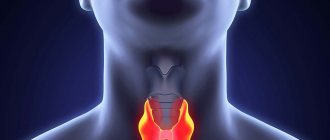
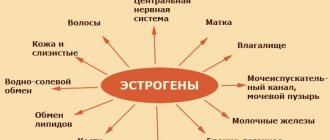
When the frequency of the disease in the region of surveys conducted among children of primary and secondary school age exceeds 5%, goiter is considered endemic. Diffuse euthyroid goiter is a pathology of the young part of the population and it develops before the age of 20 in more than 50% of cases, while affecting women 2-3 times more often than men, especially during periods of increased body need for iodine - during puberty , bearing a child and breastfeeding him.
Diffuse nontoxic goiter predominantly develops against the background of iodine deficiency, when the thyroid gland undergoes compensatory hyperplasia to compensate for the deficiency of thyroid hormones.
The growth of thyroid tissue is directly influenced by autocrine factors that stimulate thyrocytes: fibroblast, epidermal and transforming growth factors.
In addition to an insufficient amount of iodine in the diet, DEZ is provoked by taking specific medications, smoking tobacco, the presence of a long-term stressful condition and an infectious disease, poor nutrition with a deficiency of vital microelements responsible for iodine metabolism, as well as congenital defects of certain enzymes, age, gender and predisposition to the disease patient.
Development mechanism and reasons
Euthyroidism of the thyroid gland refers to pathological changes in the structure of the gland that are reversible. The tissues of the organ grow rapidly, which leads to its diffuse growth or enlargement of nodes.
At the same time, the level of thyroid-stimulating and thyroid hormones remains unchanged, although the likelihood of a hormonal surge is very high. The formation of several nodes means the development of a multinodular goiter. Against the background of a short-term euthyroid state, pathological processes develop that accompany hyper- or hypofunctionality of the thyroid gland. Given this fact, if euthyroidism is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment. The endocrine system has increased sensitivity to exogenous and endogenous factors. The thyroid gland is most vulnerable in this regard.
The occurrence of thyroid gland euthyroidism is caused by the following reasons:
- stress;
- ecology;
- iodine deficiency;
- thyroid pathology of an inflammatory nature;
- aggravated heredity;
- hyperthyroidism in pregnancy;
- chronic autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT).
Euthyroidism during pregnancy occurs due to the fact that a woman's hormonal levels undergo significant changes. As a rule, the disease disappears with the normalization of hormonal levels.
If necessary, drug therapy should be resorted to to ensure the preservation of the fetus.
Women suffering from increased thyroid function should be observed by an endocrinologist before and during pregnancy.
In addition to the main causes, the development of the disease can be triggered by the following factors:
- the use of drugs that suppress the functioning of the thyroid gland (drug euthyroidism);
- excessive stress of a psychological or physical nature;
- poisoning with active components (arsenic, strontium).
Clinical euthyroidism of the thyroid gland can last for several years without deterioration, being a stage of autoimmune type thyroiditis.
Combination therapy
Thyreostatic drugs are administered only to achieve euthyroidism, and then they are used together with thyroxine, for example, 20 mg of methizol + 50 mcg of thyroxine. The purpose of administering thyroxine is to prevent the onset of hypothyroidism and to prevent the goiter from enlarging due to unblocking of TSH.
Be aware of the beneficial effects of beta blockers, B vitamins, and possibly sedatives.
Beta blockers - the main effect of drugs in this group is to block beta receptors, which reduces the activity of the adrenergic system. Let us recall that with hyperthyroidism there is an increase in the sensitivity of beta receptors to catecholamines and an increase in their density.
Combination therapy
These drugs also reduce the conversion of peripheral T4 to T3.
The most commonly used:
- propranolol at a dose of 80-160 mg/day;
- Metocard at a dose of 100-200 mg/day;
- Atenolol at a dose of 50-200 mg/day.
In case of contraindications to the use of drugs from this group, calcium channel blockers, for example, Isoptin, can be prescribed as an alternative.
Additional notes:
- During the initial period of treatment, physical activity should be avoided (valid medical certificate);
- the course of treatment may be aggravated by stress factors;
- preventive vaccinations are contraindicated;
- the patient should be instructed about the possibility of granulocytopenia and associated symptoms, as well as the need to consult an endocrinologist if they occur;
- granulocytopenia can also be a symptom of Graves' disease itself, so its detection before treatment is not a contraindication to the use of thyreostatic drugs;
- If Graves' disease has been cured, iodine should not be given as this medicine may cause the disease to recur.
