to use medications until it becomes clear which one is most suitable.
For ordinary patients, just like pregnant women, doctors prescribe thyroid medications, for example, L-thyroxine. Patients are required to donate blood regularly. This is done so that the doctor can better examine the overall clinical picture and determine whether the treatment is successful.
Reasons for the strong increase in At-TPO
AT-TPO is highly elevated in women in several cases:
- Graves' disease. In another way it is called diffuse toxic goiter, or Graves' disease.
If At-TPO is elevated in women, a goiter appears.
This is the most common pathology of the thyroid gland, in which there is an increase in the production of thyroid hormones. Their gradual accumulation in the body leads to poisoning (thyrotoxicosis). The impetus for the development of the pathological process can be given by infectious diseases, mental and traumatic brain injuries, and inflammation of the nasopharynx. The peak incidence occurs in middle age - 30-50 years, and among women the prevalence of the disease is 8 times higher than among men. Pregnant women and menopausal women are also at increased risk. In newborn children, high levels of antibodies may be due to the presence of this disease in the mother. The Ab-TPO value in this disease increases on average by 40-60% of normal. - Hashimoto's thyroiditis (autoimmune thyroiditis). The essence of this pathology is that a chronic inflammatory process develops in the thyroid gland, which leads to changes in its tissues. As a result, the production of thyroid hormones decreases and hypothyroidism develops. The incidence of this disorder among women is also higher – 3-5 times than among men. Most often, the disease manifests itself over the age of 40 years. It tends to have familial forms and often accompanies other autoimmune disorders - hypercortisolism (pathology of the adrenal glands, in which there is increased production of the hormone cortisol), type I diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, alopecia, vitiligo and others. Provoking factors for the development of the disease are injuries and surgical operations on the thyroid gland, infectious and inflammatory diseases, radiation exposure, deficiency or excess of iodine in the body. However, this disease is less common in the human population than the previous one - 3-4%.
- De Quervain's thyroiditis . This pathology develops 3-6 weeks after viral infections and is a non-purulent inflammation of the thyroid gland. Women over 30 years of age are most susceptible to this disease. It can often recur with infectious pathologies and hypothermia.
- Nodular toxic goiter. With this disease, benign formations (cysts, adenomas) are detected in the thyroid gland, which may be accompanied by reduced function of this organ or, conversely, thyrotoxicosis. Risk factors for the occurrence of pathology are lack of iodine in food and genetic predisposition.
- Postpartum thyroid dysfunction. During pregnancy, women's immunity decreases. This is a normal physiological process that serves as a “prevention” of fetal rejection. After childbirth, immune reactions are activated, which can lead to autoimmune disorders (Graves' disease and thyroiditis).
An increase in the concentration of antibodies is also detected if the rules for blood sampling are violated and if the diet before the analysis is not followed (with a high content of fat in the serum).
Treatment for elevated levels of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase
The symptoms and causes of Graves' disease are of interest to many.
Treatment of deviations in the volume of AT TPO, as a rule, consists of eliminating the autoimmune diseases that lead to this pathology. In order to determine an accurate diagnosis, doctors need to study the patient's medical history, carry out various additional diagnostic procedures, and also carry out a detailed blood test.
If elevated antibodies to TPO are detected, then treatment of underlying pathologies is required:
- Postpartum thyroiditis. Often this disease goes away with virtually no symptoms. Young women encounter it, as a rule, in the first years after the birth of a baby. The most common complaints of patients are fatigue, increased irritability, rapid heartbeat, trembling in the arms and legs. As with the autoimmune type of the disease, symptomatic treatment is required. A table of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase is presented below.
- Graves' disease. This pathology manifests itself in weakness, tremors of the limbs, the formation of toxic goiter, high blood pressure, increased sweating and is accompanied by arrhythmia. True, such a disease can be treated quite successfully, especially in its first stages. The drugs most often prescribed as medicinal methods are Propicil and Thiamazol. These drugs block thyroid functions. In addition, patients may be given radiotherapy to the thyroid gland.
- Symptoms of autoimmune thyroiditis. This pathology has symptoms such as decreased concentration and performance, tremors, sudden weight gain, dry skin and hair, sweating, and arrhythmia. General therapy of the disease is reduced to alleviating the main symptoms. At the moment there are no special drugs to treat this disease. It is important to note that the detection of antibodies in the blood is not considered a clear reason for determining an accurate diagnosis. It is not uncommon for such a deviation to be observed among absolutely healthy people. If the patient’s TSH level is normal, this indicates that there is no disease.