In cases of drug intolerance, relapse of hyperactivity after treatment or very strong patient resistance, we turn to radical treatment, that is, 131 I treatment, or nowadays, less commonly, to surgical treatment.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease called euthyroidism of the thyroid gland is a list of the following symptoms:
- enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- disruption of circadian rhythms (human internal clock);
- difficulty swallowing;
- insomnia;
- the formation of a nodular goiter (a goiter with one node, with multiple nodes - both autonomously located and combined with each other) and diffuse tissue proliferation;
- pain in the larynx, aching and pressing type;
- chronic fatigue, apathy;
- emotional exhaustion.
Patients also complain to the doctor about the presence of a false foreign body in the throat and a lack of air when inhaling. This indicates that the organs of the endocrine system are not working properly. Euthyroidism, the symptoms of which include the presence of nodular goiter, is accompanied by weight loss, extrasystole and other disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle.
Which doctor is treating you?
First of all, people with complaints about the thyroid gland should consult a therapist. He can identify a problem in the organ, but does not treat it.
An endocrinologist conducts tests, studies them, and develops therapeutic measures. He detects symptoms - enlargement of the thyroid gland and disruption of hormonal production, and also finds the cause of the pathology.
Very often, an endocrinologist requires the help of related doctors. If part of the thyroid gland has to be removed, a surgeon will be needed. If cancer cells are detected, they resort to the help of oncologists.
Classification
According to clinical data, the disease is divided into 4 forms:
- nodular goiter of the 1st degree with one enlarged node;
- nodular goiter of the 2nd degree with many enlarged nodes;
- multiple nodes are combined with each other;
- goiter, which is caused by a lack of iodine in the body.
Generally accepted classification of the degree of manifestation of the disease:
- when palpating the iron, it is practically not felt and any deviations are not externally noticeable;
- upon external examination, the goiter is not visible, but is noticeable upon palpation;
- The goiter is clearly visible upon examination and can be easily palpated.
If a patient develops a nodular non-toxic goiter, the following symptoms may appear:
- feeling of fullness in the chest, presence of a foreign body;
- sudden weight loss;
- heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia.
If you notice such symptoms, you must go to the clinic and undergo an examination.
About etiology
If we talk about why such a disease begins to progress, there are several reasons. First of all, it is necessary to note the increased sensitivity of the endocrine system to various factors of exogenous and endogenous type. Moreover, the thyroid gland is the most vulnerable. As for euthyroidism itself, it is perceived by many doctors as a borderline condition.
It should be noted that the ratio of thyroid hormones can change quickly, both up and down. And this can already cause the formation of pathology.
So, the causes of the disease may be as follows:
- the concentration of iodine in the body is insufficient, it is for this reason that more pathologies develop that affect the thyroid gland, here we can talk about endemic goiter, hypothyroidism and other ailments;
- the external environment is unfavorable;
- hereditary factor;
- pathological conditions in which the thyroid gland is located, which are inflammatory in nature (it is in such cases that the symptoms are expressed most clearly);
- frequent stressful situations;
- severe mental and physical stress;
- long-term consumption of medications that have a depressing effect on the thyroid gland;
- The human body contains various types of active substances - cobalt, arsenic and others.
Complications
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of pathology in time, they can result in serious consequences. An increase in euthyroid goiter leads to compression of the vessels and arteries located in the neck. Such people have difficulty breathing, pain occurs when swallowing, their voice becomes hoarse, and over time it disappears altogether.
Improper functioning of the thyroid gland affects the human nervous system, as a result of which irritability develops into permanent depressive states. Such people experience deterioration in memory and attention, as well as a decrease in reaction.
A lack of iodine-containing hormones leads to an increase in cholesterol levels in the blood, causing atherosclerotic heart and vascular disease. The reproductive system also undergoes changes. In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and in men, erection deteriorates. In the future, infertility may develop.
The most dangerous consequence of nodular goiter is the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
What is the danger of euthyroidism?
Euthyroidism can be considered a safe condition, but only as long as a person maintains normal levels of hormones in the blood. If the disorder develops quickly, the patient will develop a nodular goiter. This pathology requires emergency treatment.
If the disease is ignored, serious complications may arise after some time. The likelihood of the formation of a malignant tumor or compression of the trachea increases. In such a situation, the thyroid gland has to be removed.
Other complications of euthyroidism include:
- Deterioration or loss of memory.
- Panic attacks.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
- Primary infertility.
- Depression.
- High blood cholesterol levels.
Video: surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences Viktor Nikolaevich Kosovan will talk about methods of treating nodular goiter with euthyroidism:
Diagnostics
Diffuse euthyroid goiter can be easily detected during a routine examination or by palpation. To clarify the exact volume and structure of the thyroid gland (to classify the type of damage), ultrasound diagnostics is performed.
If during the examination the presence of nodular changes in the gland tissue was proven, then scintigraphy and fine-needle biopsy are prescribed.
Research in the laboratory includes:
- Analysis of an immunogram that determines the presence of lymphocytes, antibodies for thyroglobulin and thyroid cells.
- Determination of the level of TSH, T3, T4, as well as the presence of thyroglobulin in the blood.
During a severe form of euthyroidism (severe compression of the neck, active growth of goiter), the patient is sent for a contrast X-ray.
What is a goiter
Experts use the term “thyroid goiter” when it is necessary to differentiate several diseases associated with this organ.
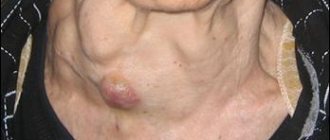
As a rule, a goiter is a pathological condition of the gland, manifested by a significant proliferation of its tissues, which is expressed in an increase in volume. Visually, this can be determined due to the fact that the connective and integumentary tissues at the base of the human neck thicken.
There are several types of goiter:
- With hypothyroidism, the functional activity of the organ is reduced. Characteristic of endemically disadvantaged areas. And also for autoimmune lesions.
- With euthyroidism, the functional activity of the organ is not impaired. Often occurs in the initial stages of endemic disease, as well as in pregnant women.
- With hyperthyroidism – the activity of the gland is increased. Characteristic of thyrotoxicosis and toxic organ damage, multinodular goiter. Diagnosed with thyroid adenoma.
The purpose of the thyroid gland is to produce special iodine-containing hormones - iodothyronines, which are responsible for the complete absorption of calcium and phosphorus from foods, which are required for the proper formation of the human bone skeleton. A change in the amount of iodine consumed leads to a significant proliferation of organ tissue - endemic goiter.
Normally, the size of the thyroid gland in women does not exceed twenty centimeters, and in men – twenty-five centimeters.
Treatment of euthyroidism
The euthyroid state does not always require drug treatment. Thus, with minor diffuse changes in the thyroid gland and 1-2 nodes with a diameter of up to 0.8 cm (for example, with autoimmune euthyroidism), endocrinologists recommend only active observation: once every 6 months. You should undergo an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
For a patient who wants to maintain his health, such tactics will not cause difficulties: ultrasound examination is affordable in terms of cost.
If quite serious structural changes in the thyroid tissue are detected in a patient against the background of severe symptoms, a course of drug treatment is prescribed.
- To normalize the patient's condition and, at a minimum, stop tissue proliferation, iodine preparations (Microiodine, Camphodal, Antistrumin and others) or L-Thyroxine (Levothyroxine) are prescribed.
Dosages of drugs are determined individually. If monotherapy fails, a combination of Levothyroskine with iodine-containing drugs may be prescribed.
Control ultrasound is performed every 3-6 months, after which the treatment regimen can be adjusted. A good result of treatment is the elimination of symptoms that bother the patient with euthyroidism and the absence of further tissue enlargement.
With effective treatment, over time, the thyroid gland returns to normal: the nodes disappear or become smaller (0.8 mm or less), and regression of diffuse growth is noticeable.
Symptoms
The primary symptoms of euthyroidism are common to all pathologies that cause an enlarged thyroid gland. First, increasing neurological signs appear: irritability, fatigue, loss of strength. The patient's circadian rhythm is disrupted - he suffers from insomnia at night and constant drowsiness during the day. Headaches become more frequent.
Over time, changes in the thyroid tissue become visually visible. If at the first stage the use of diagnostic equipment is necessary to determine them, then in the future only palpation (stage 2) or visual inspection (stage 3) may be required. At the fourth stage, the organ is clearly visible, at the fifth stage it reaches enormous sizes.