Elevated antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are often found.
Thus, regular monitoring of thyroid function is recommended for all women. In addition, patients may be prescribed replacement therapy. In cases of failure of the normal activity of the heart muscle, it will be necessary to use appropriate medications. Vitamin therapy and adherence to standard recommendations for a healthy lifestyle are also considered mandatory. Against the background of dysfunction of the thyroid gland, hormonal therapy may well become a lifelong measure.
We looked at antibodies to thyroid peroxidase; what they are is now clear.
Symptoms
The main signs of diseases in women, in which high Ab-TPO values are detected, are shown in the table below.
| Pathology | Symptoms |
| Graves' disease |
|
| Hashimoto's thyroiditis |
|
| De Quervain's thyroiditis |
|
| Nodular toxic goiter |
|
Medicines
Against the background of such treatment, therapy is carried out using the following means:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- glucocorticoids, for example, Prednisolone.
For some patients, surgery is necessary, and the indications for surgery may be as follows;
- Graves' disease;
- nodular toxic goiter;
- iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis.
In order to generally strengthen the entire body, patients are recommended to take vitamins and adaptogens. Subsequently, doctors prescribe medications that you will have to take throughout your life.
Traditional medicine will also be useful in treatment when the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase begins to increase. As a rule, for three to four months the patient drinks tea, for example, from celandine, chamomile or licorice root, and at the end of the period it will be advisable for him to switch to other remedies.
If AT to TPO is elevated, treatment should be comprehensive and timely.
You can prepare herbal preparations yourself. An example is persimmon tincture, which will help normalize hormone levels. The procedure is as follows:
- squeeze the juice out of the fruit;
- mix two hundred milligrams of the resulting substance with a couple of drops of alcohol;
- leave the product for two days;
- drink one tablespoon of the resulting infusion before meals three times a day.
Treatment
There are several ways to treat thyroid diseases:
- conservative, with the help of medications;
- radiotherapy (exposure to radioactive radiation);
- surgical intervention.
The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- large size of the thyroid gland, compression of the trachea or blood vessels of the neck;
- persistent decrease in leukocytes in the blood;
- severe heart rhythm disturbances;
- if cancer is suspected in the nodes or their rapid growth;
- with toxic adenoma.
Medicines
The main medications used in the treatment of the above diseases are given in the table.
| Disease | Drugs | Daily dosage, mg/day | Reception features |
| Graves' disease | Mercazolil (Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil) | Therapeutic: 30-40 (in severe cases up to 80) Supportive: 10-15 | Duration of treatment: 0.5-2 years A blood test is performed every 2-4 weeks. |
| Hashimoto's thyroiditis | Iodides (Lugol's solution, potassium iodide) | 100-200 (2-4 mg/kg body weight) | Used to eliminate thyrotoxic crisis and to prepare for surgery . Prescribed for short-term use. |
| Lithium carbonate | 900-1500 | Complete elimination of symptoms is possible only for mild forms of the disease. | |
| Thyreostatics (Mercazolil, Propylthiouracil) | Mercazolil: mild course of the disease – 30; severe – 60 Propylthiouracil – 400-600 (in 4 doses) | The total duration of therapy is 1-1.5 years. | |
| Thyroid hormones (Thyroxine) | 0,05-0,1 | They help reduce the production of TSH, their level is monitored after 1.5-2 months. | |
| De Quervain's thyroiditis | Glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) | 30-60 | Duration of treatment is 3-4 weeks. |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 2-3 | Reduced symptoms of inflammation. | |
| Nodular toxic goiter | Thyroxine and iodine preparations | Listed above | — |
Folk remedies
Ab-TPO is highly elevated in women when thyroid function is impaired.
The following traditional medicine recipes will help restore the functioning of this organ:
- 1 tbsp. l. flax seeds pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and cook over low heat for 3-5 minutes. Add 1-2 slices of lemon to the broth. After cooling to room temperature, add 1 tsp. flower honey, stir. This remedy is drunk in 3 doses during the day before meals. This recipe is applicable for all thyroid diseases.