At the third stage of goiter, it can even be diagnosed visually
Naturally, the process of change is felt by the patient himself. There is an unpleasant sensation of a foreign body in the neck and upper chest. When swallowing, you feel a lump in the throat, and a causeless dry cough may develop. More severe symptoms vary depending on the underlying medical condition.
The asymptomatic or subclinical stages of many thyroid diseases are limited to the mild manifestations described above. Their course can be identified only by conducting targeted studies (ultrasound diagnostics) and biochemical blood tests (specific antibodies).
In some cases, the cause of problems with the thyroid gland can be autoimmune processes, in which the body's defense system attacks its own tissues. Such phenomena are the most common cause of thyroid problems that develop in childhood and adolescence. Against the background of these diseases, there is weakness throughout the body, inflammatory processes in the joints, and dull pain in the extremities. Damage to the hair follicles and, as a result, hair loss are likely. With severe manifestations, bleeding is likely - nasal, intestinal, uterine.
Problems with the thyroid gland that occur in women during pregnancy and immediately after childbirth can reveal similar symptoms. According to statistics, an enlarged thyroid gland develops in 5–9% of all women giving birth, but in most cases it disappears naturally.
If tissue inflammation is caused by an infectious process, intoxication of the body and swelling of the throat are possible. The thyroid gland becomes extremely sensitive to mechanical influences; when swallowing and palpating, a sharp pain occurs in it, radiating to the jaw or back of the head.
An enlarged gland leads to the formation of a so-called goiter. Its growth may be accompanied by the development of compactions, or continue without them. Depending on this, nodular and diffuse forms of the disease are distinguished.
The forms of goiter are distinguished by the presence of compactions in the thyroid tissue
The nodular form can be characterized by the presence of one or several seals, often merging with each other. Diffuse goiter occurs without the formation of nodes. There is also a known form of mixed or diffuse nodular goiter, most often found in women over 40 years of age. With it, small foci of compaction develop in the homogeneous tissue of the thyroid gland.
An enlarging goiter causes new symptoms:
- Neurological: depression, mild excitability, pain in the heart, trembling fingers;
- Skin: urticaria, darkening, itching, sweating, redness;
- Cardiovascular: arrhythmia, tachycardia, poor tolerance to high temperatures;
- Metabolic: sudden weight loss or gain with a unchanged diet.
Physiotherapeutic methods
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe the patient various physiotherapeutic procedures that help to get rid of euthyroidism more quickly.
- Ultrasound therapy. This method of physiotherapy is based on the influence of high-frequency environmental vibrations. The body is exposed to thermal and mechanical effects, which makes it possible to fight many diseases. Thanks to the effect on the front surface of the neck, blood circulation improves, metabolism is restored and the thyroid gland gradually decreases in size.
- Magnetic laser therapy. This procedure is a method of local exposure using electromagnetic radiation of the low-intensity optical spectrum. This method has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Patients recover faster, the process of restoration and normalization of metabolism begins.
- Laser therapy. Laser therapy is based on the use of radiation of a certain range, the source of which is a laser. The procedure has a vasodilating effect, stimulates the processes of regeneration and restoration of DNA after damage, which can also be caused by radiation. The metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates also improves, which helps speed up the healing process with euthyroidism.
- Apipunktura. Apipunkture involves applying bee venom to specific areas of the body. In small quantities, it has a beneficial effect on the human nervous system, stimulates blood circulation, eliminates insomnia and headaches. This method does not cure euthyroidism, but it can help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of this condition.
- Singlet-oxygen cocktails. Using a special device, the steam-water mixture is activated, after which oxygen is excited and it goes into the singlet state. Treated water helps activate internal processes, restore ionic permeability of cell membranes, remove toxins, and improve blood circulation. All these properties of cocktails help patients recover faster when goiter appears.
Symptoms
There are no noticeable symptoms when a first-degree goiter develops. Visually, one can detect the growth of gland tissue, as well as the volume of skin in the neck area, which serves as an indicator of significant development of the pathological process.
Timely detection is facilitated by regular medical examinations, with the determination of the functional parameters of the organ. There are some symptoms that make a person wary and consult a specialist:
- Sudden development of fatigue and fatigue, which was not previously typical for the individual.
- Weakness in muscle mass - “legs like jelly.”
- Increased irritability - herbal sedatives do not help.
- Excessive sweating - deodorants do not help.
- Emotional imbalance – tearfulness, euphoria.
- Stool disorder - alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- The menstrual cycle becomes unstable.
- Tremor of the limbs.
- Sudden attacks of tachycardia - the heart beats “like a hare’s tail.”
- Exophthalmos is an overly pronounced displacement of the eyeball from the orbit.
When diagnosing a goiter of the first degree visually and by palpation, a specialist is unlikely to detect anything; instrumental and laboratory confirmation will be required. A goiter of the second degree is characterized by a slight increase in the volume of the thyroid gland, amenable to palpation. Visual identification of excess tissue in the neck area will indicate a third-degree goiter.
Against the background of diffuse growth of organ tissue, the increase in size occurs evenly, whereas nodular goiter will be characterized by an increase in one of the organ’s lobes. Multinodular goiter should be alarming in terms of oncopathology.
Diet and nutrition
The best way to replenish iodine deficiency in the body are sea shellfish (mussels, squid), crustaceans (crabs, shrimp, lobsters), fish (halibut, herring, tuna, cod). They are recommended for use at least 2-3 times a week. Sea kale, or kelp, is an accessible source of iodine. The daily dose of its consumption is approximately 50 g in raw form, and about 1 tsp. - dry.
It is better to choose egg yolks, beef, and poultry as a source of animal proteins. It is advisable to prepare it by stewing or boiling. It is better to avoid excessively fatty and spicy foods. Strong broths are also not recommended for consumption. You should not neglect dairy products: kefir, yoghurt, low-fat cottage cheese.
According to the recommendations of modern nutritionists, for diseases of the thyroid gland in the daily diet it is necessary to limit or completely exclude such foods as:
- alcohol;
- rich soups;
- Brussels sprouts and cauliflower;
- turnip;
- marinades;
- canned food and preserves;
- turnip;
- rutabaga;
- jam;
- honey;
- margarine;
- confectionery.
To lose weight, you need to consume a sufficient amount of plant fiber, obtained from porridge (buckwheat, oatmeal), greens (celery, dill), vegetables (onions, carrots, radishes, garlic), and nuts.
It is better to replace sugar with honey. To obtain a sufficient amount of carbohydrates, it is recommended to include in the diet berries (grapes, wild strawberries, viburnum, strawberries, cranberries, gooseberries, blueberries), dried fruits (raisins, figs, dried apricots), fresh fruit juices, and rosehip decoction.
It is better to adhere to moderation in nutrition, eat little, but often - about 4-5 times a day. Fluid consumption should exceed 1.5–2 liters.
Treatment with folk remedies
Euthyroidism can be treated not only with pharmaceuticals, but also with folk remedies. The following recipes are used:
- Grind the chokeberry berries in a blender and mix with sugar in equal proportions. Use the mixture 3 times a day, 1 tsp. before meals. Euthyroidism should be treated with this remedy for 2 weeks, then you should take a break for 14 days and repeat the course.
- Using a coffee grinder, make a powder from the dry herb of European sage grass, combine it with honey in a 1:1 ratio. The product should be consumed 1 tsp. before each meal, with water.
- 2 tbsp. l. Brew crushed oak bark in a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Moisten the gauze generously in the resulting decoction and make a compress on the area of the thyroid gland, wrapping it in additional woolen cloth.
Treatment with folk remedies is not recommended without the permission of a specialist. Plant raw materials have a high biological effect and, if used uncontrolled, can cause significant harm to health.
Treating an Overactive Thyroid: Graves' Disease
If Graves' disease is diagnosed, treatment with thyreostatic drugs begins. Treatment should last 12-24 months - longer use of thyreostatic drugs increases the likelihood of long-term remission.
When predicting the effectiveness of conservative treatment, you should remember about situations that worsen the prognosis, such as:
- patient age under 20 years;
- coexistence of Graves-Graves disease in other family members;
- high titers of antibodies to TSH receptors;
- thyrotoxicosis T3.
This group of patients may pose therapeutic challenges and require specialized care. Medicines used to treat hyperactive disorder (thyroiditis) include:
- Metizol – tablets 5 mg;
- Methylthiouracil – 100 mg tablets;
- Propylthiouracil – 50 mg tablets.