- Pour 100 g of walnut partitions into 500 g of vodka and leave for 1 month in a dark place. Drink 1 tsp. 3 times a day before meals. The duration of treatment is 2 months, then a break of 2 weeks and the course is repeated. Since septum contains a lot of iodine, this recipe is used only for insufficient thyroid function.
- Grind the celandine grass along with the flowers and place it in a glass jar (preferably made of dark glass). The occupied volume should be half the capacity. Fill the remaining space of the jar with vodka. Leave for 2 weeks. Start taking the product with 2 drops, diluted in a glass of boiled water. This amount is drunk once a day. Every day the amount of infusion is increased by 2 drops, ultimately bringing it to 16 drops. The course of treatment lasts 1 month. This remedy is indicated for suppression of thyroid function.
- A decoction of medicinal plants - birch leaves, buds, chicory herb, calamus root, burdock root, chamomile flowers - is taken in a ratio of 2:1:2:1:1:2. 2 tbsp. l. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water into this mixture and cook for 10 minutes over low heat. After cooling, dilute 1 tbsp. l. honey You need to take the product 100 ml 4 times a day (before meals).
Diet therapy
Dietary recommendations depend on whether the thyroid gland is malfunctioning - a decrease in hormonal activity (hypothyroidism) or an increase (hyperthyroidism).
In the first case, the following products are prohibited:
- with a high content of omega-6 unsaturated fatty acids (sunflower, corn, soybean oil, oats, lentils and chickpeas);
- refined carbohydrates (sugar, honey, concentrated fruit juices, baked goods, cakes, sweets);
- vegetables with a high starch content (potatoes, radishes, carrots, Jerusalem artichokes, beets, melons - zucchini, pumpkin);
- with trans isomers of fatty acids (margarine, spread), as well as fatty meat and poultry.
It is also recommended to reduce the consumption of dairy products, as they contribute to an increase in the load on the gastrointestinal tract.
You should include foods such as:
- sources of omega-3 unsaturated acids (flax seeds, white chia, eggs, avocado, spinach, dill, beans);
- to replenish missing iodine reserves - kelp, shrimp, mussels, sea fish;
- vegetables rich in fiber (eggplant, all types of cabbage, onions, cucumbers, herbs, sweet peppers, garlic) as well as bran, sesame and flax seeds.
If you have hyperthyroidism, you should first of all abstain from those dishes that contain a high iodine content (listed above).
The following products are also not recommended:
- drinks: chocolate and cocoa, strong tea, coffee, alcohol;
- first courses: strong broths;
- flour: cakes, pastries, baked goods with yeast dough;
- other products: hot, spicy foods, animal fat.
If you have indigestion, you should not eat foods that can worsen diarrhea (radishes, radishes, mushrooms, fruits) and flatulence (baked dough, cabbage, tomatoes, spicy foods).
An example menu for both cases is shown in the table below:
| Thyroid condition | Reduced function | Enhanced function |
| Breakfast | Instant oat flakes with prunes. Season the porridge with linseed oil Fruits Tea | Milk rice porridge Omelette Crackers Tea with milk |
| Lunch | Fruit salad, cut into pieces (banana, pear, apple, orange or tangerine) | Curd casserole Juice |
| Dinner | Vegetable soup with Brussels sprouts in low-fat chicken broth Salad of allowed vegetables Compote | Vegetable soup Bread Stuffed cabbage rolls or meatballs Salad Kissel |
| Afternoon snack | Grapefruit or one of the permitted fruits | Yogurt |
| Dinner | Salad of seaweed, fish fillet and squid, dressed with sesame oil Juice At night - yogurt | Buckwheat porridge on water Steamed river fish Juice At night - kefir |
Why does TSH increase?
If TSH is elevated even slightly, this means that the thyroid gland has reduced the synthesis of iodine-containing hormones. Why this happened needs to be found out as soon as possible, before their lack disrupts metabolism throughout the body. Among the reasons why the thyroid gland has decreased its activity and the level of TSH has increased in women, men, and children are the following ailments:
- hypothyroidism – the thyroid gland has reduced the production of hormones;
- tumors of the thyroid gland or pituitary gland;
- removed gallbladder;
- heredity;
- problem with the adrenal glands;
- overdose of iodine-containing drugs;
- antibodies to the thyroid gland, TSH receptors;
- gestosis – complications during pregnancy;
- stress, insomnia;
- poor nutrition.