Their mechanism of action is two-way. They work in the thyroid gland itself, where they inhibit hormone production by interfering with tyrosine iodination, and in the periphery by inhibiting the conversion of T4 to T3. In addition, they have an immunosuppressive effect. Side effects depend mainly on the dose used and usually occur during the first three months of taking the drug (Table 2).
Table 2. Side effects of thyroid drugs
| Percentage of cases | Clinical symptoms | Procedure |
| 1-5% | rash, skin itching, dyspeptic disorders, hair loss, joint pain | additionally Hydroxyzine, dose reduction, change in thyreostatic |
| 0,2-0,5% | agranulocytosis | stop taking medications immediately, treat radically |
| less than 0.2% | aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, hepatitis, pseudomotor symptoms | stop taking medications immediately, treat radically |
Surgery for euthyroidism
In the absence of a minimal therapeutic effect (stabilization of the condition) from drug therapy, the endocrinologist may suggest surgical intervention.
The operation involves minimal excision of pathological elements (growing nodes) and partial resection of diffusely overgrown tissue.
Now such operations are performed endoscopically through mini-incisions. These achieve minimal tissue trauma, which leads to a short period of hospitalization (2-3 days) and rapid recovery. This achieves an excellent cosmetic effect: only barely noticeable small scars remain on the neck.
The difficulty of surgery for euthyroidism is that it is necessary to accurately determine the volume of tissue to be excised. Excessive excision can lead to postoperative hypothyroidism, and insufficient excision will not provide the necessary therapeutic effect. Therefore, to perform such a surgical intervention, you need to contact only an experienced endocrinologist-surgeon.
Characteristics of the disease
A characteristic feature of euthyroid goiter is that the process of hormone production is not disrupted, and accordingly their level remains normal. This disease is otherwise referred to as “diffuse non-toxic goiter” or euthyroidism.
The volume of the thyroid gland in men on ultrasound is normally no more than 25 ml, in women – 18 ml. Deviations from the established indicators in a larger direction indicate an increase in the organ.
The development of the disease is associated with low iodine content in the environment in a number of regions, which is why residents of these areas consume insufficient quantities of the microelement in food.
Depending on the prevalence, endemic and sporadic goiter are distinguished. If the incidence rate among children 6–14 years old is 5%, they speak of an endemic pathology. The second type occurs with congenital and acquired disorders of the production of hormones T3 and T4. The formation of sporadic goiter has nothing to do with the amount of iodine consumed.
Euthyroid goiter is most often diagnosed in people under 20 years of age. Women are more susceptible to the disease due to the fact that during pregnancy, breastfeeding and puberty they need large amounts of microelements.
Prevention
Doctors diagnosing diseases, especially during preventive examinations, should pay attention to patients who have a genetic predisposition to thyroid diseases.
People who have developed euthyroidism should avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, reduce exposure to stressful situations, and take sanitary measures for frequent diseases of the nasopharynx. You should also avoid living in environmentally unfavorable areas.
Please note: you should be especially careful when taking medications, in particular antibiotics and hormonal medications.
During pregnancy, women who are prone to thyroid pathology should take iodine preparations for preventive purposes, since pregnancy leads to overstrain of the body's enzyme and hormonal systems and the rapid development of a deficiency of essential minerals, elements and iodine.
People who have been diagnosed with euthyroidism should undergo regular examinations with an endocrinologist, take tests and undergo an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
Forecast
Euthyroidism itself is more of a collection of gradually increasing symptoms than a disease. Elimination of its manifestations is carried out using proven methods, which are often limited to nutritional correction and light physiotherapeutic procedures. Thus, the prognosis for treatment of uncomplicated euthyroidism is quite favorable.
Severe consequences can develop with delayed diagnosis and untimely treatment. With a sharp growth of goiter, the following are possible:
- impaired neck mobility;
- decreased cerebral circulation;
- atrophy of the laryngeal nerve.
An enlarged thyroid gland becomes vulnerable to inflammation and bleeding, and oncological modifications of cells are likely in the formed nodes.
Thyroid cyst: symptoms and treatment Hypothyroidism Thyrotoxicosis of the thyroid gland: what is it and how to treat it? Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) Cyst in the mammary gland Thyrotoxic crisis