Having discovered the cause, treatment must be started immediately, otherwise it can provoke serious problems in the body of women, men, and children. For example, hypothyroidism, antibodies to TSH receptors and other problems in the mother's body can greatly affect the child. In an infant, the thyroid gland may be so small that it will lead to growth retardation and cause cretinism. Therefore, if a newborn child has been diagnosed with hypothyroidism, antibodies to TSH receptors and other problems associated with the functioning of the thyroid gland, treatment should be started immediately, in the first two weeks of life. Otherwise, hypothyroidism in a child will lead to irreversible consequences.
Therefore, after the cause is discovered, it is imperative to follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor: on your own, without the help of medications, the thyroid gland rarely recovers, and ignoring the problem leads to death. The consequences are especially serious if the problem is caused by a tumor.
During therapy, the patient will have to undergo tests more than once. This should be done to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. This means that if therapy for hypothyroidism or another ailment is successful, deciphering the results will let the doctor know that you can stop taking the medications. Particularly good results can be achieved if hypothyroidism, antibodies to TSH receptors and other ailments were detected at a stage when the level of thyrotropin has risen, but the concentration of other hormones has not yet changed.
In some cases, lifelong therapy is prescribed. In this situation, the analysis should be done regularly, at the same time, and TSH values should range from 0.3 to 3 µIU/ml. Such monitoring will allow the doctor to timely adjust the treatment regimen if indicators change.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis of the disease depends on its severity, timely diagnosis and treatment initiated. Thus, with de Quervain's thyroiditis, the patient's condition is completely restored within 1.5-2 months. In asymptomatic carriers of Ab-TPO antibodies, the risk of developing pathology in the thyroid gland increases with pregnancy.
During this period, the following complications are also possible:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- the formation of anomalies during fetal development;
- development of postpartum thyroiditis.
Patients with Graves' disease have a good prognosis if diagnosed early, but hypothyroidism may develop if treated surgically.
TPO Ab is a diagnostic marker for autoimmune thyroid diseases. It can be greatly increased in women with inflammation of this organ, hyperthyroidism and the formation of nodes in it. To make an accurate diagnosis and adequate treatment, additional studies are necessary, among which the most informative are ultrasound, scintigraphy and biopsy.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
For what symptoms is a test prescribed?
Testing for antibodies to TPO is carried out as part of a chemiluminescent immunoassay (CHLA). It is based on the interaction of antigens and antibodies (approximately as in radioactive analysis), but instead of radioactive isotopes, special non-radioactive substances that are capable of emitting a glow (luminesce) are used as a “tag”. This way it is possible to record the density of antibodies. This method is very effective and quite accurate. But carrying out this analysis requires highly qualified laboratory technicians, good technique and a serious attitude towards the anti-TPO test on the part of the patient.
This analysis is prescribed:
- if there are disturbances in the amount of TSH, T3 or T4;
- for symptoms of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism;
- with the formation of goiter, nodes, tumors;
- for cancer of the thyroid gland;
- when pregnancy is confirmed or after childbirth, with questionable diagnoses during pregnancy;
- when planning surgery or after surgery;
- when using weight loss techniques.
It is important to note that such an analysis is not self-sufficient. It is carried out in conjunction with other studies:
- blood test for lymphocyte content;
- immunogram for the presence of not only antibodies to TPO, but also TSH and TG (thyroglobulin);
- analysis for the amount of T3 and T4 (total and free);
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination);
- biopsy (fine needle), if necessary.
All these studies make it possible to clarify the diagnosis, analyze both the general condition of the body and specifically the thyroid gland, and diagnose the presence of iodine deficiency.
The interpretation of the anti-TPO analysis is carried out by an endocrinologist, taking into account gender, age, as well as information on heredity, diet, lifestyle and use of medications, in particular those containing antipsychotics or glucocorticoids.
Features of thyroid-stimulating hormone
When trying to independently determine what to do if the TSH test is elevated, you should take into account the normal daily variability of its level. The range of physiological fluctuations in values can be 1-3 mU/l. The highest concentration is observed late at night - at 2-4 o'clock. Then a slight decrease occurs. Thyrotropin is secreted in a pulsating manner.
The highest concentration is also observed at 6 am, and the lowest - in the period of time preceding the evening (17-19 hours). If a woman’s standard sleep-wake pattern is disrupted, the rhythm of secretion changes and a shift occurs to a later date. The circadian rhythm normally persists in old age and during pregnancy.
Individual variability (variability) of indicators, due to the use of different methods and test systems by laboratories, is of clinical importance. When interpreting the result of the study, it is important to exclude the influence of drugs that can increase the concentration of thyrotropin.
Reference range for women
This term is the most correct and correct. It replaced the concept of “TSH norm”, which cannot fully reflect all the results. Clearly defining the norm when it is necessary to take into account the influence of many factors (gender, age, race, weight, previous diseases, health status, etc.) is not an easy task. In healthy women, the content of thyrotropin varies widely.
Compared to men, women have higher TSH concentrations (approximately 20%). Some laboratories accept the range of 0.4-5.0 mIU/l as normal (this is the same as the unit of measurement mU/l), other clinics consider values in the range of 0.3-4.5 normal. In a situation where the analysis form says, for example, “TSH 4.8,” you should focus on the normal parameters that were determined and approved by the specific laboratory that conducted the blood test.
It is important to know, according to the latest data, patients whose TSH concentration in the analysis goes beyond the values of 2.5-3 are considered to be at an early stage of hypothyroidism (mild form). Such women are recommended to undergo repeated tests, because even at relatively low concentrations, various dysfunctions of the endocrine gland can manifest themselves.
Thyroid diseases: 5 tips
Since we're talking about the thyroid gland, I'll take this opportunity to give a few more important recommendations.
Ultrasound does not provide insight into how the thyroid gland works
- Most regions of Russia are in the zone of iodine deficiency. Buy only iodized salt and use it instead of regular salt.
- Sea kale does not contain as much iodine as is commonly believed. You can use seaweed to make salads if you like, but this does not mean at all that you can abandon traditional methods of iodine prophylaxis (iodized salt or pharmacological doses of iodine for pregnant women).
- You cannot use an alcohol solution of iodine for “prevention and treatment of the thyroid gland,” as is sometimes recommended in TV shows and pseudoscientific books about health. “Iodine nets,” a solution of iodine in sugar or milk, can quickly lead to the accumulation of toxic doses of iodine in the thyroid gland and the development of thyrotoxicosis.
- There is no need to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland just in case. If the function of the thyroid gland is not impaired, and the gland itself is not enlarged and no formations are palpable in it, then an ultrasound “just in case” will do more harm than good. Detection of small nodular formations, fear of detecting cancer, unjustified repeated punctures, repeated ultrasounds - this is what awaits a person who has set foot on this slippery path of multiple unnecessary examinations.
- A healthy adult needs to have their TSH level determined once every 5 years. If you have previously been diagnosed with subclinical hypothyroidism, subclinical thyrotoxicosis, or if you are taking the antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone, then take a TSH blood test once every 6 months.
What factors affect TSH levels?
High levels of the hormone TSH – this may be due to:
- long-term iodine deficiency, defects in its absorption;
- intense physical activity, prolonged training on an exercise bike (overload can provoke a 4-fold increase in concentration);
- taking radioactive iodine;
- lead poisoning;
- use of medications, hormone therapy;
- medical actions - thyroid surgery, gallbladder removal, ECT, blood purification;
- hypocorticism;
- diseases associated with aging women, gynecological problems;
- absence of menstruation (from 6 months) in a woman of reproductive age;
- to give up smoking;
- psycho-emotional overload.
The age of a woman does not have a significant effect on thyrotropin levels - it increases slightly, and concentration peaks at night become less pronounced.
Why is an increase in TSH dangerous?
An increase in thyrotropin secretion is observed relatively rarely; it manifests itself as hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis. Symptoms usually progress quickly. High concentrations of thyrotropin in women often cause infertility, difficulties with conception, spontaneous abortion in the early stages, severe toxicosis, bleeding, fetal hypoxia, developmental delay and even fetal death. The consequence of high TSH can also be problems with the heart, vision, mucous edema, thyrotoxic crisis, atherosclerosis, and disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system. Without medical care, a woman's quality of life can seriously deteriorate.
With timely, competent treatment and strict adherence to all medical recommendations, the prognosis is generally favorable.